Module 2 - Hardware (Part 1)
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What is File Transfer Protocol (FTP)?
Allows a client to upload and download files from a network server. It is often used to upload files to websites.
What are FTP port 21/TCP and port 20/TCP used for respectively?
After the Control Connection on Port 21 is established the server can then initiate Port 20 for Data Connection. The data connection port is used for sending and receiving file data.
What is Telnet?
Used to make an unsecure connection to the command-line interface of a server. It is both a protocol and a terminal emulation software tool that transmits shell commands and output between a client and the remote host.
What is Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)?
Transfer email messages across a network. It specifies how email is delivered from one mail domain to another. The SMTP server of the sender discovers the IP address of the recipient SMTP server by using the domain name part of the recipient's email address.
The SMTP servers for the domain are ___________________.
Registered in DNS using Mail Exchange (MX) and host (A/AAAA) records.
What is port 587/TCP used by?
Used by mail clients—message submission agents (MSAs)—to submit messages for delivery by an SMTP server.
What is Domain Name System (DNS)?
It facilitates the identification of hosts by name alongside IP addressing.
What is Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)?
Protocol used to automatically assign IP addressing information to hosts that have not been configured manually.
What is the difference between DHCP port 67/UDP and DHCP port 68/UDP?
Port 67/UDP is the DHCP SERVER, it supplies an IP address configuration to clients. Port 68/UDP is the DHCP CLIENT, it requests a dynamic IP address configuration from a server.
What is HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)?
Application protocol used to provide web content to browsers.
What is Internet Mail Access Protocol (IMAP)?
It retrieves email messages from a server mailbox.
What is NetBIOS over TCP/IP?
It supports networking features of legacy Windows versions.
What is Post Office Protocol (POP)?
It supports networking features of legacy Windows versions.
What is Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)?
It queries information about network users and resources.
What does the S stand for in HTTPS, IMAPS, etc?
Secure.
What is the difference between POP and POP3?
POP3 is the newest version of POP and the secure version.
What is Server Message Block (SMB)?
It implements a Windows-compatible file and printer sharing services on a local network (also sometimes referred to as Common Internet File System [CIFS]).
What is Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)?
It makes a secure connection to the graphical desktop of a another person’s computer.
What is Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) used for?
Used when the application protocol cannot tolerate missing or damaged information. It does this by establishing a connection between the sender and recipient using a three-way handshake sequence of SYN, SYN/ACK, and ACK packets.
What are the steps of TCP’s three-way handshake?
1.) Assigns each packet a sequence number so that it can be tracked.
2.) Allows the receiver to acknowledge (ACK) that a packet has been received OR Allows the receiver to send a negative acknowledgement (NACK) to force retransmission of a missing or damaged packet.
3.) Allows the graceful termination of a session using a FIN handshake.
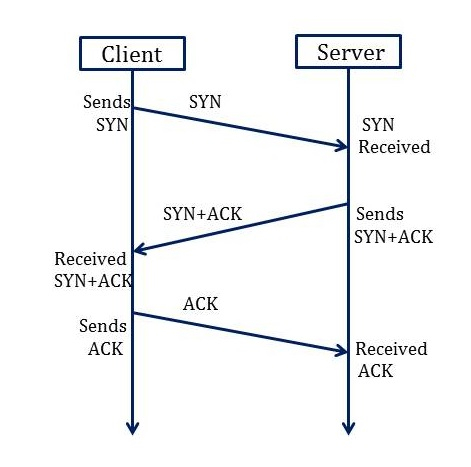
What is User Datagram Protocol (UDP) used for?
A connectionless, non-guaranteed method of communication with no sequencing or acknowledgments. Used for applications that do not require ACK and can tolerate missing or out-of-order packets. Is often used by applications that transfer time-sensitive data but do not require complete reliability, such as voice or video.
TCP vs UDP:
1.) TCP is more reliable but requires multiple header fields and can add 20 bytes or more to the size of each packet.
2.) UDP is less reliable but faster than TCP.
3.) UDP is typically used for stuff like streaming and video games, and TCP for emails and web browsing.
Every Wi-Fi device operates on a _____________________.
Specific radio frequency range within an overall frequency-band.
Each wireless frequency band is split into a series of smaller ranges referred to as a ________.
Channel
How do Frequency Channels work?
Act as lanes through the frequency band allowing wireless networks to operate on the same wireless band without interfering with each other.
The width or size of each channel is determined by ______________________.
The frequency band and the access point configuration.
All channels are the same width, but ____________________________.
Some wireless standards allow for channels to be bonded together creating a wider channel. The larger the channel width, the more data that can flow down it.
The three main frequency bands in use by wireless networks:
2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz
Pros and Cons of 2.4 GHz:
Pros: Better at propagating through solid surfaces, giving it the longest signal range.
Cons:
1.) Does not support a high number of individual channels.
2.) Is often congested with other Wi-Fi networks and even other types of wireless technology, such as Bluetooth.
3.) There is increased risk of interference, and the maximum achievable data rates are typically lower than with 5 GHz.
2.4 GHz Normal Indoor Range for Wi-Fi:
45 m (150 feet)
The 2.4 GHz band is subdivided into ____________________________.
Up to 14 channels, spaced at 5 MHz intervals from 2,412 MHz up to 2,484 MHz.
Pros and Cons of 5 GHz:
Pros: The band supports more individual channels and suffers less from congestion and interference, meaning it supports higher data rates at shorter ranges.
Cons: Less effective at penetrating solid surfaces, thus it does not support the maximum ranges achieved with 2.4 GHz standards.
5 GHz Normal Indoor Range for Wi-Fi:
30 m (100 feet)
The 5 GHz band is subdivided into __________________________.
23 non-overlapping channels, each of which is 20 MHz wide.
Clients identify an infrastructure WLAN through ____________________________.
The network name or Service Set IDentifier (SSID) configured on the access point.
How many bytes in length can an SSID be? And what should it use for maximum compatibility?
An SSID can be up to 32 bytes in length and, for maximum compatibility, should only use ASCII letters and digits plus the hyphen and underscore characters.
If you use the same SSID when configuring an access point, ___________________. If you configure separate names, _______________.
1.) The access point and client device will use a probe to select the band with the strongest signal.
2.) The user can choose which network and band to use.
For each frequency band, you also need to select the operation mode. This determines _____________________.
Compatibility with older standards and support for legacy client devices. Supporting older devices can reduce performance for all stations.
Multiple access points whose ranges overlap →
Should be configured to use non-overlapping channels to avoid interference.
An access point can be left to autoconfigure the best channel, _______________. You can also configure wide channels (bonding) for more bandwidth, _____________________.
1.) But this does not always work well.
2.) But this has the risk of increased interference if there are multiple nearby wireless networks.
Along with the Wi-Fi frequency band and channel settings, you should also ______________________.
Configure security parameters to control who is allowed to connect.
Every Wi-Fi device operates on __________________ and each wireless frequency band is __________________.
1.) A specific radio frequency range within an overall frequency-band.
2.) Split into a series of smaller ranges referred to as a channel.
Pros and Cons of 6 GHz:
Pros:
1.) Latest wireless band that can be used by wireless networks.
2.) Has a much faster than either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bands.
3.) It also has less congestion which means a more stable and reliable connection.
Cons:
1.) Less effective at penetrating solid surfaces than the 5 GHz band.
2.) Cannot achieve the longer ranges the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands can
6 GHz Normal Indoor Range for Wi-Fi:
15 m (50 feet)
What is Long Range Fixed Wireless?
It is wireless technology that can be used to configure a bridge between two networks. Can be a more cost-effective and practical solution than laying cable. However, regulation of the radio spectrum means that the transmitters required to cover long distances must be carefully configured.
What does Point-to-Point Line-of-Sight Fixed Wireless use?
Uses ground-based high-gain microwave antennas that must be precisely aligned with one another.
What does “high gain” mean for an antenna?
"High-gain" means that the antenna is strongly directional. They are pointed directly at the other and can transmit signals at ranges of up to about 30 miles. Are typically affixed to the top of tall buildings or mounted on tall poles to reduce the risk of obstructions.
What does Long-Range Fixed Wireless use in terms of licensing?
Can be implemented using licensed or unlicensed frequency spectrum.
Licensed (in reference to bands and networks) means that the ________________.
Network operator purchases the exclusive right to use a frequency band within a given geographical area from the regulator.
Who is the US Regulator wherein if any interference sources are discovered, gives the network operator the legal right to get them shut down?
Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
Unlicensed Spectrum (in reference to bands and networks) means that the ________________.
Operator uses a public frequency band, such as 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, and 5 GHz. Anyone can use these frequencies, meaning that interference is a risk. To minimize the potential for conflicts, power output is limited by regulatory requirements.
A wireless signal’s power has three main components:
1.)Transmit power is the basic strength of the radio, measured in dBm.
2.) Antenna Gain → The amount that a signal is boosted by directionality - focusing the signal in a single direction rather than spreading it over a wide area. Gain is measured in decibels per isotropic.
3.) Effective Isotropic Radiated Power(EIRP): The sum of transmit power and gain, expressed in dBm.
Lower frequencies that propagate farther have ______________.
Stricter power limits than higher frequencies. However, higher EIRPs are typically allowed for highly directional antennas. This allows point-to-point wireless antennas to work over longer ranges than Wi-Fi APs.
IEEE 802.11a “Unofficial Wi-Fi 2” Frequency Standard and Data Rate:
Uses the 5 GHz frequency only
Data Rate: 54 Mbps
IEEE 802.11b “Unofficial Wi-Fi 1” Frequency Standard and Data Rate:
Uses the 2.4 GHz frequency only
Data Rate: 11 Mbps
The signal encoding methods used by 802.11b are inferior to ______.
802.11a
IEEE 802.11g “Unofficial Wi-Fi 3” Frequency Standard and Data Rate:
Uses the 2.4 GHz frequency only
Data Rate: 54 Mbps
Made to have the data rates of 802.11a, but use the 2.4 GHz frequency of 802.11b.
Vendors could design 802.11g devices that could offer __________________.
Backward support for legacy 802.11b clients.
IEEE 802.11n “Wi-Fi 4” Frequency Standard and Data Rate (Both Min. and Max.):
Uses the both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies
Minimal Data Rate: 72 Mbps
Max Data Rate: 600 Mbps
802.11n introduced _____________.
Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO)
MULTIPLE INPUT MULTIPLE OUTPUT (MIMO):
“A wireless technology that multiplies the capacity of a radio link using multiple transmit and receive antennas” (Wikipedia). Essentially, more antennas on both the transmitting and receiving end = better performance for a Wi-Fi network.
IEEE 802.11ac “Wi-Fi 5” Frequency Standard and Maximum Throughput:
Uses the 5 GHz frequency only
Max throughput with all channels: 7 GB
802.11ac uses what kind of MIMO?
Multi-User MIMO (MU-MIMO)
MULTI-USER MIMO (MU-MIMO):
A set of multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) technologies for multipath wireless communication, in which multiple users or terminals, each radioing over one or more antennas, communicate with one another.
802.11ac uses ____ Channels.
8 Channels
In basic 802.11 operation modes, bandwidth is shared between all stations. An AP can __________________.
Communicate with only one station at a time; multiple station requests go into a queue. Wi-Fi 5 products partially address this problem using Multiuser MIMO.
In Wi-Fi 5, downlink MU-MIMO (DL MU-MIMO) ________________.
Allows the access point to use its multiple antennas to send data to up to four clients simultaneously.
IEEE 802.11ax “Wi-Fi 6” Frequency Standard and Maximum Throughput:
Uses both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies
Max throughput with all channels: 9.6 GB
802.11ax also uses MU-MIMO, however it uses both the ________________.
Uplink and downlink.
802.11ax introduces another technology to improve simultaneous connectivity called _________________.
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access
OFDMA can work alongside MU-MIMO to improve ______________________.
Client density - sustaining high data rates when more stations are connected to the same access point.
IEEE 802.11be “Wi-Fi 7” Frequency Standard and Data Rate:
Uses all three: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands
Data Rate: 46 Gbps
Wi-Fi 7 provides support for Multi-Link Operation (MLO) which _______________.
Allows devices to connect and send data over multiple bands (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz) or channels to reduce latency and improve throughput.
Another key feature of Wi-Fi 7 is the ability to use _____________.
Multi-Resource Units (MRUs).
When 802.11be uses MRUs, each channel in the 6 GHz range is ________________.
Broken down into smaller channels called MRUs which can all be different sizes based on the needs of the network. The access point dynamically allocates MRUs to different devices based on their data requirements.
Devices with higher bandwidth needs ____________, while devices with lower needs _______________.
1.) May receive more MRUs
2.) May receive fewer MRUs
Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID):
A means of identifying and tracking objects using specially encoded tags.
Unpowered Passive RFID Tag Range:
Only responds when scanned at close range (up to about 25 m).
Powered Active RFID Tag Range:
Range of 100 m.
RFID is also used to implement some types of ___________.
Access badges to operate electronic locks.