Chapter 3 Stats sentence frames
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Key terms for Test Chapter 3 CN AP STATS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Coefficient of determination→ r² or r
About __%___ of the variability in y-context is accounted for by the LSRL.
About __%___ of the variability in y-context is accounted for by the LSRL.
Coefficient of determination→ r² or r
Residual
Actual- Predicted= ?
Interpret the Residual
The actual context above/below the predicted value for x-contex/x=#
Interpret SD of residuals → s
The actual y-context is typically about (s) away from the number predicted by the LSRL.
Interpret the y-intercept.
When x-context predicted y-context is y-intercept
Interpret the slope
With each additional x-context the predicted y-context increases/decreases by slope#
Extrapolation
estimating a value that is/may be out of your data range- causes inaccurate information.
Influential Points
An outlier that affects slope, y-int, and/or correlation.
High leverage Points
Extremely low or high outlier in the graph.
D.U.F.S. + Context
Direction (+/-), Unusual Features (Outliers/Clumps), Form (Linear/ Non-linear), Strength (weak/moderate/strong), + context
Interpret r (not the sentence frame)
define only these D.F.S
Explanatory Variable
Used to predict/ input/ on the x-axis
Response
The outcome/ output/ on the y-axis
Choosing the best model requires:
check the scatterplot for a linear form.
check residual plot for a random scatter.
check the r² closest to 1 (strongest)
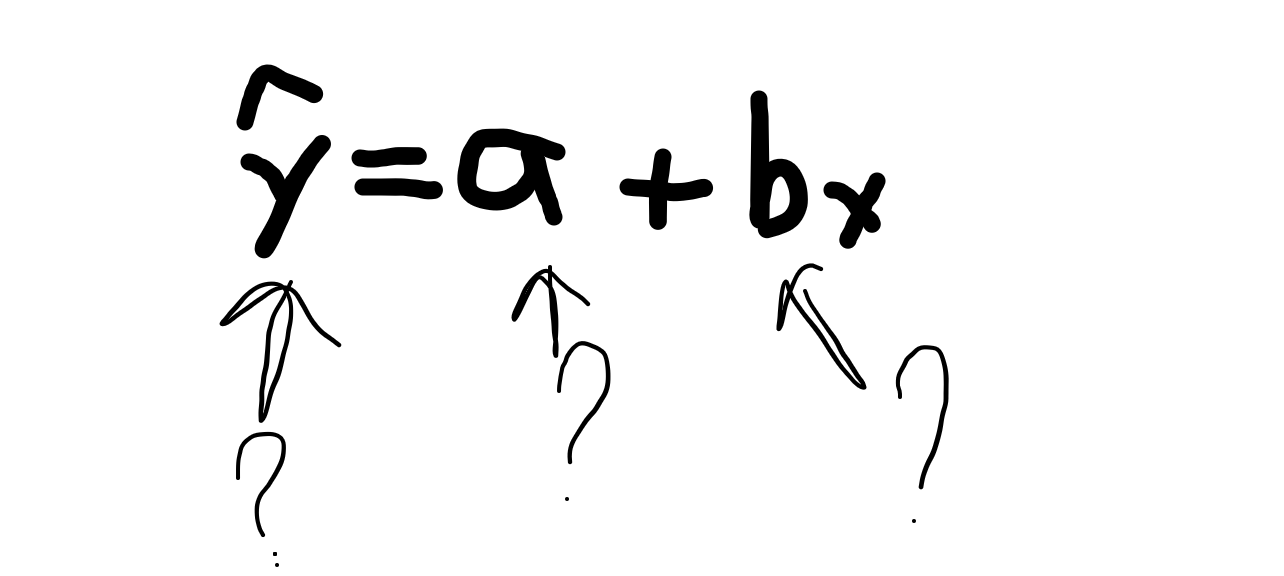
unnamed- name the variables
named
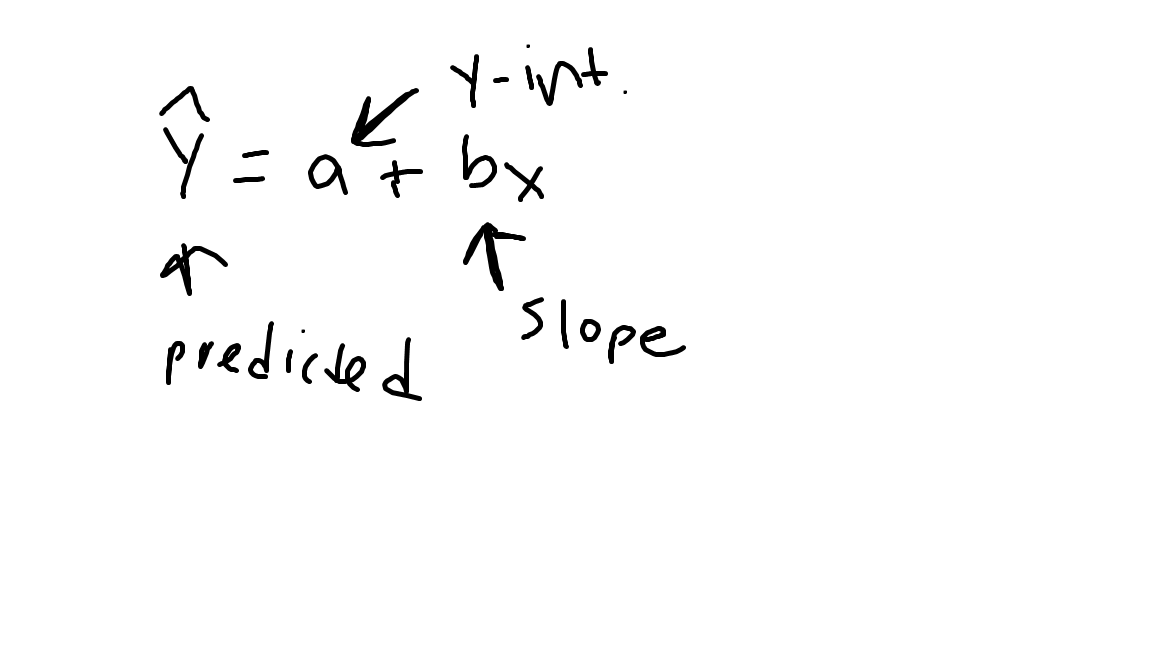
The actual context above/below the predicted value for x-contex/x=#
Interpret the Residual
The actual y-context is typically about (s) away from the number predicted by the LSRL.
Interpret SD of residuals → s
When x-context predicted y-context is y-intercept
Interpret the y-intercept.
With each additional x-context the predicted y-context increases/decreases by slope#