Cell Cultures Study Guide
- Temperature, pH, oxygen and available nutrients influence cell growth
- Liquid media gives cells better access to nutrients
Bacterial Transfer
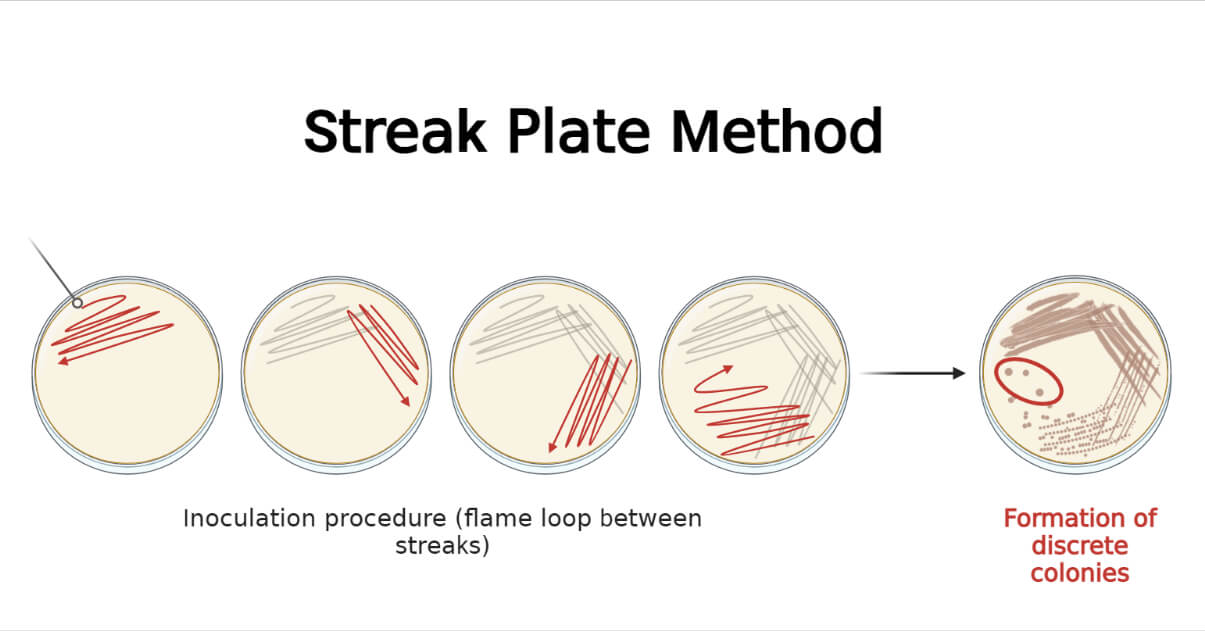
- Pick up bacteria with an inoculating loop
- Start in the 1st quadrant and draw a zig-zag
- Continue by dragging this to the 2nd quadrant, and repeat for the rest
- You can also continuously streak across the whole plate
Agar Prep
- Mix agar and water and then heat
- Wait until it is cooled down to add additives
- Pour agar when it has cooled down by holding the lid on the petri dish slightly above it (do not set the lid down)
- Store agar upside down
Koch’s Postulates
- Used to determine the relationship between diseases and pathogens
- 1st Postulate- Microbe should be in diseased person, but not healthy person
- 2nd Postulate- Microbe can be cultured from diseased person
- 3rd Postulate- Microbe from culture will cause disease when put into healthy person
- 4th Postulate- Microbe can be re-isolated and it will be the same as before
- If something fulfills these 4 postulates, it is the causative agent of the disease
- Today there are some discrepancies with the original postulate, such as unculturable microorganisms or multiple pathogens causing the same disease
Aseptic Techniques
- Methods of preventing contamination by microorganisms
- Using gloves
- Not setting lids down
- Keeping lid of petri dish over it
- Use of alcohol or other cleaners
Vocabulary
- Cell culture- process of growing cells in a laboratory
- Agar- solid media
- Broth cultures- liquid media (better access to nutrients)
- Simple media- has only a few nutrients (no special requirements)
- Selective media- has additives that allow only certain cells to grow
- Enriched media- additional growth factors (blood agar)
- Differential media- allows multiple microbes to grow but form individual colonies
- Koch’s postulates-four criteria that are used to to identify the causative agent of a particular disease
- Autoclave- sterilizes things using heat, pressure, & steam
- Lyophilization- Where the water is removed from the thing (ex. dried bacteria)
- Primary cells- Cells taken directly from animals
- Cell lines- Primary cells that are made immortal
- Contact inhibition- Where eukaryotic cells stop growing when they touch each other
- Fermenters- where large-scale cell cultures are grown in suspension broth cultures
- Microbiological tools- inoculating loops & needles
- Used to transfer cultures
- Serial dilution- diluting petri dish by a known factor (used to count numer of cells)
- Quadrant streak- Inoculating 4 quadrants on petri dish to isolate colonies
- Drag loop between each quadrant
- Used to isolate colonies
- T-streak- Same as quadrant streak but only 3 quadrants are used
- Colony forming units- number of cells
- Continuous streak- One zig-zag on petri dish
- Sterilization- to destroy all microbial life + endospores
- Disinfection- to destroy microbial life but NOT endospores
- Antisepsis- use of liquid antimicrobial chemical on skin or living tissue to destroy microorganisms
- Decontamination- process to make something safe to handle
- Cleaning- use of water and detergent to remove materials & reduce number of microorganisms
- Pluripotent stem cells- Can differentiate into any cell in the human body
- Adult stem cells- In tissue/organ and can specialize only to cells in that tissue/organ
