BME 201 Final
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I don't know how to study for this exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
What is cell therapy? How does it work?
Cell therapy encompasses the technologies that deal with replacing dysfunctional or damaged cells with fully functional and healthy new cells. Blood transfusion is an example in which blood from a healthy donor of the same blood type as the patient (healthy & functional blood cells) are introduced into the donor.
What are the advantages of peripheral blood stem cell transplantation as compared to bone marrow stem cell transplantation?
Peripheral blood stem cell sourcing is less painful (no giant needles stuck into your bone)
Faster recovery time for hematopoietic cells and the immune system (allogenic → from member of the same species)
Faster recovery time for blood count (autologous → self)
Some medical conditions prevent people from receiving bone marrow stem cell transplants but allow peripheral blood stem cell transplants
(T/F) Bone marrow stem cells can be collected from the peripheral blood stream.
True, bone marrow stem cells can be collected by chemically-induced migration of stem cells into the blood and then collection from the blood.
(T/F) Stem cells are type of cells that can self-renew and differentiate into different cell lineages. Progenitor cells can also differentiate into different cell lineages. Thus, they can self-renew as well.
False. Progenitor cells have a limited number of divisions, they can only self renew up to a certain point.
Primary Cells
cells taken directly from a culture
Cell Lines
cells taken from a culture of a culture and beyond - not directly from the tissue
Stem cells can divide into…
2 stem cells or 2 progenitors cell or 1 stem cell and 1 progenitor cell
Asymmetric Division
Each daughter cell has a different fate. Most common one stem cell one progenitor.
Environmental asymmetry
Daughter cell determined by the environment
Divisional asymmetry
Internal asymmetry, fate of daughter cells is determined at time of division
Red marrow
more prevalent in younger organisms
turns to yellow with age
stem cells for blood & platelets
Yellow marrow function
stores fat
Disadvantages of Peripheral blood stem cells
lower concentration (10 blood donations from 10 people for one marrow transplant vs. one donation for bone marrow stem cells)
use growth factors to combat this (expensive)
Fewer stem cells
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
produce blood
need VERY specific signal proteins
need stromal cells to live/not differentiate
Stem Cell Therapy Challenges
immune rejection & cancer challenges
Osteoclast
Large multinuclear cell that breaks down bone tissue and helps remodel and heal damage to bones
Osteoblast
Bone forming cells, synthesize and secrete new bone matrix
Osteogenic cells
Give rise to Osteoblast & Osteoclasts
Respond to trauma, reform & remodel bone
Bioreactor
3D environment for rapid and orderly development of functional 3D tissue structures
Bioreactor Functions
Make in vitro environment similar to the body
Establish proper and uniform concentrations of cells within a 3D scaffold
Control culture conditions (temp, pH, osmolality, O2, nutrients, metabolites, growth factors)
Provide physiologically relevant physical signals (intersitial flow, stress, pressure, compression)
Formula for cell differentiation
(change in cell population over time) + (rate of cell differentiation)*(change in population from differentiation state) = (# of cells)*[rate of cell proliferation - rate of cell death]
![<p>(change in cell population over time) + (rate of cell differentiation)*(change in population from differentiation state) = (# of cells)*[rate of cell proliferation - rate of cell death]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2bfa1894-59ba-4c1d-bdcb-1ff123a98acc.jpeg)
Formula for cell growth
specific growth rate = ln(2) / (time of doubling)
also applicable to decay rate and half life
(change in cell population over time) = (specific growth rate)*(number of cell in the population)
Half Life & Nuclei Amount Formulas
(Final Amount) / (Initial Amount) = e^[(-decay rate)*(time)] = decimal % remaining
Amount at time t = (initial amount)*e^[(decay rate)*t)]
Concentration Formulas
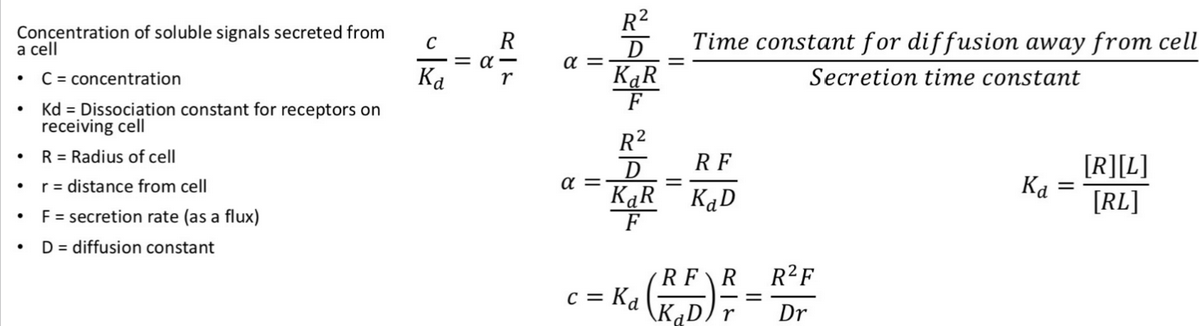
Higher dissociation constant → ________ concentration.
Higher
If the concentration is equal to the dissociation constant then ___% of the signals are bonded to their receptors.
50
Equilibrium for bound and unbound recepter-ligand formula
Dissociation constant for receiving receptors = ???????
[G]*[R] / [G:R]
Convection
Pressure differences → transport of molecules IN blood
Diffusion
concentration gradients → OUT blood into tissue
endothelial cell migration & proliferation
How does one prevent their implant from being destroyed by the immune system?
Make its pores too small for antigens and immune system components to go through but big enough for insulin and glucose
What does pore structure determine?
Size
Distribution
Continuity of individual pores
Biodegradable implants are open devices meaning…
All molecules and cell transport can go through them
Toxic biomaterial
Tissue around biomaterial dies
Nontoxic reabsorbable biomaterial
Biomaterial is eventually replaced by the surrounding tissues
Nontoxic inactive biomaterial
A thin non-adherent fibrous capsule forms around the biomaterial
Nontoxic bioactive biomaterial
An interfacial bond forms between the biomaterial and the tissue connecting them
Stress formula
stress = force / cross sectional area
Strain formula
Strain = [(deformed length - original length)/(original length)] x 100%
Brittle
high young’s modulus, completely breaks (bone)
Ductile
tougher, low yield strength (tendon)
Stress vs. Strain graph gives you the…
Ultimate tensile strength, yield strength/stress, and fracture/failure point
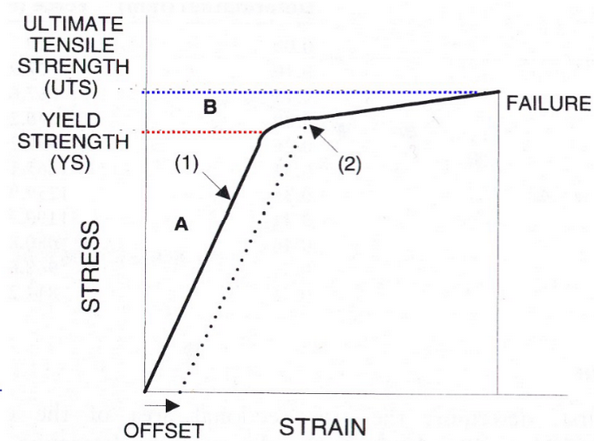
Tensile biomechanical test
Stretch until failure
Flexure biomechanical test
Bend until failure
Nanoindentation biomechanical test
Use an atomic force microscope to map nanoscale stiffness
Cyclic fatigue biomechanical test
Inflict cyclic stress below the ultimate tensile strength and measure endurance
Theranostic
combination of therapeutic and diagnostic functions
Challenges to Cell Therapy
Identifying usable cells for cell therapies
Cells must “learn” to function with bodily tissue
Immune rejection
Cancer
What components does an MRI use?
Water, radio waves, magnets
How does a T1 MRI work?
p+ atoms line up with a magnetic field and then fall back down to a normal energy state releasing a photon equivalent to the change in energy state which can be measured
How does a T2 MRI work?
Spin of H2O - differences in brightness, brighter
X-Rays
Good for bones, cannot do soft tissue, shadow images, fractures
Roentgen
Measure of radiation quantity and effect on surrounding objects (radioactive exposure)
Curie
disintegrations per unit time (radioactive activity)
How would you get consistent drug level release within the body?
pH sensitive biodegradable pill with a pressure expansion through chemical reaction to stick out a “needle” to stick into intestine lining
CAR-T
Modified T-cells for cancer recognition and treatment
How long does bone marrow take to regenerate?
2-3 days
Allogenic
From a donor to a patient → some immune rejection
Human Leukocyte Antigens (HLA)
immune system genetic markers, chromosome 6
Artificial Skin Grafts
Transplant dermal fibroblasts
Pancreatic Beta-Islet Cell Therapy
Langerhans transplant, isolate islets from donor, inject with long needle, requires immunosurpressants, needs hollow fiber bioreactor
Cartilage
Chordrocyte transplantation, no direct blood supply
Serum is made of…
blood plasma without clotting factors (fibronectin)
Skeletal muscle
Long strong fibers, precursor myoblast fusion
Heart/Cardiac muscle
shorter, stronger fibers
Metals as a biomaterial
high strength
fracture resistance, elastic
Electrically and thermally conductive
Corrodes
Stent
metal mesh scaffold used to expand arteries, inserted with a balloon, lasts for 2-6 years
Materials for hip replacement
Titanium or cobalt-chrome
Thermoplastic
Linear or branched polymer, PGLA, degreaded through hydrolysis, can heat/melt/mold/recycle
Thermosetting
Crosslinked polymers, heat degrades
Poly-A tribisn
Pressure → liquidity, bioink
ECM is secreted by the ______ which require a vascular system lined with ______ cells.
Fibroblasts, endothelial
Endothelial cells control…
Passage of materials and white blood cells in the vascular system
Mechanoreceptors
Endothelial have, allows for development of blood vessels in regards to stress
Angiogenesis
Formation of new capillaries that sprout from existing small vessels, VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor)
HIF-1
Hypoxia-inducible factor, low oxygen → VEGF
How does one suppress HLA genes?
Target Beta-2-microblobulin with silencing RNA using lentiviral vectors or CRISPR CAS-9
Islet cell transplant process
Collangenase enzymes into donor organ to isolate islets, purify, Ficoll to separate beta islets, xrays and ultrasounds to place catheter and insert the islet cells
Deep Cartilage Defects Treatment
Insert outside developed chondrocyte (produce cartilage)
Types of White Blood Cells
Neutrophils - phagocytose and destroy bacteria
Eosinophils - destroy large parasites and modulate allergic inflammatory response
Basophils - release histamine (allergic reaction)
Monocytes - become tissue macrophages, digest invading microorganism
Lymphocytes - B cells (make antibodies) T cells (kill infected cells)
Platelets
Cells circulating in blood that are part of primary hemostasis → blood clots
Albumin
made in liver, bonds small molecules for transport through blood, maintains osmotic pressure of blood
Globulins
Alpha - thyroxine and retinol
Beta - iron transporting (tranferrin)
Gamma - antibodies
Skeletal muscle cells
large, muscle fibers
Heart muscle cells
orderly actin and myosin, striated
Smooth muscle cells
no striation, propel food, raising hair
Myoepithelials
no striation, in epithelial, from ectoderm, expel shit from glands, eye’s iris muscle
Osteoporosis
Rate of bone absorption > rate of bone formation
Osteocytes
have secreted bone tissue surrounding, regulate calcium
Bone-lining cells
along surface of adult bones, regulate calcium and phosphate into and out of the bone matrix
Hyperplasia
Cell replication → increasing number of cells keeping the same size
Hypertrophy
DNA synthesis without cytokinesis
more volume, bigger cells, same number
Cyclin-dependent kinases
Drive the cell cycle
S phase
DNA synthesis, 10-12 hours, half of cell cycle time
M phase
mitosis, chromosomes segregate, less than an hour, nuclear and cell division
Cytokines
small growth factors, chemically stable with long half lives
Chemokines
Small cytokines, induce cell migration
Secretion?????????? (4 of ln 12)