PHYS test multiple choice questions
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Which one of the following statements concerning waves is false?
a. A wave can have both transverse and longitudinal components.
b. A wave carries energy from one place to another.
c. A wave does not result in the bulk flow of the material of its medium.
d. A wave is a traveling disturbance.
e. A transverse wave is one in which the disturbance is parallel to the direction of travel
e. A transverse wave is one in which the disturbance is parallel to the direction of travel
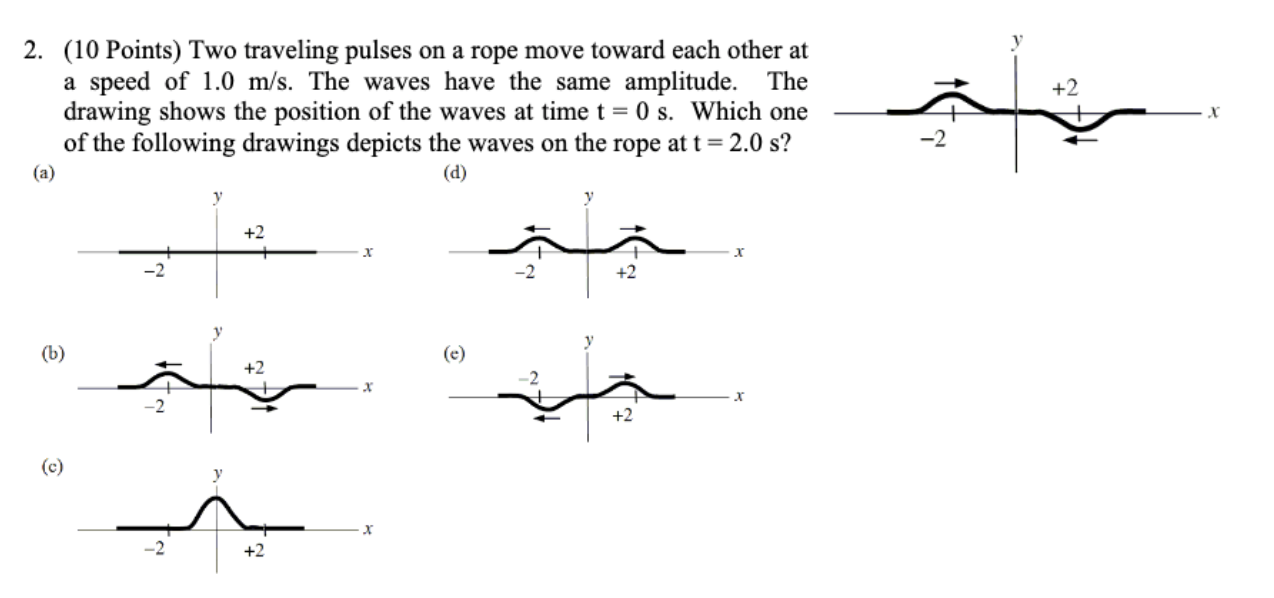
Two traveling pulses on a rope move toward each other at
a speed of 1.0 m/s. The waves have the same amplitude. The
drawing shows the position of the waves at time t = 0 s. Which one
of the following drawings depicts the waves on the rope at t = 2.0 s?
a
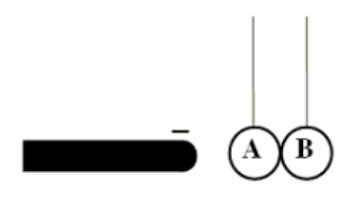
Two uncharged conducting spheres, A and B, are suspended from insulating threads so that
they touch each other. While a negatively charged rod is held near, but
not touching sphere A, someone moves ball B away from A. How will
the spheres be charged, if at all?
Sphere A Sphere B
a. 0 +
b. - +
c. 0 0
d. - +
e. + -
e. + -
Which one of the following statements best explains why it is possible to define an electrostatic potential in a region of space that contains an electrostatic field?
a. Work must be done to bring two positive charges closer together.
b. Like charges repel one another and unlike charges attract one another.
c. A positive charge will gain kinetic energy as it approaches a negative charge.
d. The work required to bring two charges together is independent of the path taken.
e. A negative charge will gain kinetic energy as it moves away from another negative charge
d. The work required to bring two charges together is independent of the path taken.
The outer surface of the cardboard center of a paper towel roll
a. is a possible Gaussian surface
b. cannot be a Gaussian surface since it is an insulator
c. cannot be a Gaussian surface since it encloses no charge
d. cannot be a Gaussian surface since it isn’t a closed surface
e. none of the above
d. cannot be a Gaussian surface since it isn’t a closed surface
A certain physics textbook shows a region of space in which two electric field lines cross each other. We conclude that:
a. at least two point charges are present
b. an electrical conductor is present
c. an insulator is present
d. the field points in two directions at the same place
e. the author made a mistake
e. the author made a mistake
A positively charged insulating rod is brought close to an object that is suspended by a string. If the object is attracted toward the rod we can conclude:
a. the object initially had an excess of positive charge
b. the object initially had an excess of negative charge
c. the object was initially uncharged
d. either (b) or (c) may be true
e. that none of the above are true
d. either (b) or (c) may be true
Experimenter A uses a test charge q0 and experimenter B uses a test charge 2q0 to measure an electric field produced by stationary charges. A finds a field that is:
a. the same as the field found by B
b. greater than the field found by B
c. less than the field found by B
d. either greater or less than the field found by B, depending on the masses of the test charges
e. either greater or less than the field found by B, depending on the accelerations of the test charges
a. the same as the field found by B
A hollow metal sphere is charged to a potential V. The potential at its center is:
a. V
b. 0
c. –V
d. 2V
e. need more information
a. V
Electric field lines:
a. are vectors in the direction of the electric field
b. form closed loops
c. are trajectories of a test charge
d. cross each other in the region between two point charges
e. are none of the above
c. are trajectories of a test charge
A point charge is placed at the center of a spherical Gaussian surface. The flux ΦE is changed:
a. if the sphere is replaced by a cube of the same volume
b. if the sphere is replaced by a sphere of one-tenth the volume
c. if the point charge is moved off center (but still inside the original sphere)
d. if the point charge is moved just outside the sphere
e. all of the above change ΦE
d. if the point charge is moved just outside the sphere
A battery is used to charge a parallel plate capacitor after which it is disconnected. Then the
plates are pulled apart to twice their original separation. This process will double
a. capacitance
b. surface charge density
c. stored energy
d. electric field between the plates
e. charge on each plate
c. stored energy
A certain wire has resistance R. Another wire, of the same material, has twice the length and
twice the diameter as the first wire. The resistance of the second wire is:
a. R/4
b. R/2
c. R
d. 2R
e. 4R
b. R/2
The sum of the currents into a junction equals the sum of the currents out of the junction” is a result of:
a. Newton’s third law
b. Ohm’s law
c. Newton’s second law
d. Conservation of energy
e. Conservation of charge
e. Conservation of charge
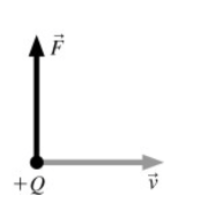
A positive charge is moving to the right and experiences a
vertical (upward) magnetic force. In which direction is the magnetic field?
a. To the right
b. To the left
c. Upward
d. Out of the page
e. Into the page
e. Into the page
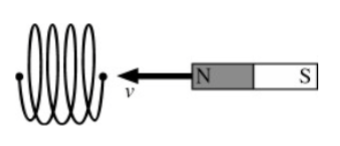
While a magnet is moved towards the end of a solenoid, a voltage difference is induced between the two
ends of the solenoid wire. The voltage difference would be larger if
a. the speed of the magnet were increased.
b. the solenoid contained more loops (while having the same
length).
c. the bar magnet produced a stronger magnetic field.
d. All of the above statements are true.
e. Only two of the above statements are true
d. All of the above statements are true.
Which of the following scenarios will cause radiation to be emitted?
a. a charged particle moving in a circle at a constant speed.
b. a charged particle moving in a straight line at constant speed.
c. a stationary solid sphere with its total charge varying in time.
d. All of the above.
e. Only two of the above
e. Only two of the above
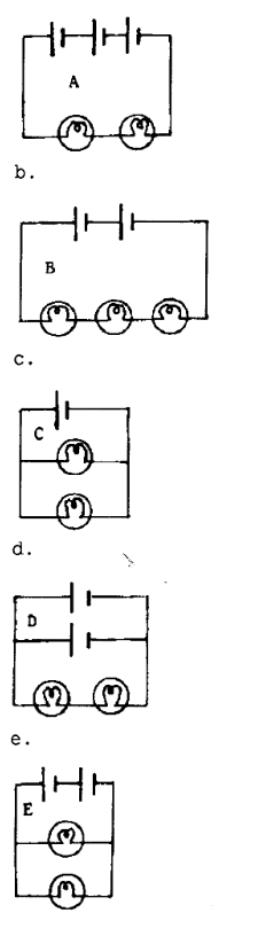
In the diagrams to the right, all light bulbs are identical and all
batteries are identical. In which circuit (a,b,c,d or e) will the bulbs be the
dimmest? (circle the correct circuit)
D
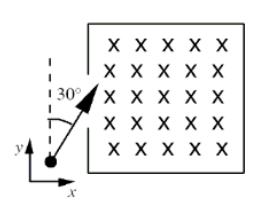
An electron enters a region that contains a magnetic field
directed into the page as shown. The velocity vector of the electron
makes an angle of 30° with the +y axis. What is the direction of the
magnetic force on the electron when it enters the field?
a. up, out of the page
b. at an angle of 30° below the positive x axis
c. at an angle of 30° above the positive x axis
d. at an angle of 60° below the positive x axis
e. at an angle of 60° above the positive x axis
b. at an angle of 30° below the positive x axis
Complete the following statement: The electromotive force is
a. the maximum potential difference between the terminals of a battery.
b. the force that accelerates electrons through a wire when a battery is connected to it.
c. the force that accelerates protons through a wire when a battery is connected to it.
d. the maximum capacitance between the terminals of a battery.
e. the maximum electric potential energy stored within a battery.
a. the maximum potential difference between the terminals of a battery.
An ac voltage source that has a frequency f is connected across the ends of an inductor. Which one of the following statements correctly indicates the effect on the inductive reactance when the frequency is increased to 2f?
a. The inductive reactance increases by a factor of two.
b. The inductive reactance increases by a factor of four.
c. The inductive reactance is unchanged.
d. The inductive reactance decreases by a factor of four.
e. The inductive reactance decreases by a factor of two
a. The inductive reactance increases by a factor of two.
Which one of the following statements concerning the wavelength of an electromagnetic wave in a vacuum is true?
a. The wavelength is independent of the speed of the wave for a fixed frequency
b. The wavelength is inversely proportional to the speed of the wave
c. The wavelength is the same for all types of electromagnetic waves
d. The wavelength is directly proportional to the frequency of the wave
e. The wavelength is inversely proportional to the frequency of the wave
e. The wavelength is inversely proportional to the frequency of the wave
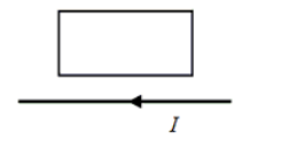
A long, straight wire is in the same plane as a rectangular, conducting loop. The wire carries a constant current I as shown in the figure. Which one of the following statements is true if the wire is suddenly moved toward the loop?
a. There will be no induced emf and no induced current.
b. There will be an induced emf, but no induced current.
c. There will be an induced current that is clockwise around the
loop.
d. There will be an induced current that is counterclockwise around the loop.
e. There will be an induced electric field that is clockwise around the loop.
d. There will be an induced current that is counterclockwise around the loop.
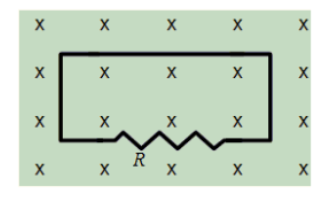
The figure shows a uniform magnetic field that is normal to the plane of a
conducting loop with resistance R. Which one of the following changes will cause an induced current to flow through the resistor?
a. decreasing the area of the loop
b. decreasing the magnitude of the magnetic field
c. increasing the magnitude of the magnetic field
d. rotating the loop through 90° about an axis in the plane of
the paper
e. all of the above
e. all of the above
Which one of the following statements is not a characteristic of a plane mirror?
a. The image is real.
b. The magnification is +1
c. The image is always upright.
d. The image is reversed right to left.
e. The image and object distances are equal in magnitude
a. The image is real.
The bending of light as it moves from one medium to another with differing indices of refraction is due to a change in what property of the light?
a. Amplitude
b. Period
c. Frequency
d. Speed
e. color
d. Speed
What happens to the de Broglie wavelength of an electron if its momentum is doubled?
a. The wavelength increases by a factor of 2
b. The wavelength decreases by a factor of 2
c. The wavelength decreases by a factor of 4
d. The wavelength increases by a factor of 4
e. The wavelength increases by a factor of 3
b. The wavelength decreases by a factor of 2
Complete the following statement: For the ground state of the hydrogen atom, the Bohr model correctly predicts (CJ 30-10)
a. only the energy
b. only the angular momentum
c. only the angular momentum and the spin
d. the angular momentum and the energy
e. the energy, the angular momentum and the spin
a. only the energy
What is the total number of electrons that can have n=3? (CJ 30-44)
a. 3
b. 6
c. 7
d. 9
e. 18
e. 18
Complete the following sentence: In the condition known as population inversion, (CJ 30-64)
a. the amount of one type of gas atoms is larger than that of another in a mixture
b. the number of energy levels that are populated is larger than that of unpopulated levels
c. there are more electrons occupying lower energy levels than occupy higher energy levels
d. there are more electrons occupying higher energy levels than occupying lower energy levels
e. there are more photons than electrons in a given system
d. there are more electrons occupying higher energy levels than occupying lower energy levels
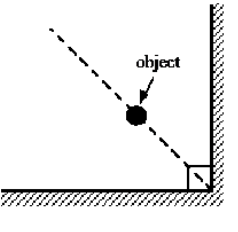
n object is placed near two perpendicular plane mirrors as shown in the figure. How many images will be formed?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
(e) 5
(c) 3
A beam of light passes from air into water. Which is necessarily true?
(a) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength increases.
(b) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength decreases.
(c) The wavelength is unchanged and the frequency decreases.
(d) Both the wavelength and frequency increase.
(e) Both the wavelength and frequency decrease
(b) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength decreases.
What does one observe on the screen in a Young’s experiment if white light illuminates the double slit instead of light of a single wavelength?
(a) a white central fringe and no other fringes
(b) a dark central fringe and a series of alternating white and dark fringes on each side of center
(c) a white central fringe and a series of colored and dark fringes on each side of the center
(d) a continuous band of colors with no dark fringes anywhere
(e) a dark screen since no constructive interference can occur
(c) a white central fringe and a series of colored and dark fringes on each side of the center
Complete the following statement: The photon description of light is necessary to explain
(a) polarization
(b) photoelectric effect
(c) diffraction of light
(d) electron diffraction
(e) interference of light
(d) electron diffraction
Which one of the following statements is the assumption that Niels Bohr made about the angular momentum of the electron in the hydrogen atom?
(a) The angular momentum of the electron is zero.
(b) The angular momentum can assume only certain discrete values.
(c) Angular momentum is not quantized.
(d) The angular momentum can assume any value greater than zero because it’s proportional to the radius of the orbit.
(e) The angular momentum is independent of the mass of the electron.
(b) The angular momentum can assume only certain discrete values.
White light enters a glass prism, but the color components of the light are observed to emerge from the prism. Which one of the following statements best explains this observation?
(a) The separation of white light into its color components is due to the increase in the speed of light within the glass.
(b) Some of the color components of the white light are absorbed by the glass and only the remaining components are observed.
(c) The index of refraction of the glass depends on the wavelength, so the color components are refracted at different angles.
(d) Only some of the color components are refracted by the glass; and these are the ones that are observed.
(e) White light is separated into its color components by total internal reflection within the prism.
(c) The index of refraction of the glass depends on the wavelength, so the color components are refracted at different angles.
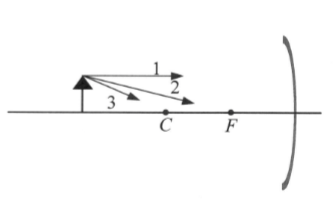
An object is placed in front of a concave spherical
mirror as shown below. The three rays 1, 2, and 3, leave the
top of the object and, after reflection, converge at a point on the
top of the image. Ray 1 is parallel to the principal axis, ray 2
passes through F, and ray 3 passes through C.
(5 points) Which ray(s) will pass through F after reflection?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. 3 only
D. both 1 and 2
E. 1, 2 and 3
(5 points) Which ray(s) will reflect back on itself (themselves)?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. 3 only
D. both 1 and 2
E. 1, 2 and 3
(5 points) Which one of the following groups best describes the image?
A. Real, upright, enlarged
B. Real, inverted, reduced
C. Virtual, upright, enlarged
D. Real, inverted enlarged
E. Virtual, inverted, reduced
A. 1 only
C. 3 only
B. Real, inverted, reduced