Pharmaceutical Medicinal Organic Chemistry - Endocrine Drug
1/199
Earn XP
Description and Tags
It maintains body functions and homeostasis by releasing hormones which are used for several body functions like growth, reproduction and defenses. Its primary use is for replacement therapy, treatment for disorders, and diagnostic purpose.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
200 Terms
_____________________ are agents that stimulate the release of insulin from the beta cells of the pancreas.
• Agents: _________________ and _________________
Insulin secretagogues are agents that stimulate the release of insulin from the beta cells of the pancreas.
• Agents: Sulfonylureas and Meglitinides
Composed of several hormone-releasing organs
Endocrine System
____________________ usually work like hormones as a __________, semi-synthetic or _____________ compound.
• Its primary use is for replacement therapy, treatment for disorders, and diagnostic purpose.
Endocrine drugs usually work like hormones as a natural, semi-synthetic or synthetic compound.
• Its primary use is for replacement therapy, treatment for disorders, and diagnostic purpose.
Classification of Endocrine Drugs (Based on Structure)
__________ (majority) and Steroidal (adrenal cortex/____________)
Classification of Endocrine Drugs (Based on Structure)
Peptide (majority) and Steroidal (adrenal cortex/sex hormones)
True of False
Diabetes is an actual disease
False (Abnormality in your blood sugar)
What are the 3 Cardinal Signs of Diabetes
Polyuria, Polyphagia, Polydipsia
3 Cardinal Signs of Diabetes
Si patient ay ihi nang ihi
Polyuria
3 Cardinal Signs of Diabetes
Si patient ay kain nang kain
Polyphagia
3 Cardinal Signs of Diabetes
Si patient ay palaging uhaw
Polydipsia
Types of Diabetes
Insulin-dependent; has a juvenile onset, patients require insulin therapy for their lifetime
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1
Types of Diabetes
Insulin-independent; has a adult onset (commonly), patients may or may not require insulin therapy.
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Types of Diabetes
Glucose intolerance during pregnancy
Gestational Diabetes
Types of Diabetes
Results for non-usual causes or from other diseases present in the patient.
Secondary Diabetes Mellitus
Therapy is directed at maintaining ___________ (normal blood sugar)
Therapy is directed at maintaining euglycemic states (normal blood sugar)
__________ is a 51-amino acid protein with two chains linked by a disulfide bond. It is produced by the ________ of the pancreas.
• MOA: transports glucose into _________ and ___________ by releasing glucose transporter (GLUT 4)
• SAR:_____ and _____terminals of the amino acid Chain A and B are essential for insulin receptor binding
Insulin is a 51-amino acid protein with two chains linked by a disulfide bond. It is produced by the beta cell of the pancreas.
• MOA: transports glucose into adipose and muscle cells by releasing glucose transporter (GLUT 4)
• SAR: N- and C- terminals of the amino acid Chain A and B are essential for insulin receptor binding
Insulin is produced via ______________________ of proinsulin
Insulin is produced via proteolytic modifications of proinsulin
____________ is formed by removal 24-amino acid from _______________
Proinsulin is formed by removal 24-amino acid from preproinsulin
Classification and Pharmacokinetics of Insulin Preparation
Give the example for this type:
Rapid-acting
Lispro, Aspart, Glulisine
Classification and Pharmacokinetics of Insulin Preparation
Give the example for this type:
Short-acting
Human Insulin (Regular)
Classification and Pharmacokinetics of Insulin Preparation
Give the example for this type:
Intermediate-Acting
Lente, NPH* insulin (isophane)
Classification and Pharmacokinetics of Insulin Preparation
Give the example for this type:
Long-acting
Ultralente, Glargine, Detemir
What is the meaning of NPH?
Neutral Protamine Hagedorn
DOA of Rapid-acting
3hrs
Onset of Rapid-acting
5-10 mins
DOA of Short-acting
2-3hrs
Onset of Short-acting
30-60 mins
Numbers of crystalline zinc of Lente
2
Numbers of crystalline zinc of Ultralente
4
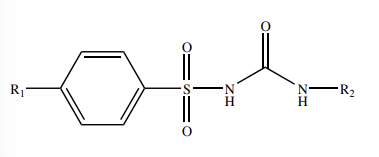
Name the Structure
SULFONYLUREA PHARMACOPHORE
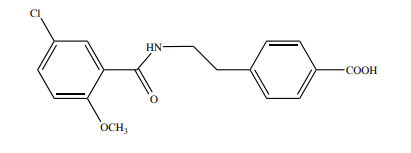
Name the structure
MEGLITINIDE
Sulfonylureas
• MOA: binds to ___________________________________ at ATP-sensitive K-channel and opens the voltage-gated Ca-channel leading to increased intracellular Ca and ___________release of insulin.
Sulfonylureas
• MOA: binds to sulfonylurea receptor type 1 (SUR1) at ATP-sensitive K-channel and opens the voltage-gated Ca-channel leading to increased intracellular Ca and exocytotic release of insulin.
SAR of Sulfonylureas (TRUE OR FALSE)
1st Generation: small lipophilic at R1, alkyl/cyclic substituent at R2; high dose, long plasma T1/2, long DOA, low chance for ADR (hypoglycemia)
FALSE
1st Generation: small lipophilic at R1, alkyl/cyclic substituent at R2; high dose, long plasma T1/2, short DOA, high chance for ADR (hypoglycemia)
SAR of Sulfonylureas (TRUE OR FALSE)
2nd Generation: has large p-(β-arylcarboxyamidoethyl) group at R1; high potency, rapid onset, short plasma T1/2, long DOA
TRUE
Anti-Diabetic Agents (TRUE OR FALSE)
FIRST GENERATION includes Tolbutamide, Glipizide, Acetohexamide
FALSE
FIRST GENERATION includes Tolbutamide, Chlorpropramide, Acetohexamide
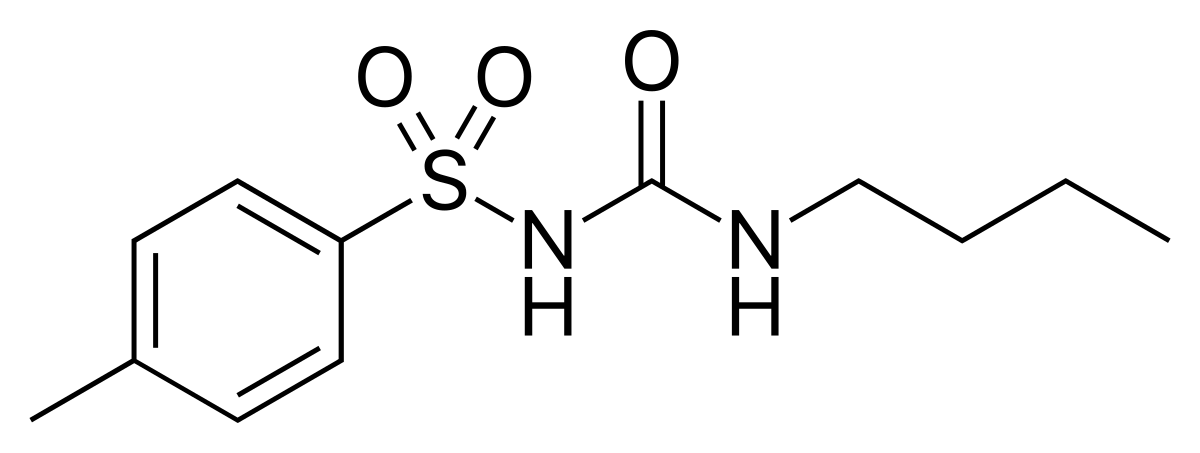
Name the structure
TOLBUTAMIDE
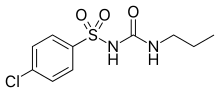
Name the structure
CHLORPROPRAMIDE
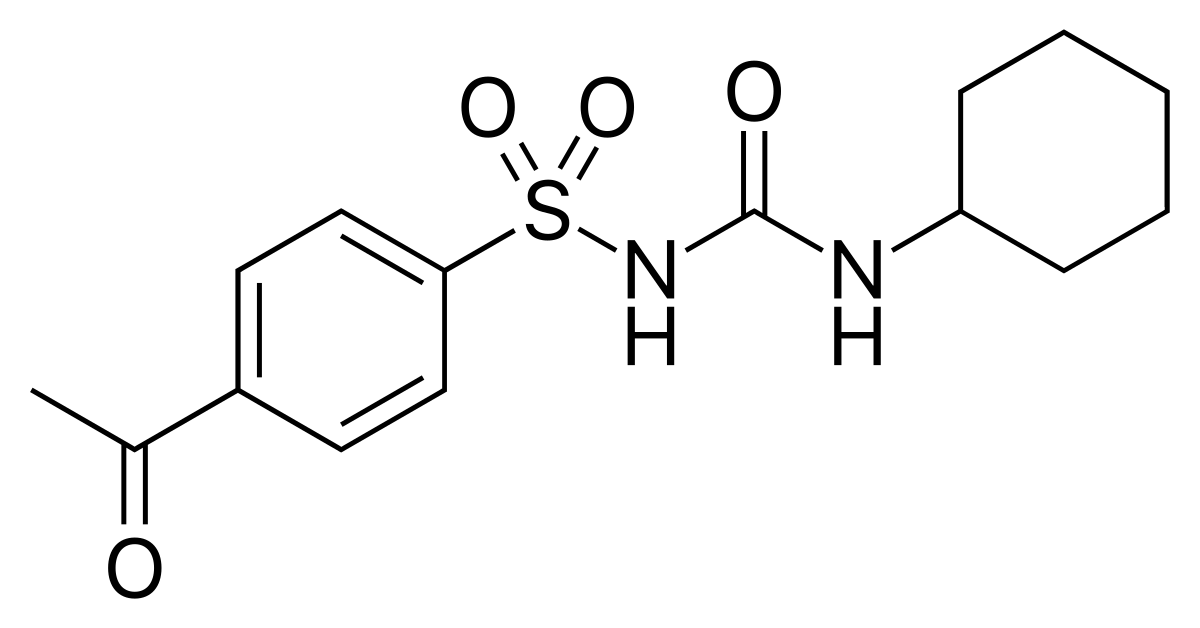
Name the structure
ACETOHEXAMIDE
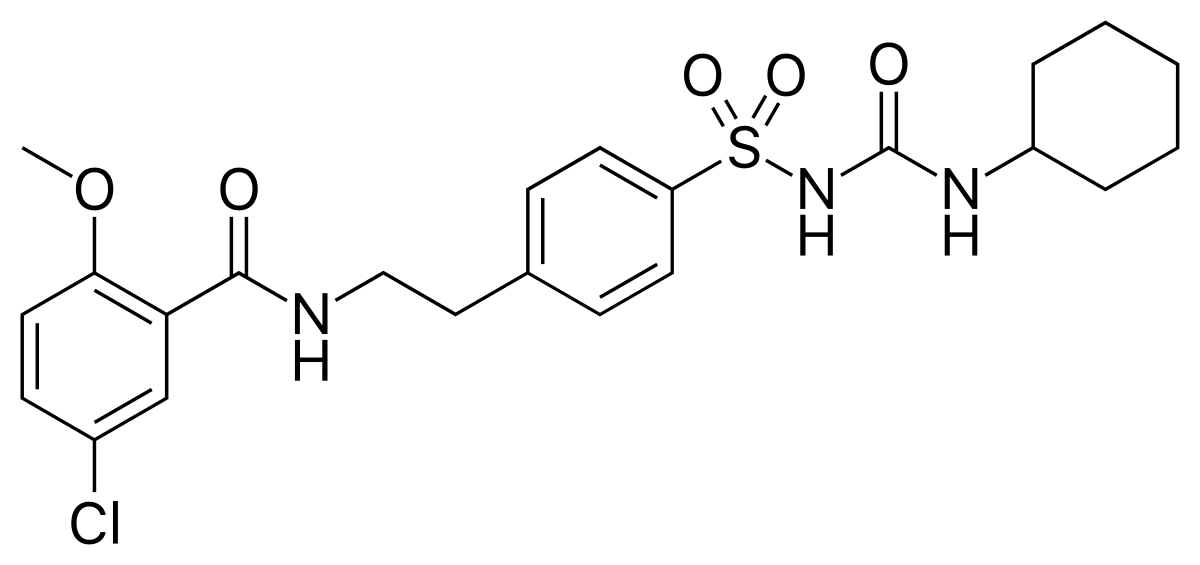
Name the Structure
GLYBURIDE/GLIBENCLAMIDE
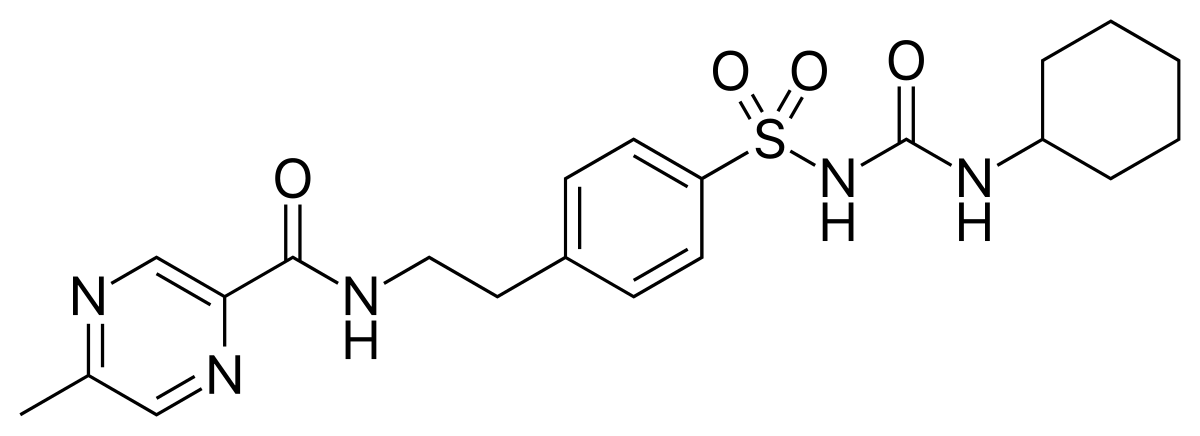
Name the structure
GLIPIZIDE
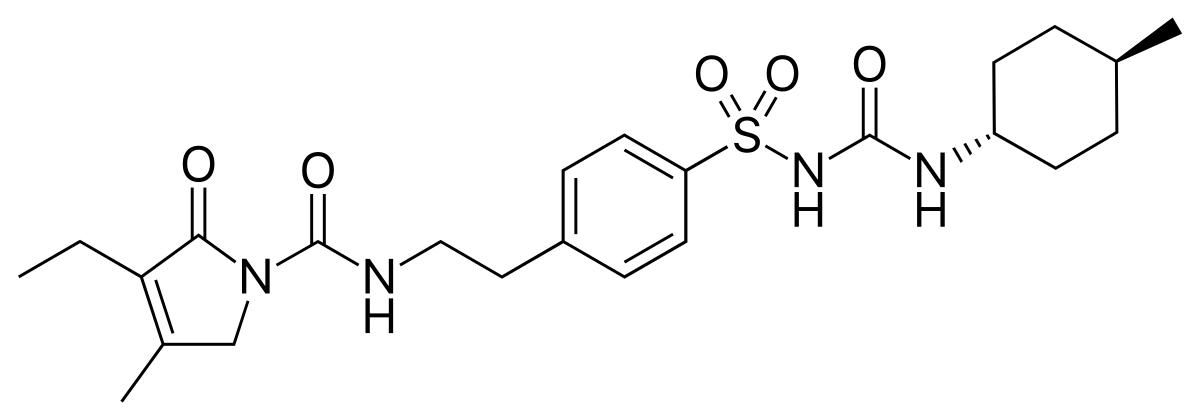
Name the structure
GLIMEPIRIDE
_____________
• MOA: similar to sulfonylureas; _____________ binds also to SUR1, SUR2A and SUR2B leading to ______________ effects.
• SAR: Meglitinide is a prototype structure — it is a __________________________of the non-sulfonylurea moiety of _______________________
Meglitinides
• MOA: similar to sulfonylureas; Repaglinide binds also to SUR1, SUR2A and SUR2B leading to extrapancreatic effects.
• SAR: Meglitinide is a prototype structure — it is a benzoic acid derivative of the non-sulfonylurea moiety of glibenclamide/glyburide
Metabolism of Meglitinides
Repaglinide
CYP ______ and 3A4 hydroxylation of piperidine ring and ________________
CYP 2C8 and 3A4 hydroxylation of piperidine ring and glucuronidation
Nateglinide
CYP 2C9 (____ %) and __________________ of isopropyl moiety
CYP 2C9 (70%) and 3A4 hydroxylation of isopropyl moiety
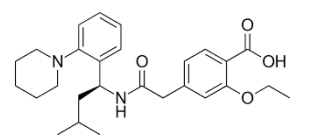
Name the Structure
It has rapid onset, short DOA & does not cause prolonged hyperinsulinemia
REPAGLINIDE
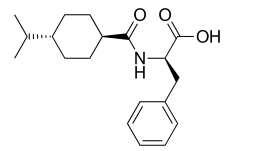
Name the Structure
It has rapid onset, longer DOA
NATEGLINIDE
Biguanides
• _____________________ with lifestyle change. It is highly distributed and excreted ________________ in the urine
Biguanides
• 1st line treatment with lifestyle change. It is highly distributed and excreted unchanged in the urine
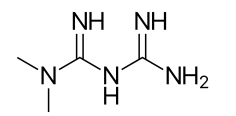
Name the structure
It is the only biguanide approved for use may cause GI discomfort, lactic acidosis, metallic taste
METFORMIN
MOA of Biguanides (TRUE OR FALSE)
• increases gluconeogenesis
• decreases glycogenolysis and glycoslysis.
• decreases insulin sensitivity
FALSE
• decreases gluconeogenesis
• increases glycogenolysis and glycoslysis.
• increases insulin sensitivity
SAR of Biguanide (TRUE OR FALSE)
structure is made of 2 linked guanidine moiety.
TRUE
meaning of PPAR-Agonists
Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Agonists
Insulin Sensitizers / PPAR-Agonists
• MOA: • PPAR controls gene expression, ________ (gamma) agonist __________ glucose transporter expression leading to increasing ________________ of the body.
• ______________ gluconeogenesis and lower systematic fatty acids.
• SAR: It has a ________________ pharmacophore.
• For agonist activity: R must be a _______ substituted phenyl ring attached to the pharmacophore with a __________ bridge
Insulin Sensitizers / PPAR-Agonists
• MOA: • PPAR controls gene expression, PPARɣ (gamma) agonist increase glucose transporter expression leading to increasing insulin sensitivity of the body.
• Slows down gluconeogenesis and lower systematic fatty acids.
• SAR: It has a thiazolidinedione pharmacophore.
• For agonist activity: R must be a para- substituted phenyl ring attached to the pharmacophore with a methylene bridge
Metabolism of Insulin Sensitizers/PPAR-Agonists (TRUE OR FALSE)
CYP2C9 (most metabolites are still possess agonist activity)
TRUE
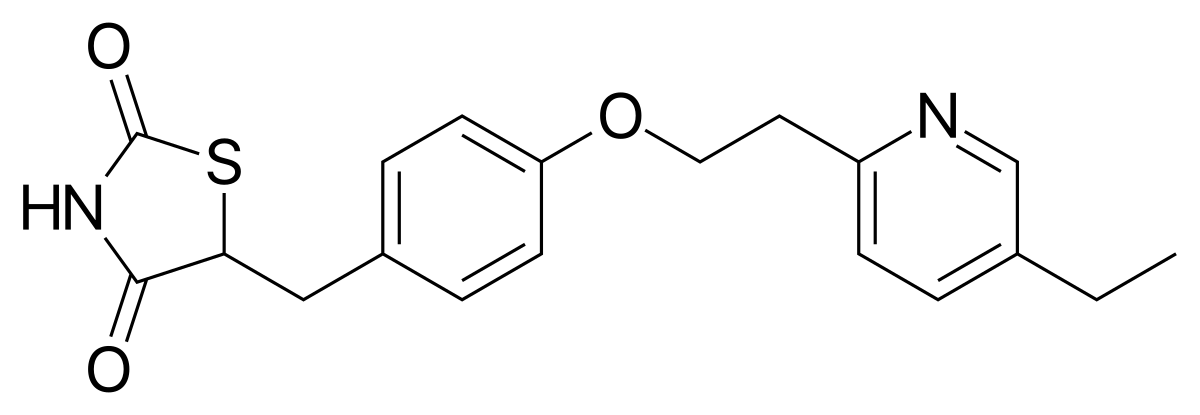
Name the structure
only available “glitazone” in the market useful for patients that cannot tolerate sulfonylurea or metformin
PIOGLITAZONE
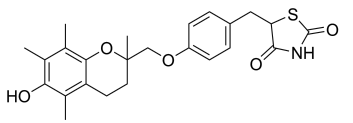
Name the structure
not used due to severe hepatotoxicity
TROGLITAZONE
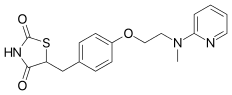
Name the structure
limited availability due to increase cardiovascular effects
ROSIGLITAZONE
Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
• _________________ is an enzyme made of _________, sucrase, ___________, and glucoamylase found in the ______________.
• MOA: inhibits α-glucosidase to inhibit _______________________ which prevents absorption of mono/disaccharides leading to inhibition of ___________________________
• SAR: inhibitors mimic the __________________ of α-glucosidase by having similar structures.
Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
• α-glucosidase is an enzyme made of maltase, sucrase, isomaltase, and glucoamylase found in the small intestine.
• MOA: inhibits α-glucosidase to inhibit carbohydrate breakdown which prevents absorption of mono/disaccharides leading to inhibition of post-prandial hyperglycemia.
• SAR: inhibitors mimic the natural substrates of α-glucosidase by having similar structures.
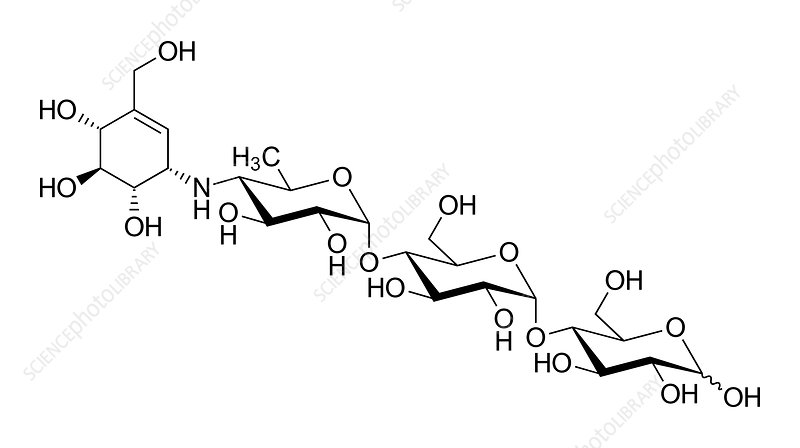
Name the structure
extremely low oral bioavailability
ACARBOSE
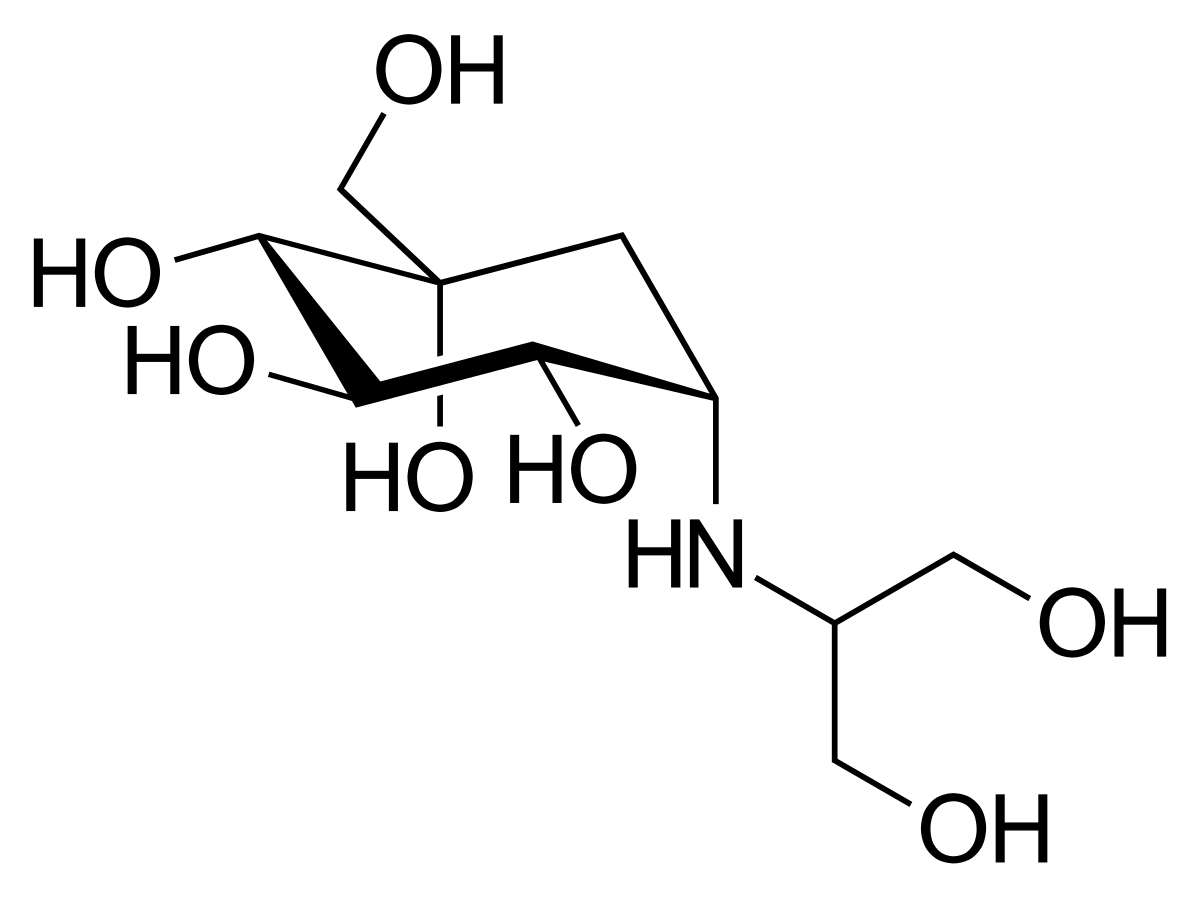
Name the structure
poorly absorbed
VOGLIBOSE
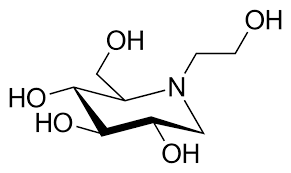
Name the structure
absorbed orally, not metabolized excreted unchanged
MIGLITOL
It aids in mimicking natural disaccharide substrate
POLYHYDROXY Groups
Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Agonist
• GLP-1 is a __________ amino acid peptide produced by prohormone convertase enzymes from __________________. It is indicated for additional therapy with ______________ or metformin to reach HbA1c <___%
• MOA: GLP-1 is released from _________ of GIT in response to ________. GLP-1 promotes __________ secretion from pancreas.
• SAR: GLP-1 agonist analogs have _______________ amino acid modification to resist metabolism by _____________________
Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Agonist
• GLP-1 is a 30-31 amino acid peptide produced by prohormone convertase enzymes from proglucagon. It is indicated for additional therapy with sulfonylurea or metformin to reach HbA1c <7%
• MOA: GLP-1 is released from L-cells of GIT in response to food. GLP-1 promotes insulin secretion from pancreas.
• SAR: GLP-1 agonist analogs have penultimate amino acid modification to resist metabolism by Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV)
4 Agents of GLP-1 Agonist
Exenatide, Liraglutide, Albiglutide, Dulaglutide
Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitors (DPP IV Inhibitors)
• MOA: binds to the _____________ site in DPP-IV, alternatives to GLP-1 agonist analogs
• SAR: It has 3 pharmacophore structure: ________________________, ______________, and pyrimidine-2,4-dione.
• The ____________ binds to the active serine site in DPP-IV.
• It can be taken alone or with _______________ or _______________; it rarely causes hypoglycemia.
Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitors (DPP IV Inhibitors)
• MOA: binds to the active serine site in DPP-IV, alternatives to GLP-1 agonist analogs
• SAR: It has 3 pharmacophore structure: 𝛼-aminoacylpyrrolidine, xanthine, and pyrimidine-2,4-dione.
• The cyano group binds to the active serine site in DPP-IV.
• It can be taken alone or with metformin or thiazolidinedione; it rarely causes hypoglycemia.
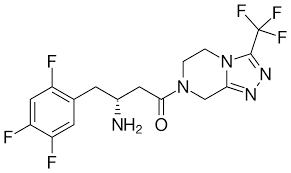
Name the structure
has piperazine fused pyrazole with α-aminoacyl moiety (most popular drug)
SITAGLIPTIN
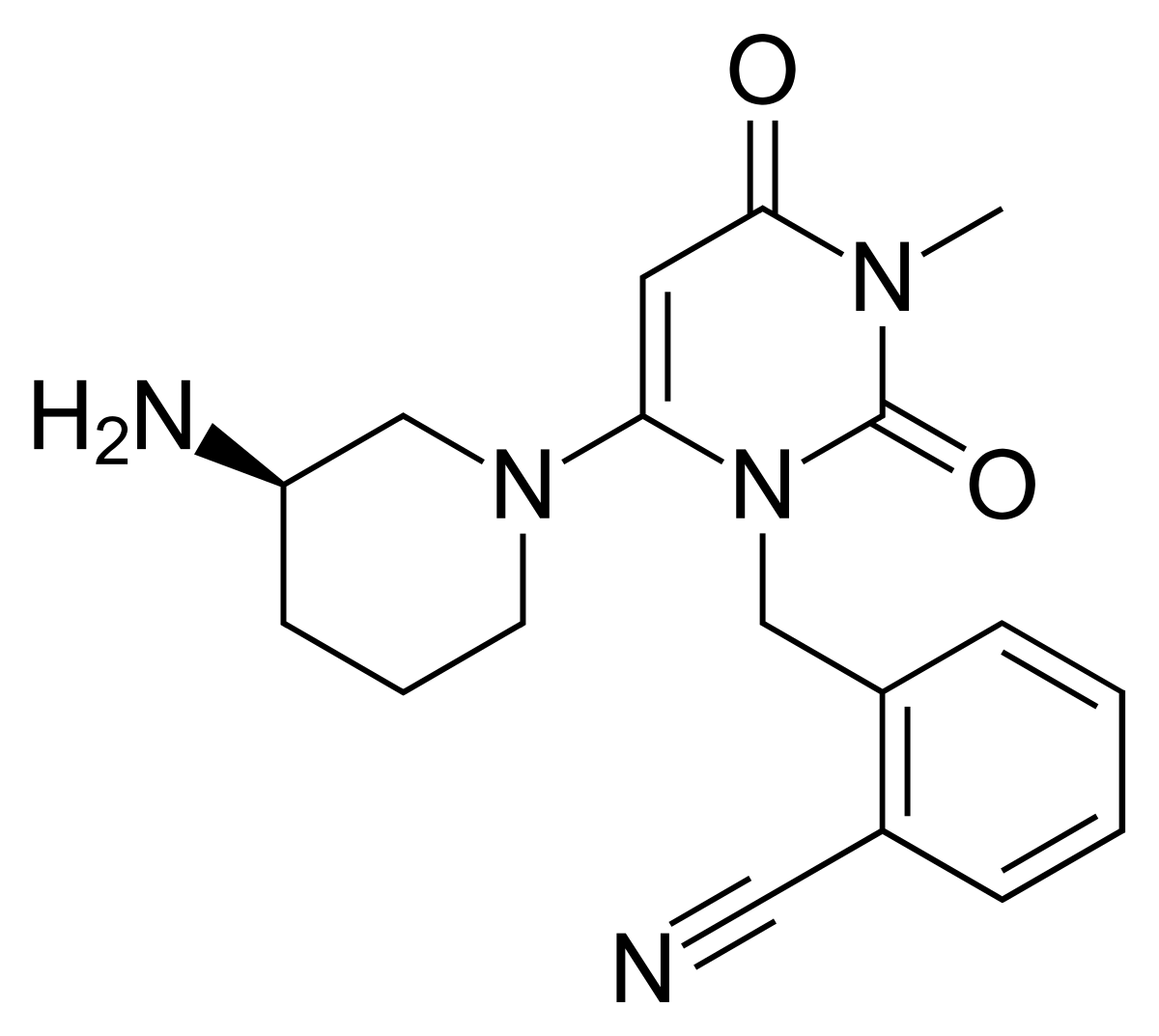
Name the structure
pyrimidine-2,4-dione pharmacophore
ALOGLIPTIN
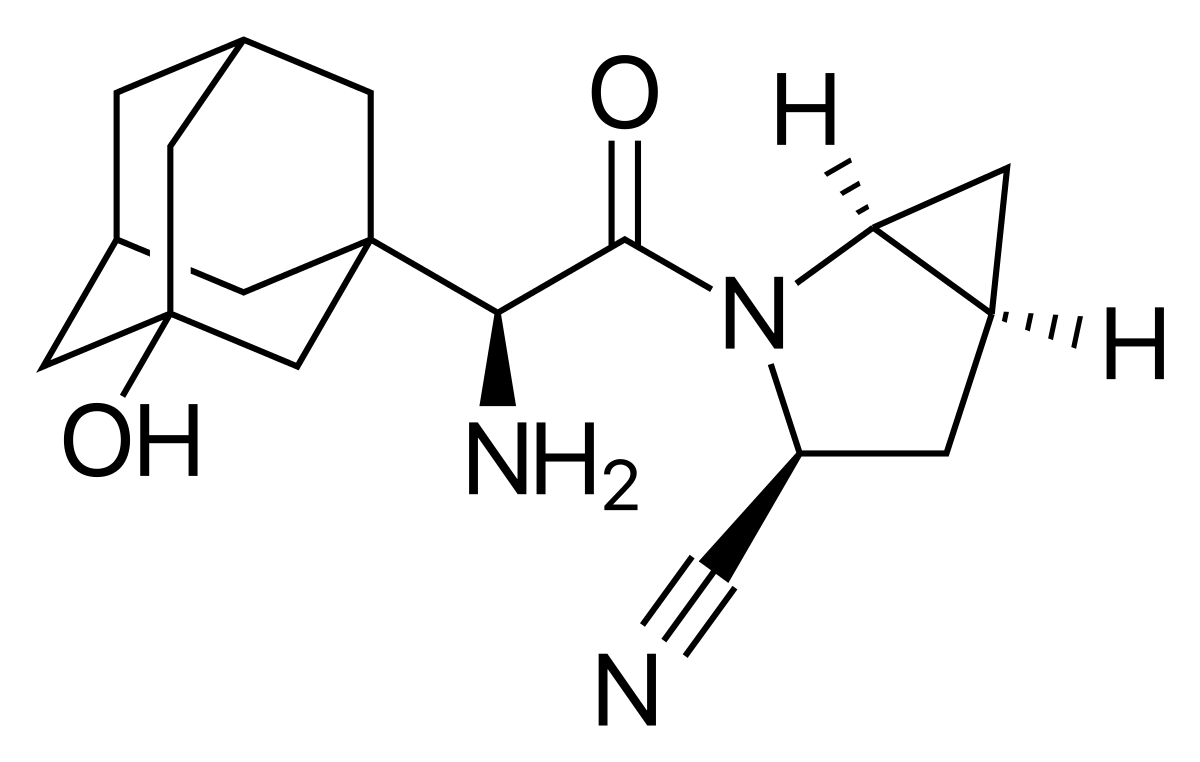
Name the structure
α-aminoacylpyrrolidine pharmacophore
SAXAGLIPTIN
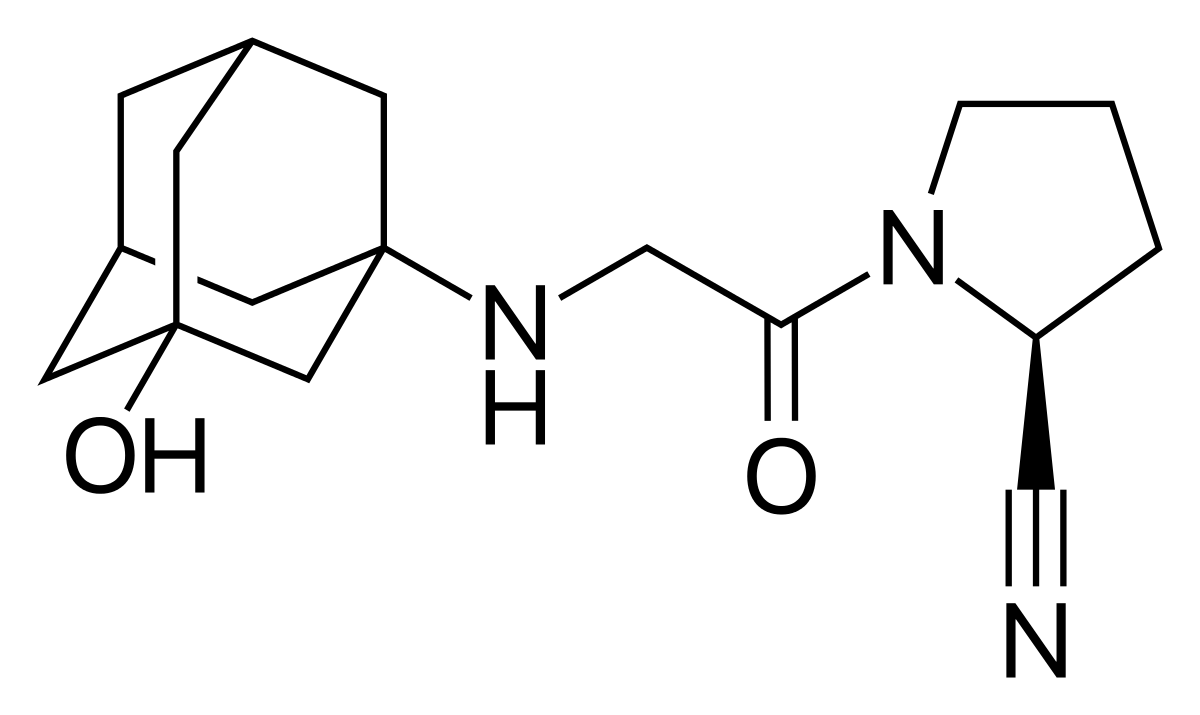
Name the structure
α-aminoacylpyrrolidine pharmacophore
VILDAGLIPTIN
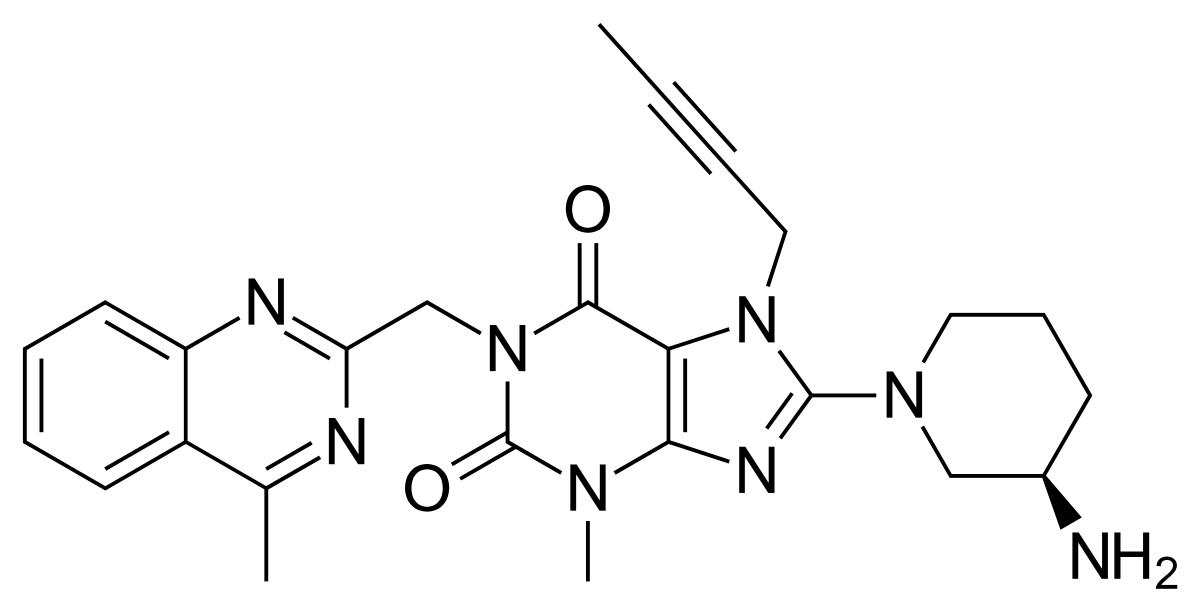
Name the
structure
xanthine pharmacophore
LINAGLIPTIN
Amylin Agonist
• Amylin is a ____-amino acid hormone released with ________.
• MOA: suppress ___________________ , delaying ______________________, to modulate appetite centers which aids in maintaining glucose plasma level.
• SAR: _______________ is an amylin agonist analog.
• Proline replacement for _______, Ser28, Ser29
Amylin Agonist
• Amylin is a 37-amino acid hormone released with insulin.
• MOA: suppress glucagon secretion, delaying gastric emptying time, to modulate appetite centers which aids in maintaining glucose plasma level.
• SAR: Pramlintide is an amylin agonist analog.
• Proline replacement for Ala25, Ser28, Ser29
It cannot be given to patient with renal impairment
Sodium Glucose Cotransporter (SGLT2) Inhibitor
Sodium Glucose Cotransporter (SGLT2) Inhibitor
• SGLT2 aids in ______________ of glucose from ________________________
• MOA: inhibit SGLT2 leading to ______________ renal threshold for glucose which results to ____________ urinary glucose excretion.
• SAR: It has a ____________________________ and a glucose moiety that binds to __________ and ___________ moiety of the transporter.
• Not recommended for ________ diabetes and patients with __________________
Sodium Glucose Cotransporter (SGLT2) Inhibitor
• SGLT2 aids in reabsorption of glucose from renal proximal tubules
• MOA: inhibit SGLT2 leading to decreased renal threshold for glucose which results to increased urinary glucose excretion.
• SAR: It has a phlorizin pharmacophore and a glucose moiety that binds to Thr156 and Lys157 moiety of the transporter.
• Not recommended for Type 1 diabetes and patients with renal impairment.
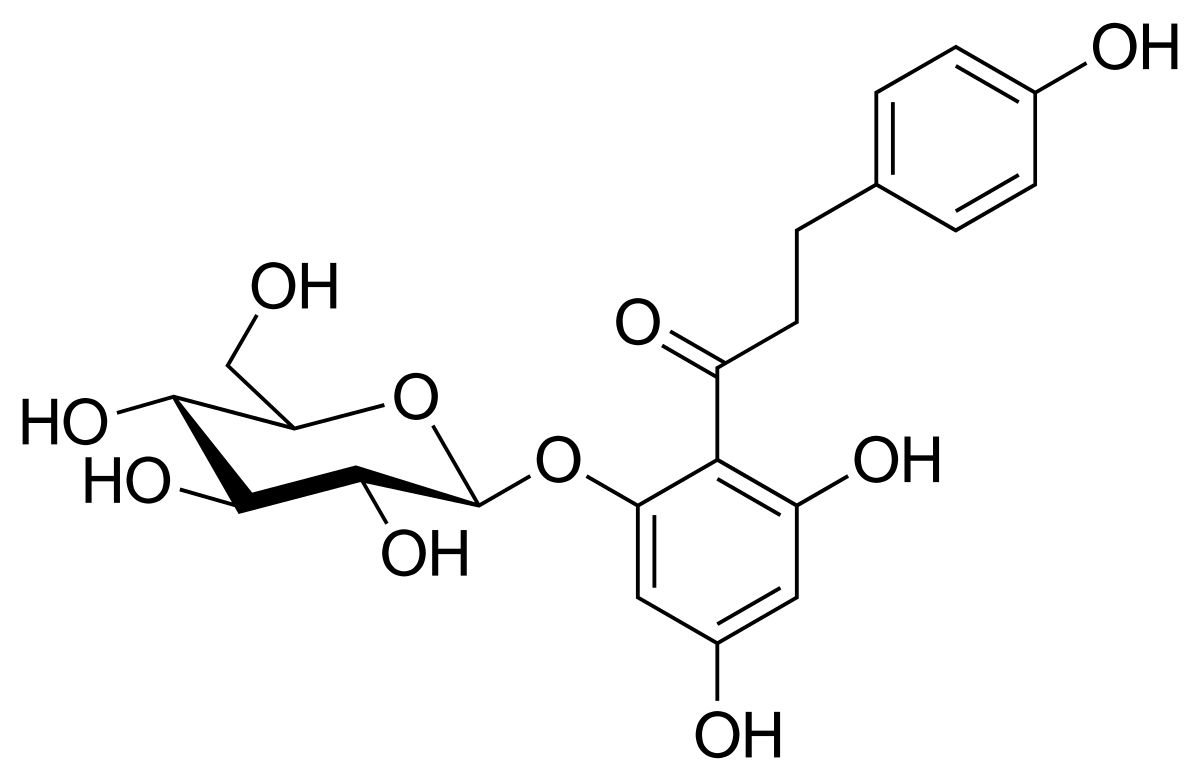
Name the structure
pharmacophore w/glucose
PHLORIZIN
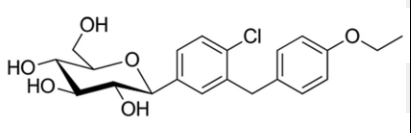
Name the structure
most commonly prescribed
DAPAGLIFLOZIN
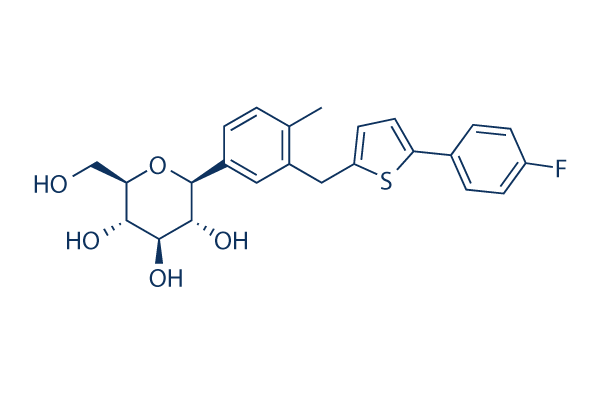
Name the structure
most commonly prescribed
CANAGLIFLOZIN
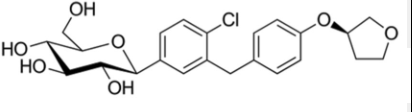
Name the structure
EMPAGLIFLOZIN
It is the only mamalian organ that can incorporate iodine into organic molecule
Thyroid gland
Formation of thyroid hormone
Organification
Thyroid gland is the only mamalian organ that can incorporate iodine into organic molecule and is the source of _____________and _____________________.
• These hormones are needed for__________________________ and adult metabolism.
• Disorders associated to thyroid gland function are usually due to _______________ (hyper-) or ______________ (hypo-) that is diagnosed through levels of TSH, ____ and ____.
• Medications are _________________________________________ and/or antithyroid drugs
Thyroid gland is the only mamalian organ that can incorporate iodine into organic molecule and is the source of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
• These hormones are needed for fetal development and adult metabolism.
• Disorders associated to thyroid gland function are usually due to overactivity (hyper-) or underactivity (hypo-) that is diagnosed through levels of TSH, T3 and T4.
• Medications are hormone replacement therapy and/or antithyroid drugs
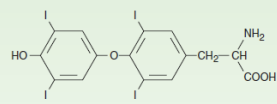
Name the structure
THYROXINE
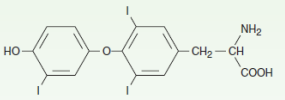
Name the structure
3,5,3’-Triiodothyronine (T3) - Activated
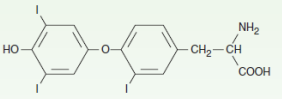
Name the structure
3,3’ ,5’-Triiodothyronine (T3) - Inactivated
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Bradycardia, reduced cardiac output
HYPOTHYROIDISM (CV)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Stiffness, decreased deep tendon reflex
HYPOTHYROIDISM (Musculoskeletal)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Nervousness, tremor
HYPERTHYROIDISM (CNS)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Pleural effusions, hypoventilation
HYPOTHYROIDISM (Respiratory)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Warm, moist skin (more secretions), Plummer’s nails, pretibial dermopathy
HYPERTHYROIDISM (Integumentary)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Dyspnea
HYPERTHYROIDISM (Respiratory)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Tachycardia (most prominent), increased cardiac output
HYPERTHYROIDISM (CV)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Pale, cool skin (reduced secretions), brittle hair and nails
HYPOTHYROIDISM (Integumentary)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Normochromic anemia
Both
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Infertility, decreased libido, impotence, oligospermia
HYPOTHYROIDISM (Reproductive)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Weakness, increased deep tendon reflex
HYPERTHYROIDISM (Musculoskeletal)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Polyuria, increased renal blood flow
HYPERTHYROIDISM (Renal)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Reduced appetite
HYPOTHYROIDISM ( GIT)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Weight gain (reduced metabolism)
HYPOTHYROIDISM (Metabolism)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Retraction of upper eyelid Exophthalmos (protrusion of eyeball)
HYPERTHYROIDISM (Face)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Impaired water excretion, decreased renal blood flow
HYPOTHYROIDISM (Renal)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Drooping of eyelids, puffy face, large tongue
HYPOTHYROIDISM (Face)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Weight loss (increased metabolism)
HYPERTHYROIDISM (Metabolism)
(HYPOTHYROIDISM/HYPERTHYROIDISM)
Lethargy, slowing of mental processes
HYPOTHYROIDISM (CNS)