11-01: Humans and Our Environment
0.0(0)Studied by 3 people
Card Sorting
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:22 AM on 5/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
1
New cards
Plant pollen
________ shows species that were alive.
2
New cards
Animals
________ can be smothered by oil or be poisoned by ingesting it.
3
New cards
infinite development
Many cultures act as if ________ as growth is their goal /that humans are separate and above their environment.
4
New cards
Dust particles
________ are less than 10 microns5.
5
New cards
natural gas
Coal, oil, and ________ extraction take a heavy toll on ecosystems.
6
New cards
radiation
Smoke, ionising ________, hydrocarbons, workplace chemicals, arsenic, asbestos.
7
New cards
spine
Can cause damage to brain, ________, and nerves.
8
New cards
Killarney
Rocks in many Ontario ecosystems can not neutralize the acid and can result in dead lakes like in ________.
9
New cards
Dams
________ for hydroelectric power can devastate the environment they are in tooWaste Tragedies.
10
New cards
Workplace chemicals
________ such as herbicides, solvents and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can also harm humans in an indoor or outdoor environment.
11
New cards
Increases levels
________ of heavy metals in soils such as aluminum; these metals can be toxic to fish, plants, birds, and other animals.
12
New cards
basic nutrients
Reduces ________ such as calcium and magnesium from soil by leaching.
13
New cards
Industrial revolution
Invention of the steam whistle, Boom in industry, Beginning of all environmental issues today
14
New cards
The growing human population
~7 billion people, population is constantly growing. With abundant resources, populations of living things tend to increase exponentially. The carrying capacity for humans has been drastically increased by technologies: carrying capacity: particular ecosystems have certain number of resources and in order to support life everything must have sufficient resources to survive. Because of advantages in medicine, food, growth, technology, etc. we have the ability to live longer. Our large population has a large impact on the environment and technology has helped us live longer and help the population grow at a very fast rate.
15
New cards
Tragedy of the commons
Shared resources are often collectively over-used by many and under maintained - often depleting or spoiling the resource. As a population, impacts are massive - everyone needs to do their part
16
New cards
Energy tragedies
Coal, oil, and natural gas extraction take a heavy toll on ecosystems. Dams for hydroelectric power can devastate the environment they are in too
17
New cards
Waste tragedies
Limited landfill space - eventually these will fill up - increasing quantities of hazardous wastes & single use plastics are major contributors
18
New cards
Agricultural tragedies
Pesticides and fertilizer use - soil degradation, if not used carefully all of these resources all of these resources will be used up
19
New cards
Monocrop farming
Growing one plant at a time - sustainable farming is rotating crops and letting the land rest. this is an issue bc we now have the technology to assess demand and choose what to plant based on what will make the most money
20
New cards
overfishing
Fishing practices aren't always regulated properly. If we catch too many fish too quickly, the fish population will dwindle and won't reproduce properly
21
New cards
Biodiversity
We don't know what will happen when things go extinct. A balanced ecosystem requires equal amounts of predators and prey, as well as balanced resources
22
New cards
Deforestation
Ultimately does impact humans and their comfort. Species may not be able to survive in changing conditions because of deforestation. Habitat and species loss: We lose populations due to changing conditions, Invasive species - Habitat fragmentation
23
New cards
Pollution
Pollution: when a human activity causes the release of a substance that harms the environment. Pollutant: waste material from human activity that can cause harm to an ecosystem. Environmental contaminants: are substances that can harm humans and other living things. Pollutants and contaminants are types of environmental factors that affect our environment and both living and non living things
24
New cards
air pollution
5 major gases: carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, hydrocarbons
25
New cards
carbon monoxide
Toxic: removes oxygen from airways, suffocates humans by preventing them from breathing in oxygen. A clear colourless odourless gas. We get it from the partial burning of organic matter like gas, coal and wood. Released from car exhausts and cigarettes
26
New cards
sulfur dioxide
One of the contributors that causes acid rain. Smells like rotten eggs. Produced by burning sulphur containing fuels
27
New cards
nitrogen oxides
Nitrogen is the most abundant element (air has ~78% nitrogen). One of the contributing factors to acid rain. Everything has a pH that tells us how acid or basic something is, rain water has a certain level of acidity and when exposed to certain things, its PH changes and thus it becomes acidic and then changes the nature of the soil (and plants have a low tolerance for acidity). Produced by burning fossil fuels
28
New cards
particulate matter
Tiny particles in the air that shouldn't be there, hard to filter out. Range of particles that includes ash from factories, smoke from fires, soil and fertiliser from farming. Pollen, dust and mould are natural particulates. Particulates can cause a range of health problems for humans. E.g. the people who helped clean up 911 dealt with this. Dust particles are less than 10 microns
29
New cards
hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons come from fuels that can evaporate into the air. From the air, they can react with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight to produce photochemical smog, in particular, it's the nitrogen oxides
Smoke + Fog = Smog
The mix of compounds in smog can damage plants and injure lungs. Nitrogen dioxide is in the air, Nitrogen oxides are formed when solar energy hits, and it mixes with water, when that mixture mixes with other chemicals, then they are left to be in the air
Smoke + Fog = Smog
The mix of compounds in smog can damage plants and injure lungs. Nitrogen dioxide is in the air, Nitrogen oxides are formed when solar energy hits, and it mixes with water, when that mixture mixes with other chemicals, then they are left to be in the air
30
New cards
CFCs - chlorofluorocarbons
Comes from refrigerators, aerosol cans, air conditioners, Causes ozone in the upper atmosphere to break down - this allows for more UV light to reach Earth and cause issues (e.g. skin cancer). Ozone layer: protective layer blocking harmful rays from the planet. Ozone layer is thinning out
31
New cards
GHG, greenhouse gas
Contribute to global warming, Cause heat related deaths. Damage to the ecosystems, especially at the poles. Greenhouse: heat cannot leave - It is like a blanket hugging the Earth
32
New cards
workplace chemicals
Workplace chemicals such as herbicides, solvents and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can also harm humans in an indoor or outdoor environment - VOCs have been often used in paints. WHMIS symbols warn of dangers
33
New cards
pathogens
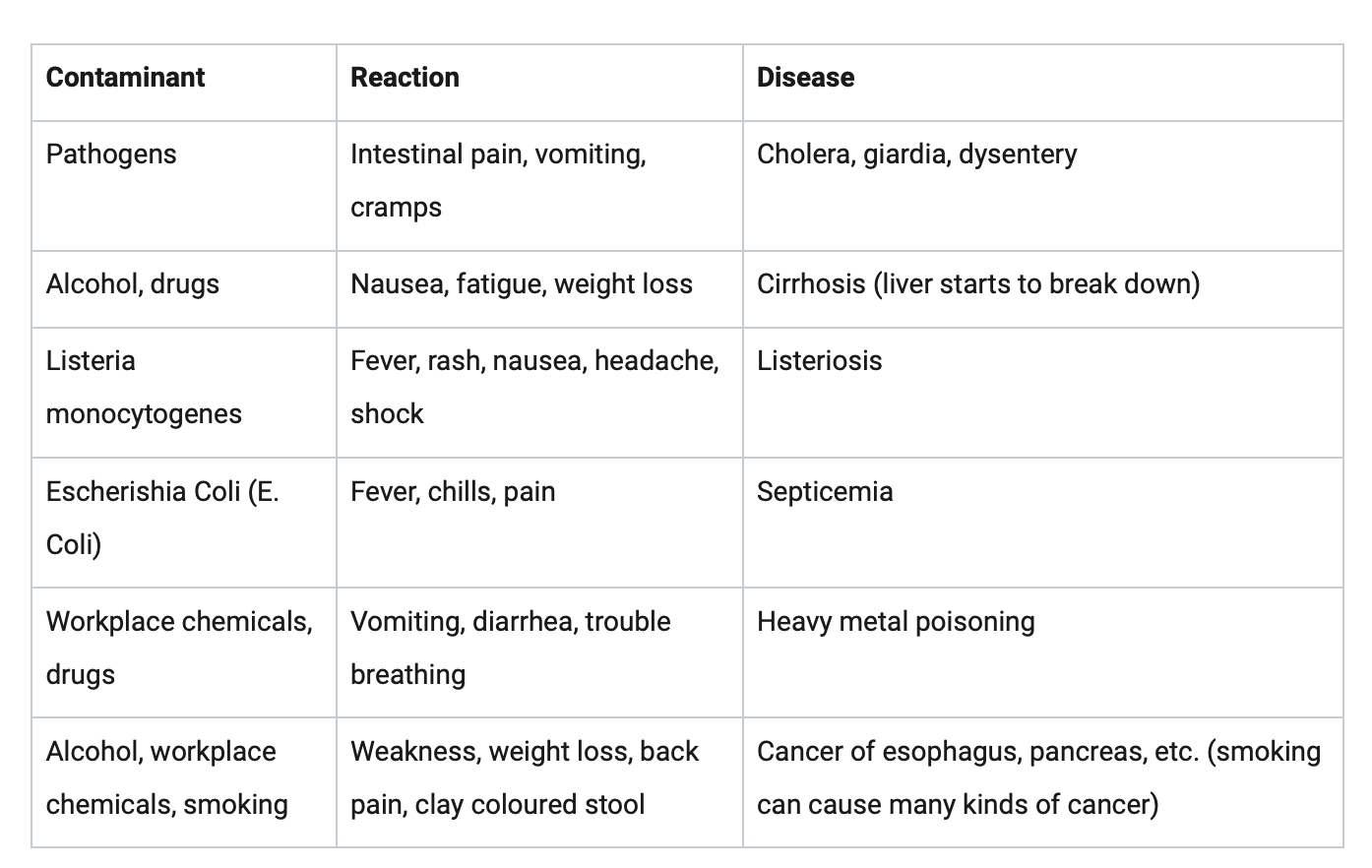
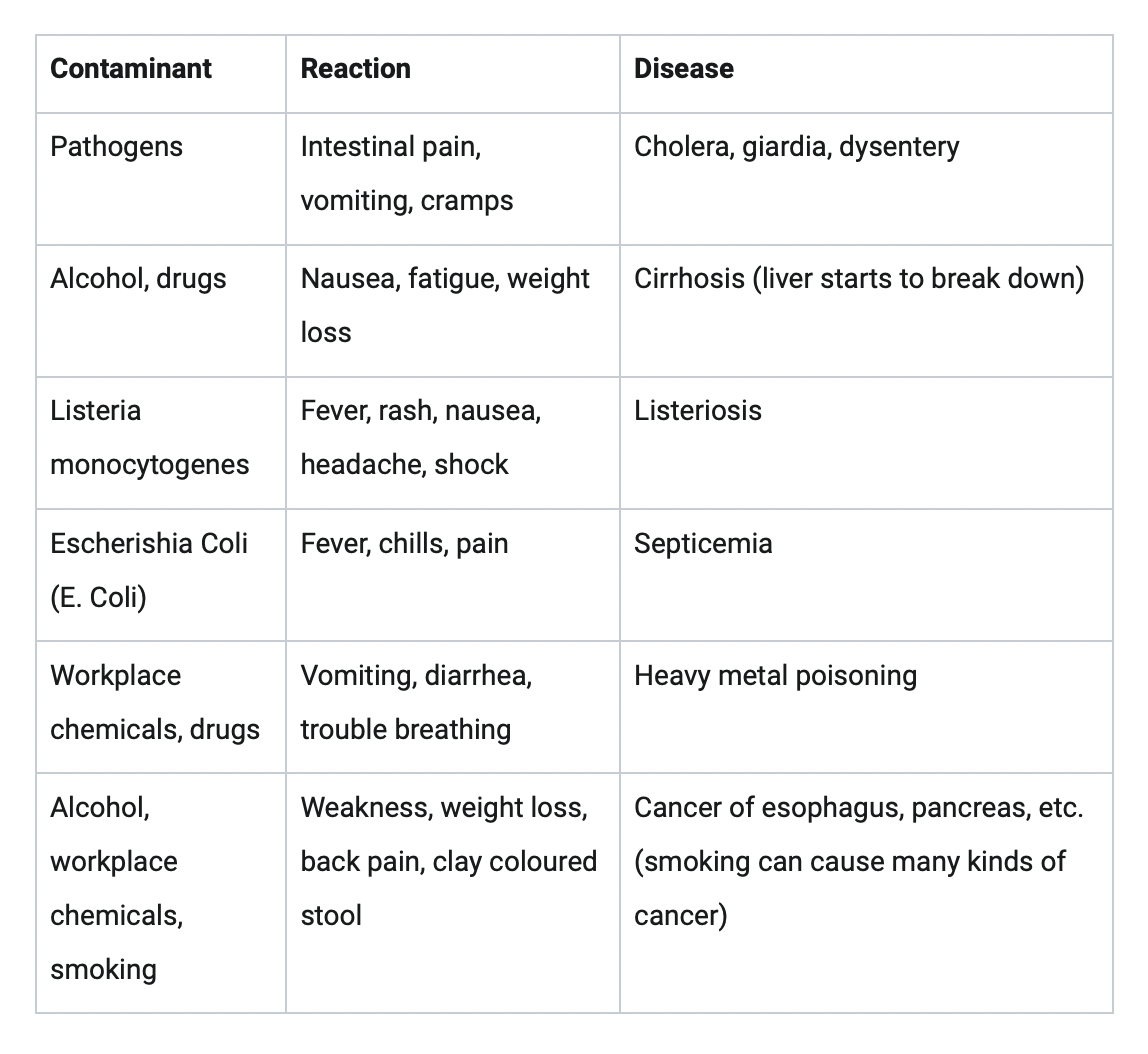
Pathogens: harmful to humans (i.e. disease) that is transmitted from person to person (organic). COVID is a pathogen, Disease causing bacteria, viruses, single celled organisms and fungi can be transmitted through air, food or water, Animals can also carry pathogens such as West Nile virus (bitten by a mosquito) and Lyme disease (bitten by a tick)
E.g.: Salmonella, E. Coli, etc.
E.g.: Salmonella, E. Coli, etc.
34
New cards
entering the body
Environmental contaminants can enter the body in many ways. We can inhale it, it can be absorbed, we can eat it (ingestion), or it can be injected
35
New cards
inhalation
Your respiratory system ends with alveoli which can absorb inhaled contaminants. Body secretes mucus and has cilia (hairs and little flaps of skin that are hair-like) to trap small amounts of many particles (e.g. bacteria, dust). We have no defence for pollutants like VOCs and pesticides
36
New cards
ingestion
Ingest: to eat, comes down to your digestive system. Ingested contaminants can be absorbed by the digestive system. Body defences include vomiting and blood filtration by the liver
When you ingest contaminants, you may vomit because the body wants to purge itself of the contaminants
When you ingest contaminants, you may vomit because the body wants to purge itself of the contaminants
37
New cards
absorption and injection
Skin is the first line of defence for our bodies. It contains protective layers but also capillaries that can absorb contaminants. Skin is the largest organ and it is a layer of protection for our bodies. Oils, tar, cleaning products, and pesticides can all enter this way
Pathogens like the West Nile Virus can enter skin by injection
Outer layer, inner layer, subcutaneous layer
Once the skin is breached, it can get anywhere in the body because it enters the bloodstream
Pathogens like the West Nile Virus can enter skin by injection
Outer layer, inner layer, subcutaneous layer
Once the skin is breached, it can get anywhere in the body because it enters the bloodstream
38
New cards
harm to skin
Rashes, hives, itching, hair loss, burns, and skin cancer can come from exposure to environmental factors such as cleaning fluids, workplace chemicals, drugs, and radiation
39
New cards
circulatory and lymphatic system
Workplace chemicals and pathogens like parasites can cause harm to your circulatory and lymphatic system. Lymph is fluid found in spaces between cells. Bacteria and wastes are filtered out at lymph nodes and by spleen
40
New cards
nervous and reproduction systems
Pesticides, workplace chemicals, antiseptics, bacteria and viruses, etc. can cause damage to brain, spine, and nerves - Sperm, eggs, and sex organs can be damaged or result in cancers caused by environmental contaminants as well. Meningitis: inside the brain there is an area called the meninges. There are no sensors on the brain for touch, but if a bacteria gets there then it can become swelled and eventually may lead to death
41
New cards
measles
Measles is a childhood infection caused by a virus pathogen that lives in the mucus of the nose and throat. It is very contagious - even before symptoms like the rash show up. Measles infections afflict 20 million people every year and results in 100 000 deaths per year. Symptoms: runny nose, cough, tiredness, loss of appetite, fever, sensitivity to light, spots all over the body and inside mouth, conjunctivitis (pink eye)
42
New cards
vaccine protection
Vaccines can protect humans from many pathogens like the measles. They work by exposing your body to weakened forms of a microbe so that the body can learn to fight off an infection. White blood cells or antibodies (soldiers) learn to fight this: Antibodies are very specific. If a certain number of people are vaccinated against a disease then the whole group becomes less likely to get it: This is called herd immunity. Recent anti-vaxx movements have endangered many lives unnecessarily. They claim that they can cause Autism and other negative effects, Anti mask rallies and protests
“This years flu strain is 65% effective” → means that you are either 100% or 0% protected, certain people will be protected and others will not - on average 65/100 will be protected and the other 35 will not be
“This years flu strain is 65% effective” → means that you are either 100% or 0% protected, certain people will be protected and others will not - on average 65/100 will be protected and the other 35 will not be
43
New cards
medication
Asthma reactions triggered by environment can be treated with medication- Antimalarial medications can kill the parasites that can cause malaria to protect a person from the disease
No medication or vaccine is 100% effective
No medication or vaccine is 100% effective
44
New cards
non medical protection
Sunscreen and UV protective clothing can protect humans from UV light that can burn skin - the sun protection factor (SPF) tells you how effective it is
45
New cards
air purifiers
Pollutants on the air can be removed by air purifying respirators. Really toxic environments may need a supplied air respirator
After 911, people tried to clean up the rubble without protection and they are sick because of what they inhaled
After 911, people tried to clean up the rubble without protection and they are sick because of what they inhaled
46
New cards
hand washing
The most effective way to prevent the spread of disease is to wash your hands, No need to buy a special antibiotic soap
Soap forms a reaction with certain particles and so when you wash away the soap you wash away the new compound (thus washing away the bacteria and other icky things on your hands)
Soap forms a reaction with certain particles and so when you wash away the soap you wash away the new compound (thus washing away the bacteria and other icky things on your hands)
47
New cards
safe food handling
Every year ~12 million Canadians get a food borne illness such as botulism which is caused by a bacterium that can live in improperly preserved food, Food poisoning - eating food that hasn't been prepared properly will make you sick
Very important to know how to handle things
Step 1: clean - protects by getting rid of any bacteria that could be harbored on your fingers
Step 2: separate raw meat from other food when preparing it - don't eat meat raw
Step 3: cook your food - don't eat anything that you shouldn't at a level of underpreparedness
Step 4: chill your food - bacteria cannot thrive when it's too cold and it will slow down their growth - the colder it is, the slower bacteria growth
If you cook it for a certain amount of time over a certain amount of heat then this will also keep your food safe as most bacteria can't exist over a certain temperature
Very important to know how to handle things
Step 1: clean - protects by getting rid of any bacteria that could be harbored on your fingers
Step 2: separate raw meat from other food when preparing it - don't eat meat raw
Step 3: cook your food - don't eat anything that you shouldn't at a level of underpreparedness
Step 4: chill your food - bacteria cannot thrive when it's too cold and it will slow down their growth - the colder it is, the slower bacteria growth
If you cook it for a certain amount of time over a certain amount of heat then this will also keep your food safe as most bacteria can't exist over a certain temperature
48
New cards
indoor air quality
Canadians spend ~ 90% of time indoors
Smoke: fireplaces, wood burning stoves, cigarettes, etc. all release particulate matter
Poor circulation: airtight homes, dirty air in HVAC systems, attics, basements, etc. all remain in the home
Toiletries: aerosols, lotions, vinyl shower curtains, airborne chemicals
Mold: bathrooms and kitchens, always test
Cooking: high level of particles
Candles and electronics: release toxins that can lead to headache, fatigue, etc
Cleaners and detergents: VOCs
VOCs: toxic vapours that are gassed off of manmade materials (e.g. furniture, bedding, carpets)
Certain homes have filters to combat this
Smoke: fireplaces, wood burning stoves, cigarettes, etc. all release particulate matter
Poor circulation: airtight homes, dirty air in HVAC systems, attics, basements, etc. all remain in the home
Toiletries: aerosols, lotions, vinyl shower curtains, airborne chemicals
Mold: bathrooms and kitchens, always test
Cooking: high level of particles
Candles and electronics: release toxins that can lead to headache, fatigue, etc
Cleaners and detergents: VOCs
VOCs: toxic vapours that are gassed off of manmade materials (e.g. furniture, bedding, carpets)
Certain homes have filters to combat this
49
New cards
air quality technology
Opening windows, Turning on a fan, Electronic air purifiers
Our bodies are exposed to many things - even interacting with others can lead to damage to our bodies
Our bodies are exposed to many things - even interacting with others can lead to damage to our bodies
50
New cards
carbon footprint
The use of fossil fuels since the industrial revolution have massively increased the amount of CO2 and other GHG emissions into the environment
Deforestation also increases the amount of carbon as trees are carbon sinks
Deforestation also increases the amount of carbon as trees are carbon sinks
51
New cards
primary and secondary Carbon footprint
Primary carbon footprint measures GHG emissions from burning fuels for energy and transportation
Secondary carbon footprint measures GHGs from food, products, and services you buy
Everything has a carbon price tag
Secondary carbon footprint measures GHGs from food, products, and services you buy
Everything has a carbon price tag
52
New cards
footprint cause and effect
Some countries produce more GHG than others
Effects of climate change including fires, drought, and extreme weather often affect poorer people and countries more than wealthier people and countries- wealthier people and nations output more carbon overall
Effects of climate change including fires, drought, and extreme weather often affect poorer people and countries more than wealthier people and countries- wealthier people and nations output more carbon overall
53
New cards
oil spills
Humans spill oil in marine ecosystems which can be devastating. Oil spills on land can also end up in freshwater ecosystems like lakes, rivers, and wetlands. Less dense parts of oil float and form a thin layer called a slick. More dense parts of oil sink and form tar balls that can wash ashore long after a spill. Use kerosene to get the oil spills off you when swimming
54
New cards
effect of oil spills
Seagrass and kelp can be covered and killed by oil. Animals that depend on these plants for food and shelter also die. Animals can be smothered by oil or be poisoned by ingesting it. Oil also mats down fur and feathers of mammals and birds which can cause the to freeze to death and reduce their ability to swim, float, or fly
55
New cards
acid precipitation
Humans produce massive amounts of gasses that make acid rain or snow. Acid precipitation can be episodic or chronic. Snowmelt vs. Water bodies that are permanently acidic. We pump in gasses like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides
Chronic: always precipitation is acidic
Epositic: something precipitation is acidic
If it falls down as snow, the snow will melt and then run off, some changes are more permanent (e.g. if the water is completely acidic then it will have drastic impacts)
Chronic: always precipitation is acidic
Epositic: something precipitation is acidic
If it falls down as snow, the snow will melt and then run off, some changes are more permanent (e.g. if the water is completely acidic then it will have drastic impacts)
56
New cards
effects of acid precipitation on soil
Reduces basic nutrients such as calcium and magnesium from soil by leaching. Loss of these nutrients slows down plant growth and makes them more vulnerable to insects, diseases and drought. Increases levels of heavy metals in soils such as aluminum; these metals can be toxic to fish, plants, birds, and other animals. Rocks in many Ontario ecosystems can not neutralize the acid and can result in dead lakes like in Killarney
57
New cards
non native species
Native species are adapted to live in the climate, soil, water and with the other creatures found naturally in their habitat
Non native species are introduced by humans into new habitats where they are normally not found. This happens due to travel, agriculture, perts, live bait use, etc.
Non native species are introduced by humans into new habitats where they are normally not found. This happens due to travel, agriculture, perts, live bait use, etc.
58
New cards
effects of invasive species
Invasive species are non native species that harm native species by competing with them for resources, they may also lack predators and their population can grow quickly
E.g. purple loosestrife: In the early 1800’s people brought it over from Europe for its pretty flowers and medicinal uses. Here it has taken over many wetlands and outcompetes other plants like milkweed and cat tails which also impacts the animals that would eat them for food!
E.g. purple loosestrife: In the early 1800’s people brought it over from Europe for its pretty flowers and medicinal uses. Here it has taken over many wetlands and outcompetes other plants like milkweed and cat tails which also impacts the animals that would eat them for food!
59
New cards
sampling and monitoring the environment
In order for us to address environmental issues scientifically, we need info
Soil, water, & air can be sampled and monitored over time to determine if changes are happening
Soil, water, & air can be sampled and monitored over time to determine if changes are happening
60
New cards
soil sampling
Soil core sample is a common way to measure the quality of soil to be used for agriculture
Soil exists in layers called horizons
At a lab, the technicians will measure components such as phosphorus, potassium, magnesium and nitrogen
Soil exists in layers called horizons
At a lab, the technicians will measure components such as phosphorus, potassium, magnesium and nitrogen
61
New cards
water sampling
Water is also sampled at different depths to monitor the amount and location of different pollutants. Drinking water is also sampled constantly by towns and cities
62
New cards
drinking water tests
Microbiological tests: bacteria or coliforms are living things that could be harmful to humans. Chemical tests: chemicals like nitrates or lead might indicate contamination from sewage or rusty leaking pipes. Radiological tests: some places have natural levels of uranium that must be monitored. We have a certain amount of radiation that were exposed to daily - the level must be considered
63
New cards
air sampling
Industrial plants often release exhaust from smokestacks that are monitored for emissions of sulfur, mercury, and carbon
Particulate matter is also closely monitored because of its effects on human health
Particulate matter is also closely monitored because of its effects on human health
64
New cards
air quality index
In ontario, the AQI provides information about levels of smog in the air. Air monitoring stations throughout the province provide data on 6 key air pollutants, and meteorologists update the AQI hourly. If the AQI gets really bad they will issue a smog alert to the public
65
New cards
ice core samples
Places where ice has been accumulating for thousands of years can provide air and water samples about conditions in the past. Plant pollen shows species that were alive. Ice crystal shape is related to temperature and humidity. Air bubbles show levels of oxygen and CO2
66
New cards
quadrat sampling
biodiversity can be measured by counting the number of each species found in a square of given size - measures how well things are growing - measures how well things are growing in a given area
67
New cards
environmental impact assessment
This is a study done before a project that may affect the environment. Factors include whether the project may impact aquatic species, migrating birds, Indigenous uses
68
New cards
rapa nui
Isolated island alone in the pacific ocean, Natives cut down palm trees to build canoes & monuments to their gods, New palms couldn't grow due to rats, Eventually, the last palm was cut and the population collapsed, Often viewed as a cautionary tale for us on this little earth on vast space
Consequence when nations are not sustainable - Just like in Rapa Nui we must understand the problems we have
We have a variety of growing environmental problems that could drastically affect our way of life if not dealt with effectively
Informed citizens can act to make changes that will address these problems in a scientific way
Consequence when nations are not sustainable - Just like in Rapa Nui we must understand the problems we have
We have a variety of growing environmental problems that could drastically affect our way of life if not dealt with effectively
Informed citizens can act to make changes that will address these problems in a scientific way
69
New cards
evidenced
All claims about environmental issues start with evidence
Monitoring levels of pollutants/number of species in a given area will show changes over time that can inform our decisions
We don't know what progress could stem from having these animals go extinct
Monitoring levels of pollutants/number of species in a given area will show changes over time that can inform our decisions
We don't know what progress could stem from having these animals go extinct
70
New cards
theories and models
Predictions can be made about the future using theories about how the world works
New theories displace older ones when new evidence is found
Compute models use theories to make long term predictions about complex data
E.g. geocentric VS. heliocentric ways of thinking
Science can be used to prove a theory wrong
New theories displace older ones when new evidence is found
Compute models use theories to make long term predictions about complex data
E.g. geocentric VS. heliocentric ways of thinking
Science can be used to prove a theory wrong
71
New cards
Paradigms
In order to motivate and change people’s mindsets - we need to get people to think differently. Many cultures act as if infinite development as growth is their goal/that humans are separate and above their environment- The traditional Indigenous paradigm of connectedness of all things and sustainability is different
Current sustainability model: economy, people and nature are separate and dealt with differently
Other ideas view nature as most important - e.g. Indigenous POV’s
72
New cards
paradigm shift
Most business models and governments have a very short term view. How do I make money now? How do I get elected now?
A longer term view is needed for long term survival & sustainability
A longer term view is needed for long term survival & sustainability
73
New cards
Critical thinking
The skills that we should be developing from school. To solve environmental problems, we must be critical thinker who can seek new facts, learn new skills, form new ideas to test
Reasoning
Evaluation
Problem solving
Cycle of critical thinking
Reasoning
Evaluation
Problem solving
Cycle of critical thinking
74
New cards
technological advances
Critical thinkers have produced new technologies that can help with many environmental problems
Renewable energy
Only works in some conditions
Must be able to store energy for when it can't collect the energy
Takes up a lot of space
Solar panels
Taking food scraps and isolating them - composting
Composting: organic material decomposes and forms soil that can be used - the nutrients are recycled
Not everything put in the “blue bin” is recycled - only about 30-40% (e.g. bottles, bags, etc.)
Renewable energy
Only works in some conditions
Must be able to store energy for when it can't collect the energy
Takes up a lot of space
Solar panels
Taking food scraps and isolating them - composting
Composting: organic material decomposes and forms soil that can be used - the nutrients are recycled
Not everything put in the “blue bin” is recycled - only about 30-40% (e.g. bottles, bags, etc.)
75
New cards
success stories
Ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere was detected by satellite technology
Aerosol CFCs were banned in 1987 when it was determined that they were causing the loss
Since then, the ozone levels have increased and continue to improve
Freeon used to release CFC, it worked well at cooling things down (e.g. fridges, coolers, AC)
Aerosol CFCs were banned in 1987 when it was determined that they were causing the loss
Since then, the ozone levels have increased and continue to improve
Freeon used to release CFC, it worked well at cooling things down (e.g. fridges, coolers, AC)