Cellular Respiration Study Guide
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Cellular Respiration
Process in which cells make ATP by breaking down organic compounds (Glucose).
Heterotrophs
Relies on others for food.
Autotrophs
Make their own food.
Anaerobic
Process that does not require Oxygen.
Aerobic
Process that does require Oxygen.
Glycolysis
The breakdown of glucose into private acid (3 Carbon Compound).
Glucose
6 Carbon Compound
Where does Glycolysis occur?
The cytosol in the cytoplasm.
Step 1 of Glycolysis
2 Phosphates are attached to a Glucose, forming a new 6 Carbon Compound, with 2 Phosphates called Fructose.
How are the Phosphates in step 1 of Glycolysis supplied?
By 2 ATPs converted into 2 ADPs.
Step 2 of Glycolysis
The 6 Carbon Compound splits into 2 3 Carbon Compounds (G3P) Glyceride 3 Phosphate.
Step 3 of Glycolysis
The G3P molecules are oxidized and each receives a Phosphate Group forming 2 new 3 Carbon Compounds.
Oxidized
A chemical reaction which a reactant loses one or more electrons becoming more positive in charge.
Step 4 of Glycolysis
The Phosphates are removed from the 3 Carbon Compounds, which produces 2 3 Carbon Compounds.
Final Conclusion of Glycolysis
2 Pyruvic Acids
4 ATPs but a net gain of 2
2 NADHs
NADH
A coenzyme of oxidization that accepts 2 Hydrogen atoms from a substrate and carries them to another electronic sceptor.
Transition Reaction
Pyruvic acid combines with coenzyme A to form acetyl CoA (acetic acid).
Does Transition Reaction require Oxygen?
Yes.
Where does the Transition Reaction occur?
The Matrix.
Matrix
The space inside the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
2 Carbon Compound
Acetyl CoA
3 Carbon Compound
Pyruvic Acid
6 Carbon Compound (Glycolysis)
Glucose
4 Carbon Compound
Oxaloacetic Acid
6 Carbon Compound (Krebs Cycle)
Citric Acid
Final Conclusion of Transition Reaction
2 Acetic Acids
2 NADHs
Made 2 CO2s
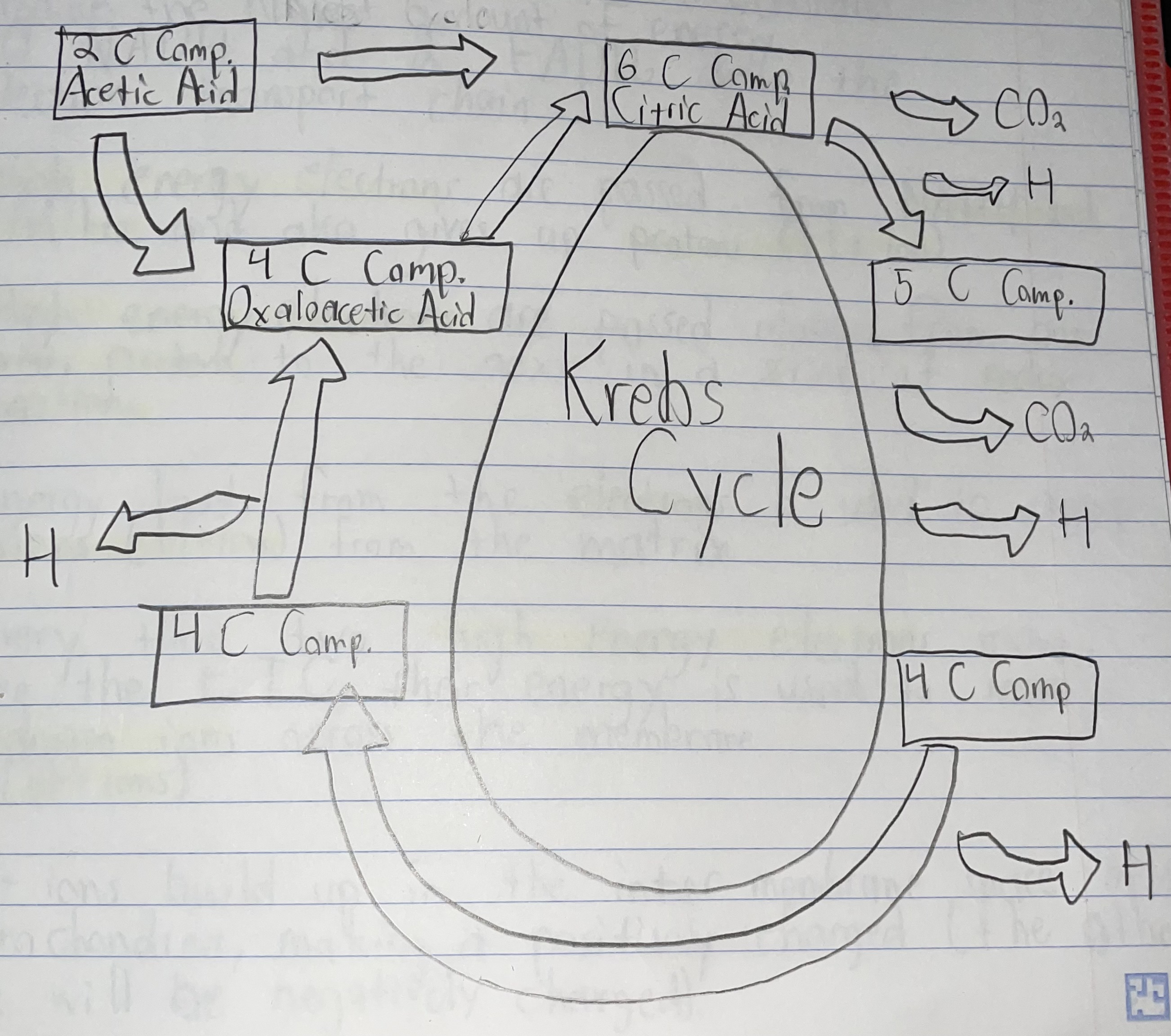
Krebs Cycle
Biochemical pathway of the oxidation of glucose that began in Glycolysis.
How many times does the Krebs Cycle occur?
Two
Does the Krebs Cycle require Oxygen?
Yes
Where does the Krebs Cycle occur?
In the cristae of the mitochondria.
Step 1 of the Krebs Cycle
The 2 Carbon Compound, Acetic Acid, combines with a 4 Carbon Compound, oxaloacetic acid, to produce a 6 Carbon Compound, Citric Acid.
Step 2 of the Krebs Cycle
Citric Acid releases a CO2 and a Hydrogen atom to form a 5 Carbon Compound.
Step 3 of the Krebs Cycle
The 5 Carbon Compound releases a CO2 and a Hydrogen atom to form a 4 Carbon Compound.
Step 4 of the Krebs Cycle
The 4 Carbon Compound loses a 4 Hydrogen ion to become another 4 Carbon Compound.
Step 5 of the Krebs Cycle
The 4 Carbon Compound releases a Hydrogen atom to regenerate a 4 Carbon Compound called oxaloacetic acid.
Final Conclusion of the Krebs Cycle
2 ATPs
6 NADHs
2 FADH2s
4 CO2s
Be able to label a diagram of the Krebs Cycle.
Redox Reaction
Where electrons are transferred between atoms.
Electron Transport Chain
A series of carrier proteins in a membrane that transfers electrons from one molecule to another.
Does the Electron Transport Chain require Oxygen?
Yes
Where does the Electron Transport Chain occur?
The cristae of the mitochondria.
How many NADHs are produced in ETC?
Ten
How many FADH2s are produced in ETC?
Two
Step 1 of ETC
High energy electrons are passed from NADH and FADH2 and also gives up protons (H+ion).
Step 2 of ETC
High energy electrons are passed along from one carrier protein to the next in a series of redox reactions.
Step 3 of ETC
Energy lost from the electrons is used to pump protons (H+ion) from the matrix.
Step 4 of ETC
Every time two high energy electrons move down the ETC, their energy is used to move hydrogen ions (H+ions) across the membrane.
Step 5 of ETC
H+ions build up in the inter membrane space of the mitochondria, making it positively charged (the other side will be negatively charged).
Step 6 of ETC
As H+ions pass through a channel in the protein, they release energy.
Step 7 of ETC
The concentration and electrical gradient (positive charge) of protons drive the synthesis of ATP by Chemiosmosis.
Step 8 of ETC
Oxygen is h the final acceptor of electrons that have passed through the chain.
What is the final electron acceptor in ETC?
Oxygen
Chemiosmosis
The process in which the movement of protons down their concentration gradient across a membrane is coupled to the synthesis of ATP.
ATP Synthetase
An enzyme that uses the energy to convert ADP to ATP.
Diagram of ETC
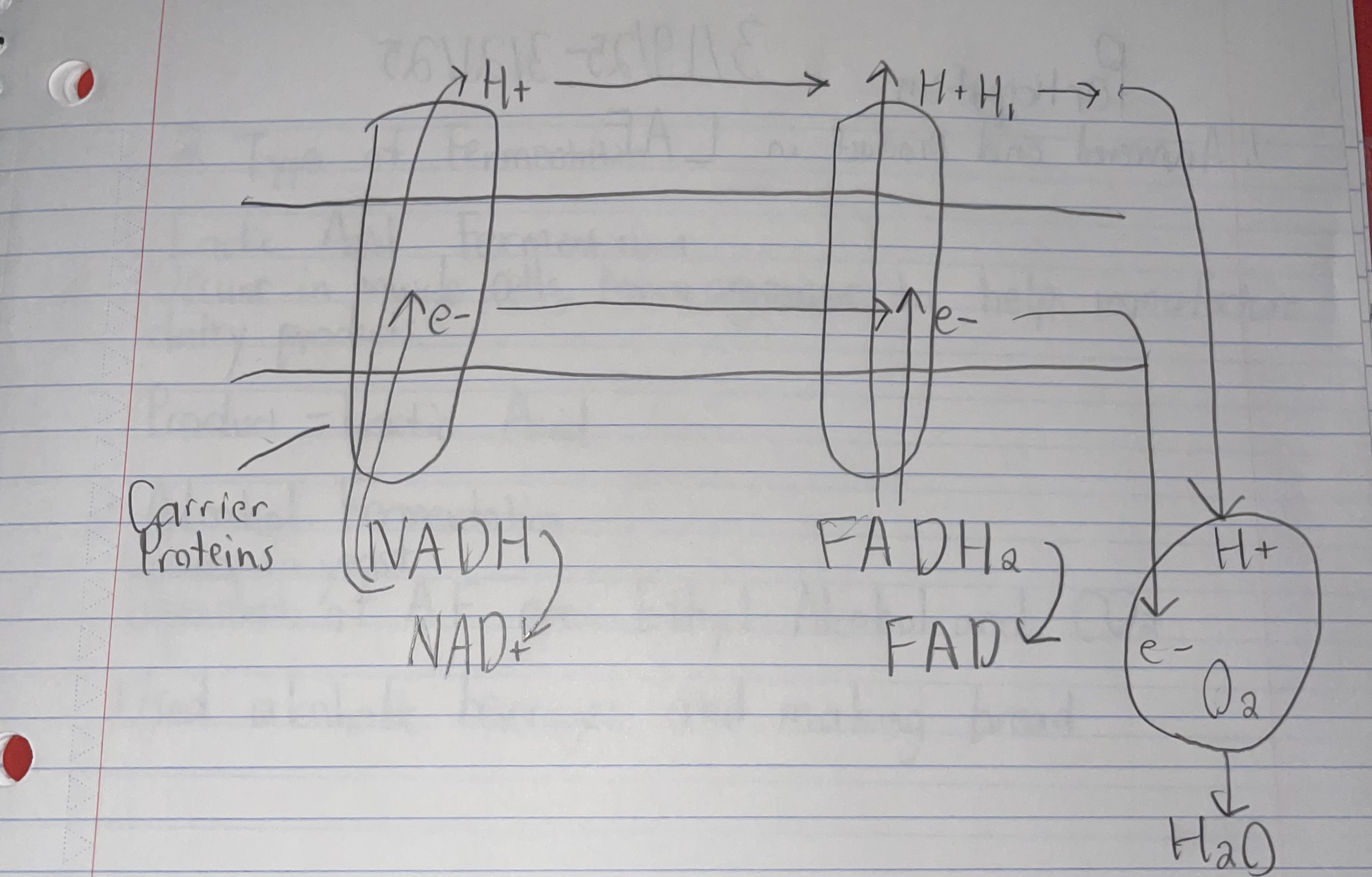
Final Results of ETC
6 waters (12 are made but 6 are used)
34 ATP
How many ATPs are made for every one glucose?
38
How many ATPs are made in Glycolysis
2
How many ATPs are made in the Krebs Cycle?
2
How many ATPs are made in the ETC
34
Fermentation
Glycolysis followed by the conversion of pyrrhic acid to some other end product.
Does Fermentation require Oxygen?
No
Where does Fermentation occur?
The cytosol of the cytoplasm
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Occurs in muscle cells, micro organisms to help manufacture dairy products
Product is Lactic Acid
Alcohol Fermentation
Occurs in yeast. Biproducts are Ethylene Alcohol and CO2.
Used in alcoholic beverages and making bread.