Test Muscle Physiology
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:01 AM on 2/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1
New cards
What are the 7 functions of muscle
1. Body Movement
2. Maintain Posture
3. Respiration
4. Produce body heat
5. Communication
6. Construction of organs and vessels
7. Heart Beat
\
==not that important to remember==
2
New cards
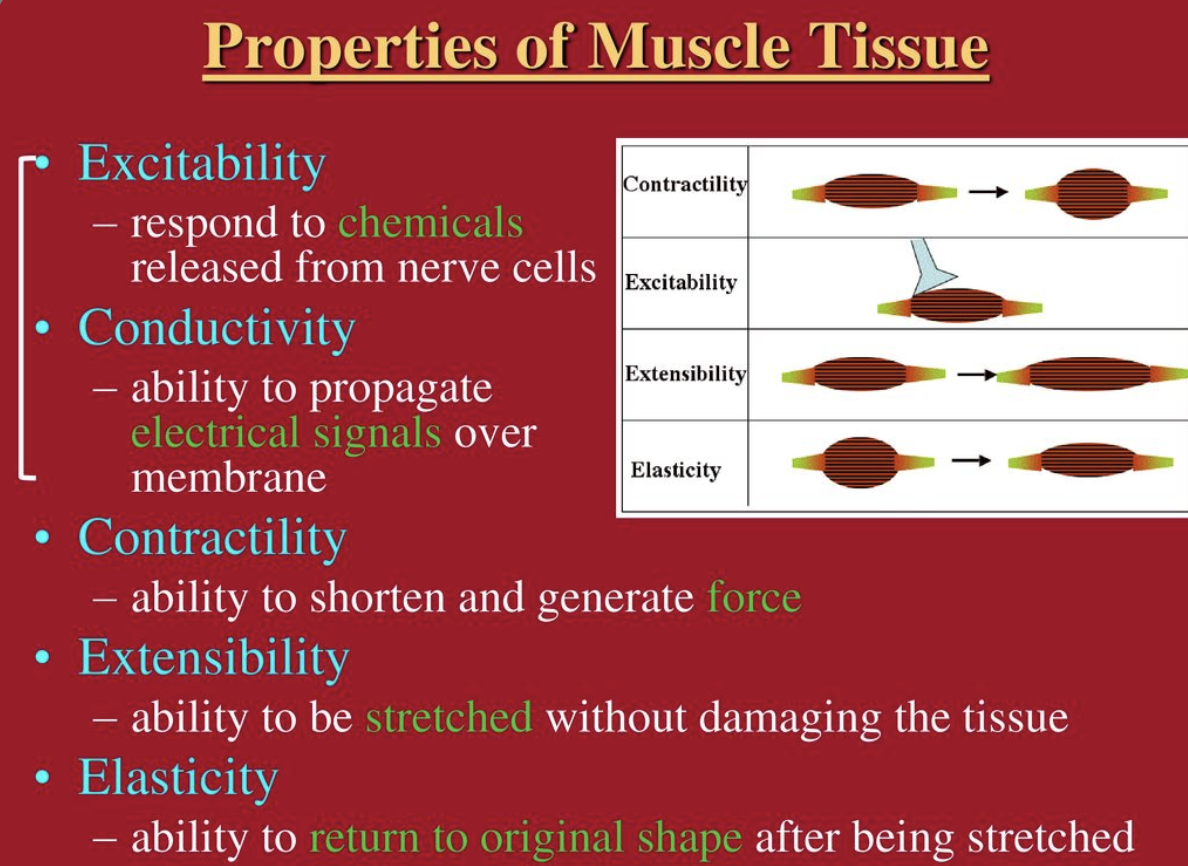
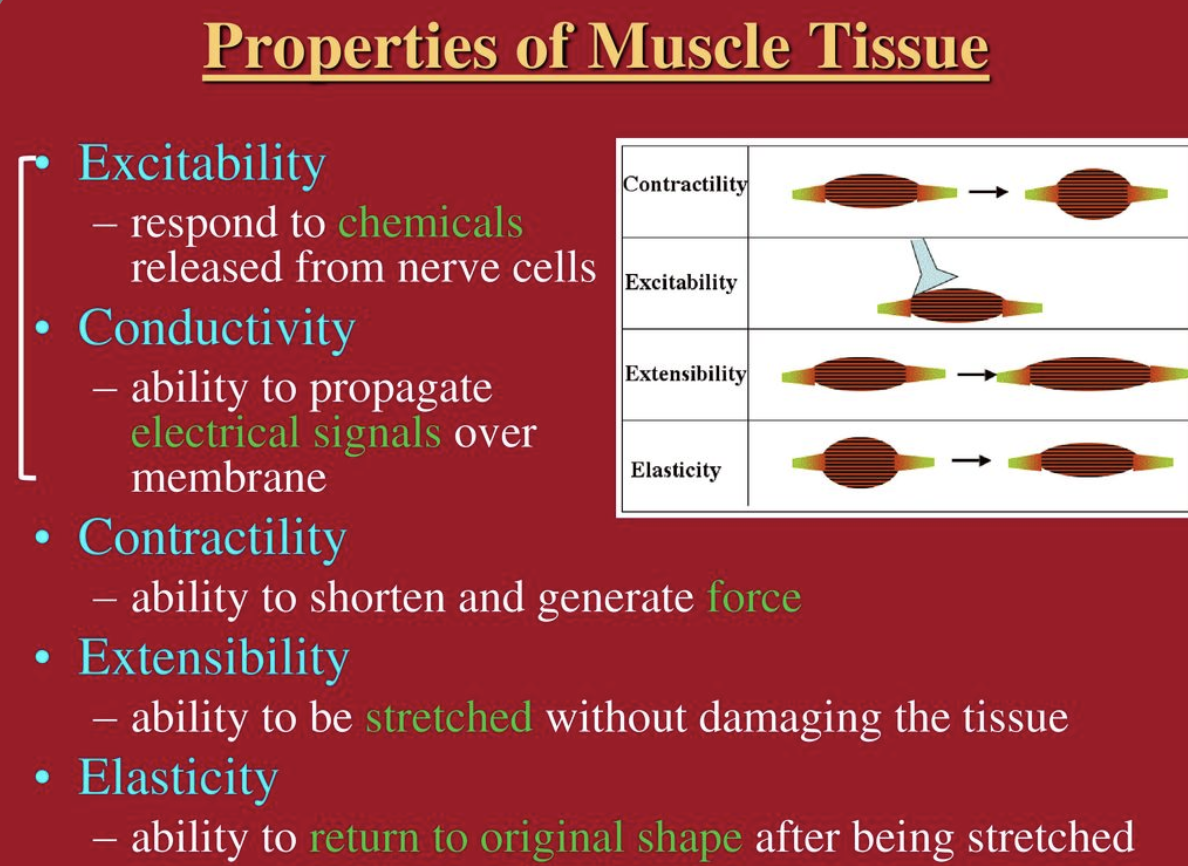
What are the 4 properties of muscles
Contractility, Excitability, Extensibility and Elasticity
\
==Remember using CEEE==
\
==Remember using CEEE==
3
New cards
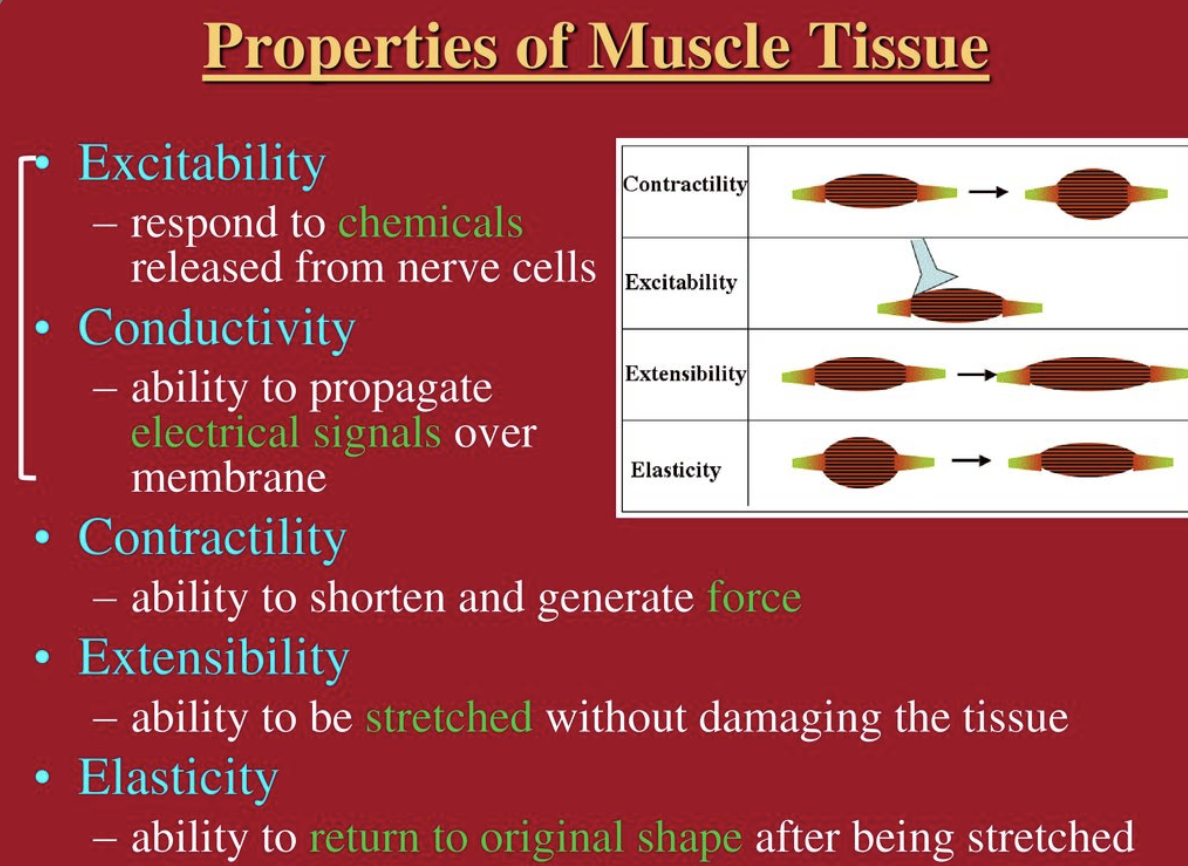
What is ==contractility==?
ability to shorten when an adequate stimulus is received
4
New cards
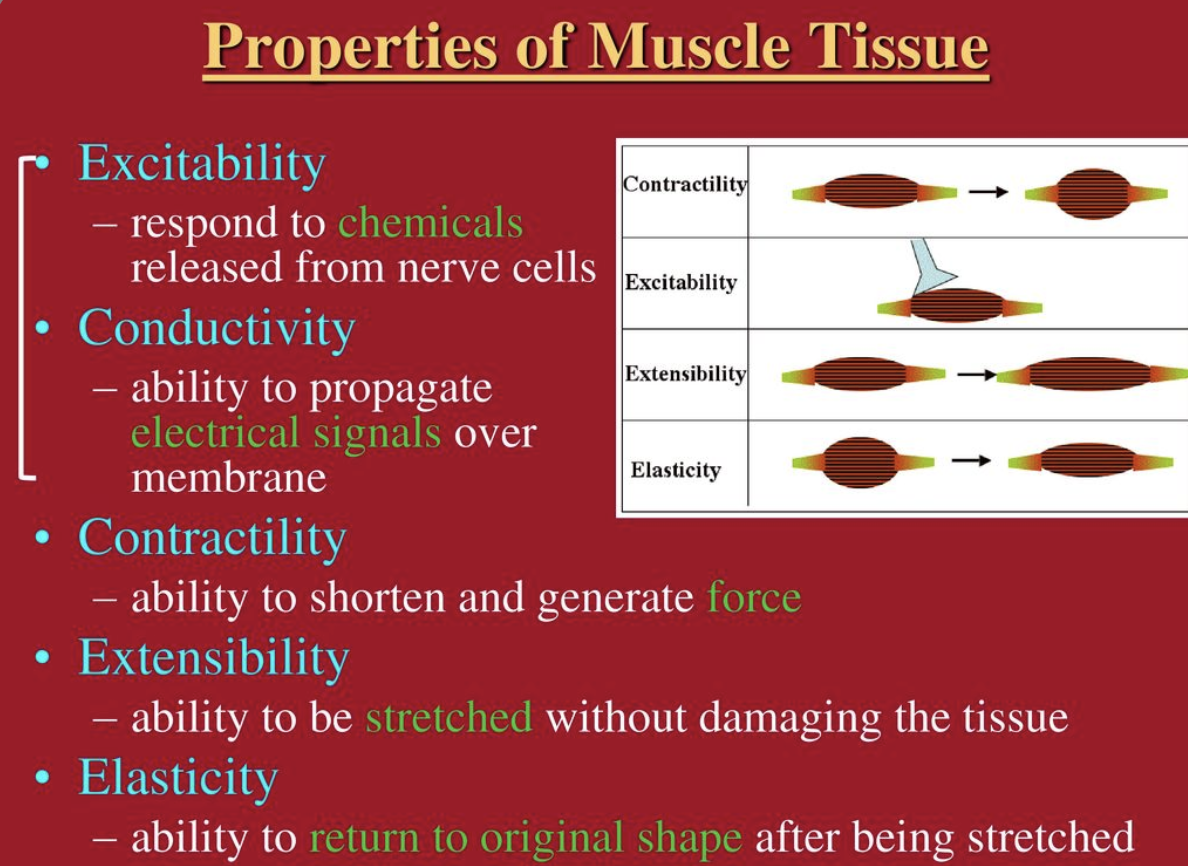
What is ==excitability==?
ability to receive and respond to a stimulus
5
New cards
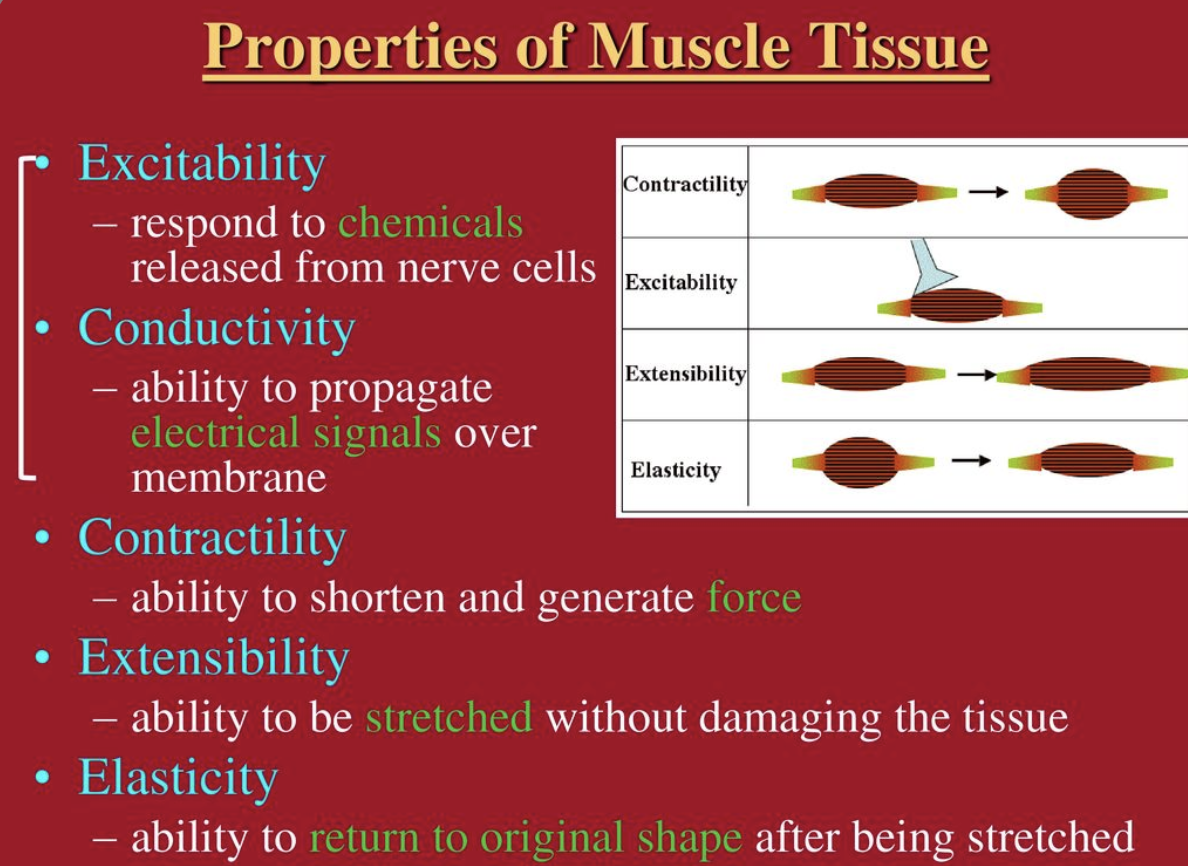
what is ==extensibility==?
ability to lengthen when an adequate stimulus is received
6
New cards
what is ==elasticity==?
ability to return to standard shape
7
New cards
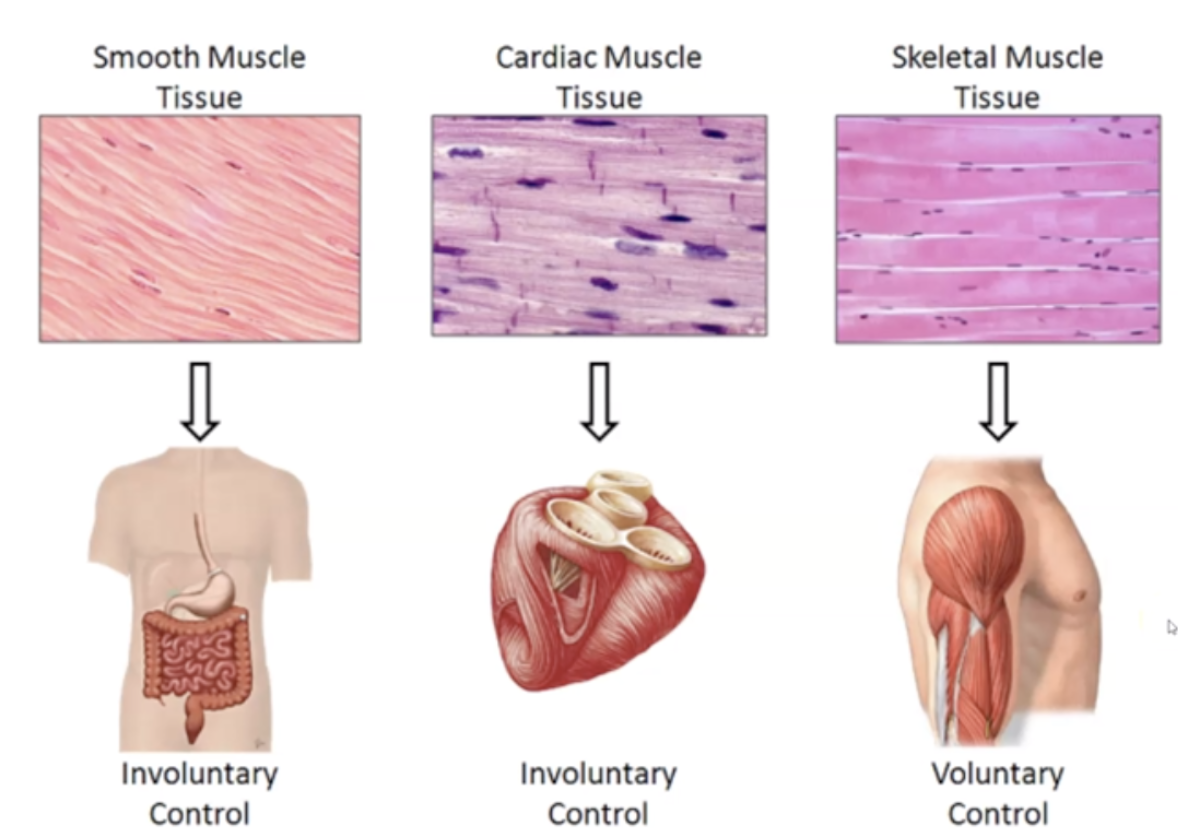
What are the 3 muscle types?
Skeletal Muscles, Cardiac muscles and Smooth muscles
8
New cards
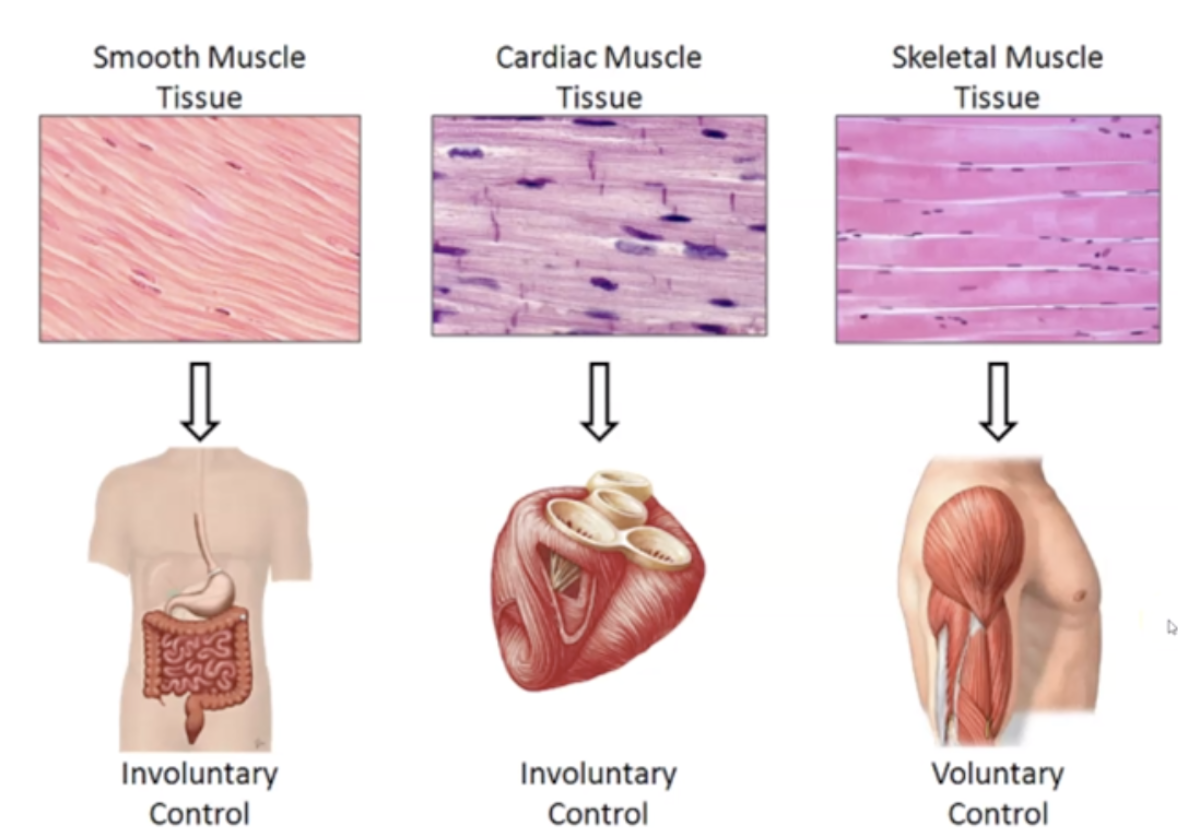
==Skeletal Muscles== location, function, nuclei type and appearance
1. Attached to bone
2. Body movement
3. Voluntary Control
4. Striated
5. Multinucleate
9
New cards
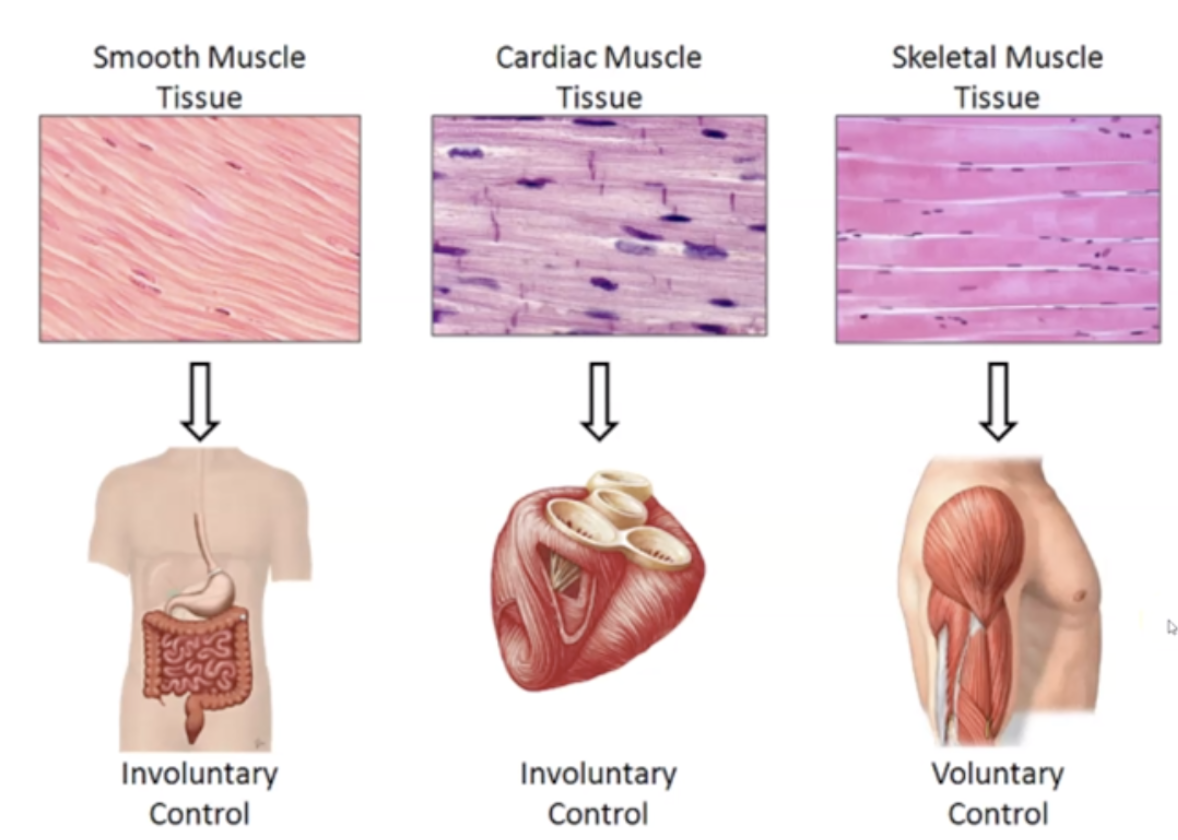
==Cardiac Muscle’s== location, function, nuclei type, and appearance
\
\
1. Found in Heart
2. Involuntary Contraction
3. Single Nuclei
4. Intercalated disks
5. Circulate blood
10
New cards
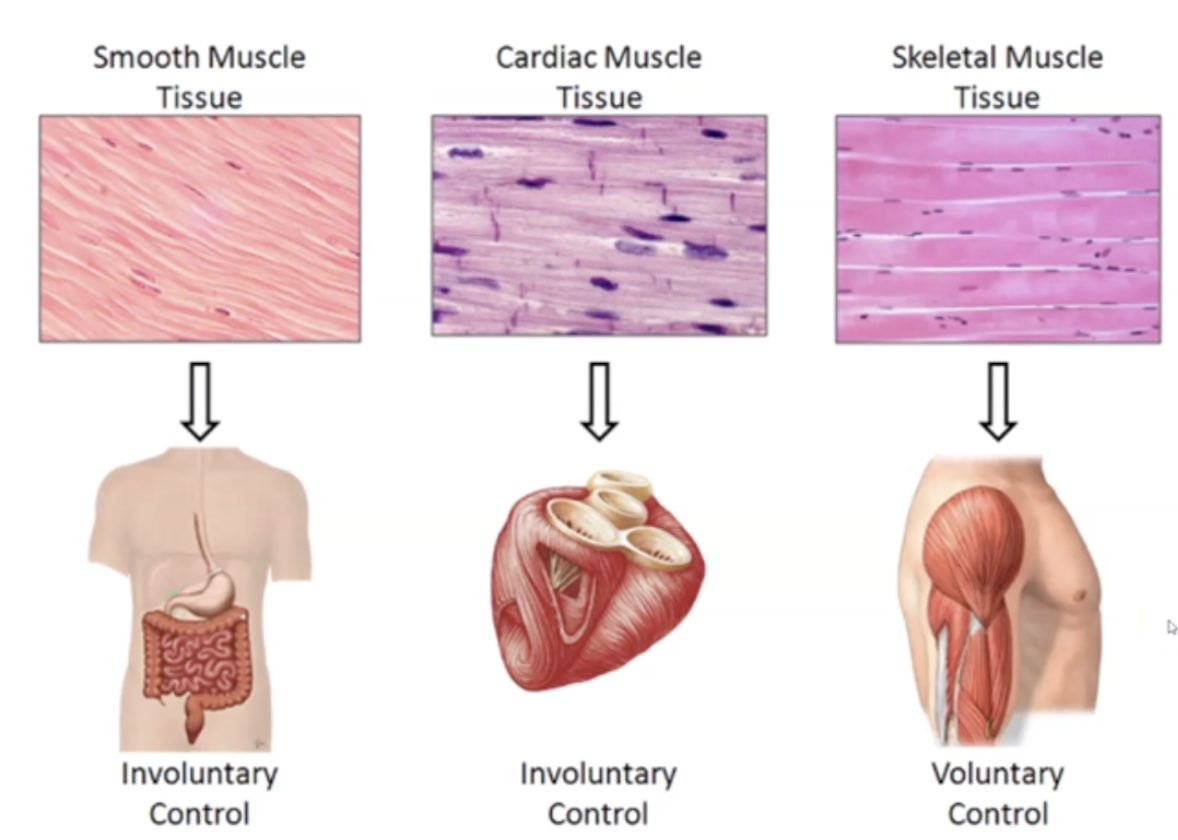
==Smooth Muscle’s== location, function, nuclei type, and appearance
1. Found in blood vessels, glands, etc
2. Spindle Shaped
3. Single Nuclei
4. Involuntary contraction
5. No striations
11
New cards
Muscles can only ___(push/pull) and donot ___(push/pull)
pull; push. Just remember Muscles cannot push thats it
12
New cards
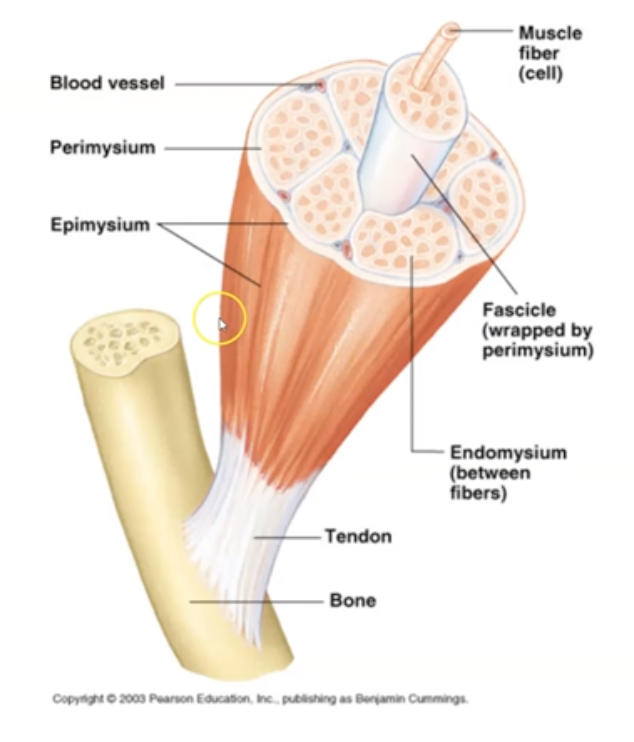
What are the 5 muscle components?
Muscle, Fascicle, Muscle Fiber, Myofibril and Myofilament
==Remember: (m, f, mf, m, mm)==
==Remember: (m, f, mf, m, mm)==
13
New cards
write the correct order from largest to smallest
muscle, fascicle, muscle fiber, myofibril, myofilament
(m, f , mf , m , m)
(m, f , mf , m , m)
14
New cards
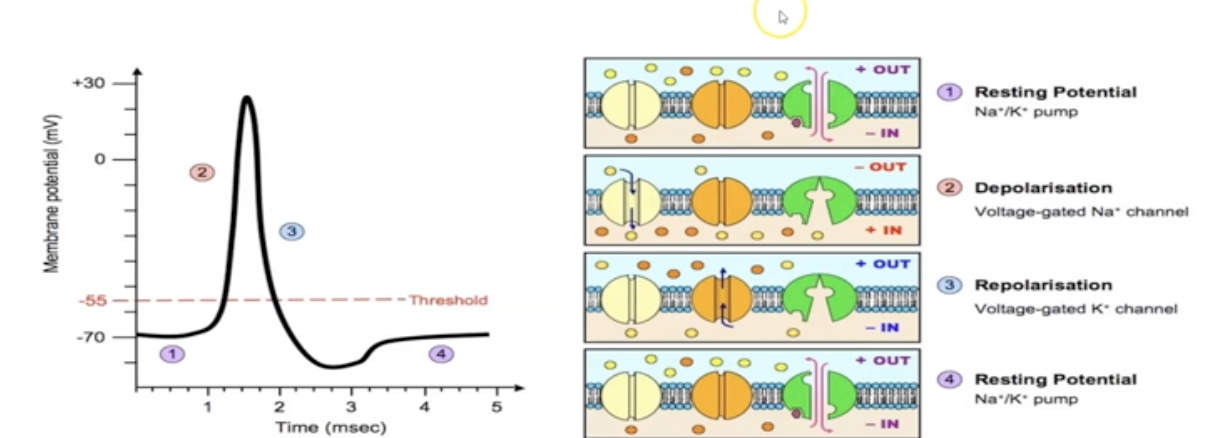
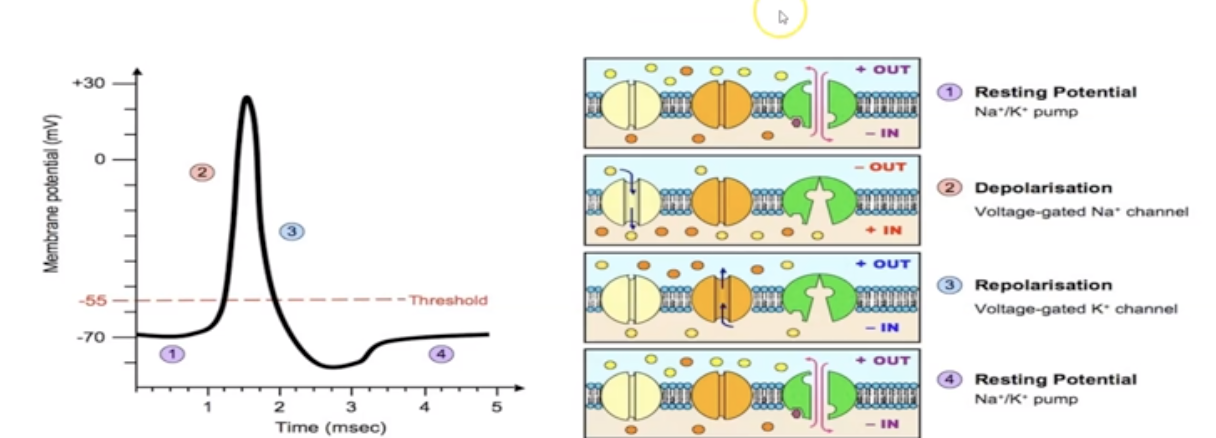
What is Action Potential?
rapid sequence of changes in the voltage across a membrane
15
New cards
What is resting state?
Cytosol (inside part of cell) has slightly negative charge.
Remember: Salty Banana (Na+ outside and K+ inside)
Remember: Salty Banana (Na+ outside and K+ inside)
16
New cards
What is depolarization?
Influx of Na+ ions into neuron
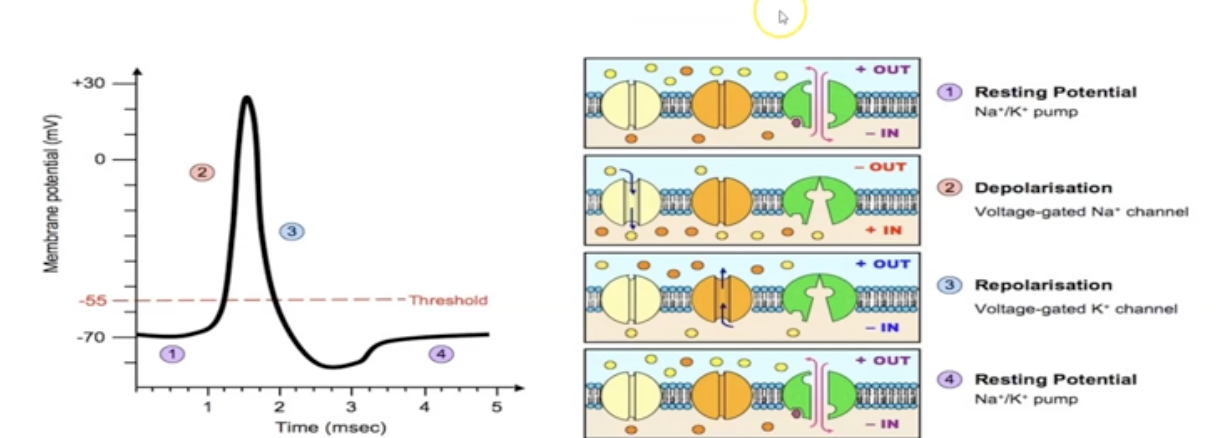
17
New cards
What is repolarization?
attempt to restore. (K+ moves out, trying to balance contents inside cell)
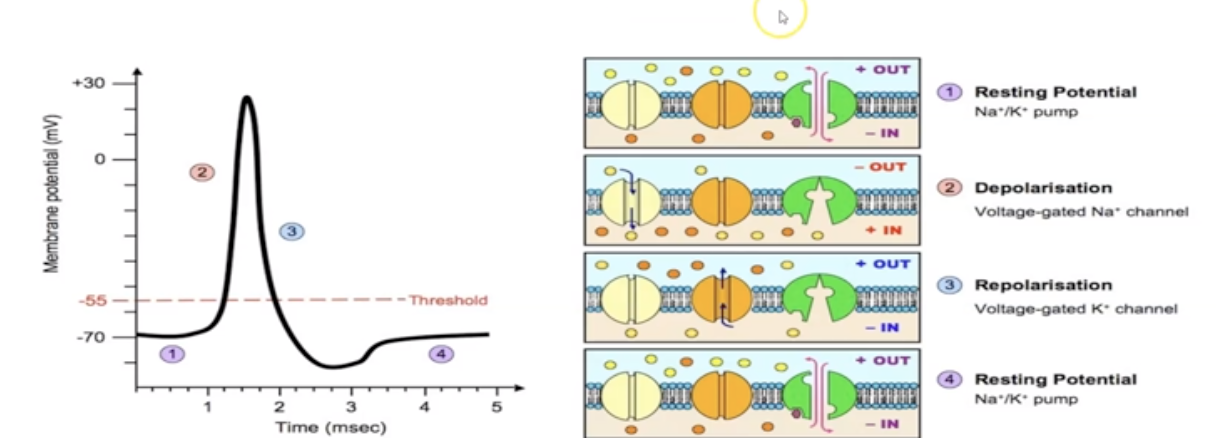
18
New cards
What is Na+/ K+ pump?
Transports Na+ and K+ ions. Requires energy
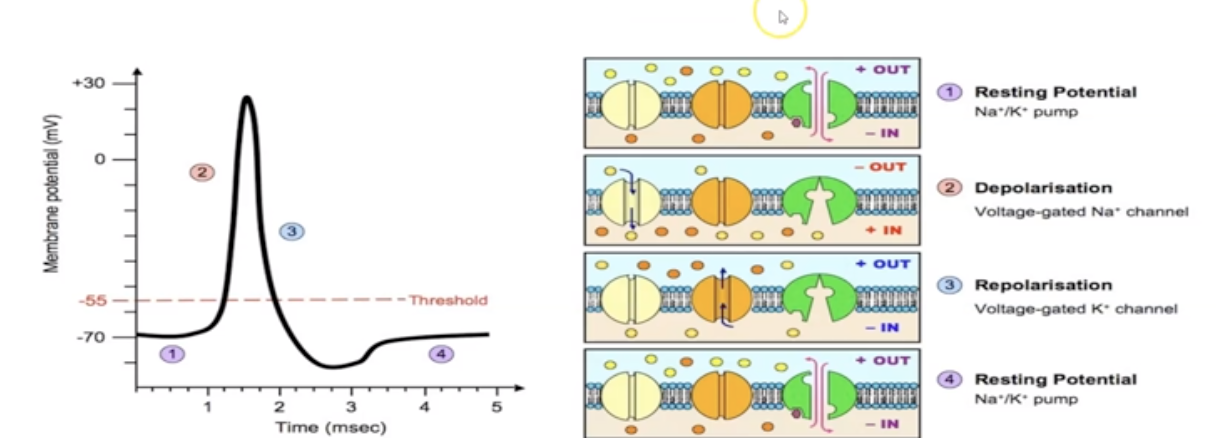
19
New cards
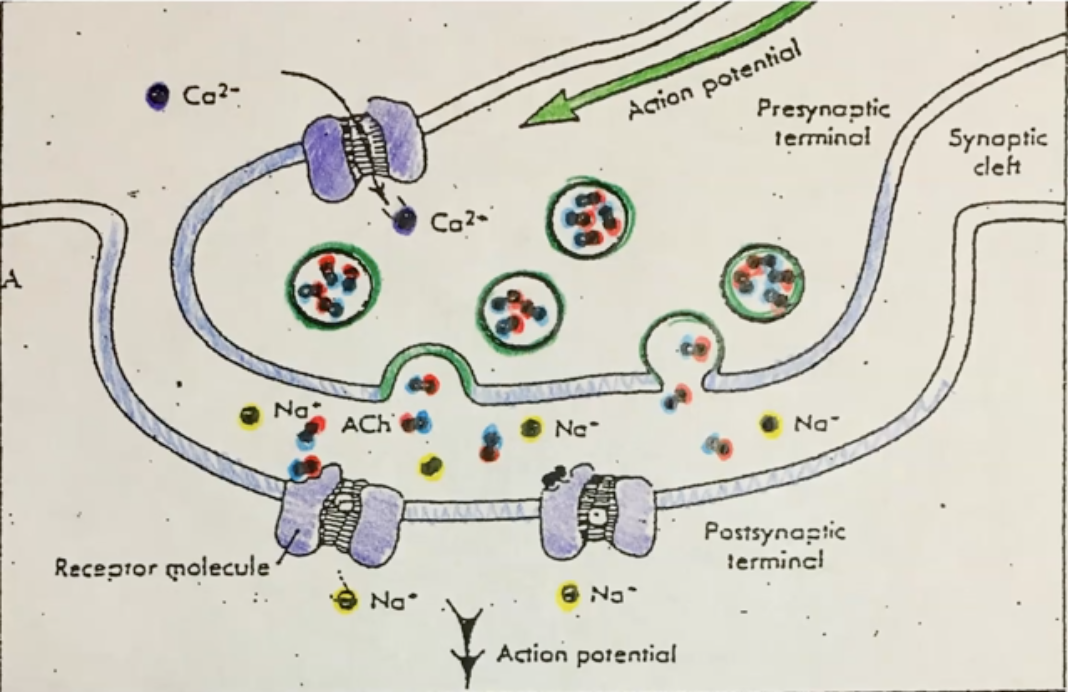
Explain how Ach gets into synaptic cleft in Neuromuscular Junction
1. Action potential is sent along a neuron to axon terminal
\
2. The AP causes Ca2+ channels to open and thus allowing calcium in
\
3. Ca2+ causes vesicles containing the neurotransmitter Ach to fuse with the membrane of axon terminal and release Ach into synaptic cleft
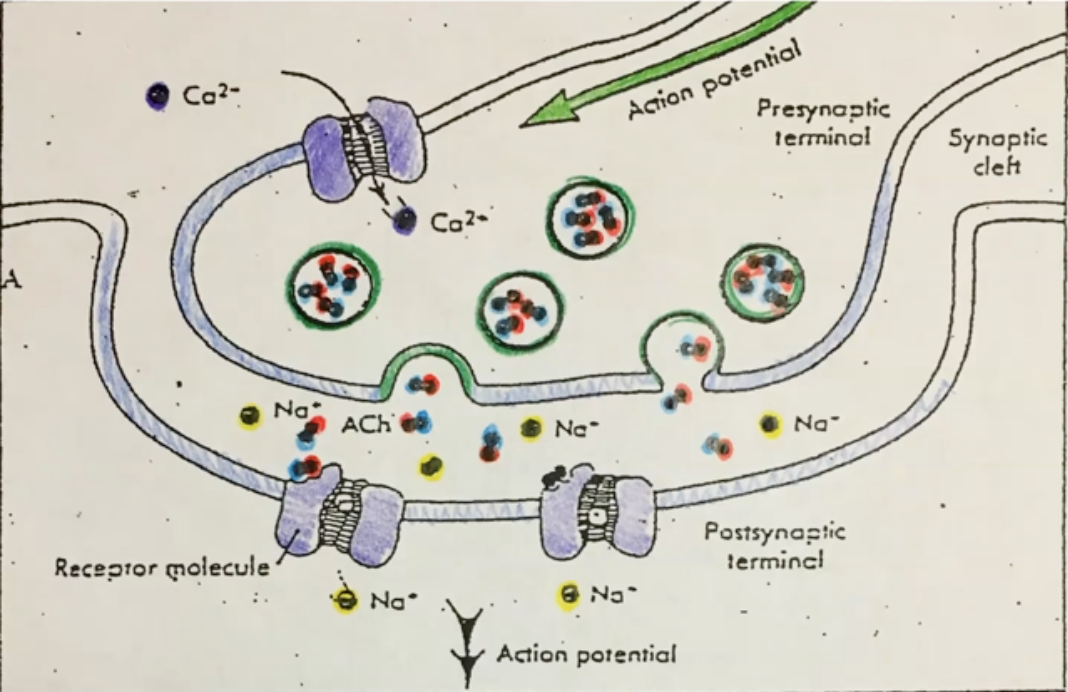
20
New cards
Explain what happens after Ach reaches synaptic cleft in Neuromuscular Junction
4. Ach drifts through the synaptic cleft and binds with Na+ channels cuasing channels to open and allow Na+ to flow into cell and continue action potential
21
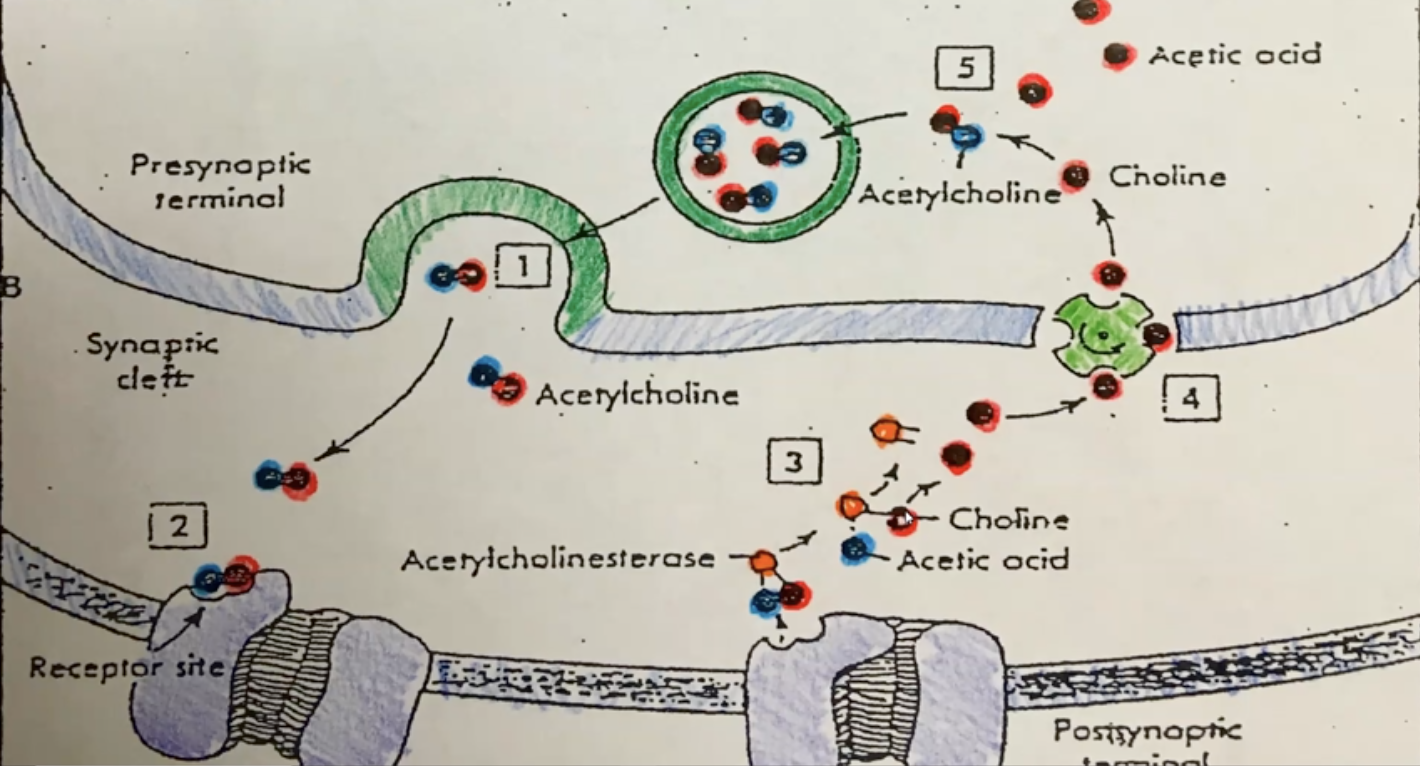
New cards
what does Achase does at Neuromuscular Junction
5. Once the Ap has continued the enzyme Achase will begin to breakdown excess Ach into components: acetic acid and choline
\
6. Acetic acid is waste while choline is moved back into axon terminal where it combines with new acetic acid forming Ach. This new Ach will get stored in vescile
22
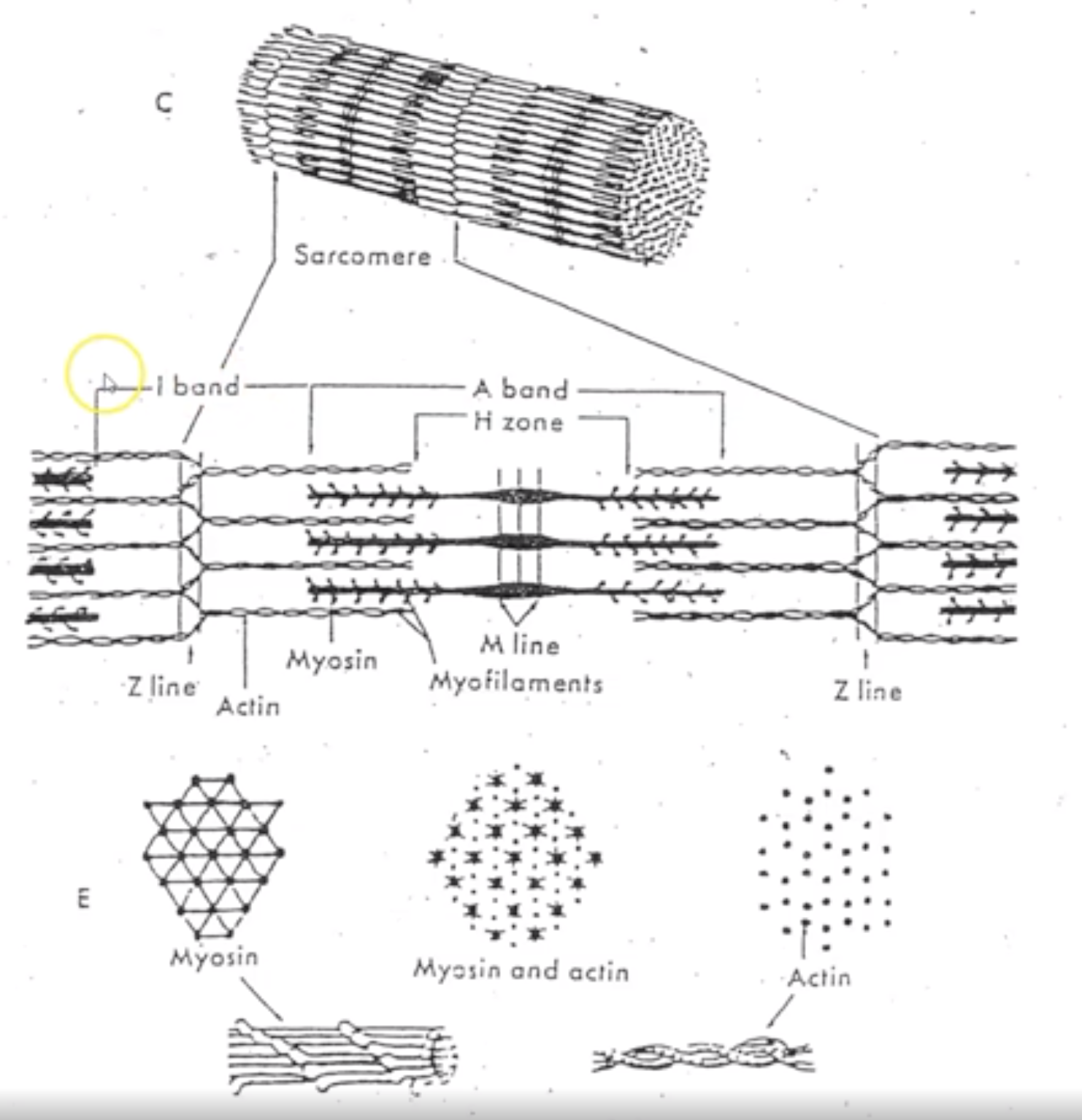
New cards
What is myofibrils composed of?
overlapping myofilaments called actin and myosin.
They slide over each other to contract the muscle fiber
They slide over each other to contract the muscle fiber
23
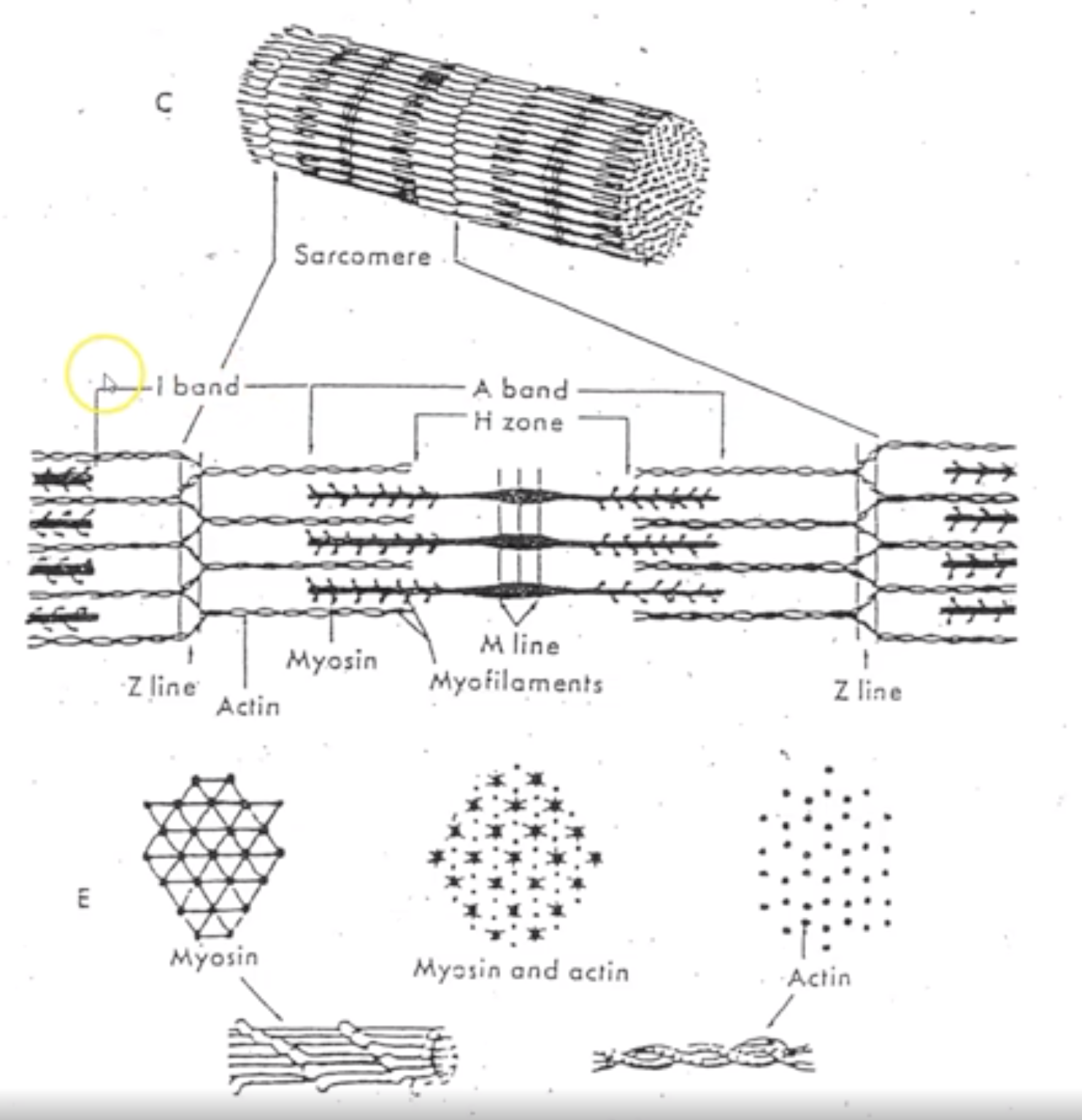
New cards
What does sliding filament theory state?
Actin and myosin pull the z-line closer the M-line, shortening the length of the sarcomere
24
New cards
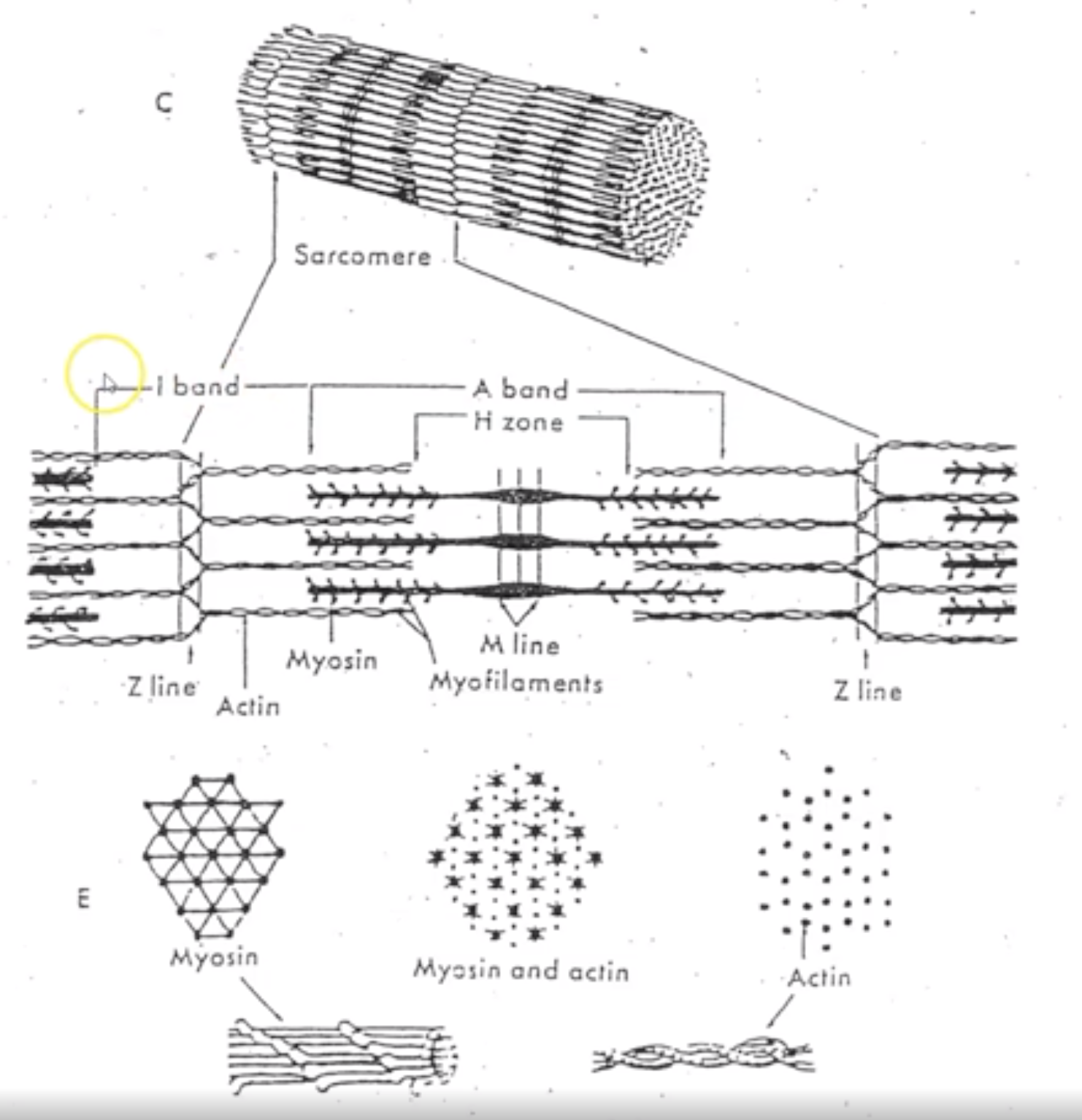
Explain Z-lines, I bands, Hzone and A bands?
Z-lines: ends of sarcomere
I bands: only contain thin filament (actin)
H zone: only thick filament (mysoin)
A band: center of sarcomere where think (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments overlap
I bands: only contain thin filament (actin)
H zone: only thick filament (mysoin)
A band: center of sarcomere where think (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments overlap
25
New cards
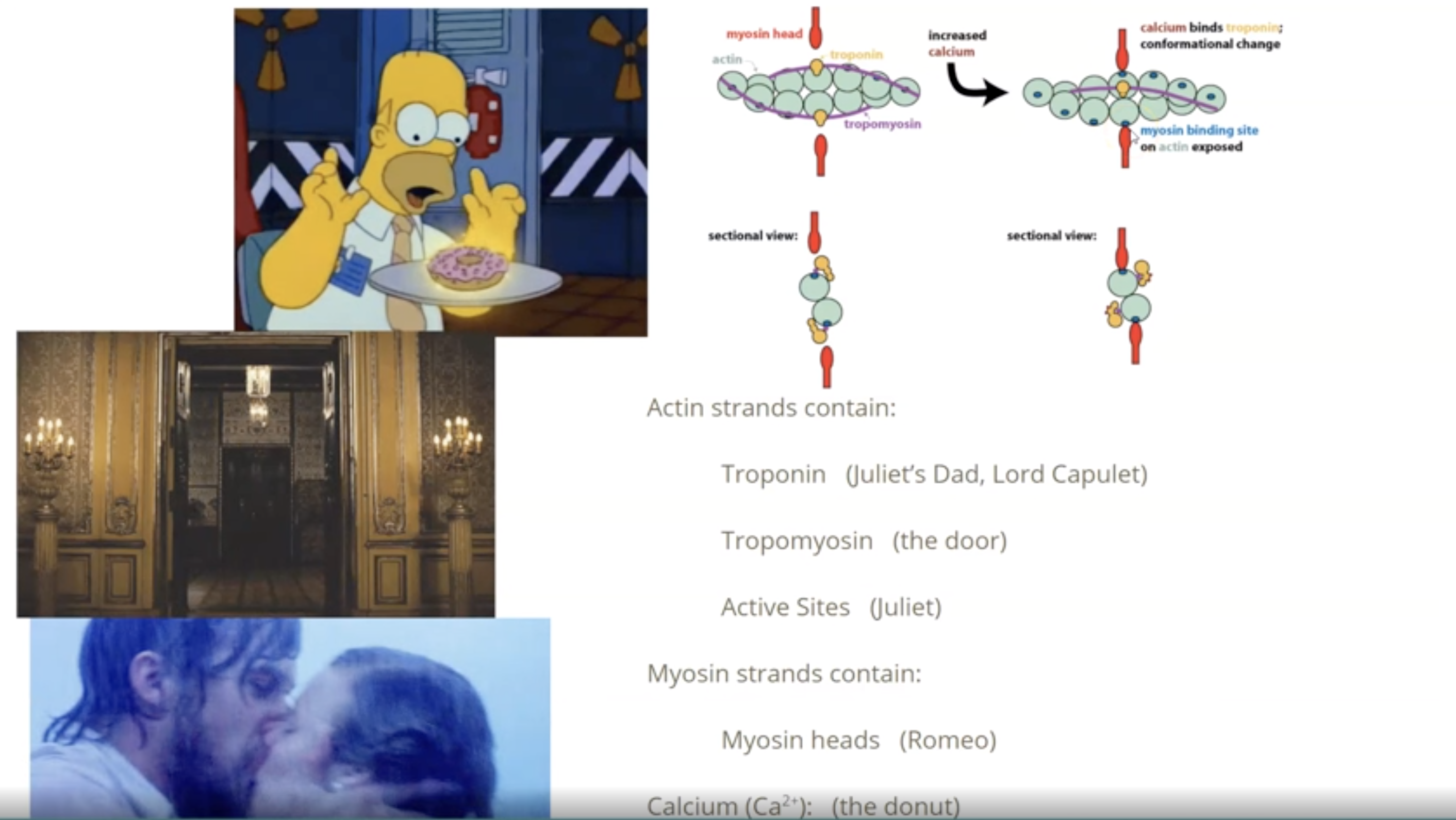
Analogy to remember Sliding filament theory
Actin strands contain:
Troponin (Juliet’s dad, Lord capulet)
Tropomyosin (the door)
Active sites (Juliet)
\
Myosin strands contain:
myosin heads (Romeo)
\
Cacium Ca2+ (the donut)
\
Romeo gives donut to the door and then door leaves, allowing Romeo to meet Juliet in Lord capulet’s castle
Troponin (Juliet’s dad, Lord capulet)
Tropomyosin (the door)
Active sites (Juliet)
\
Myosin strands contain:
myosin heads (Romeo)
\
Cacium Ca2+ (the donut)
\
Romeo gives donut to the door and then door leaves, allowing Romeo to meet Juliet in Lord capulet’s castle
26
New cards
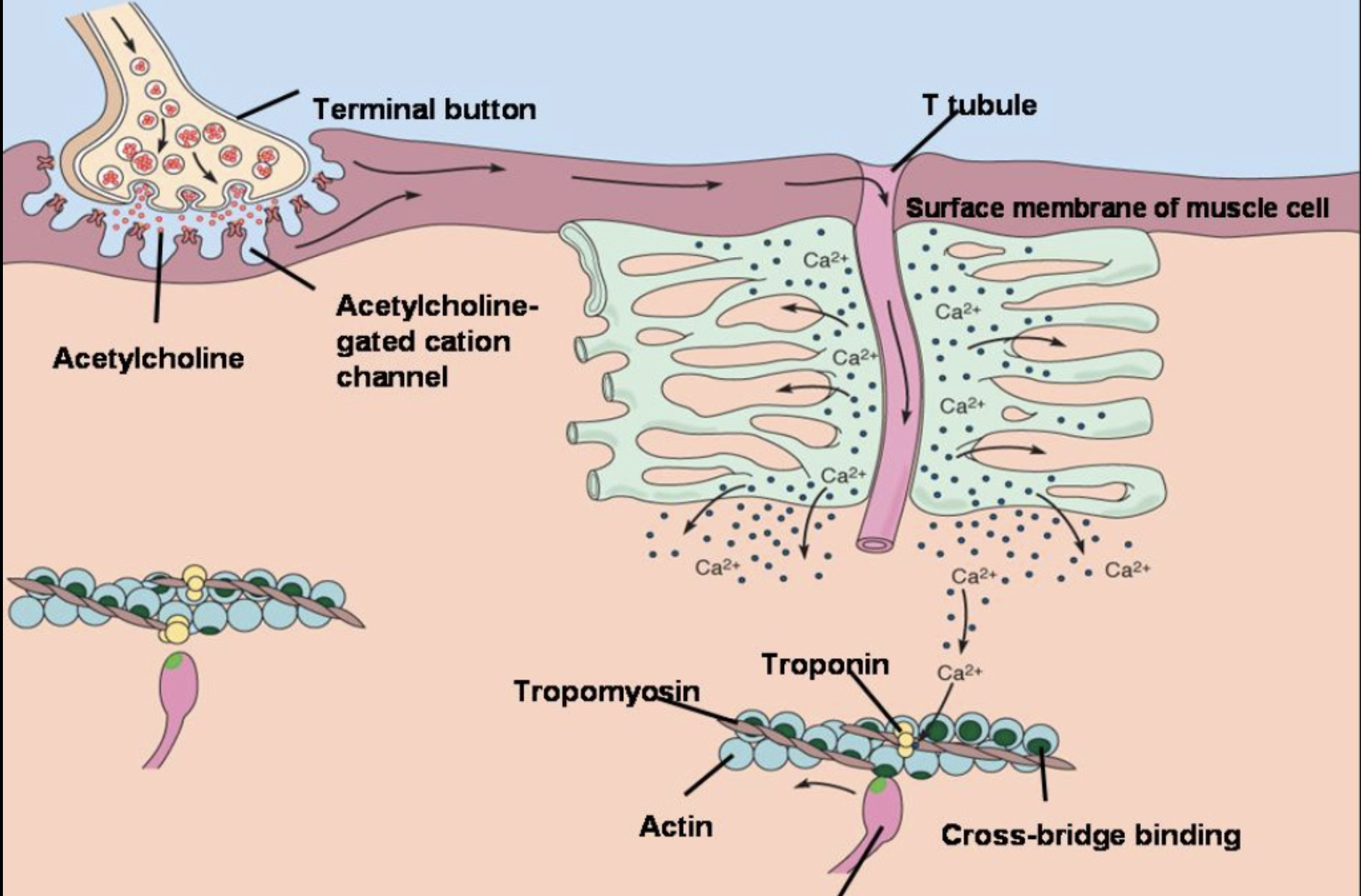
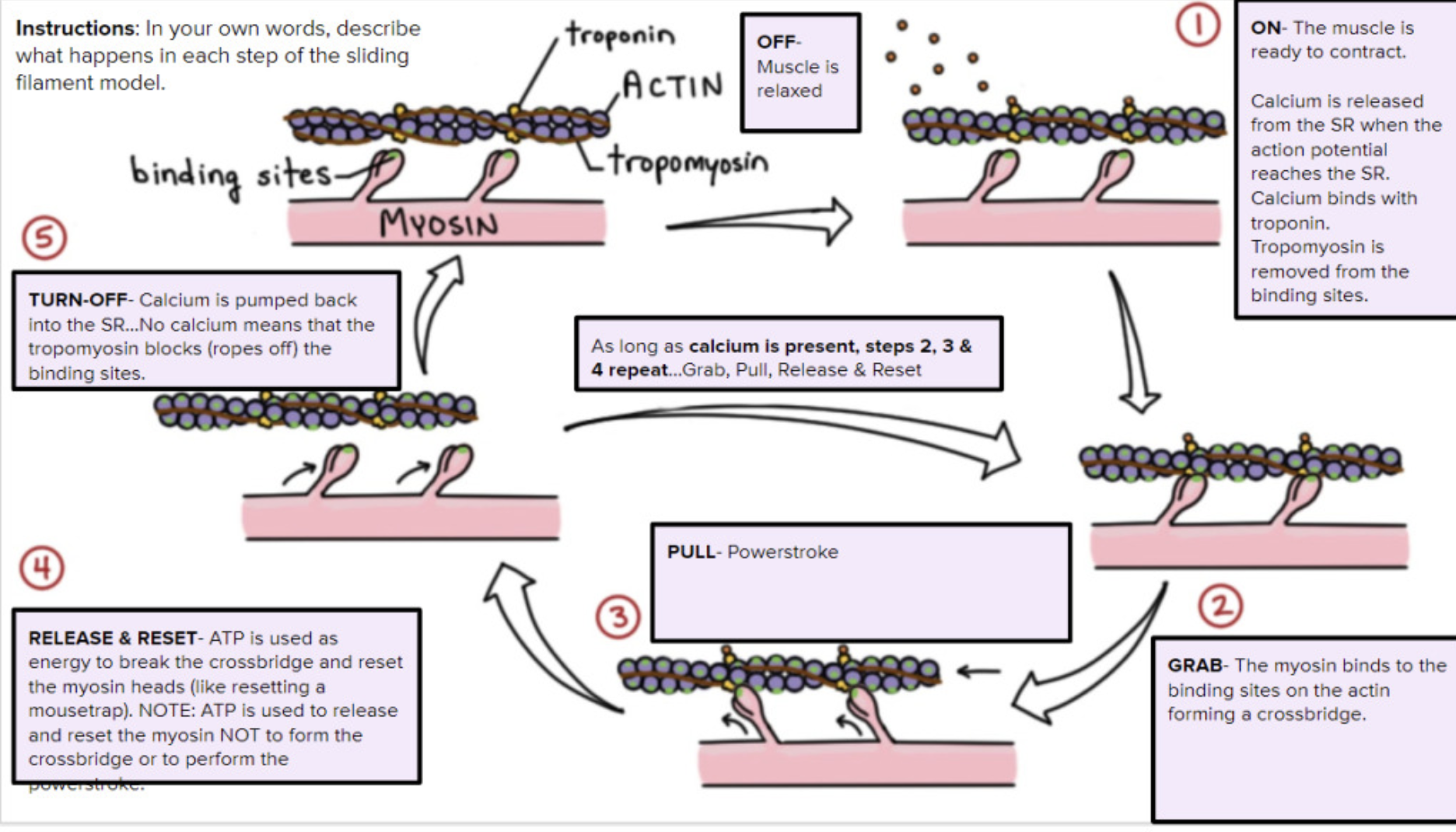
First 4 steps of Sliding Filament Theory (No need to memorize, just know Romeo’s Analogy)
1. Action potential along the sarcolemma travels through the T tubules causing the release of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum
\
2. Increase in calcium causes it to bind to troponin cuasing a conformational change (shape changes)
\
3. This change is shape causes tropomyosin to move away from the active sites on actin exposing them
\
4. The myosin head will bond with the active site on actin, forming a cross bridge and push the actin forward
\
27
New cards
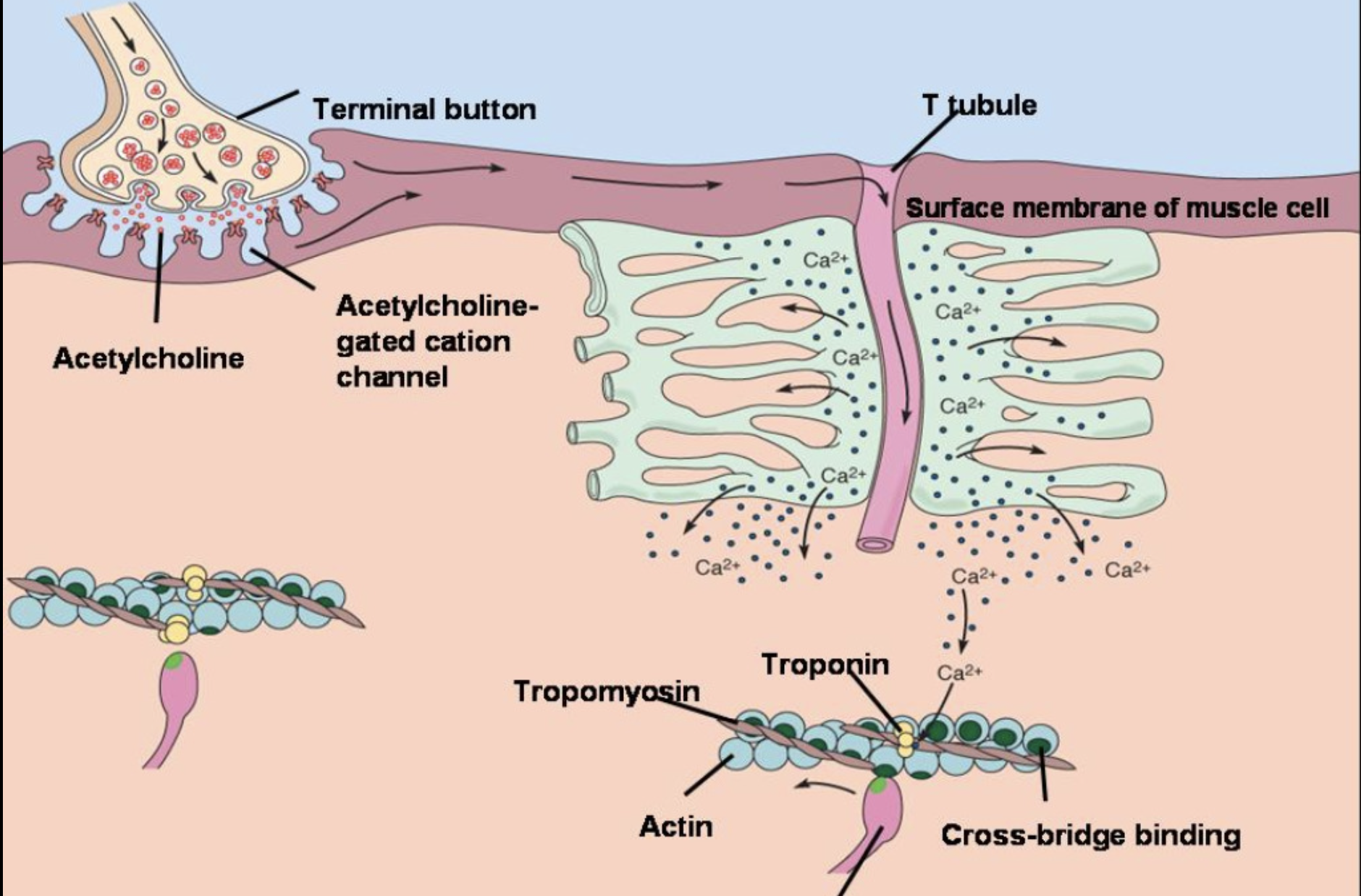
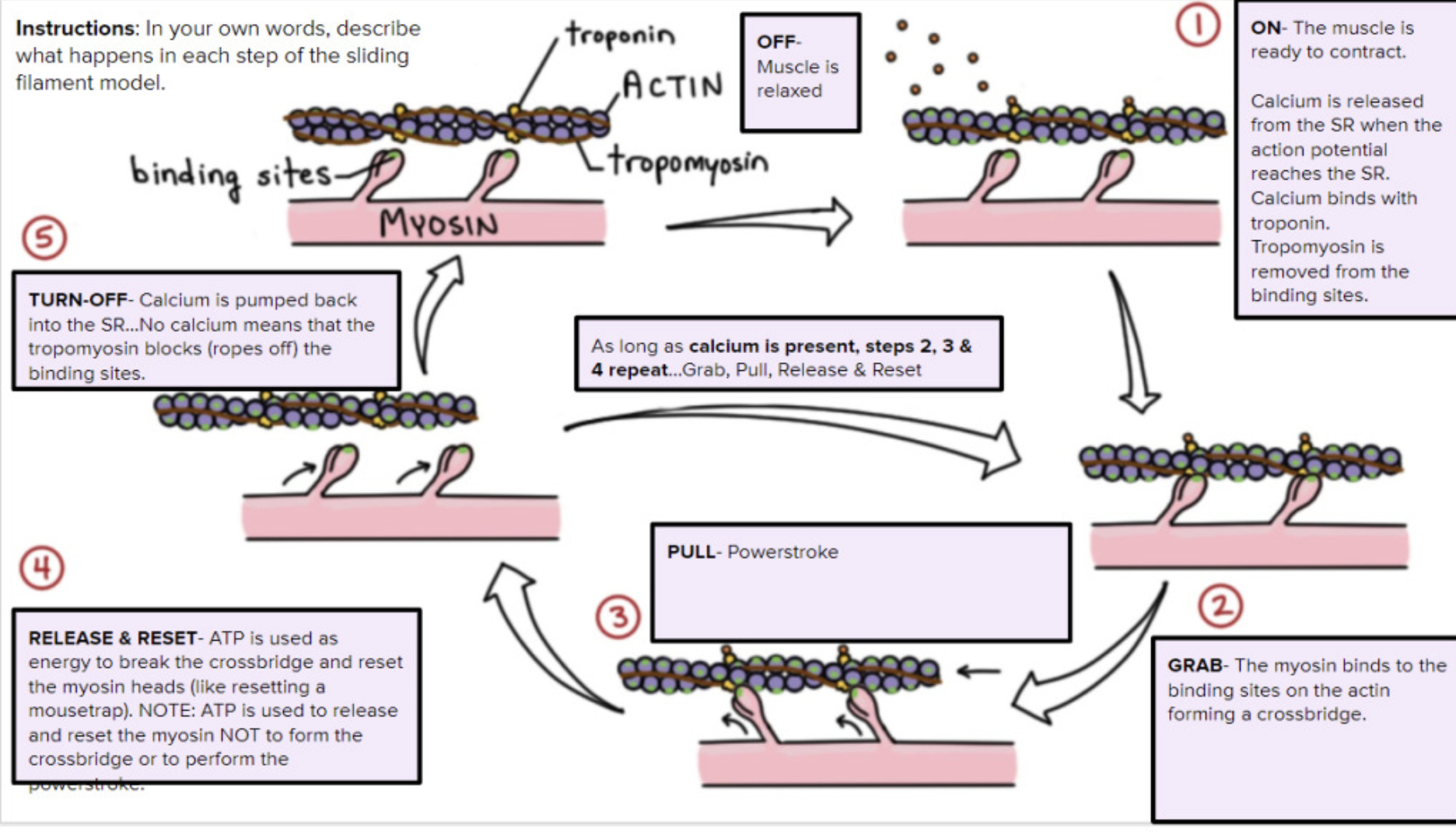
Last 8 steps of Sliding Filament Theory (No need to memorize, just know Romeo’s Analogy)
5. As ATP binds to myosin head, the head detaches from the actin
\
6. The myosin head splits the ATP into ADP+P becomes re-energized and reorients
\
7. Myosin head attaches to actin
\
8. Myosin head rotates to the center of the sarcomere and pulls/pushes the actin to the center
\
9. When the action potential ends, Ca2+ is reabsorbed via active transportation into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
\
10. As Ca2+ moves out of the sarcomere, it unbinds with troponin
\
11. Without Ca2+, troponin moves the tropomyosin back into active sites
\
12. Myosin moves back to starting position.
28
New cards
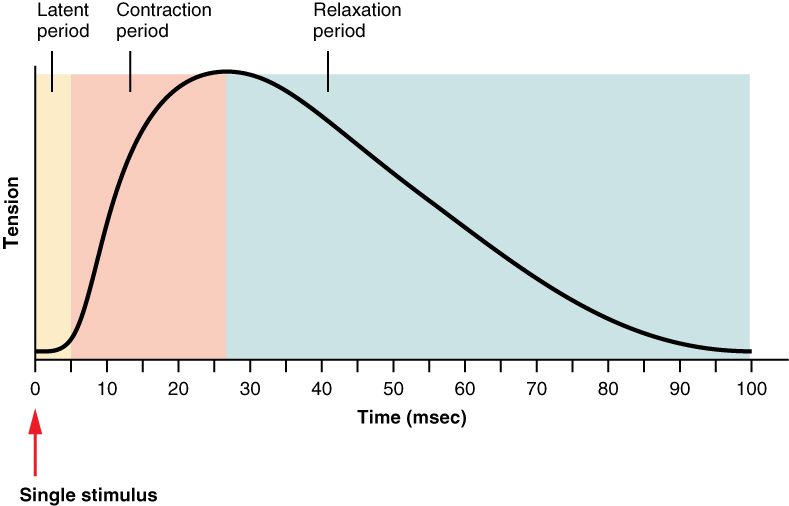
What is a muscle twitch?
a single contraction of a single muscle fiber in response to a single action potential. Can last 10 to 100ms
29
New cards
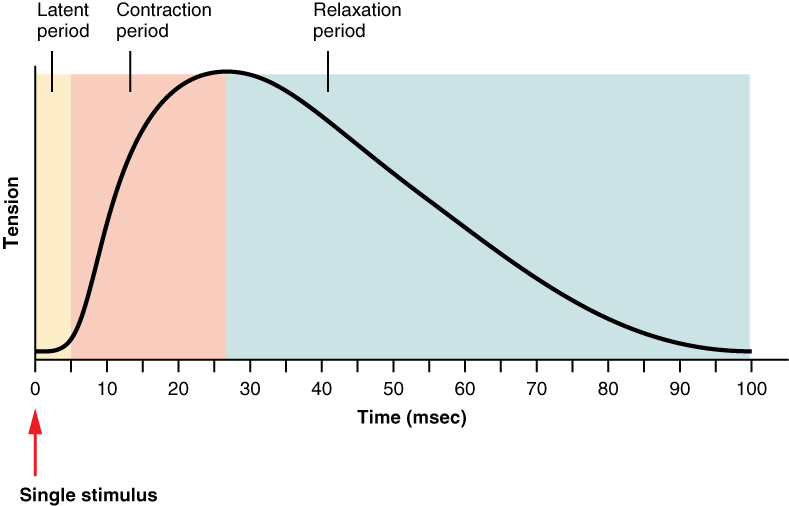
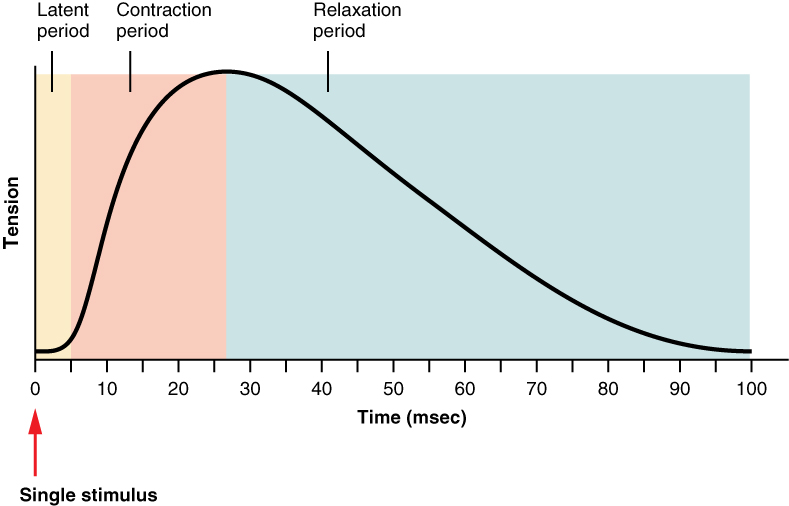
What are the three parts of muscle twitch?
1. Latent period (lag phase)
2. Contraction phase
3. Relaxation phase
30
New cards
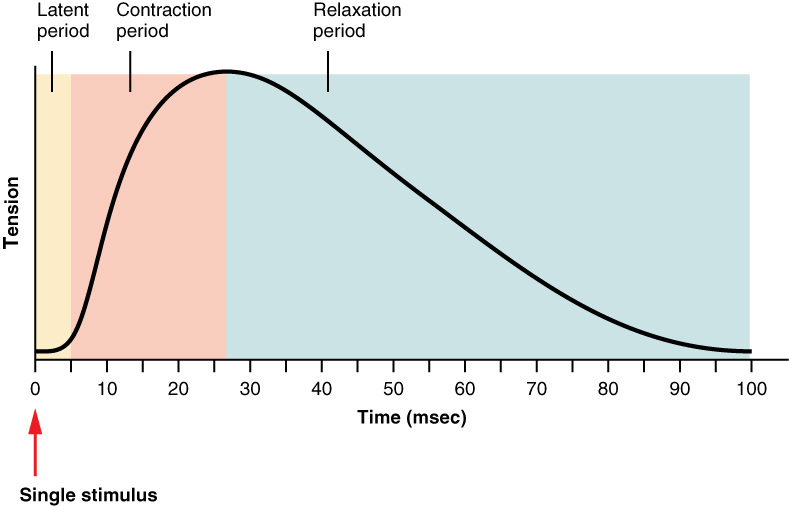
What is latent period?
A short delay from the time AP reaches the muscle until the tension in the muscle.
31
New cards
What is the contraction phase?
cycling of cross-bridges (myosin and actin contractions)
32
New cards
What is relaxation phase?
Muscle return to normal length
33
New cards
What is Threshold stimulus?
Stimuli must meet a minimum threshold to produce a response
34
New cards
What is submaximal stimuli?
As stimulus continues (gets stronger) the more motor units that will be respond
35
New cards
What is motor unit?
Single motor neuron and all attached muscle fibers.
Remember:
1. Small = more coordinated but less power. Ex: hands
2. large = less coordinated but more power. Ex: legs
Remember:
1. Small = more coordinated but less power. Ex: hands
2. large = less coordinated but more power. Ex: legs
36
New cards
What is maximal threshold?
Maximum tension that can be achieved
37
New cards
What are supramaximal stimuli?
the continued stimulus at maximum tension will continue to have all motor units responding
Example: the sudden bursts of energy where you can push a car to protect something
Example: the sudden bursts of energy where you can push a car to protect something
38
New cards
What is the difference between incomplete tetanus and complete tetanus?
muscles take time to relax in between stimuli.
1. incomplete tetanus means muscles fibers may only partially relax
2. cmplete tetanus means signal reaching high frequency and making muscle fibers not relax at all
1. incomplete tetanus means muscles fibers may only partially relax
2. cmplete tetanus means signal reaching high frequency and making muscle fibers not relax at all
39
New cards
What are the 2 types of contractions?
Isometric and Isotonic.
Isotonic is further divided into Concentric and Eccentric
Isotonic is further divided into Concentric and Eccentric
40
New cards
What is Isometric?
Same length but muscle tension changes.
Example: holding barbell, wall sits and planks
Example: holding barbell, wall sits and planks
41
New cards
What is Isotonic?
Same muscle tone but muscle length changes.
42
New cards
What is concentric?
Muscle tension is generated as muscles shorten.
43
New cards
What is Eccentric?
Muscle tension is generated as muscle length
44
New cards
What are the 3 types of energy sources?
1. Creatine phosphate
2. Glycolysis (Anaerobic)
3. Cellular Respiration (Aerobic)
45
New cards
What is Creatine phosphate?
ADP reacting with creatine phosphate to produce ATP.
Occurs very quickly but can only provide energy about 10 seconds
Occurs very quickly but can only provide energy about 10 seconds
46
New cards
What is Glycolysis (Anaerobic)?
Doesn’t require oxygen. Produces 2 ATP and 2 Lactic acid for every glucose.
Quick but only sustains for 1-3 minutes
Quick but only sustains for 1-3 minutes
47
New cards
What is Cellular Respiration (Aerobic)?
Requires oxygen. Most efficient with 38 ATP for 1 glucose.
Sustains longer (but slower) muscle contraction activity
Sustains longer (but slower) muscle contraction activity
48
New cards
What is Type I Fibers
Slow Twitch
1. Lots of Mitochondria
2. Depend of Cellular respiration for ATP
3. Resistant to Fatigue
4. Rich in myoglobin (red color, dark meat of turkey)
5. Activated by slow conduction, small diameter motor neurons
6. Dominant in muscles used for endurance and tonus. Ex: posture
7. Marathon / Cross Country runner’s
1. Lots of Mitochondria
2. Depend of Cellular respiration for ATP
3. Resistant to Fatigue
4. Rich in myoglobin (red color, dark meat of turkey)
5. Activated by slow conduction, small diameter motor neurons
6. Dominant in muscles used for endurance and tonus. Ex: posture
7. Marathon / Cross Country runner’s
49
New cards
What is Type II Fibers
Fast twitch
1. Few Mitochondria
2. Rich in glycogen
3. Depend on creatine phosphate & glycongen for ATP
4. Fatigue easily with production of lactic acid
5. Low in myoglobin (white meat of turkey)
6. Activated by fast - conducting, large diameter motor neurons
7. Dominant in muscles used for rapid movement. Example: Eyes
8. Sprinters.
1. Few Mitochondria
2. Rich in glycogen
3. Depend on creatine phosphate & glycongen for ATP
4. Fatigue easily with production of lactic acid
5. Low in myoglobin (white meat of turkey)
6. Activated by fast - conducting, large diameter motor neurons
7. Dominant in muscles used for rapid movement. Example: Eyes
8. Sprinters.
50
New cards
Congratulations, that’s the end of all terms.
make sure to practice using cfu’s and near pods.