Transport in Flowering Plants
Xylem - water and animals
Phloem - sugars
Objectives
State the functions of the xylem and phloem
Identify the positions of the xylem and phloem tissues as seen in transverse section of roots, stems and leaves
Investigate the using a suitable stand the pathway of water in cut stem and identify the process involved in the uptake of water
Xylem
the more narrow the tube the faster it is
- Long narrow cylindrical vessels found in plants
- Water rises in these narrow tubes by capillarity
- Capillarity is the upward movement of water in any liquid in narrow spaces, passively(requires no energy)
- Water molecules have strong adhesive forces (stick to other surfaces) and strong cohesive forces (sticks to itself
- To transport Water and minerals through the plant

 xylem is hollow, dead tissue which allows water and minerals to move upwards
xylem is hollow, dead tissue which allows water and minerals to move upwards
Water enters by osmosis from root hairs and continues until it reaches the xylem vessels

(root hair cells are thin to maximise water input)
Steps
- Water enters root hair by osmosis
- The water molecules continues to move towards the xylem in the root by root pressure. The molecules push against and generate a force that pushes the molecules towards the xylem
- Once the water molecules reach the xylem they move upwards by capillary action
- As water is lost from the leaves from transpiration(ie from the stomata) a pulling force is generated and this is a called transpiration force
List of factors that affect transpiration
Temperature: As temperature increases, so does the rate of transpiration. This is because higher temperatures cause water molecules to move faster, which increases the rate of evaporation from the leaves.
Humidity: The amount of moisture in the air, or humidity, affects transpiration because it determines the concentration gradient between the plant and the air. When humidity is low, there is a greater concentration gradient, which causes water to evaporate more quickly from the leaves.
Wind: Wind can increase the rate of transpiration by removing the layer of humid air that surrounds the leaves. This allows for more water to evaporate from the leaves.
Light: Light can also affect transpiration because it stimulates the opening of stomata. When stomata are open, more water can escape from the leaves.
Phloem (Translocation)
The process by which sugars, amino acids and fats are transported from one location to another in phloem vessel
Leaves act as as sources(where sugars are made) and all other plant parts as sinks(where sugars are used)

- Some plants store food in sinks for
- Overcome drought conditions, adverse condition
- For reproduction
Phloem is composed of living cells arranged end to end. Unlike xylem, phloem vessels contain cytoplasm which goes through holes from one cell to the next.
Phloem transports sucrose and amino acids up and down the plant in a process called translocation. Generally, this occurs between where these substances are made (the sources) and where they are used or stored (the sinks).
This means, for example, that sucrose is transported in the following ways:
- From sources in the root to sinks in the leaves during springtime.
- From sources in the leaves to sinks in the root during the summer.
- Applied chemicals, such as pesticides, also move through the plant via translocation.
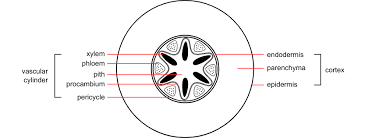
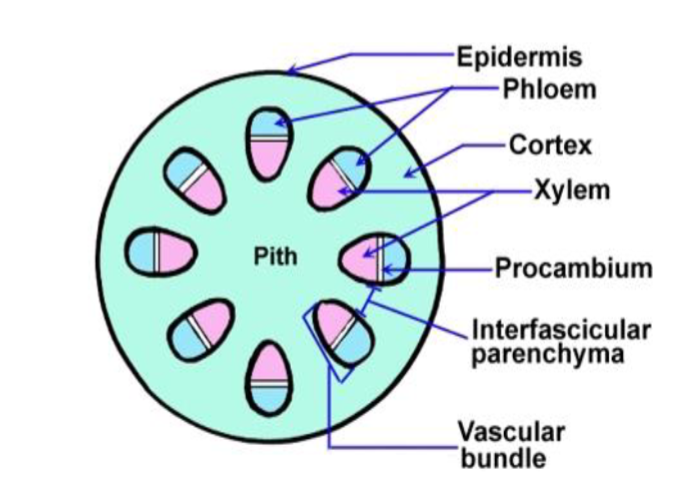
Vascular Bundles
Xylem and phloem tissues are found in groups called vascular bundles. The position of these bundles varies in different parts of the plant. In a leaf, for example, the phloem is usually found closer to the lower surface, while the xylem is typically located closer to the upper surface.
Root:
- Xylem vessels in the root are tough and strong, so the vascular bundles are positioned in the centre to withstand forces that could potentially uproot the plant.
Stem:
- The stem needs to withstand compression and bending forces caused by the weight of the plant and wind. The vascular bundles are arranged near the edge of the stem, with the phloem on the outside and the xylem on the inside.