Apex Respiratory Monitors and Equipment practice questions and flashcards
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Resistance
The force that acts opposite the relative motion of object
At what cm/H2O does the risk of barotrauma increase?
35 cm/H2O
If barotrauma exists,
Reduce plateau pressure by reducing TV, inspiratory flow, and PEEP.
Sedation could also be used
Compliance
Ability of the lungs to stretch and expand
Also the change in volume for a given change in pressure
Static Compliance
Static= Not moving
Assesses pressure required to keep the lung inflated to a given volume when there is no air movement
Pressure required to keep the lung inflated to a given volume is a function of the tendency of the lung/chest to collapse (no airflow = no resistance to overcome)
Dynamic Compliance
Dynamic= movement
Dynamic compliance is the lung/ chest wall during movement
Pressure required to inflate the lung to a given volume is a function of airway resistance and tendency of the lung/chest to collapse
Formula for Dynamic Compliance
Tidal volume/ (Peak Inspiratory Pressure- PEEP)
What is dynamic compliance impacted by?
Airway resistance and the tendency of the lung/chest to collapse due to the elasticity of lung tissue and the chest wall.
Peak inspiratory pressure
The maximum pressure in the patients small airways and alveolli during when target TV is delivered.
Plateau Pressure
Pressure in the small airways and alveoli after the target tidal volume is achieved
Reflects elastic recoil of the lungs and thorax during inspiratory pause (no gas moving in or out of the lungs)
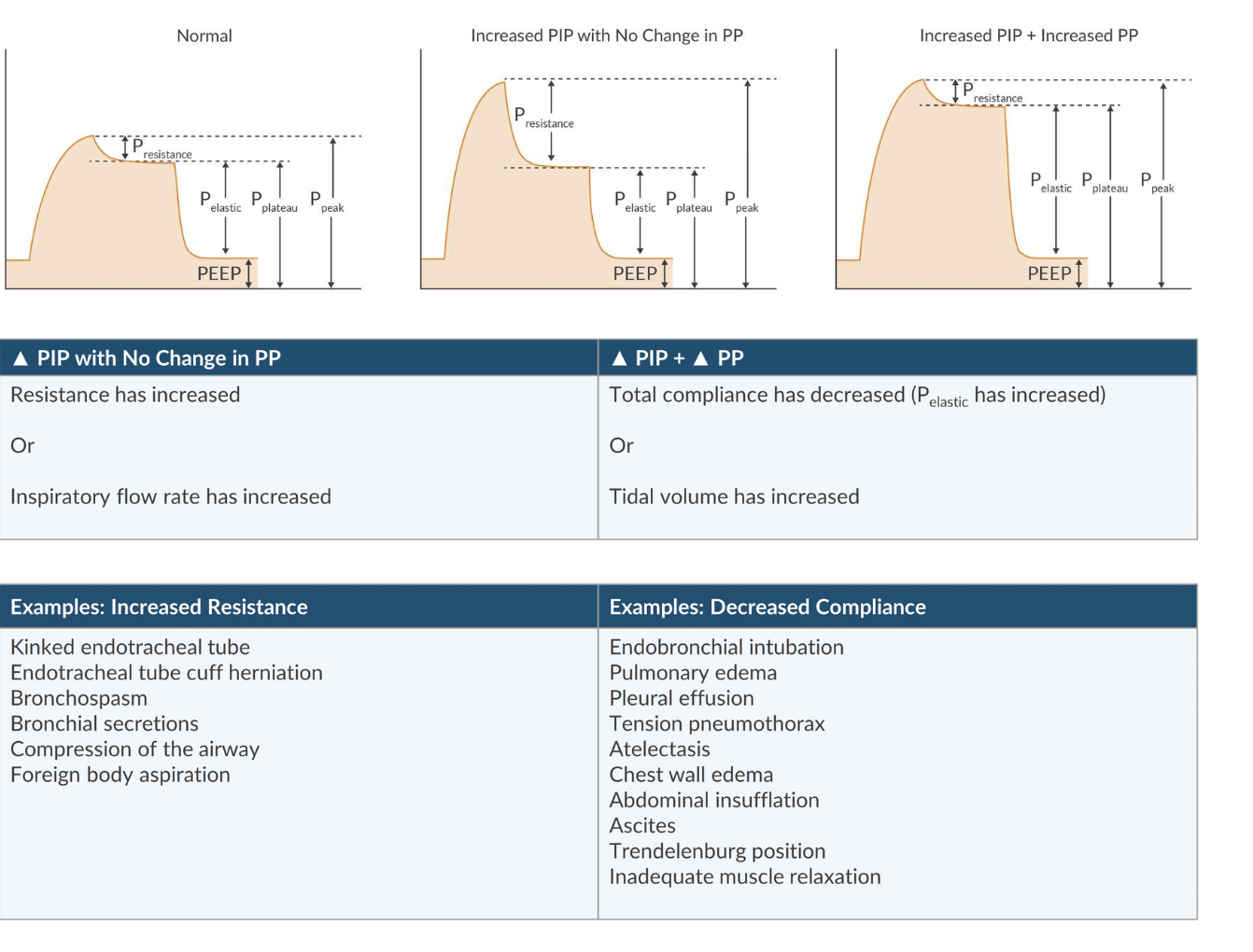
How does increased resistance present?
Increased PIP with a normal Plateau pressure'
Ex. Kinked endotracheal tube and bronchospasm
How does decreased pulmonary compliance present?
Increased PIP and Plateau pressure
Ex. Endobronchial intubation and pulmonary edema
What is the formula to calculate airway resistance?
[P(airway) - P(alveolar)] / Gas Flow Rate
What is the formula for airway compliance?
delta of V/Delta of P
What factors influence compliance?
Muscle tone
Degree of lung inflation
Alveolar surface tension
Amount of interstitial lung water
Pulmonary fibrosis
What is the formula to calculate dynamic compliance?
Tidal volume / (peak inspiratory pressure - PEEP)
What is the formula for calculating static compliance?
Tidal volume / (Plateau pressure - PEEP)
What is the normal range for adult static compliance?
35-100 cm/H2O
What is the normal range for pediatric static compliance?
>15 cm/H2O
What are complications of elevated plateau pressure?
Ventilator associated lung injury
Pneumothorax
Pneumomediastinum
Subcutaneous emphysema
What does it mean when there is an increase in PIP with no change in plateau pressure?
Resistance has increased
Inspiratory flow rate has increased
What does it mean when PIP increases and plateau pressure increases?
Total compliance has decreased (elastic pressure has increased)
Tidal volume has increased
What are examples of increased resistance?
Kinked ETT
Endotracheal tube cuff herniation
Bronchospasm
Bronchial secretions
Compression of the airway
Foreign body aspiration
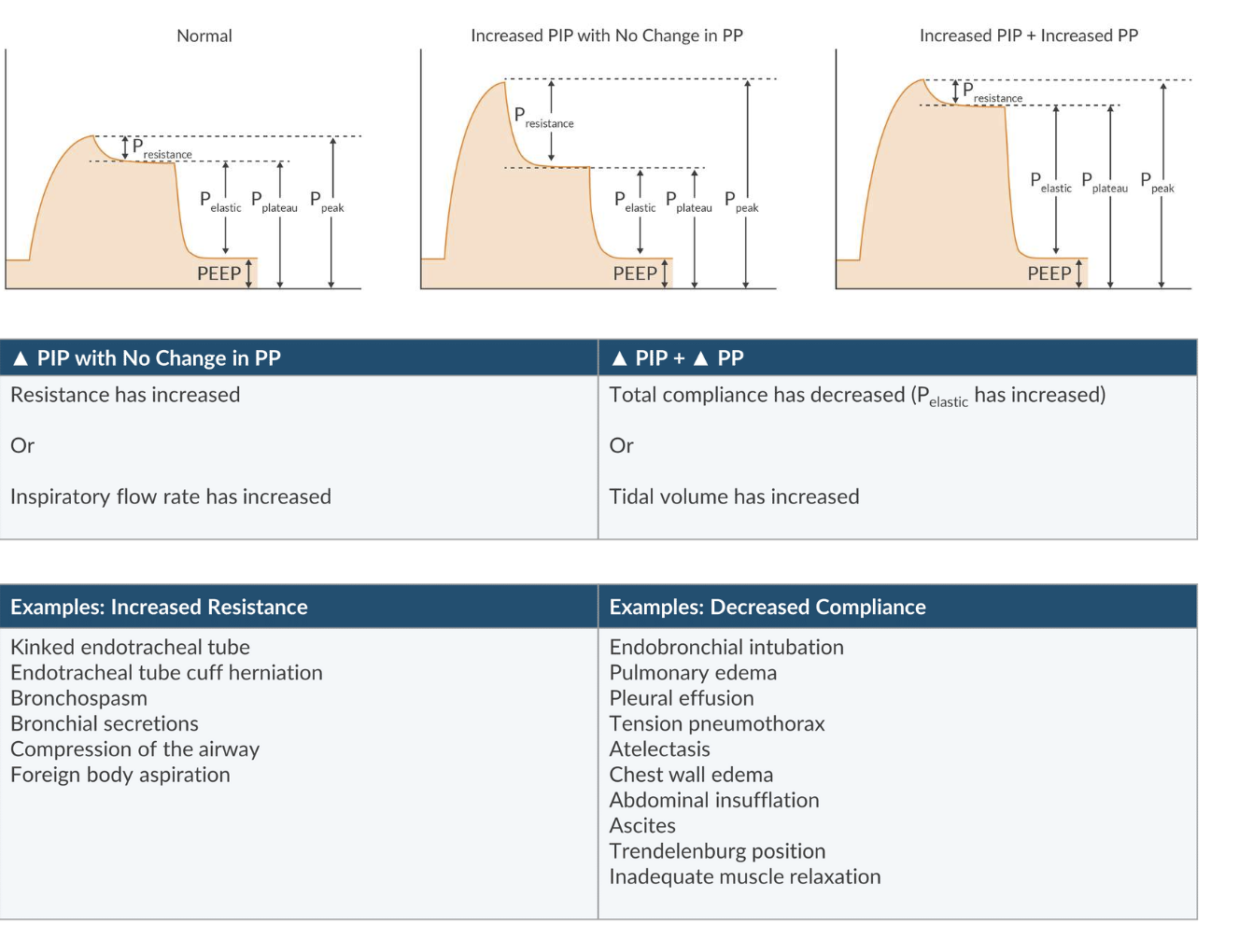
What are examples of decreased compliance?
Endobronchial intubation
Pulmonary edema
Pleural effusion
Tension pneumothorax
Atelectasis
Chest wall edema
Abdominal insufflation
Ascites
Trendelenburg
Inadequate muscle relaxation
What type of pulmonary compliance is a function of both airway resistance and the elasticity of the chest wall?
Dynamic compliance
What type of pulmonary compliance is a function of the elasticity of the chest wall only?
Static compliance
What does capnography measure?
End tidal CO2 concentration over time
What can capnography assess?
Continuous assessment of metabolism, circulation, ventilation
Provides insight to equipment related problems like airway obstruction and rebreathing
What does an increased alpha signal suggest?
Expiratory airway obstruction
What does an increased beta angle suggest?
Rebreathing due to a faulty inspiratory valve
What are the two methods of carbon dioxide analysis?
Mainstream (in-line)
Side stream (diverting)
What is CO2 the final product of?
Aerobic metabolism
How does CO2 move from the tissue and enter venous circulation?
By diffusion
How does the rate of CO2 transfer toward the lungs get affected?
By cardiac output
In the lungs how does CO2 diffuse across the alveolocapillary membrane?
By following a concentration gradient
Once CO2 is in the alveolus, how is CO2 eliminated from the body?
By ventilation
What does phase one of the capnography waveform represent?
(A-B): Exhalation of an atomic dead space
What does phase 2 of the capnography waveform represent?
(B-C): exhalation of the anatomic dead space and alveolar gas
What does phase 3 of the capnography waveform represent?
(C-D): exhalation of alveolar gas
What does phase 4 of the capnography waveform represent?
(D-E): inspiration of fresh gas that does not contain CO2
What is the normal angle for Alpha Angle?
100-110 degrees
Where is the alpha angle measured?
Point C
What does an increased alpha angle signify?
Expiratory airflow obstruction like COPD, bronchospasm, kinked endotracheal tube
Where is the beta angle measured?
Point D
What causes an increased beta angle?
Rebreathing specific to a faulty inspiratory valve
When will a beta angle appear normal despite rebreathing?
Exhausted CO2 absorbent
What are the pros to a mainstream CO2 analyzer?
Faster response time
Doesn't require a water tap/pumping mechanism
What are the cons to a mainstream CO2 analyzer?
Increases apparatus dead space
Adds extra weight
How does a side stream CO2 analyzer work?
Pumping mechanism continuously aspirates gas sample from the breathing circuit, causing a slower response time and requires a water trap to prevent contamination of device
Which method of CO2 analysis will take longer to reveal a circuit disconnect?
Sidestream (diverting) because it has a longer response time
The sample must travel through long tubing before it reaches the monitor
What are the characteristics of an airflow obstruction on capnography?
Prolonged upstroke with an increased alpha angle
COPD, bronchospasm, kinked ETT
What creates oscillations on a cardiac oscillation waveform on capnography?
The heart beating against the lungs, more commonly occurring in children due to close proximity of the heart to the lungs
What causes the Curare Cleft waveform on capnography?
Spontaneous breaths during inspiration
Inadequate muscle relaxation or inadequate muscle relaxant reversal
What causes a low EtCO2 waveform on capnography?
Hyperventilation - light anesthesia, metabolic acidosis
decreased CO2 production - hypothermia
increased alveolar dead space - hypotension, pulmonary embolism
What causes an elevated EtCO2 with a normal baseline on capnography?
Increased CO2 production - MH, sepsis, fever, hyperthyroidism
Decreased alveolar ventilation - hypoventilation, narcotics
What does it mean when capnography presents with no return to baseline?
Rebreathing! Due to exhausted CO2 absorbent, incompetent expiratory valve, hole in inner tube of Bain system, inadequate FGF with Mapleson circuit or rebreathing under the drapes in a non-intubated patient
How will an incompetent inspiratory valve present on capnography?
Widened beta angle (decreased slope during inspiratory phase)
What causes the peak at the end of plateau with a leak in sample line waveform on capnography?
Positive pressure during inhalation pushing CO2 rich gas through the sample line
What do the first and second peaks represent in biphasic expiratory plateaus on capnography?
First peak: alveolar gas from the transplanted lung with normal time constant
Second Peak: alveolar gas from the diseased lung with a longer time constant due to air trapping
What causes increased EtCO2?
Increased CO2 production and delivery to lungs
Decreased alveolar ventilation
Equipment malfunction
What causes decreased EtCO2?
Decreased CO2 production and delivery to lungs
Increased alveolar ventilation
Equipment malfunction
For EtCO2 to be detected, what requirements must be met?
Carbon dioxide must be produced during metabolism
Must be adequate pulmonary blood flow to deliver CO2 to the lungs for elimination
Must be an adequate ventilation to transport CO2 to breathing circuit
Must be intact sampling system
What are examples of increased CO2 production and delivery to the lungs resulting in increased EtCO2?
Increased BMR
MH
Thyrotoxicosis
Fever
Seizures
Sepsis
Laparoscopy
Tourniquet or vascular clamp removal
Sodium bicarbonate administration
Shivering
Increased muscle tone - after NMB reversal
Medication side effect
Which law is pulse oximetry based on?
Beer-Lambert Law
What are the examples of decreased alveolar ventilation resulting in increased EtCO2?
Hypoventilation
CNS depression
Residual neuromuscular blockade
COPD
High spinal anesthesia
Neuromuscular disease
Metabolic alkalosis (if spontaneous ventilation)
Medication side effect
What are examples of equipment malfunction resulting in increased EtCO2?
Rebreathing
CO2 absorbent exhaustion
Unidirectional valve malfunction
Leak in breathing circuit
Increased apparatus dead space
What are examples of decreased CO2 production and delivery to the lungs resulting in decreased EtCO2?
Decreased BMR
Increased anesthetic depth
Hypothermia
Decreased pulmonary blood flow
Decreased cardiac output
Hypotension
Pulmonary embolus
V/Q mismatch
Medication side effect
Pain/anxiety (if breathing spontaneously)
What are examples of increased alveolar ventilation resulting in decreased EtCO2?
Hyperventilation
Inadequate anesthesia
Metabolic acidosis (if spontaneous ventilation)
Medication side effect
What are examples of equipment malfunction resulting in decreased EtCO2?
Ventilator disconnect
Esophageal intubation
Poor seal with ETT or LMA
Sample line leak
Airway obstruction
Apnea
At what nm does oxygenated hemoglobin absorb light?
940 nm - near infra red light
At what nm does deoxygenated hemoglobin absorb light?
660 nm - red light
What is the Beer-Lambert Law?
Relates the intensity of light transmitted through a solution (blood) and the concentration of the solute (hemoglobin) within a solution
At the trough of the pulse waveform, what is there a greater amount of in the tissue sample?
Venous blood
At the peak of the pulse waveform, what is there a greater amount of in the tissue sample?
Arterial blood
What is the formula for calculating SpO2?
Oxygenated Hgb / (oxygenated Hgb + deoxygenated Hgb) x 100%
List the pulse oxymetry sites from most to least responsive
Fast - ear, nose, tongue, esophagus, forehead
Middle - finger
Slow - toe
What wavelength of light is preferentially absorbed in venous blood?
Red light (660 nm) is preferentially absorbed by deoxyhemoglobin (higher in venous blood).
What wavelength of light is preferentially absorbed in arterial blood?
Near-infrared light (940 nm) is preferentially absorbed by oxyhemoglobin ( higher in arterial blood).
The pulse oximeter reads 80%. You estimate the PaO2 is approximately:
50 mmHg
The pulse oximeter reads 70%. You estimate the PaO2 is approximately:
40 mmHg
The pulse oximeter reads 90%. You estimate the PaO2 is approximately:
60 mmHg
What does a left shift signify on a oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve?
Increased affinity for O2 (left = love), occurs in the lungs
What does a right shift signify on a oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve?
Decreased affinity for O2 (right = release)
What are some causes of a left shift in the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve?
Decreased temperature
Decreased 2,3-DPG
Decreased CO2
Decreased H+
Increased pH
Increased HgbMet
Increased HgbCO
Increased HgbF
What are some causes of a right shift in the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve?
Increased temperate
Increased 2,3_DPG
increased CO2
Increased H+
Decreased pH
What are methods to improve SpO2 signal?
Warm extremity
Protect extremity from ambient light
Apply a vasodilating cream
Administer an arterial vasodilator (extreme)
Place a digital block (extreme)
The pulse oximeter is a useful monitor of:
Vascular compression
The pulse oximeter is a noninvasive monitor of:
Hgb saturation
HR
fluid responsiveness(PPV)
perfusion
Where does the innominate artery (1st branch of aortic arch, 3rd branch off aorta) supply blood?
Right arm
Head
Neck
What is the formula for calculating alveolar oxygen?
FiO2 x (Pb - PH2O) - (PaCO2/RQ)
The pulse oximeter is not a good monitor of:
Anemia
Ventilation
Bronchial intubation
What can affect the reliability of the pulse oximeter?
Dysfunctional hemoglobin (methemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin)
Decreased perfusion
Altered optical characteristics (dyes, nail polish [blue, green, black]
Non-pulsatile flow
Motion artifact
How does methemoglobin falsely estimate SpO2?
Falsely underestimates SpO2 if O2 is greater than 85%
Falsely overestimates SpO2 if O2 is <85%
How does carboxyhemoglobin falsely estimate SpO2?
Reads the sum of CO-Hgb and Oxy-Hgb = overestimates SpO2
What does not affect the reliability of the pulse oximeter?
Hemoglobin S
Hemoglobin F
Jaundice
Fluorescein
Polycythemia
Acrylic Fingernails
How does mass spectrometry analyze exhaled gas?
Bombards a gas sample with electrons creating ion fragments
How does Raman Scatter Spectrometry analyze exhaled gas?
Uses a high power argon laser to produce photons, which in turn collide with the gas molecules
How do Piezoelectric crystals analyze exhaled gas?
Detects inspired, expired and breath-to-breath changes of a particular gas by incorporating a lipid layer on the crystal
How does infrared absorption analyzed exhaled gas?
Different gases absorb different wavelengths of infrared light, each having a "fingerprint".
Diatomic molecules don't absorb IR light
During anesthetic induction the SpO2 fails to display on the monitor. the circulating nurse notes that the patient is wearing green nail polish. What is the most appropriate intervention at this time?
Rotate the probe 90 degrees on the finger