ivc bio units 1-6
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
10 characteristics of life
1 - programmed by DNA
2 - share same chemical composition ( organic molecules, mostly water, use atp)
3 - made up of at least one cell
4 - converts energy and matter in enzyme driven pathways
5 - highly organized
6 - grow and develop in specific patterns (seed → sprout → plant)
7 - reproduction, either asexual (complete) or sexual (partial)
8 - maintain relatively constant internal conditions (homeostasis)
9 - populations evolve genetically over time (gene frequency shifts)
10 - dependent on each other + environment ( e.g. carbon cycle)
organic
has at least one carbon to carbon bond
autotroph
produces their own food/organic molecules
heterotroph (includes decomposers)
consumes others organic molecules
ribosome
enzyme that manufactures proteins using mRNA
cytoplasm
watery liquid within the plasma membrane that makes up the interior of a cell
homeostasis
the maintenance of relatively stable internal conditions (e.g internal temperature → we sweat to cool ourselves down, shiver to warm ourselves uo)
mutation
a change in gene frequency through deletion or substitution of nucleotides in a sequence
evolution
changes in gene frequency in a population over time, occurs through mutation and/or dominant vs recessive genes becoming the prevalent trait
experiment
a controlled set of experiences to test a scientific idea
empirical
relating to the senses
variable
something that changes in value during the course of experiment
hypothesis
an idea that can be scientifically tested
theory
a set of statements based on tested scientific facts that acts to describe, explain, or predict aspects of a given phenomenon. these are constantly updated
some of the 15+ senses
tensile (weight, determined my stretch receptors in tendons)
balance
thermal 1 (hotter) and thermal 2 (colder)
humidity
pressure
vestibular 1 (am I moving? what direction)
vestibular 2 (am I rotating?)
scientific method
empirical observations
forming hypothesis
running a series of experiments
make conclusions based on data
publication + peer review
more testing
theory building
control
a control group in an experiment is a group thats identical to the experimental group, apart from the experimental variable. say, testing fertilizer on plants. the control group is the same plant species, with the same sunlight, water, environment conditions, etc. those variables are controlled. the only thing that changes is the fertilizer.
this ensures that the results of the experiments are caused by the experimental variable (fertilizer) not any other factors.
nature of science
relies on probability based conclusions, not absolute truth → this is because new information will update what is considered “scientific fact”
“there is 95% this is true based on the experiment we’ve done and the information we have:
atom
smallest component of an element that retains the properties of that element
element
substances that cant be broken down into other substances
matter
anything that takes up space + has mass
substance
particular kinds of matter with identifiable physical/chemical properties
→ e.g. : iron, glucose, mud, salt, literally anything
compound
a molecule with different elements in a fixed ration (e.g.: water is always 2 hydrogens: 1 oxygens)
major 4 elements
carbon hydrogen oxygen nitrogen
minor 3 elements
phosphorous, potassium, sulfur
radiation
when an unstable nuclei emits subatomic particles (e.g.: throws off neutrons)
half-life
the amount of time it will take for a radioactive substance to decay to half of it’s initial value
radiations effect on living things
kills cells, damages tissues and DNA, causes cancer (leukemia from atomic bomb), and death
learning objective four ( what do protons, electrons, and neutrons change within atom?)
protons → change elemnt identity, atomic number, contribute to atomic mass
neutrons → contribute to atomic mass, determine isotope
electrons → form ions, determine the number of possible bonds an atom can form
electrolyte
disassociated, dissolved ions
valence shell
the outermost shell of electrons
chemical bond
an attraction between 2+ atoms from sharing/transfer of electrons
molecule
2+ atoms united by chemical bonding
organic molecules
molecules with at least one carbon to carbon bond
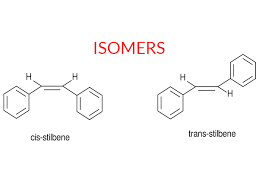
isomer
two molecules with the same atoms arranged in a different structure
amphiphatic
both hydrophilic and hydrophobic
hormone
compound produced by cells in one organ/tissue that is transported within the organism to stimulate cells in another organ/tissue
four functions of carbs with specific examples
quick energy with monosaccharides (glucose)
energy transfer with disaccharides (lactose)
long term energy storage with glycogen
plant wall structure with cellulose
four functions of lipids with specific examples
long term energy storage with triglycerides
lubricant for skin, hair, feathers (unsaturated)
makes up plasma membrane in cells (phospholipids + cholesterol)
makes up our arteries (saturated fat)
four functions of proteins
transports oxygen through our blood (hemoglobin)
digests lactose (lactase)
instructs cells to open up and let glucose in, regulating blood sugar and feeding cells (insulin)
forms hair, scales, and feathers (keratin)
unsaturated fats
oily at room temperature, has at least one double carbon bond, kinked chain, and mostly plant sourced
saturated bond
solid at room temperature (think butter!) , stackable, no double carbon bond, and mostly animal sourced
cis vs trans configuration
cis is both things on one side, trans is where theyre on opposite sides
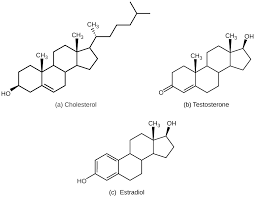
three positive functions of cholesterol
makes all hormones
precusor to vitamin D
protects artery walls from inflammation by forming an arterial plaque layer
one drawback to cholesterol
too much arterial plaque building from low density lipoproteins (big packages of cholesterol) can clog arteries, resulting in a heart attack
carb monomer and polymer
monomer: monosaccharide
polymer: polysaccharide
fats monomer and polymer
monomer: 3 fatty acids + glycerol
polymer: triglyceride
phospholipid monomer and polymer
monomer: 2 fatty acid, glyerol, phosphate group, and choline group
polymer: phospholipid
protein monomer and polymer
monomer: amino acid
polymer: polypeptide
nucleic acid
monomer: nucleotides
polymer: polynucleotide
primary structure of protein structure
made up of peptide bonds, in a linear chain
secondary structure of protein structure
formed by hydrogen bonds in helices, pleated sheets, and random coils
tertiary state of protein structure
made up of ionic bonds, sulfur bonds, hydrophilic+hydrophobic interactions, and forms a globular or fibrous shape
what does water dissolve?
water dissolves polar solutes, because water itself is a polar molecule. this is because the attraction forces between the polar solute and solvent pull the solute apart, helping the solute break down and dissolve.
it doesn’t dissolve non-polar hydrophilic molecules, thus it is not a universal solvent
solute
collection of particles
solvent
liquid
solution
solute dissolved in water
why is water resistant to vaporization?
oxygen has high electronegativity, hydrogen has low, thus the bonds between them are polar covalent.
water is polar, thus it has hydrogen “bonds” with itself. the positive oxygen on water is attracted to negative hydrogens on other water molecules. when enough heat hits one molecule to make it vaporize for its 18 daltons of weight, that heat is dispersed through the network of hydrogen bonds.
think like, you’re trying to lift a really heavy weight by yourself. with one person, you’ll get crushed, but with multiple people supporting the weight, you’re fine. the heat is being shared, the same way the weight is being shared.
but if there is too much heat, and all the water molecules are already carrying so much heat that you can’t just pass it off anymore, then the hydrogen bonds hold the water molecules in place, preventing them from vaporizing.
it’s like if the group of people are all handcuffed together as they try to support the weight, and the weight has to be strong enough (or for water, the heat has to be hot enough) to break those bonds in order for the water to finally vaporize, thus, making it very resistant to vaporization for its small size.
polarity
the possession of an axial distribution of charge
heat
total molecular motion in a system
temperature
average molecular motion of a system
electronegativity
tendency to attract electrons
hydrogen bonding
NOT AN ACTUAL BOND, SO ELECTRONS ARE BEING SHARED OR TRANSFERRED
its simply the electromagnetic attraction between a partially positive hydrogen of one molecule and the partially negative atom of another molecule
cohesiveness
the ability for a substance to stick to itself
(if you put a droplet of it on a surface, does it hold itself into a droplet, or does it immediately collapse into a puddle?)
vaporization
two types:
evaporation where vapor forms at surface and its heated from above
boiling where vapor forms in pockets within the liquid (the little bubbles) and it’s heated from below
adhesiveness
how well does it stick to other similar subtances, for example other charged substances
e.g.: water on glass ( i think dont quote me )
evapotranspiration
the thing with the trees with a big water chain pulled up by hydrogen bonds and water in leaves going up the tree trunk.
surface tension
the tension at the surface of a liquid. water must bond in a flat plane at the surface, which is calle d the lamination effect. this flat plane is what makes belly flopping very painful.
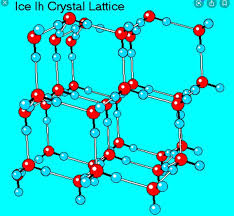
what is waters density as it freezes and why does it matter?
when water freezes, it must form a lattice structure, creating pockets of empty space between molecules. this means it has lower density, which allows it to expand and float as it freezes.
this is cool for lakes, because the fish still get to live when lakes freeze over
this is not cool for us, because when we freeze, the water in our bodies and cells expand, killing us.
more useful energy is….
more organized, more predictable, more concentrated, less random (e.g.: gasoline)
less usable energy is…
less organized, less predictable, less concentrated, more random (e.g.: CO2)
First Law of Thermodynamics
energy can be converted, but not created or destroyed
Second Law of Thermodynamics
everytime we convert energy some is converted to a less usable form
photon
light. some people say its a weightless particle, some people say its a wave. for now, it’s just light.
energy
the ability to do “work” → move matter through space
calorie
enough energy to increase the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree celsius
equation for photosynthesis
6(H2O) + 6(CO2) —photons→ C6H12O6 + 6(O2)
equation for cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6(O2) → 36 ATP + 6(CO2) + 6(H2O)
what does ATP do
it’s the it girl of energy sources. it’s what all living things run off of.
trophic efficiency
energy gained/energy available