Cells GCSE
1/25
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
State 4 common features of a plant and animal cell
Cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, cytoplasm
State 3 features of a plant cell that are not in an animal cell
Cell wall, vacuole, chloroplasts
What is the function of the nucleus?
Contains the genetic information for the organism
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Controls what enters and leaves the cell
What is the function of the mitochondria?
Aerobic respiration (chemical reactions of respiration)
What does the nucleus contain?
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
What is the function of the chloroplasts?
Site of photosynthesis
Why do muscle cells have many mitochondria?
Muscles require a lot of energy
What is the function of the cell wall?
Provides support and stops the cell from bursting when there is too much water
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
Where the chemical reactions take place
What is the function of the vacuole?
Provides support and contains cell sap
What do chloroplasts contain?
Chlorophyll
Why do all plant cells not have chloroplasts?
Not all cells need to carry out photosynthesis so not all need to trap light
Where are the mitochondria located?
In the cytoplasm of the cell
What is a plant cell wall made of?
Cellulose
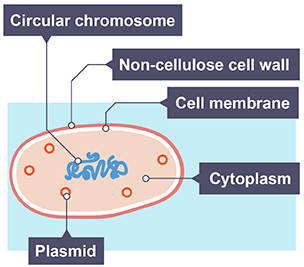
How is the DNA arranged in a bacterial cell?
Circular chromosome, loose in the cell
Why would we use the high power lens?
When we need to view cells in greater detail
What do we call the sample we are viewing under the microscope?
Specimen
What can we use to see specimens more clearly?
Stains
Why must the coverslip be lowered carefully?
To avoid air bubbles
What do we use to view cells?
Microscope
Why do we start viewing through the low power lens?
Allows you to find the specimen more easily
State the names of the 2 types of lens
Eye piece lens and objective lens
What process happens to cells to allow them to be specialised?
Differentiation
What is formed when cells with the same specialised structure and function are grouped together?
Tissues
What name is given to organs that are grouped together?
Organ systems