DDS Study Set: Lectures 13+14
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Describe various otic dosage forms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are the two types of intraocular administration?
Intravitreal (injections into the aqueous humor) and intracameral (injections into the anterior chamber)
When is intravitreal administration typically employed?
Intravitreal administration is employed for severe posterior segment diseases
What is a significant advantage of intravitreal administration?
It results in high bioavailability in the posterior segment
What are some disadvantages of intraocular administration?
It is an invasive route of administration
It can increase the risk of hemorrhage, especially while treating chronic diseases of the eye
When is periocular administration typically used?
Periocular administration is usually employed for treating anterior segment diseases when topical administration has failed
What are the two types of periocular administration?
Periocular administration may be either subconjunctival or sub-Tenon
How is injection administered in subconjunctival administration?
Injection is made underneath the conjunctiva in the case of subconjunctival administration
How do drugs administered via periocular route enter the eye?
By diffusing through the sclera, which has high permeability compared with the cornea
What is transscleral administration?
Transscleral administration is a viable alternative to deliver drugs to the posterior segment
Why is transscleral administration considered a viable alternative?
Due to the sclera's large surface area and high permeability characteristics
What type of therapeutics is transscleral administration suitable for?
Protein therapeutics
What are the advantages of topical ocular administration?
Convenience
Noninvasiveness
Ease of self-administration
Fewer systemic drug effects
What are the disadvantages of topical ocular administration?
Low ocular bioavailability
Ineffective in the treatment of posterior segment diseases
In the context of topical formulations, solutions sometimes have viscosity enhancers, why are they used?
Increase precorneal residence time to increase ocular bioavailability
What is a key characteristic of ophthalmic suspensions?
They provide slow dissolution and prolonged release of drugs
What are some characteristics of ophthalmic ointments and gels?
Primarily used for nighttime therapy, in contrast to eye drops used during the day
Provides longer contact time compared to solutions
Ointments are suitable for moisture-sensitive drugs
What is an Ocusert® Device?
A polymer membrane that controls release rate…
Increasing contact time
Improving bioavailability
Providing a prolonged drug release
_________ ____________ is the primary cause of blindness from contaminated ophthalmics.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
What factors determine the method of sterilization for ophthalmic products?
Depends on the product
Autoclaving for heat-stable drugs
Membrane filtration (0.22 μm for heat-labile drugs or 0.5 μm for sterility).
What is buffer capacity?
It is a measure of the resistance to change in the pH of the solution
When do we use a low buffer capacity?
When we want to allow tear fluid to adjust pH to neutrality after application to the eye
What is the relationship between buffering and bioavailability?
More buffering = more bioavailability
Why do we want the eye solutions to be isotonic?
To reduce tearing and irritation (comfort)
What tonicity values can the eye tolerate without great discomfort?
0.5% to 1.6%
What value are sodium chloride and boric acid isotonic with tears?
0.9% sodium chloride
1.9% boric acid
What happens if we administer a hypertonic eye solution?
It can draw water toward the site of the topical application
What happens when we administer a hypotonic eye solution?
It will induce the passage of water from the site of an ophthalmic application through the tissues of the eye
What can be done to increase the viscosity of an eye solution?
Adjuvants such as emollients and demulcents can be added
What are the three otic dosage forms?
Cerumen removing solutions
Solutions for ear infections
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic preparations
Why would we use direct pulmonary drug delivery for a local effect in the lungs?
We need a small dose
Lessen the systemic side effects
Works faster
Can do it yourself
Why would we use direct pulmonary drug delivery for a systemic effect?
Avoids the first pass effect
Increased drug absorption (large surface area of the lungs)
Works faster than oral
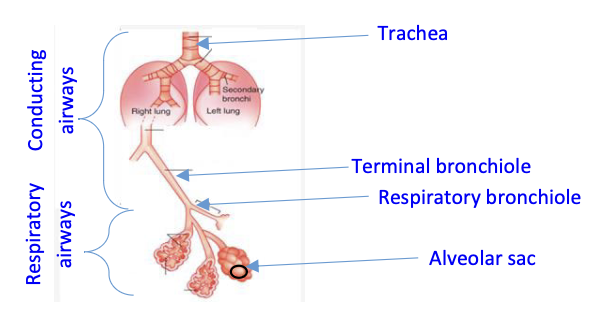
Where are the respiratory and conducting airways?
See image
What is mucocilliary clearance and how does it work?
It is a significant barrier to pulmonary drug delivery and it moves deposited particles from the conducting airways to the oropharyngeal space
What is the primary factor impacting the deposition of a particle in the airway?
The size of the particle
What airway will deposition occur if the particles are large (5-10μm)?
Oropharnynx and upper airways through inertial impaction
What airway will deposition occur if the particles are smaller (1-5μm)?
Smaller bronchioles and the alveolar region through gravity sedimentation
What airway will deposition occur if the particles are less than 0.5μm?
Alveolar region though brownian diffusion
What is the mechanism of aerosolization for jet nebulizers?
Pressurized compressed air
What does a spacer do?
Can slow the aerosol spray before it reaches the mouth
Allows reduction of aerosol particle size before reaching the mouth
Reduces oropharyngeal deposition of the medication particles
Eliminates the need for coordination of inhalation and actuation
Why is the respiratory region an important site for drug absorption?
It is the largest region in the nasal cavity with rich blood supply
What kind of dose is needed for a local nasal effect, small or big?
Small
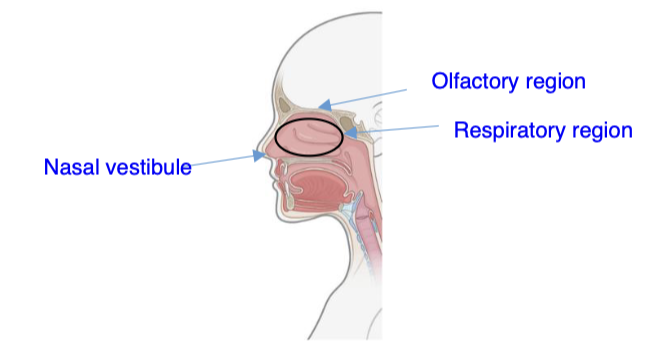
Identify the location of the nasal vestibule, the respiratory region, and the olfactory region.
See image