Period 1 Notes
(ignore red highlights)
Southernization
Basics
Definition: Southernization is the process by which ideas, technology, and culture from South and Southeast Asia spread to other parts of the world, shaping global development. Creates a prosperous south.
Order of expansion:
Starts during the 5th Century at India
By that time it goes to China
8th Century it goes to the Middle East/The lands of Muslim Caliphates
13th century its affecting the Christian Mediterranean
Diffused Via: Trade
The Indian beginnings
Indian cotton textiles start Southernization
High demand causes Indian trade of these to significantly increase “India virtually clothed the world"
Search for new sources of Bullion forces Indian sailors to travel
Siberia was India’s main source of gold—>nomadic disturbances in Central Asia disrupt their trade—> Indian sailors travel to find an alternative source—> ethiopia merchants that had lots of gold became India’s most important trade partners
Achievements
Learn how to crystalize sugar and popularize this product
Became leaders of astronomy, medicine, & math
Math: Lay foundation of modern math, “Arab” numerals came from India, and invest cero, extremely advanced in this area
Advanced artistically, musically, & philosophically
Invent chess & hair dye
The Malay Sailors
First to start riding the monsoons
Extremely talented sailors that used nature to navigate
Establishes first contact between India & Southeast Asia
Desire/Demand for Silk
Arrived & Influenced Madagascar
Southernization of China
Underlayed the revolutionary social, political, economic, and technological developments of the Tang & the Song
Effects:
Developed math
Established indigo & cotton
Made sugar an important crop
Introduced new varieties of rice-Champa from Vietnam
Drought-resistant & early ripening properties=begins systematic terracing with rice cultivation spreading up the hillsides, doubling area of rice cultivation, doubling the Chinese population
South area of China transfrosm to one of the most prosperous/commercialized parts of empire
Inland trade
Three technologies they developed(compass, printing, gunpowder) changes world
The Islamic Caliphates-The Arabs
Arab cavalries were in process of conquering new plains, and when they established on the Indian frontier, they became influenced by elements of southernization.
Arab conquest:
Spreads important crops and popularize them
First to import large numbers of enslaved Africans to produce sugar = (widely popularize the crop)
Discover/diffuse new sources of bullion
Adopt & advance Indian maths
Develop/improve the Chinese compass & become the first to use it for navigation
East Asia/Southeast Asia
The Song Dynasty (960-1279)
Essence
They ended Chaos after the Tang
Core of the world
Capital: Hangzhou (Urban center)
Education
Civil Service Exam: Revived with Confucianism, making a major part of the exam focus on these ideals
Had to take and pass this exam to become part of the bureaucracy and have a job.
Society was based on intellectual ability
The exam was rigged so more government workers were imperial servants, prioritizing native Chinese people, and also used this to raise taxes.
Put Confucian Scholars in charge of armies
Economy
Began producing goods for use & sale in distant market, not local consumption.
Heavily participated in World trade, available through network of waterways and them being extremely advanced at navigation.
Commerced via the silk road too
The Song were less dominant on the overland Silk Road compared to earlier Tang times though
Sea trade> land trade
Increasingly Commercialized Chinese Society
economic Development through Champa rice, Grand Canal expansion & trade across Eurasia
Grand Canal expansion
vital transportation route, facilitating the movement of goods and troops between the northern political center and the southern economic and agricultural heartland.
Champa Rice
Diffused from Vietnam
Terracing
Chinese Manufacturing significantly increases.
Robust Iron industry creates armor suits and iron arrowheads on a large scale.
War materials
Not enough metals available for minting coins = Introduction & Diffusion of paper money.
Facilitated trade by bringing costs down.
Responsible for the creation of the world's first government-issued paper money. (despite the tang being the first to start using it)
Improvements in agriculture lead to massive population growth and urbanization.
during the Song Dynasty, China's population doubled
Culture
Notable for advancements in art, literature, and philosophy; Confucianism revived and widely expanded by them.
Became the “Golden Age” for arts and literature.
Political
Created & Expanded bureaucracy & creates a more tightly centralized empire.
Bureaucracy was staffed with only the most qualified men which creates competency and efficiency.
Bureaucratic system is corrupt however (continuity)
Chinese Social Pyramid (1100s CE)
Emperor
Supreme ruler, considered divine.
Eunuchs
Trusted advisors and officials, often wielding significant power.
Elite Government Officials
Landlord Class (Scholar-Gentry Class)
Peasants
Comprising 90% of the population, essential for agriculture and labor.
Merchants
Wealthier than peasants but held lower social status due to Confucian values.
Mean People
Military force Members(Confucianism viewed them as wretehced but necesary evil), slaves, indentured servants, entertainers, prostitutes, and other marginal groups
Technology
Innovations like gunpowder, fireworks, the (magnetic)compass, iron and steel production and (woodblock) printing.
During the Song Dynasty (960-1279), significant technological advancements occurred:
Song became world leaders in shipbuilding. Watertight bulkheads improved buoyancy and protected cargo & Stern-mounted or stern-post rudders improved steering.
Religion
Basics of Confucianism
Core Concepts
Ren: Having humanity on all interactions
Li: Following proper etiquette and customs of respect
Xiao: Respecting your parents and supporting them in old age; filial piety
Social Harmony
If society was ordered and people interacted in the proper ways, then the nation would always be on the right path.
Understood the world as a hierarchy- everyone has their place & society only works if everyone behaves rightly.
Emphasizes the importance of relationships and moral integrity.
Filial piety
Ruler & Subject
Father & Son
Elder Brother & Younger Brother
Husband & Wife
Older Friend & Younger Friend
(Modern Day)Employer & Employee
Education:
Advocates for lifelong learning and self-cultivation.
Government
Belief in virtuous leadership and moral governance.
Mahayana Buddhism
Essence
Diffused to China via the Silk Road
Buddhism becomes element of Chinese popular religion
Buddhism links India & China
Growth of Chinese Buddhism was opposed by government
they ordered monks & nuns to return to normal tax paying citizens
Destroy or turn for public use monasteries, temples, & shrines
They confiscate lands, money, and serfs & prohibit gold, silver, copper, and iron gems
Buddhist scholars get scattered causing disunity, lack of control, creativity, and innovation.
Chan Schol of Chinese Buddhism:
Mahayana Buddhist school emphasizing direct experience and enlightenment through meditation
Brings unity to the followers
Monasticism
Buddhist Monks
Tied to Buddhism. Monks and nuns lived in monasteries, focusing on meditation, education, and charity.
Role in Society
Monasteries played a role in education, offered medical care, and engaged in community services.
However, the government sometimes viewed them with suspicion and tried to control or limit their influence
Messages about wealth
Wealth accumulation is good as long as a significant portion of it is donated to the monasteries
Daoism
Founded By Laozi, who’s philosophy explained the importance of understanding the forces/laws of nature
Dao=Way, if everyone lived in harmony with the “way” societies problems would be solved
Rival Philosophy to Confucianism that emphasizes flow with nature instead of stressed order.
Influenced Chinese Society
(no tanto como el confucianism pero igual estab ahai influyendo)
Neo Confucianism
Created during the Song
Draws on Daoism and Buddhism
Play role in reformulating Confucian thinking
China now becomes tolerant of people practicing multiple religious pratices form different relifgions at the same time
Gov calms down with restricting chinese to only pure confucianism
Women
In the very low of hierarchy.
With factories starting to be run by Men, Women started loosing their lucrative income from their position in the textile industry.
Foot Binding: Prevalent among the elite were the wife becomes unable to walk and therefore labor —> Husband has to hire servants —> Sign of Wealth. (Men control Woman’s bodies)
Their property rights expanded(they could inherit/own it)
Influence/Tributary System/The Vassal States/“Middle Kingdom”
Korea
Maintains political independence but participates in tributary relationships.
Would participate in the Kowtow ritual of submission in return with China giving them Bestowals/Gifts=Positive Relationship.
Korean Women have a lot of rights —> Chinese Observers disapprove and they push Confucian Orthodoxy —> Korean Flexible pattern replaced by Chinese sexist principles.
Used the Examination System
School for Confucian studies established
adopted Confucianism, Daoism, and Buddhism
China’s imposing presence caused Korea to forcibly/voluntarily borrow many more aspects from China than elsewhere. Living threat of being invaded.
Japan
Since Japan was separated from China, their extensive borrowing was voluntary, not due to pressures of threats.
Japanese Women escaped more oppressive features of Chinese Confucian Culture
Despite their efforts to copy China in creating a centralized bureaucratic state, power progressively decentralizes with local authorities developing own military forces.
Buddhism from China deeply affects their art, architecture, education, medicine, and beliefs.
Buddhist schools are established with them being calling Zen (Instead of Chinese Chan School of Buddhism.)
Unique writing system mixed Chinese characters from phonetic symbols. This led to the development of Japanese poetry incorporating Chinese themes and techniques.
Did NOT use the civil examination
Vietnam
Achieved Political independence but participated in the Tributary System
Borrowed:
Chinese Based Examination system to: establish aristocracy, create merit based scholar gentry class to staff bureaucracy
Arts/Literary styles
Confucianism, Daosim, Buddhism
A government approach: Styled rulers as emperors, mandate of heaven, Chinese court Rituals
Uniquely Vietnamese:
Language
Chewing betel nuts
Cock fighting
Created variation of Chinese Writing (chu nom) that distinguished them/ created independence/used for Women’s Education
Greater role for Women(Economically & Socially)
Female Buddha, Choose their husbands
Expands south in search for more independence
The downfall
Military:
Poor military leadership(scholars had poor military experience.)
Border people took over Northern China (Nomads such as the Mongols who lived on the outsides.)
Last emperor was defeated by Mongol forces.
Economy
Increasing centralization & treating all government workers as imperial servants required massive spending to cover new salaries.
Raising taxes causes Peasants to Revolt.
Political
Bureaucratic Corruption
Partial effect on downfall, but still contributed
Early Japan
Political/Social System
Despite their efforts to copy China in creating a centralized bureaucratic state, power progressively decentralizes with local authorities developing own military forces.
Society was made up by clans ruled by aristocratic families
Japan was divided into different territories/provinces, & all land belonged to the emperor.
All taxes=returned directly to the state, not local aristrocrats
Religion
Confucianism & later Buddhisms became the important philosophy/religion of Japan
Buddhism from China deeply affects their art, architecture, education, medicine, and beliefs. Buddhist schools are established with them being calling Zen (Instead of Chinese Chan School of Buddhism.)
Bakufu era
Essence
Military government (shogunate) in Japan
Pre
Emperor looses power and only becomes a symbol
Real power held by rival clans from daimyo class who would fight eachother to become shogun/military ruler of Japan(Bakufu)
3 Shogunates(Period different Shogun’s ruled)
Kamakura Period (1185-1333)
Established the first shogunate, leading to military governance.
Rise of samurai culture and Zen Buddhism.
initially a strong and centralized military government
Muromachi(1338-1573)
Cultural flourishing
Increased regional power of daimyos
more decentralized and faced constant internal conflicts and rebellions
Tokugawa(1600-1868)
Not important for this period
Impact
Samurai were established as permanent class in society
Development of distinct Japanese arts, literature, and philosophies.
Strengthened samurai identity and feudal structures.
Mongols were defeated twice in their attempts to force Japan to become a tributary state of Kublai Khan and the Yuan Dynasty
Impacts: Creates rigid hierarchy that shaped social roles and cultural expectations.'
Selective Borrowing
Since Japan was separated from China, their extensive borrowing was voluntary, not due to pressures of threats.
Despute this, they hevaily borrowed form the core of the world (the song)
*See more details under Song dynasty tributary states
Japanese Social Hierarchy During (1200-c.1870)
Emperor
Figurehead
Shogun(Warrior Class)
Political Leader
Daimyos(Warrior Class)
Nobles
Samurai(Warrior Class)
Warriors
Ronin(Warrior Class)
Paid Soldiers
Peasants
Farmers & Fishermen
90% of the Population
Artisans
Craftspeople
Merchants
Sales People
Lowest Class
Confucian Values
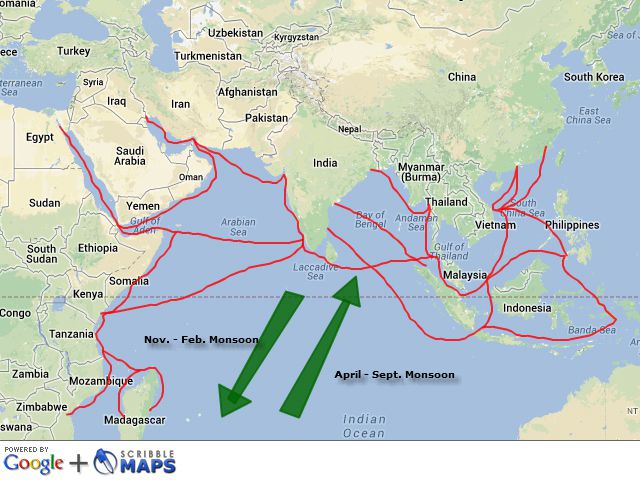
Indian Ocean Trade
Basics
Period: 800 AD-1500
Also known as "Maritime Silk Road”
Goods/Commodities & Religion diffused
3 major Religions diffused: Buddhism, Hinduism, Islam
Islam from the Middle East to East Africa & Indonesia
Buddhism & Hinduism from India to Southeast Asia
Monsoons:
Definition & Purpose: Seasonal shifts in winds, affecting the direction of the strongest winds in a region, facilitating maritime navigation by providing predictable wind patterns, enhancing trade efficiency, connecting various regions/cultures.
Cycle: Winds shift every 6 months
Sailors: Would be stuck in foreign port for 6 months
Muslim Men are allowed to have up to 4 wives & Women can request divorce
They would marry local women in each port & have children
Form Religious Communities
Widely spread Islam
Trade From India
Items:
Species/Peppers
Cotton
Textiles
Porcelain(Fom China)
Silk
Iron
Bullion
To: Middle East & East Africa
East Africa
Becomes more involved in Asian trade=Produces City States in it’s East Coast: Kilwa, Sofala, Mombasa, Malindi
General Trade
Exports:
Items: Ivory, Gold, Slaves, Wild Animal Skins
To: India, Southeast Asia, China, Middle East
Trade internally with inland kingdoms these items and then sell them to areas were items are scarce
Imports:
Items: Cotton, Silk, Porcelain
From: Asia
These items were expensive because of their scarcity
Ideal Center of Trade
Easy transportation to get here due to Monsoons
Excellent ports & harbors
Port Cities with lodging & entertainment
Relativity Peaceful Region
Ethiopia
Indian people allied with them to search for Bullion, become important trade partners
They were the only place in Africa that were Christian, NOt Arabic or Islam
They are known for building stone churches
The Swahili Coast (11th Century - 16th Century)
Overview
Time Period
Flourished primarily from around 1000 to 1500 CE, with continued importance under Omani rule into the 19th century.
Culture & Society
Cosmopolitan place that blended of African (Bantu), Arab, Persian, and Indian influences
The Swahili people spoke Swahili, a Bantu language enriched by Arabic, Persian, and Indian loanwords, and originally written in Arabic script.
Islam
Dominant religion
Integrated into daily life/governance
Promoted by Arab merchants
Cosmopolitan society
Multilingual urban elite
Economy & Trade
Centered on Indian Ocean trade
Exporting:
Gold, ivory, iron, slaves, and animal products.
Imports:
Textiles, porcelain, glassware, spices, and other luxury goods.
Used dhows
(Arab sailing ships)
Maintain trade connections with Arabia, India, Persia, and even China.
Coastal cities served as key links between African inland empires and global trade networks.
Key Swahili City-States
Kilwa
Island city-state
Peak during the 13th–15th centuries
Wealthiest and most powerful city-state
Controlled
The Southern Swahili trade routes
The trade of gold from Great Zimbabwe
Traded in ivory, slaves, and iron, and imported luxury goods like porcelain and cloth.
Known for its impressive (coral stone) architecture
The Husuni Kubwa palace
The Great Mosque of Kilwa
Sofala
Key port of the Kilwa Sultanate
Declined following the Portuguese arrival
Disrupted trade
Introduced colonial interference.
Mombasa / Malindi (super close)
A major trading port and shipbuilding center.
Maintained ties with Arabia, India, and China.
Became a focal point for Portuguese and Omani rivalry due to its strategic location on the coast.
Eventually came under Omani control, and later European (British) colonial rule.
Mogadishu / Somalia (capital/region)
One of the oldest/ most influential Swahili cities
Strong Islamic/Arab influence, strong ties w Arab/Persian traders
Known for its Islamic scholarship and architecture, with early Islamic adoption.
Famous for its textile industry
Especially fine cloth/ woven goods
Ruled by merchant elites in partnership with local clans.
Declined due to
shifting trade routes
rising regional rivals
colonial/postcolonial instability.
South Africa
Great Zimbabwe
Famous for: Massive stone structures (like the Great Enclosure)/ Capital of a powerful kingdom controlling gold trade routes
Economy: Controlled trade in gold, ivory, and cattle;
connected inland Africa to the Swahili Coast (like Sofala—key port for gold from Great Zimbabwe) and then to the Indian Ocean trade network
Decline: Around the mid-1400s — likely due to overgrazing, soil exhaustion, and shifts in trade routes
Legacy: Influenced later kingdoms like Mutapa (Mwene Mutapa), which kept trading gold and maintained regional power
Hinduism/Buddhism Influence on Major Cities
Srivijaya
Influenced by Buddhism
City of connection between commerce, state building, and religious change, that dominated critical checkpoint of India Ocean Trade
Formation: Malay sailors open sea route between India & China(Strait of Melaca)—> Ports in Malay Peninsula/Sumatra compete to attract sailors/traders—> Srivaya formed by this competition
Sucessful: Had a high supply of gold, access to high demanded spices, & levied taxes on passing ships. Used this to fund their embryonic bureaucracy, military, and naval force to protect the area.
Capital: Palembang was a major cosmopolitan city
Indian Influence/Buddhism:
Believed rulers possessed magical powers that were responsible of prosperity of people
Srivijaya becomes major center of Buddhism
Create bodhisattvas-
Kingdom of Madjapahit (Today:Indonesia/Java)
Influenced by Hinduism
One of the largest states that emerged fro the Island of Java due to it’s Hindu-Javanese cultural blend
Popular shadow puppet based on hindu epics influenced the city (Ex:Ramayana)
Hinduism establishes in Champa Kingdoms causes Shiva worships, cows honored, phallic imagery prominent
Khmer Kingdoms/Cambodia
Hinduism and Buddhism both Influence it
Fusion in the architecture of both religions
Angkorwat: Most stunning architectural expression of Hinduism(temple), that expresses understanding of cosmos(all gods live @ mythical mountmeru) later used by Buddhism as well.
Visual of Trade Routes
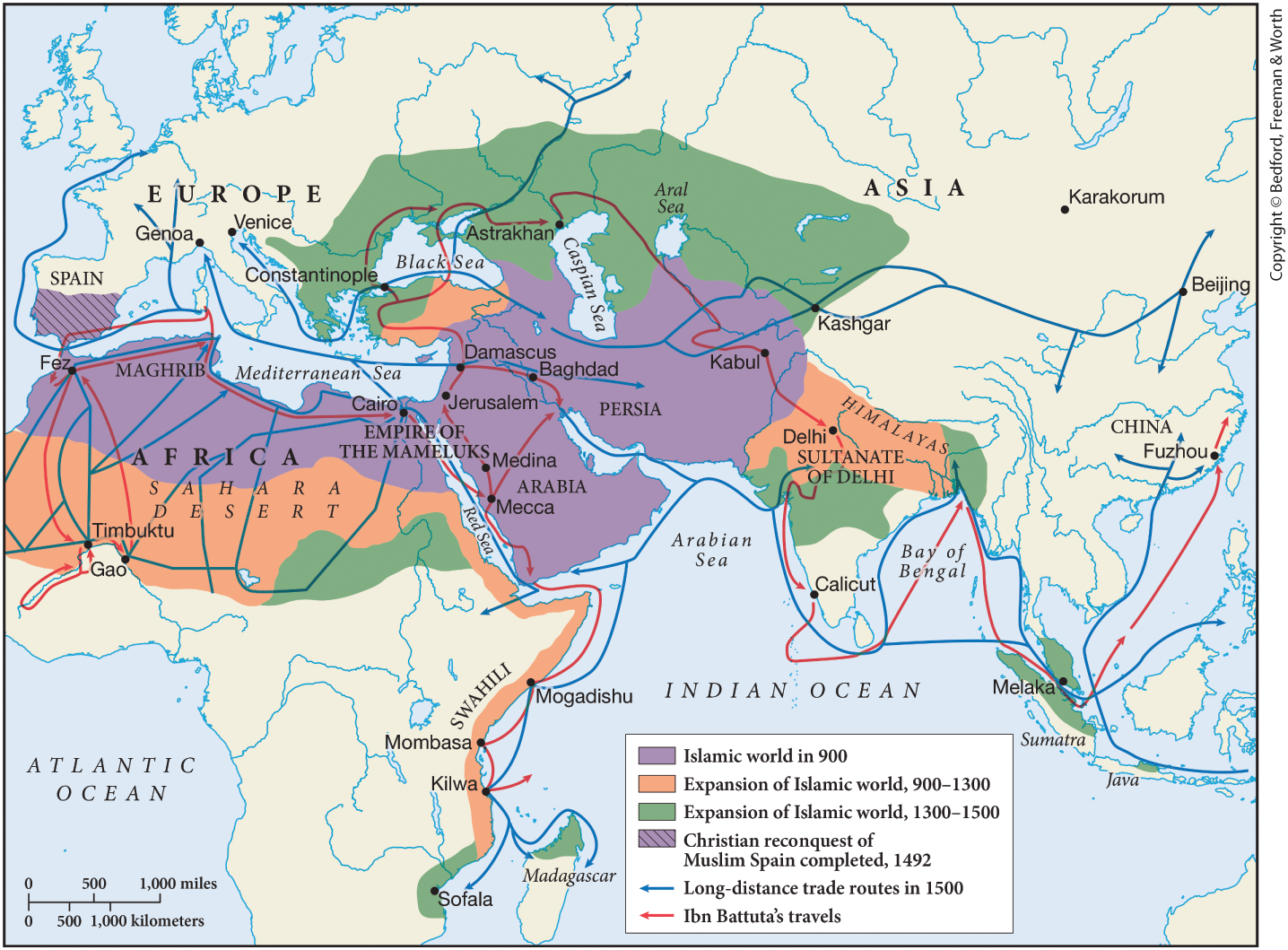
Worlds of Islam
Arab Empire Expansion
Big expansion: Post Muhammads’ Death in 632(around 100 years after) outward from the Arabian Peninsula
Islam spreads by:
Turkish Speaking Groups & Muslim Merchants/Missionaries
To: Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, North India, Southeastern Spain, Northern Asia. (Throughout Afro-Eurasia)
Heartland: The Middle East
Reasons for Expansion:
Byzantine & Persian Empires: Were weak
Islam was:
Common faith shared by many different places
Easy to convert to
Equalitarian-Everyone is equal in the eyes of Allah
Ecourages Dillusioned Buddhist & Low rank caste Hindus
Sufis are crucial to help with conversion- Spread faith with songs and dances
Cheaper than other religions(Zakat is only 2.5%)
Visual of Expansion
The two divisions of Islam - Sunni & Shia
Issue that divided Muslims
After Muhammad’s Death the Leader of Umma went to Abu Bakr(Close friend of Muhammad) who was declared the first caliph
Minority disagreed with this and believed that the caliph should’ve been a male from Muhammads’ bloodline(Ali)
Division:
Sunni
Supporters of Abu Bakar
~80-90% of Muslim Population
Shia
Supporters of Ali
~10-20% of Muslim Population
Live in Iran
The Rules
Abbasid Dynasty/Caliphate(750-1258)
Known as “The Islamic Golden Age”
Wipe out Ummayad caliphate(alcoholics, overlooked non-Arabs for leaderships positions, & ruled from Damascus)
Abu al-Abbas: New caliph who establishes new dynasty
Capital:
Baghdad becomes new capital of Islamic Empire & Jewish culture flourishes here
Priority: Consolidating Empire> Exapnding Empire (in contrast from Umayyads-First great Muslim dynasty-expanded Islam(661–750))
Their rule:
First purpose-built Hospitals to heal the sick(God creates the disease & the cure)
built around trade → used receipt and bill system
Muslim philosophers translate and spread classic Greek Philosophers teachings throughout Dar al-Islam
Spread of Islam throughout Middle East, North Africa, and Most of Iberian Peninsula
Spread Arabic language & culture through trade
New crops such as rice, sugar, lemons, and oranges are introduced to the Mediterranean
Decline
Political Fragmentation:
The Abbasid Caliphate became politically fragmented
Regional powers took control of parts of the empire, reducing the caliphs' power
Caliphs became more symbolic and spiritual leaders, with real power in the hands of local rulers
Kinda like emperors in Japan losing all power becoming symbols while shoguns truly ruled
Mongol Invasions:
The Mongols invaded the capital Baghdad(1258)
They sacked Baghdad, killed many of its residents, and ended the Abbasid Caliphate
Aftermath:
The Abbasid Caliphate’s political power ended
The caliphate title continued in Cairo, under the Mamluks
Mamluks in Egypt claimed the caliphate title until the Ottomans took control of Egypt (1517)
Seljuk Turkic Empire (1037–1194)
Who they were:
Turkish-speaking nomads from Central Asia
Originally arrived as military slaves (mamluks) in the fragmented Abbasid Empire
What happened:
Gained real political and military power
Abbasid caliphs became symbolic/spiritual leaders only
Seljuk leaders took the title of "Sultan" (means ruler in Turkish)
Impact:
Islam's heartland became divided into smaller states (sultanates) by the 1200s
Ottoman Empire(1299-1922)
Origins
Mongol invasions
Weakened the region and destroyed the Abbasid Caliphate (1258)
The Ilkhanate (Mongol empire in Persia) was established
Empire began to weaken (14th century)
Primarily due to internal conflicts/economic troubles
By the 15th century Mongol control in the Middle East had largely dissolved
Ottomans' Rise
After the Mongol collapse, Turkish warrior groups, including the Ottomans, filled the power vacuum.
The Ottomans began to expand from Anatolia, pushing out the Mongols
Importance
Became one of the largest and most powerful Islamic empires
Muslim empirrs were still around, but now the dominant empires were led by ethnic turks, not ethnic arabs(abassids were ethnically arab)
Brought political, military, economic, and cultural unity to the Islamic world
Lasted over 600 years
Controlled a diverse population, though mainly Turks
Religious continuity:
Ottoman sultans claimed the title of "caliph"
This gave them religious legitimacy, linking back to the Abbasids
Islam spread to India
Turk warrior groups spread Islam to India and there is a clash of cultures with Buddhism/Hinduism leading to violent & destructive conquest
Influence:
Cause: Due to small turk population there and them having internal conflicts limited their influence and progress on the Indian Society
Effect: Muslim Communities emerge in Northern India areas less influenced by Hinduism & Buddhism.
Islam never dominated more than 20-25%
Delhi Sultanate(1206–1526)
A Muslim empire that ruled northern India, marking the start of significant Islamic influence in the region, with its capital based in Delhi
Rajput Kingdom resisted Muslim intrusion, maintaining Hindu influence
Collection of Hindu warrior clans ruling small kingdoms in North India.
Known for military strength, resistance to Muslim invasions, and strong regional identities.
Constantly fought each other and external powers (like the Delhi Sultanate).
Vijayaner Empire(1336-1646)
A powerful South Indian Hindu kingdom that resisted Muslim invasions and promoted Hindu culture
Established in response to the decline of the Delhi Sultanate’s power over southern India and the growing pressure of Muslim invasions from the north.
Al-Andalus(711-1492)
Al-Andalus:
The territory dominated by the Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula
Cordoba: Becomes the political center of Al-Andalus
Only Umayyad who survived Abbasids(Abd al-Rahman I) fled Damascus and established the Umayyad Emirate of Cordoba, continuing Umayyad rule in Spain
75% of population converts to Islam
Arabized Christians were viewed as traitors, agnostics, and infidels
(Late 10th Century)Tolerance of different religious groups & freedom of worhips erodes causing:
Civil Wars
Fragmentation
Increased warfare between different groups
Persecution against Christians & Jews
Hatred among different groups
Impacts
Language
Thousands of Spanish words come from Arabic (e.g., almohada, aceituna, alcalde)
Agriculture
Introduced crops like rice, citrus, sugarcane, cotton, and saffron, along with advanced irrigation
Architecture & Design
Distinctive Moorish styles (arches, tilework, courtyards) seen in landmarks like the Alhambra.
Science & Knowledge
Preserved and expanded knowledge in math, medicine, astronomy, and philosophy
Music & Culture
Influenced music traditions and instruments, especially the roots of flamenco
Daily Life & Customs
Promoted hygiene (public baths, soap), urban planning, and perfume-making.
Reconquista(1492)
With fragmented Muslim state Christians retake power at Granada and force Muslims to either convert or leave
Cultural interchange persisted for a whole with Islam permanently affecting the region.
Astrolabe
Astrological and Astronomical device to read stars & skies
Hold the universe in the palm of your hand & it had multiple plates depending on what place you where at
Used:
Religiously for prayer times
Agriculturally for crops
Navigational tool to read the stars
Characteristics of Islam
Society:
Veiling: Was created and occurred before Islam, it is NOT mandated by the Qur’an
Economic Independence: People could get divorced and own businesses
Economy:
Letters of Credit: IOU’s to be paid later
Sakk: Checks
Diffused: Rice, Sugar, Lemons, and Oranges
Architecture:
Domes
Borrowed from the Byzantines
Minarets: Spires outside mosques
Art:
Show superior mathematical knowledge by using geometry
Use this because they can’t depict people
Belief that creating images of living beings could lead to idolatry
Hadiths say no to depictions of living creatures
Ibn Battuta’s Travels (1325-1354)
Who: Moroccan Muslim scholar and traveler
When: Traveled from 1325–1354 (almost 30 years!)
Where:
North Africa (his home region)
West Africa (Mali Empire — including Timbuktu and Gao)
Middle East (Egypt, Arabia, Iraq)
East Africa (Swahili Coast cities like Kilwa)
Central Asia (Persia, Afghanistan)
South Asia (India — served in the Delhi Sultanate)
Southeast Asia (Maldives, Sumatra)
China (Yuan Dynasty territory)
Purpose:
Originally for Hajj (pilgrimage to Mecca)
Later, for adventure, work (as a judge, diplomat) and exploration
Record:
His journeys were recorded in a book called the Rihla ("The Journey") — full of detailed descriptions of cultures, cities, and rulers
Importance:
His writings give historians a rare first-hand view of 14th-century Afro-Eurasian societies, especially about Islamic world connections
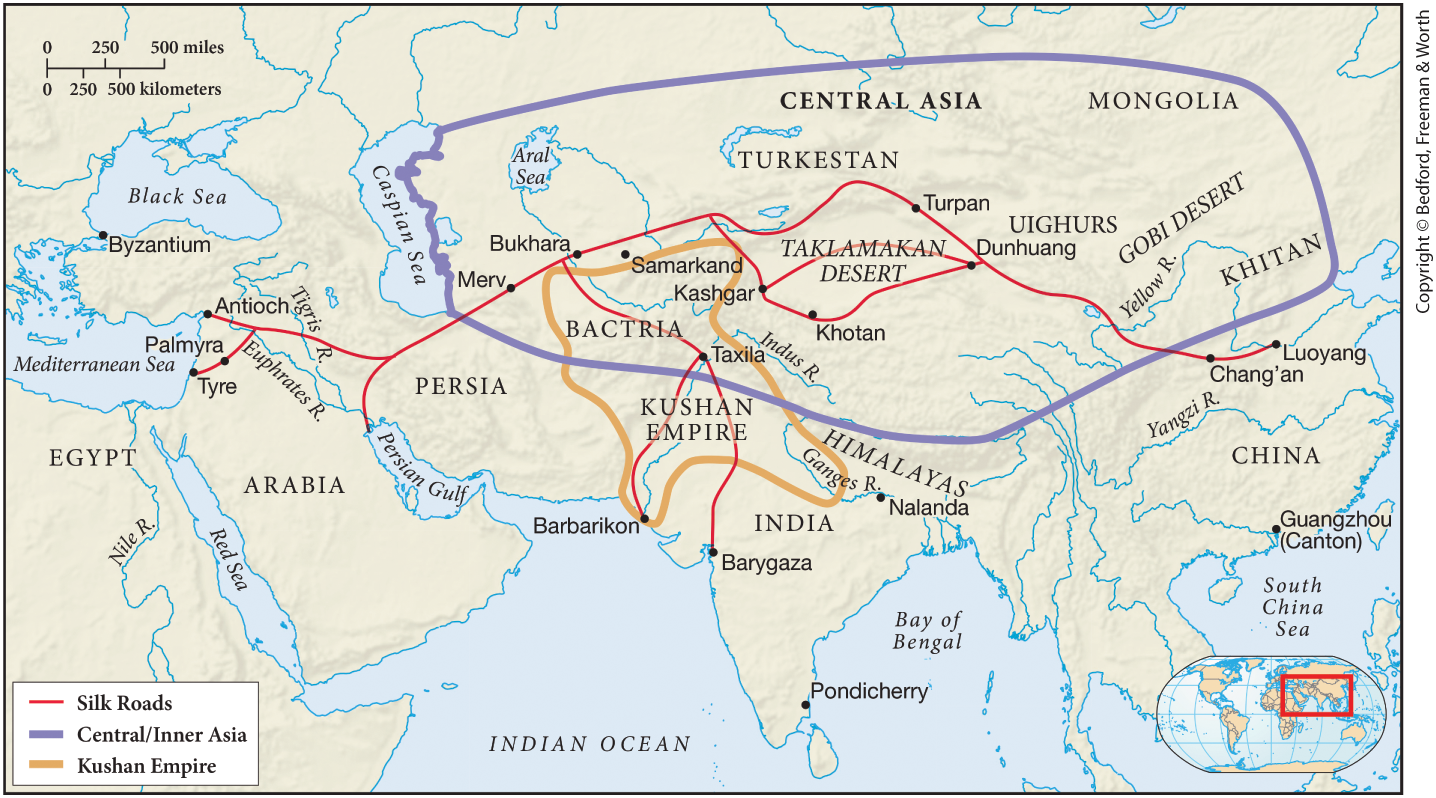
Silk Road (c. 130 B.C.E.-1453 C.E.)
Extends from
China to Europe
Camel Caravans
Where goods were carried
Caravanserai
Built by Muslims
Merchants would
Stop at inns & guesthouses located along all trade routes
Rest, exchange goods with locals, and re-ssuply
These developed into centers of cultural exchange & major commercial cities
Goods Transported
Luxurious items, not staple goods
High cost of transportation compensated by the high value of commodities
Merchants made fortunes because of the high value of trade
Silk
China: Major producer by far
South China peasants abandon food cultivation to produce: silk, paper, porcelain, lacqerware, & iron tools
Knowlegde and Technology for producing/handling raw silk diffused to Korea, Japan, India, Persia, Byzantine Empire
Supply increases but uses vary:
Central Asia: Currency & means of accumulating wealth
China/Byzantine Empire: Symbol of High status where governments would pass laws limiting the use of silk only for elites
Christians: Wall hangings, altar covers, & priests robes
Buddhist Pilgrims: As gifts to monasteries in India (In Buddhism/Chrustianism it is seen as sacred)
East Africa: Made coats for kings
Transportation improves with:
Yokes, Saddles, Stirrups, Frame and Matress
Camels can carry heavier loads
The Mongols
The Mongols revived and protected the Silk Roads during the 13th and 14th centuries, especially under Genghis Khan and his successors.
Created the largest contiguous empire in history, which made safe, long-distance trade possible from China to Europe.
Merchants, travelers, and diplomats could move across vast distances with less fear of attack or theft.
This stability boosted trade, communication, and cultural exchange.
Ideas, technologies (like printing and gunpowder), religions, and scientific knowledge traveled freely
Mongol rule helped link distant markets—China, Central Asia, the Middle East, and Europe became more economically connected than ever before.
Mahayana Buddhism
Type of Buddhism that diffused throughout the Silk Roads via Indian Traders/Buddhist Monks
Widely spread throughout Asia, adapting Buddhism to many different places
Buddha is seen as divine; god
Emphasizes salvation by faith, not with arduous study or intensive meditation
Bodhisattvas/”Living Saints”: They were approaching Nirvana but instead chose to help others achieve it
A follower didn’t need to live their life as a Buddha did: simply donating to the monastery was seen as act that merited salvation
Shift from the more spiritual/meditation/intangible aspect of Buddhism to a more tangible/materal form of it.
Pure Land School: Popular form of expression where someone repeats name of earlier Buddha(amitabha) wich ensured rebirth in heaven
Marco Polo
Who
Venetian merchant, explorer, and writer
Famous For
Traveling to China and recording his experiences in The Travels of Marco Polo
Journey
Left Venice (1271) with his father and uncle.
Traveled across the Silk Road to China.
Reached the court of Kublai Khan (Mongol emperor).
Served in Kublai Khan’s court for about 17 years (in roles like an ambassador and official)
Impact
Brought knowledge of Asia (culture, wealth, inventions like paper money) back to Europe.
His book fascinated Europeans and encouraged future exploration (including inspiring Christopher Columbus)
Legacy
Helped increase European interest in trade with Asia
Strengthened connections between East and West
Samarkand
Major trading center and a crossroads of cultures for over 2,500 years
Its strategic position along the silk roads facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between East and West
Kashgar
Major trading city on the Silk Road (modern-day western China).
Important for linking China, Central Asia, and the Middle East.
Served as a multicultural hub for goods, ideas, and religions (especially Buddhism and Islam).
Decline/End
Isolationist policies of the Ming Dynasty
Main reason
China began to avoid trading with the rapidly advancing west, and also became a more oppressive state, ultimately ending the once prosperous and widespread trade.
Fall of Important Empires
The Mongol Empire’s decline in the 14th century weakened protection and stability across Central Asia
Fragmentation made travel and trade more dangerous
Rise of maritime Trade Maritime
By the 15th century, Europeans (especially the Portuguese and Spanish) began exploring sea routes to Asia.
Maritime trade became faster, cheaper, and safer than overland travel.
Black Death (1347–1351)
The plague spread rapidly through trade routes.
Caused fear and massive population loss, reducing demand and limiting trade.
Ottoman Empire’s Control
The Ottomans gained control over key parts of the eastern Mediterranean and the Middle East.
They heavily taxed goods, making Silk Road trade more expensive for Europeans.
Visual
West Africa
Ghana Empire (830-1235)
Essence
Wealth:
Controlled gold and salt trade routes
Taxed goods entering and leaving the empire
Known for abundant gold, earning it fame in the Islamic world
Supplied Mediterrenean markets.
Government:
Powerful king with absolute authority
Bureaucracy with ministers and governors
Used tribute system from vassal states
Religion:
Indigenous African religions are dominant
Islam was introduced by Muslim traders
Coexistence of traditional religion and Islam
Military:
Strong, organized army
Used iron weapons
Protected trade routes and expanded territory
Decline
Invasions by Muslim Berbers from North Africa that tried to control the lucrative caravan trade
(Almoravids)
Disruption of trade routes
Droughts contributed
Rise of Mali Empire under Sundiata Keita, which absorbed Ghana’s territor
Mali Empire(1235-1600)
Formed: After the fall of the Ghana Empire
Territory/Ecological location: Ruled 3 different types of ecological zones
Savanna/Sudan
Sahel
Semi-arad grassland edge of the desert of West Africa
Sahara/Desert
Result:
Diversity: Mande people supplied different products & had diversity of resources causing this beneficial ecotone location to have lucrative outcomes
Their villages: were divided & organized by their specialties and the resources of the area
Expansion with Mali Cavalry
Horses: The key role
They connoted prestige & status but were the fundamental tool to expand empire & attack
Villages built protective mud walls to protect their settlements from the Mali cavalry since this stopped sudden attacks & took away their efficient element
Mali’s diverse ecological conditions were able to find the right fit to sustain their horses
Tropical Humid Africa: Presece of tsetse fly limits use of horse since it’s deadly for them. Wetter conditions gave Mali cavalry a disadvantage
Dry Climate= Horses thrive
Important Rulers
Sunjata (Sundiata Keita):
Most powerful of the Mali Rulers who legendarily and heroically unified/formed the Empire. Developed empire from the conquest & union of many smaller states
Power and Formation by Sunjata is legitimized by griots.
Tale of him connects Nyama(magic) to political power and how they influenced successful military
Mansa Munsa(King of Mali)
Islamic ruler that when doing pilgrimage to the Mecca gave away so much gold that he caused the market to crash and depressed world prices
Places like Mecca, Cairo, and Medina received most of his gold
Remebered for having been unfaithful to Mande traditions and having wasted the imperial treasury
Important Cities
Timbuktu
One of the largest and wealthiest cities in the world
Wealth was derived from its status as a trading city
gold, ivory, and salt were all traded in large quantities.
major center of trade, learning, and Islam
Gao
Important trading hub along the Niger River
Capital Niani
Where Sunjata ruled
Located at intersecting area of trade routes & different ecological zones of the empire
Trade:
Became the world’s largest producer of gold
Mali supplied almost 2/3 of the world’s gold via Caravans of gold
Trade of gold increases spread of their technology, language, ideology, and culture
Islam comes to Africa and culture is introduced/spread by the Mande
Trans Saharan Trade: Gold, Ivory, and salt were all traded in large quantities
Trade Cities of the Sahel: Timbuktu, Gao
Jobs
Oral Historians:
Spread the ideology, culture, and history of the Empire
Blacksmiths:
Provided: tools for the empire leading to their military success(Iron weapons, leather, iron trappings for horses). Said to have supernatural powers to be able to do what they did
Search for wood: Their work required a lot of wood causing them to expand empire in search of this, leading to deforestation that would be used by Cavalry
Lodges: Centers of transmission of Mande Culture created & run by blacksmiths. Offered spiritual protection and moral leadership to their community. Maitaned control of empire’s network(trade/infrastructure)
Social Divisions
Slavery: Substantial part of the commercial activity of the empire
Sexism(Gender inequality):
Male captured prisoners of war would become soldiers while females would become slaves leading to many more female slaves than males.
Women’s Role: Imperial growth depended on them and their jobs, but they lacked political/economic power. They produced goods, played their reproductive role, sometimes were concubines, and were barely mentioned in oral history.
Mali Key Language:
Mande: The people of West Africa (the society)
Griot: Oral historians- storytellers, musicians, and poets who preserve the history and culture of their people.
Nyama: Control of the supernatural/magical & mystical energy/sorcery.
Nasi: Power of darkness, a thing used to harm someone
The Mongols
Pre-Conquest/What Led To It
Harsh Environment
Mongols lived in the steppe (Central Asia) — harsh, dry, limited resources
Encouraged raiding, herding, and mobility
Tribal Conflicts
Mongol tribes were disunified, constantly fighting for survival and dominance
This created a warrior culture with strong military skills
Need for Resources (from sedentary lands)
Expansion provided wealth, land, animals, trade goods
Revenge & Retaliation
Early conquests were often in response to insults or betrayals by neighboring powers (e.g., Khwarazm Empire)
Genghis Khan’s expansion was driven in part by a desire for revenge, especially after his early life involved betrayal and conflict with rival tribes. This motivated him to unite the Mongols and expand his empire through conquest.
Weak Neighboring States
China and Central Asia were divided and vulnerable
The Mongols took advantage of this political instability
The Rise of the Mongols
Origin:
Nomadic tribes/Pastoral clans from the Central Asian steppes (modern-day Mongolia)
Lived in harsh climates, skilled in horseback riding, archery, and survival
Unification:
Genghis Khan (Temujin) united the Mongol tribes (1206)
Became the "Universal Ruler" and began expanding Mongol control
Military Power:
Highly organized army with discipline, speed, and strategy
Used psychological warfare, tolerance for useful cultures, and brutality against resistance
Horse:
Domesticated them with horsebreeidng to survive diverse climate
Thick Horses: Short & fat for cold weathers
Made it their distinct form of warfare- well armed warriors on horseback
Traveled by horse while firing arrows (multitasking)
Expansion:
Conquered China, Central Asia, Persia, the Middle East, Eastern Europe
Created the largest land empire in history
Steppe Diplomacy:
Loyalty system - courage in battle
Kinda analogous to Bushido
Steppe - Flat grassland
1200, Temujin/Chinggis Khan/Genghis Khan: The Leader who unified the Mongols and led them to victory
Empire divided among his grandsons & despite internal conflicts for power/leadership, Mongol rulers were able to implement administrative system that adapted to each location.
Key Terms:
Khan: Chief(leader/ruler), with who Mongol conquest began
Khanate: territory ruled by a Khan
Key Success Factors:
Strong leadership (Genghis Khan and successors)
Adaptability (used new tech, absorbed skills from conquered peoples)
Effective communication (relay stations across empire- courier system)
Promoted trade and stability across the Silk Road
4 Major Khanates
Yuan Dynasty—China (1271–1368)
Kublai Khan’s rule in China
The Grandson of Chinggis Khan
China’s very established system & large population:
Causes Mongols to leave their political & economic practices in place
Use what Chinese already have set up and enhance/imrpove it
Civil Serive Exam: Mongols rigg/manipulate it to give privileges to certain groups
Pro: Uigher & Mongols
Anti: Han(Native Chinese)
Confucianism:
Used Mandate of heaven to justify their rule
Women had more liberties but were still influenced by some confuain principles
Ex: Foot Binding continued
Confucian scholars protest/reject the Mongols
Beijing
New Capital
Decline:
Internal rebellion:
Han Chinese resented Mongol rule.
Heavy taxation and discrimination against native Chinese fueled uprisings.
Corruption and weak leadership:
After Kublai Khan, rulers were ineffective and court corruption increased.
Economic troubles:
Natural disasters (floods, famines) worsened hardships.
Inflation due to overprinting of paper money.
Peasant revolts:
The Red Turban Rebellion (starting in 1351) became a major threat.
Rebel groups, especially led by Zhu Yuanzhang, grew stronger.
Fall(1368)
Zhu Yuanzhang’s forces captured Beijing (then called Dadu).
Last Yuan emperor fled north to Mongolia.
Yuan rule ended in China; replaced by the Ming Dynasty.
Aftermath:
Mongols continued to rule parts of Mongolia (known as the Northern Yuan).
Han Chinese restored native rule under the Ming.
II Khanate—Persia & The Middle East (1256–1335)
Chagatai—Mongolia/Central Asia (1225–1687)
The Golden Horde—Russia & Eastern Europe (1240s–1502)
Russian prince’s pushback against the Mongols but are unsuccessful
Europeans accuse them of being brutal conquerors “Allied with Satan”
Mongols in Russia Prevented Russia from culturally developing
As they settled Ogodei(the Khan of Khans) dies and Mongol law that required all offspring to return to Mongolia to elect new khan saves Europe
Impact
This event saved Europe from full-scale Mongol conquest
The Golden Horde never returned with the same momentum
Society/Religion
Gender Roles:
Had more rights/prestige than other Women in other places
Both Men & Women tend animals
Mainly male warriors but Women were skilled/trained and could participate
Religion:
Originally Practiced
Shamanism/Tengrism: (shaman or saman) interacts with the spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance
Animism
Sky God(Belief in Tengri): With whom they justified their conquests
Post-conquest religion
Adopted the religion of their conquered peoples
Mongols were highly tolerant of other religions
Used religion politically to maintain control over diverse populations
Pax Mongolica
Definition: Mongolian Peace
Conquered people were granted many freedoms
Practice their own religion
(many Mongols convert to Buddhism/Islam)
Interest in trade safety
Mongols guarantee safety to merchants & travelers, and they try to make roads as safe as possible
Finance: they tax the trade along the roads creating a steady source of income and motivating them to make trade travel safe
Paiza: Their established passport system within the empire to protect high-level visitors/merchants
Trade through Silk Roads
Goldsmithing
They spare trained craftsmen & transport/use them to benefit their empire
Courier System
Their system of trasnportation/communication known for it’s speed & efficiency
Relay stations across empire to increase communication/connectivity
Camel & Horses were main sources of trasnport at the time
Decline of the Mongols
Too Big to Control
Empire was massive — stretched from China to Eastern Europe
Hard to manage such a large, diverse territory
Division into Khanates
After Genghis Khan’s death, empire split into 4 khanates:
Khanates became independent and rivalrous
Leadership Problems
Weak, corrupt, or fighting rulers after the strong early Khans
Succession crises weakened stability
Rebellions and Resistance
Conquered peoples began to fight back
Local rulers regained power (e.g., Ming Dynasty replaced Yuan in China, 1368)
Economic Decline
Over-expansion strained resources
Trade slowed down after initial Mongol peace (Pax Mongolica) faded
Plague (Black Death) spread via trade routes, weakening populations
End of Each Khanate
Yuan fell to the Ming (1368)
Ilkhanate collapsed (1335), Ottomans took over region
Chagatai split into smaller states
Golden Horde declined, replaced by Muscovy/Russian states by the 1500s
Medieval Europe/Middle(Dark) Ages (476-1450)
The Byzantine Empire(c.330AD-1453)
Basic Concept:
The Eastern Roman Empire that remained after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, that was overthrown by Barbarians, aiming to preserve the legacy of classical greco-roman civilization.
Empire and it’s people referred to themselves as Romans
Capital: Constantinople
Was dominated by Greek Language & Culture
Eastern Orthodox Christianity: affiliated with them seeking religion that would unify diverse people of region & legitimize ruler
Oppososed Wewstern christianism
Roman Catholicism
End: Overthrown by Muslim Ottoman Turks
Ottoman Sultan Mehemed II seizes Constantinople
Protected by water & walls so it had withstood attacks & sieges, so Turks attack through water & with cannons. Offer 3 times to spare emperor if they surrender but they don’t so after a break day of prayer they take down Constantinople and kill Constantien(emperor) fighting.
Hagia Sophia becomes the main mosque
Received no help from Western Europe
Impact of the Crusades
Essence
military campaigns by European Christians to convert Muslims and non-Christians
Religious Impact:
Deepened the divide between Christians and Muslims.
Strained relations between Western (Catholic) and Eastern (Orthodox) Christians (especially after the sack of Constantinople).
Economic Impact:
Expanded trade between Europe and the Middle East (spices, silk, goods).
Helped boost the economies of Italian city-states
Political Impact:
Weakened feudalism
many nobles died or spent too much money fighting.
Strengthened monarchies
Kings gained more power with fewer nobles challenging them
Cultural/Social Impact:
Europeans were exposed to new ideas, technologies, and goods from the Islamic world and Byzantium
Helped spark the Renaissance by reviving interest in ancient learning and global contact.
ex:greek philosopher worked diffused
House of Wisdom
Military Impact
Crusading experience introduced Europeans to new military techniques (like better fortifications, cavalry tactics).
P.S.
(the deal for the crusades was between Pope Urban II and the byzantine empire)
The Holy Roman Empire(800-1806)
Ironic Name:
Not Holy: It was called "Holy" to show a connection with the Christian Church, but the empire often had conflicts with the Pope and wasn't truly religiously unified. Still however tried to have strong ties with the Catholic Church
Not Roman: It wasn't based in Rome and had little connection to the ancient Roman Empire. It was mostly Germanic.
Not an Empire: Instead of being a strong, centralized empire, it was a collection of many small, semi-independent states ruled by princes, dukes, and bishops, with an emperor at the top, but without a single powerful ruler in control
The Habsburg Family of Austria(c.1400)
The Habsburgs held the title of Holy Roman Emperor for long periods
Many of their lands were part of the Empire.
Intermmaried in the family to: Remain in power, stay in the throne, control Emperor elections, and not have to form alliances & share power.
Characteristics of Christendom
Banking(c.1300)
With expansion of Silk Roads up North with the Mongol invasion, Europe’s trade, financial, and commercial practices increase
Start using:
Paper letters of Credit & Checks
Risky Investments
Usury done through Jews who leant money and charged interest
Usury: The practice of lending money at unreasonably high rates of interest
Christian church: Prohibits it but need for easy cash by the European society made a market for loans depenednet on Jews. As economy expands Christian Church turns to a blinded eye to money lending.
Torah: Forbids Jews to charge interest to Jews, but nothing is said about charging interest to Non-Jews(Gentiles)
Rise of Christian banking Houses:
Developed during the Middle Ages to aid trade. Along with innovations such as bills of exchange, or bank drafts, and credit, the rise of banking houses supported the development of interregional trade in luxury goods
Cities
Increase in food, economic, and political stability leads to growth of cities. Economic growth leads to urbanization which leads to a population increase.
Imperial Free Cities/Friei State: Created by financial/ecnomic strength of burghers who desired more political freedom for urban centers
New opportunities for Women in Urban Jobs, but then they were banned from these, so church provided alternative, but then they were also limited in monasteriea and convents.
Intellect improves with rising population, commercial life leads to emergence and creation of more towns/cities
Intellectual beings start encouraging ability to use human reason and logic to understand the operation of natural order
Theres a fragmented, decentralized nature in European feudal monarchies
Geography
Fact that it is located at the very end of the land mass & away from all political trade routes makes political unity difficult, so population centers were divided by geographical barriers
Moderate Climate=Productive Agriculture
Multicentered Political Systems creates states that have distinct cultures
Technological borrowing
Europeans advance shipbuilding & navigation techniques
Rivarly & war among these different states
Trade
Fairs of Champagne(La Foire de Champagne)
Basic Concept: Famous medieval trade fairs held in the Champagne region of France during the 12th and 13th centuries. Became major centers of trade & interconnected different European regions
Goods: Textiles, spices, wool, and luxury goods were bought and sold
The Hanse/ Hanseatic League
Basic Concept": German Maritime Trading Alliance
United: Northern Europe
Goods Traded: Low Value Bulk Goods
Lumber, fish, wool, wine, wood
Visual:

Europe & The Church(600-1450)
The Catholic(“Universal”) Church is led by the Bishop of Rome or the Pope
Made laws, crowned kings, sent people to war, and collected taxes
Pope became landlord and had its own army
Feudalism & Manorialism
Three estates acordidng to King Alfred the Great of England
Men of Prayer
The Monastery
Resembled small city/ self-sustaining town but was not immune to attacks so it was fortified
Monks
Men of War
Castle
Motte: Overlooked village
Bailey: Courtyard, living quarters of soldiers, shelters for horses, storehouses for grain & wine, and it is built with dirt
The Keep: Watchtower/Arsenal. Bottom is for storage & eating, top is for sleeping. It sustained the lord and their family
Visual:

Lords & Knights
Men of Work
Village
Peasants
had land for self and land for feud to farm
Lived in huts
Monasticism
Definition: A religious way of life where people dedicate themselves to spiritual work. Significantly spread Christinity
Names:
Men are Monks who live in Monasteries
Women are Nuns who live in Convents
Together make up the Clergy
Christian Monasteries:
Institutions that helped preserve art, culture, faith, and learning through scribes
Scribes: Copied manuscripts/books which were later illustrated/illuminated with pictures & gold leaf
Jobs:
Run orphanages, welcome/forster travelers(food & lodging), taught school, were missionaries, took care of local churches
St.Benedict(c.500 CE)
Remembered For: Created the Rule of St. Benedict, which became the standard for Western Christian monasticism
Before: Monks lived ascetic life (without comfort & luxuries)
His Impact:
Believed their lives had to be more purposeful
Encourages 8 hours of: sleep, prayer, and manual work
Catholic Church Hierarchy
Pope
bishop of Rome
Cardinals
elect/advise the Pope
Bishops
Supervise priests
Priests
Catholics
Countries are divided into regions called dioceses that had archbishops as leader
The Black Death- The Bubonic Plague
Essence
A disease that struck Europe in the mid-14th century, killing about a third of the population
Emerged in North China → spread rapidly across the Silk Roads and the Indian Ocean Trade routes
Middle East → Killed nearly 1/3 of their population
Europe → killed ½ of their population
Effects:
Decline of Church Authority: People lose faith in Church because it couldn't explain or stop the plague, leading to widespread disillusionment.
Shift to Secular Scholarship: With the loss of clergy and an interest in understanding the world beyond religion, people began to explore secular studies, science, and philosophy.
Birth of the Renaissance: This shift laid the groundwork for the Renaissance, a cultural revival in art, literature, and learning that emphasized humanism and individual achievement, moving away from medieval norms.
Hundred Years’ War (1337–1453)
Main Cause:
Dispute over the French throne after the death of the French king with no clear heir —>English kings (especially Edward III) claimed they had a right to the French crown.
Control of land in France and economic conflicts
(especially over wool trade).
Major Sides:
England vs. France
Joan of Arc
French peasant girl who believed she received visions from God to save France
Helped lead French forces to major victories
Ex: Siege of Orléans (1429).
Boosted French morale and helped crown Charles VII as King.
Captured by the English allies (Burgundians), tried for heresy, and executed by burning at the stake at age 19.
Later seen as a martyr and symbol of French unity
Important Changes
Rise of national identity in France and England.
Decline of feudal knights; rise of professional armies.
New weapons (longbow, cannons) changed warfare.
Outcome:
England lost almost all its territory in France
France emerged stronger and more unified.
England entered a civil war (War of the Roses).
The Aztecs & The Incas & Mayas
Aztecs
Location: Mexico
Advanced Agriculture
Performed Human Sacrifice based rituals
Mainly for their Sun god
Mainly people they captured at war
Empire was war-driven, expanding through conquest & tribute
Slavery was practiced
They worshipped many gods, especially sun and war gods
Decentralized empire
Great engineering: chinampas (floating gardens), canals
Tenochitlan founded (1325)
capital city of Aztec Empire → markets were established, commercialised
To secure their legitimacy as rulers → Mexica claimed heritage from older, more renowned Mesoamerican people
Incas
Location: Western South America (modern Peru, Ecuador, Chile)
Vast empire - Largest empire in pre-Columbian America
Expansionist - army, established bureaucracy, unified language, system of roads and tunnels
Inca road system- Qhapaq Ñan
a vast network of roads
built to facilitate communication, transportation, and military movement
enabled communication and cultural exchange between different regions, promoting a unified Inca identity and the spread of technologies, languages, and traditions.
Advanced Agriculture
Had an efficient road system/ bridges
Polytheistic religion who preformed rituals
Impressive stone architecture (Machu Picchu)
Had a highly organized centralized government, and deeply focused on the infrastructure and order of their empire
Practiced terrace farming and used the quipu for record-keeping.
Used quipus (knotted strings) for record keeping (no written language)
Did not practice slavery
Mita System
Existing system within the Inca Empire
Compulsory labor service, for projects like public works
The Spanish colonial government later repurposed and intensified this system, particularly for forced labor in mines.
Incas were used to the system and working in the mines(contrast from African slaves that had no altitude experience during the age of exploration)
Maya Civilization
Location: Yucatán Peninsula (modern Mexico, Guatemala, Belize)
Advanced writing system (hieroglyphics)
Complex calendar (solar and ritual calendars)
Built massive city-states (ex: Tikal, Chichen Itza)
Known for pyramids, astronomy, and math (concept of zero)
Society ruled by kings and elite nobles
Frequent warfare between city-states
Gradual decline before Spanish arrival (likely due to drought, warfare, overpopulation)