Section A - Natural hazards
1/404
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
405 Terms
Define: Natural Hazard.
Extreme natural events caused by natural processes that threaten or have the potential to cause damage and harm to people, environment and the economy.
Would natural hazards still occur without humans?
Yes as they are caused by natural processes.
Is a natural hazard still considered a natural hazard if it occurs nowhere near any humans or property?
No.
How can natural hazards be classified?
Tectonic hazard.
Atmospheric hazard.
Biological hazard.
Geomorphological hazard.
What is a tectonic hazard?
Hazards created through the movement of the Earth’s tectonic plates.
Give examples of tectonic hazards.
Earthquakes, Volcanic eruptions, Tsunami.
What is an atmospheric hazard?
Hazards created in the atmosphere.
Give examples of atmospheric hazards.
Tropical storm, Drought, Tornado.
What is a biological hazard?
Hazards involving living things.
Give examples of biological hazards.
Forest fires + Wildfires.
What is a geomorphological hazard?
Hazards caused by processes which occur on the surface of the earth.
Give examples of geomorphological hazards.
Landslides, Flooding, Mudflow.
What is a natural disaster?
When the damage or destruction actually takes place as a result of the natural hazard.
Define: Hazard risk
Probability or chance of a natural hazard occurring.
Suggest some factors that may affect hazard risk.
Population density and growth.
Wealth.
Urbanisation.
Deforestation.
Global warming.
Give some reasons why the incidence of natural hazards is increasing.
Population density and growth.
Urbanisation.
Deforestation.
Global warming.
Describe how population density affects hazard risk.
P - Population density has increased in recent years meaning more people live closer together.
E - In these areas, people will struggle to find safety and evacuate and resources will also be very stretched, increasing death toll.
Describe how urbanisation affects hazard risk.
P - Urbanisation is people moving from the countryside to rural areas.
E - If people live closely in small areas, they will struggle to find safety/evacuate and will continue to live in areas thought to be risky, leading to more deaths. Also, more buildings/roads built means more impermeable surfaces so surface run off may occur, leading to flooding which damages property and lives.
Describe how global warming affects hazard risk.
If global warming increases, tropical storms increase in intensity.
Describe how deforestation affects hazard risk.
Less trees means less interception and more surface run off so the likelihood of flooding increases.
Describe how wealth affects hazards risk.
P - LIC’s can’t afford MPPP strategies, technology not as advanced, protocols not in place.
E - Less prepared for hazards so more likely to die/get injured.
Name the 4 layers of the earth.
Crust, Mantle, Outer core & Inner core.
What is the crust?
The surface of the earth that we stand on on.
Name 2 types of tectonic plates.
Oceanic + Continental.
Which plate is heavier and denser: oceanic or continental?
Oceanic.
Which plate is lighter: oceanic or continental?
Continental.
Which plate is older: oceanic or continental?
Continental.
Why are continental plates older than oceanic ones?
The oceanic crust is continually being created and destroyed.
What is the thinnest layer of the earth?
Crust.
What is the thickest layer of the earth?
Mantle.
Which layers of the Earth are liquid?
Outer core.
Which layers of the earth are solid?
Crust, Mantle and Inner core.
What temperature can the inner core reach?
5,550 - 6,000°C.
Which layer of the earth is hottest?
Inner core.
Is the inner core solid or liquid?
Solid.
Is the outer core solid or liquid?
Liquid.
What material is the inner and outer core made out of?
Iron and nickel.
Which 2 layers make up the lithosphere?
Crust + Upper Mantle.
How many minor and major plates are there?
7 minor + 8 major.
What are the two type of crust called?
Oceanic and continental.
Where do most earthquakes occur on Earth?
Along the Pacific “Ring of Fire”.
What is a plate boundary?
Where 2 plates meet along the edges.
Name the 3 plate boundaries.
Destructive, constructive and transform.
What is another name for a transform plate?
Conservative.
What is the direction of plates at transform?
Side by side.
What is the direction of plates at constructive?
Away.
What is the direction of plates at destructive?
Towards.
Which plate margin has a subduction zone?
Destructive plate margin.
What landforms/hazards occur at constructive plates?
Volcanic eruptions.
Earthquakes.
Ridge Push.
Shield Volcanoes.
What landforms/hazards occur at transform plates?
Earthquakes.
What landforms/hazards occur at destructive plates?
Volcanic eruptions.
Earthquakes.
Slab pull.
Stratovolcano.
Fold mountain.
At what plates do earthquakes occur?
Transform, Constructive and Destructive.
At what plates do volcanoes occur?
Constructive and Destructive.
At what plate does a fold mountain form?
Destructive.
At what plate does a shield volcano form?
Constructive.
At what plate does a stratovolcano form?
Destructive.
What type of volcano forms at constructive plate margins?
Shield volcano.
What type of volcano forms at destructive plate margins?
Stratovolcano.
Explain how earthquakes occur at constructive plate margins.
Plates are jagged/not smooth/rough base.
Plates move apart and drag along the mantle.
Friction builds between mantle and plates until plates jolt/get stuck.
Pressure builds so seismic waves are released from focus.
Small earthquakes occur.
Explain how volcanic eruptions occur at constructive plate margins.
Crust/Plates moves apart and magma rises in the mantle as it’s less dense/hot.
Lava rises to the surface through the gap where plates have moved apart.
Volcanic eruption occurs.
Cools for new rock, forming shield volcanoes.
Explain how earthquakes occur at destructive plate margins.
Plates are jagged/not smooth/rough base.
Plates move towards each other and drag along the mantle.
Friction builds between mantle and plates until plates jolt/get stuck.
Pressure builds so seismic waves are released from focus.
Violent earthquakes occur.
Explain how volcanic eruptions occur at destructive plate margins.
Oceanic plates moves towards continental and oceanic plate subducts as its denser/heavier.
Plate sinks to mantle and melts to form magma.
Magma rises to the crust as it’s hot and less dense.
Pressure builds under the earths crust until magma escapes through the rock.
Volcanic eruption occurs.
Cools for new rock, forming stratovolcanoes.
Explain how earthquakes occur at transform plate margins.
Plates are jagged/not smooth/rough base.
Plates move side by side and drag along the mantle.
Friction builds between mantle and plates until plates jolt/get stuck.
Pressure builds so seismic waves are released from focus.
Explain how volcanic eruptions occur at transform plate margins.
They don’t occur as there is no space for magma to rise.
What is a volcano with steep sides called?
Stratovolcano.
Where do stratovolcanoes form?
Destructive plate margins.
Where do shield volcanoes form?
Constructive plate margins.
Where and how do fold mountains form?
At destructive plate margins when 2 continental plates meet.
What is formed when 2 continental plates meet at a destructive plate margin?
Fold mountain.
Suggest why new crust is formed at constructive plates.
Plates move away from each other here and volcanic eruptions occur which can form new rock.
What scale do we use to measure earthquakes?
Richter Scale.
What is the Richter Scale?
A scale to measure the magnitude of an Earthquake - 1 to 10.
What does the magnitude of an earthquake refer to?
The strength/size of an earthquake.
Define: Focus
Where the pressure is released in the crust of the earth.
Define: Epicentre
The point on the earth’s surface directly above the focus.
Define: Seismic waves
The energy released in an earthquake from the focus.
Define: Foreshock
Occurs before the main earthquake begins.
Define: Main shock
The main or largest earthquake.
Define: Aftershock
Occurs after the main earthquake has ended.
Does a shallow focus or deep focus cause more damage?
A shallow focus has larger impact as seismic wave energy is stronger.
Why does magma rise?
It’s hot and less dense.
What is the old theory for tectonic plate movement?
Convection currents.
Describe convection currents.
Inner core reaches 6000°C.
Heat heats up the magma, causing it to rise in the mantle because it’s less dense and very hot.
When it gets near the crust, the heat splits and cools, becoming dense so it sinks back to the core.
Reheated and process repeats.
How did geographers disprove convection currents?
Using modern imaging techniques - x rays could not identify any convection currents that are strong enough in the mantle.
What is the new theory for tectonic plate movement?
Ridge push slab pull.
What is the key force in ridge push slab pull?
Slab pull.
What plate margin is the slab pull at?
Destructive.
What plate margin is the ridge push at?
Constructive.
Why do oceanic plates sink beneath continental plates?
Oceanic plates are heavier, thicker and denser. Gravity speeds up the process.
Which plate is thicker, denser and heavier - Oceanic or Continental?
Oceanic.
Is the oceanic or continental crust older?
Continental.
Is the oceanic or continental crust younger?
Continental.
Explain how ridge push and slab pull cause plate movement.
Ridge push - Magma rises as the plates move apart. The magma cools to form new plate material. As it cools It becomes denser and slides down away from the ridge. This causes other plates to move away from each other.
Slab pull - The denser oceanic plate sinks back in to the mantle under the influence of gravity. It pulls the rest of the plate along behind it.
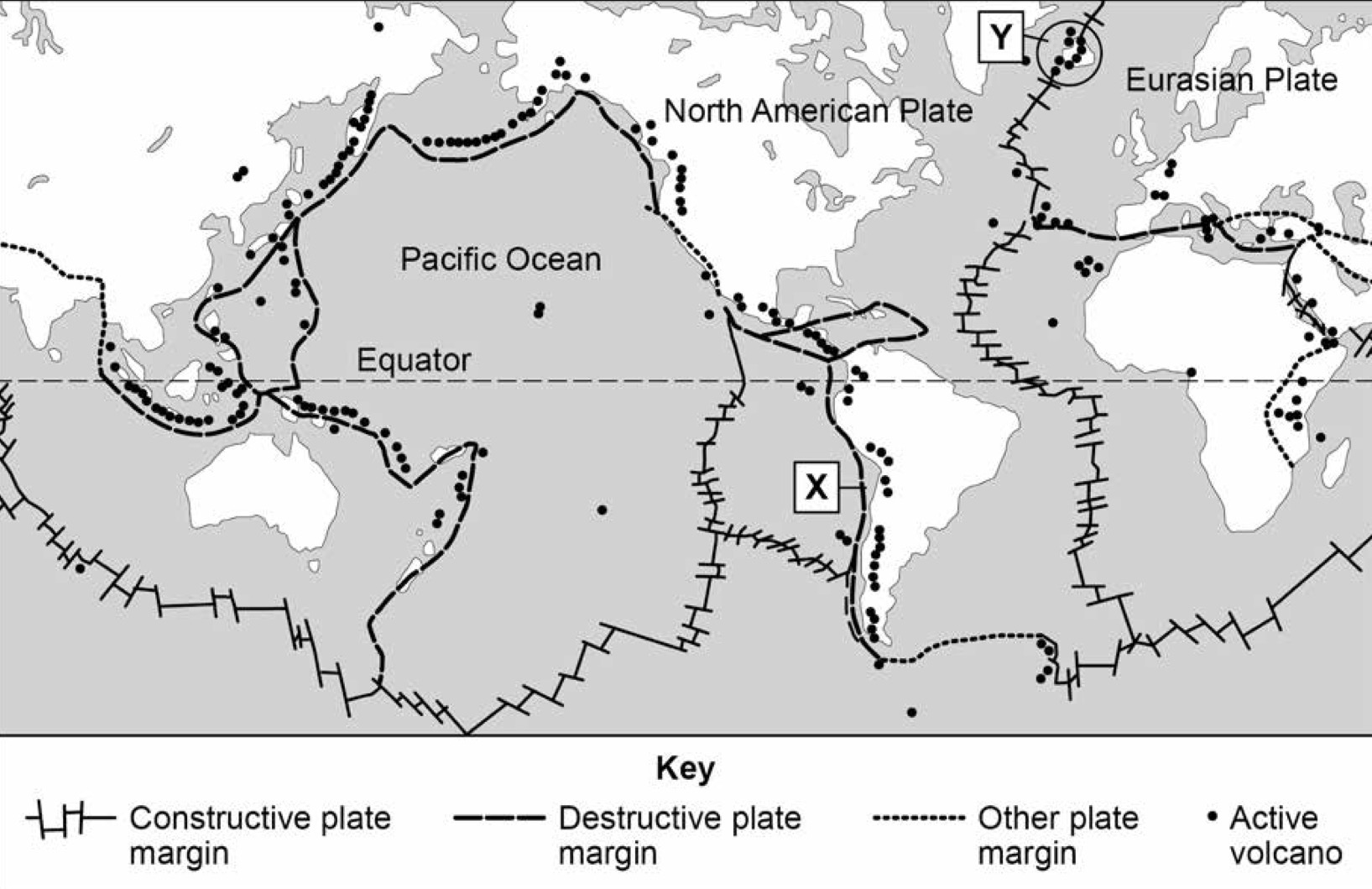
Describe the movement of plates along plate margin X.
Plates move towards each other.
Oceanic plate subducts beneath the continental plate.
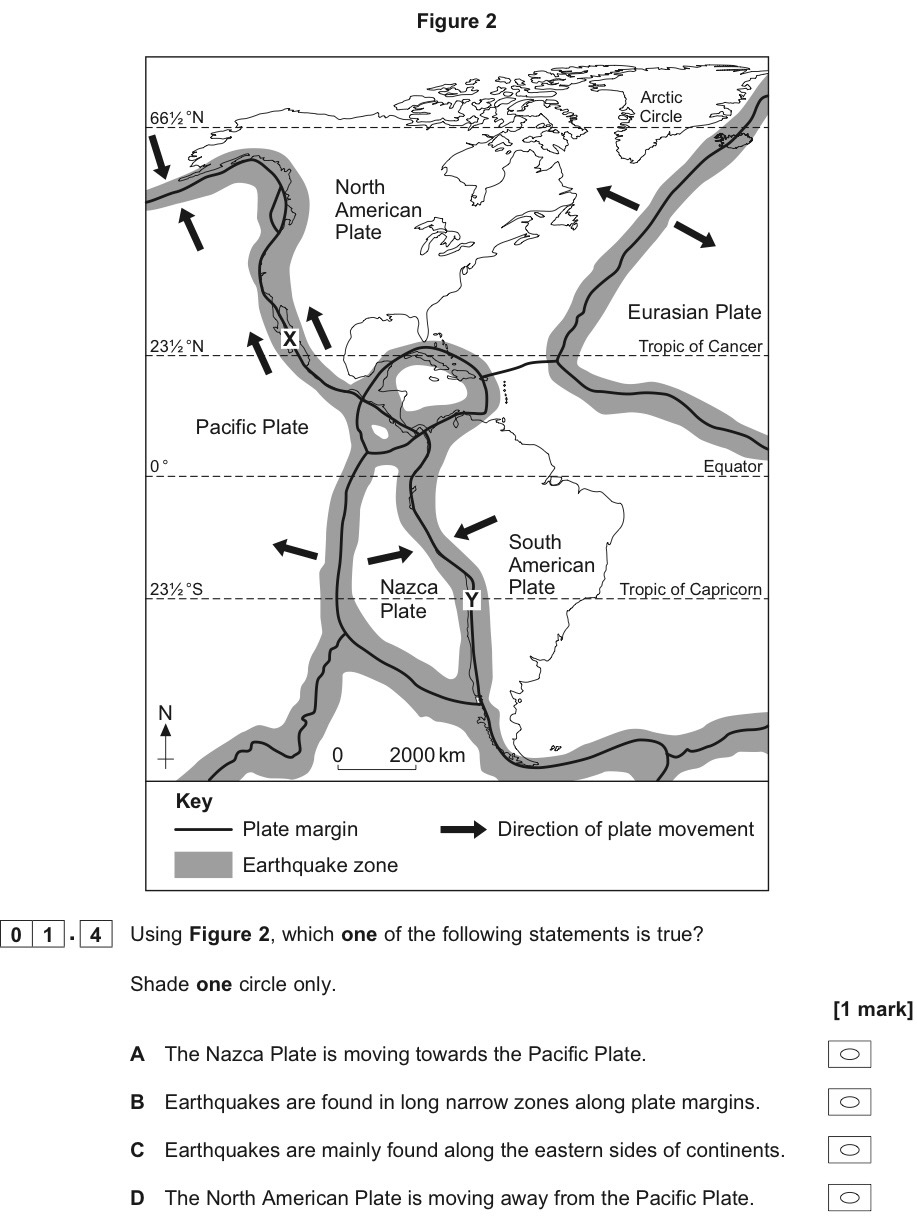
Select a statement.
B.
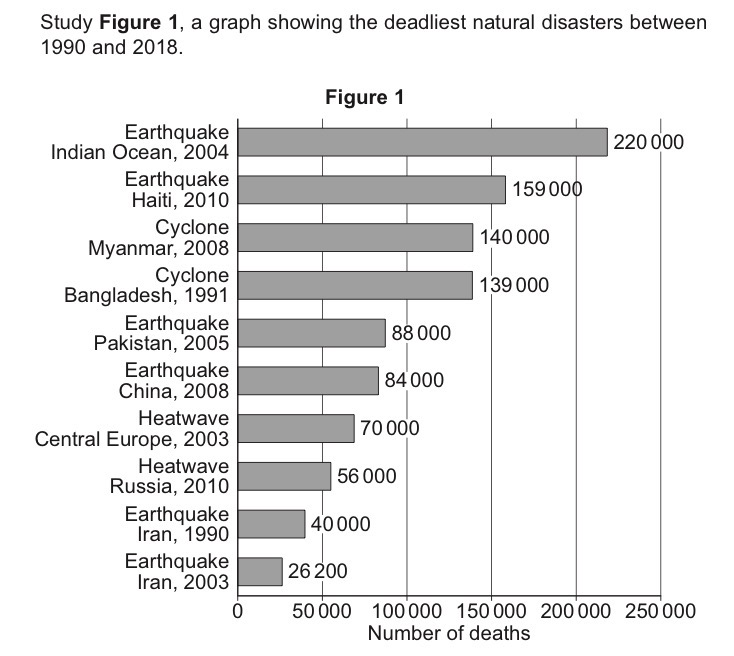
Using figure 1, which natural disaster caused the greatest number of deaths?
Earthquake.
What is the difference between primary and secondary effects?
Primary occur immediately after the earthquake happens (direct effect) whilst secondly occur later as a result of the primary effects (indirect effect).
What is the difference between immediate and long term responses?
Immediate responses occur within days or hours of the disaster whilst long term responses occur within months or weeks.
What factors can influence the effects of an earthquake?
Wealth; LIC or HIC.
Rural or urban areas.
Magnitude of earthquake.
Distance from epicentre.
Time of day.
Development of MPPP strategies in place.
State some general primary effects of an earthquake.
Buildings destroyed and damaged.
People injured and killed.
Transport routes damaged.
Water, gas, electricity supplies cut.