AP Biology Unit 2 - Cell Structures and Functions
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Cell
smallest unit of life

Subcellular
existing or occurring within a cell

Organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
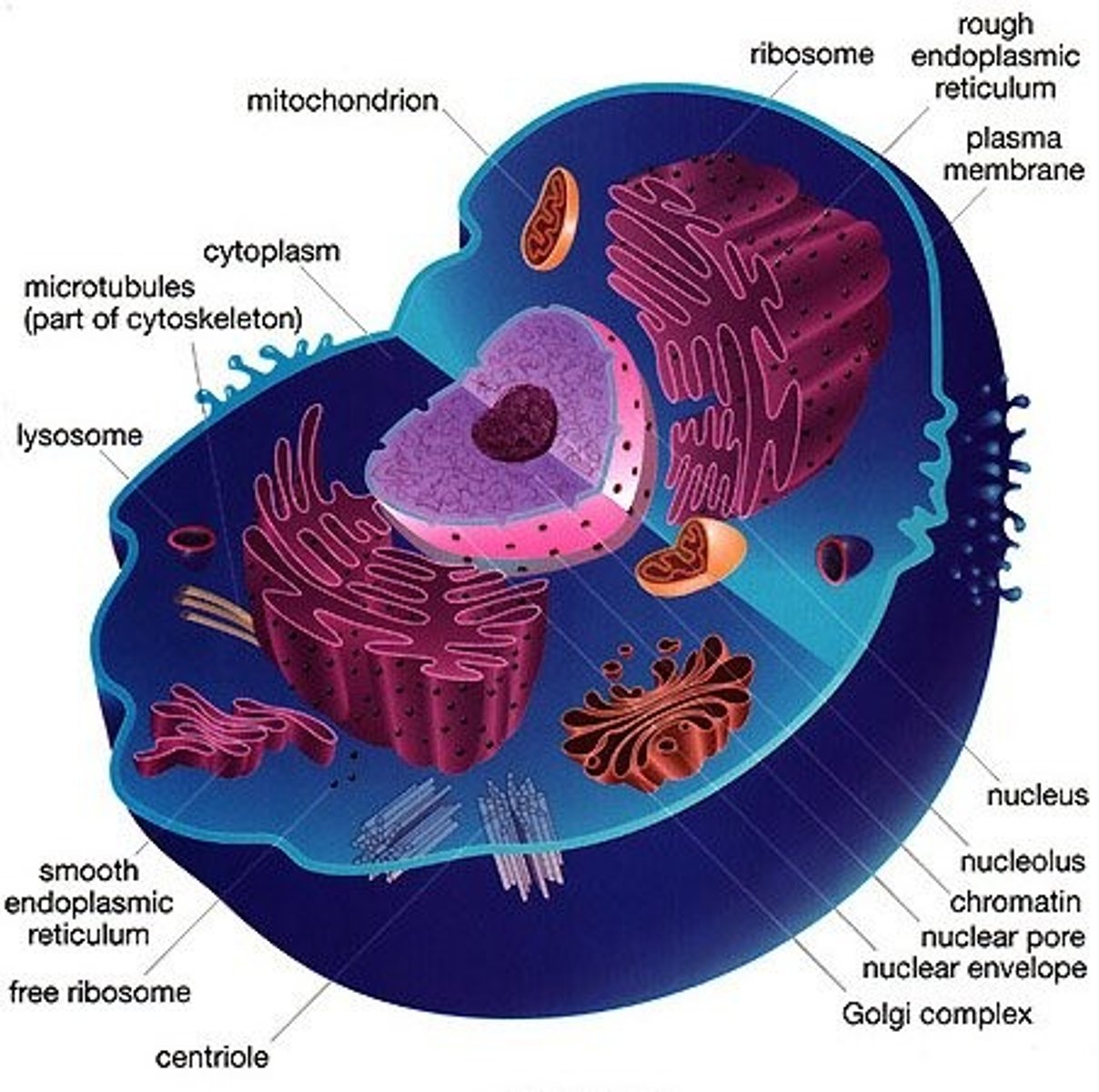
endomembrane system
A group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins
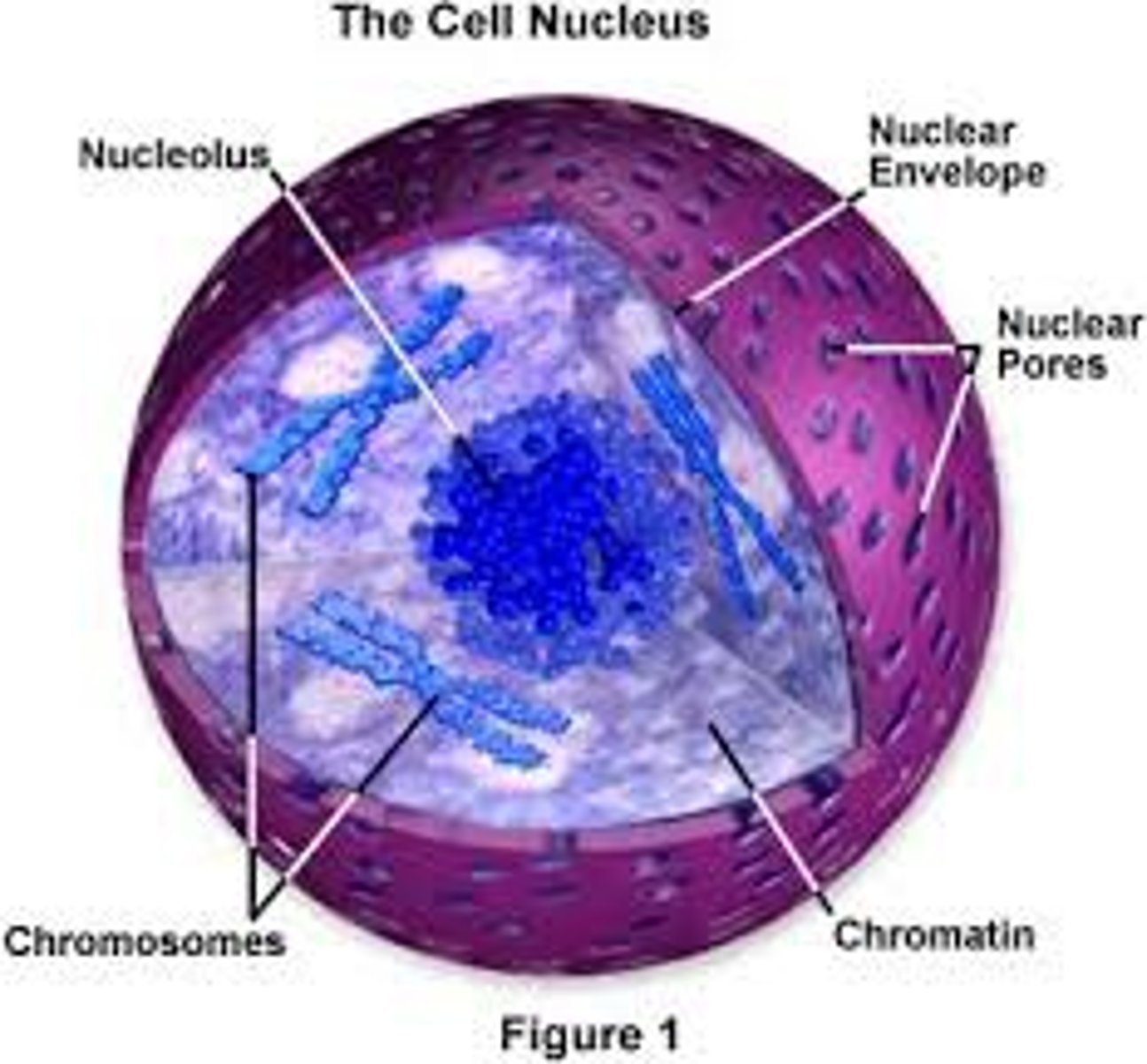
Nucleus
The most visible organelle in a eukaryotic cell that contains the DNA not found in the mitochondria or chloroplasts. Enclosed by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope and contains a nucleolus (which makes ribosomes).
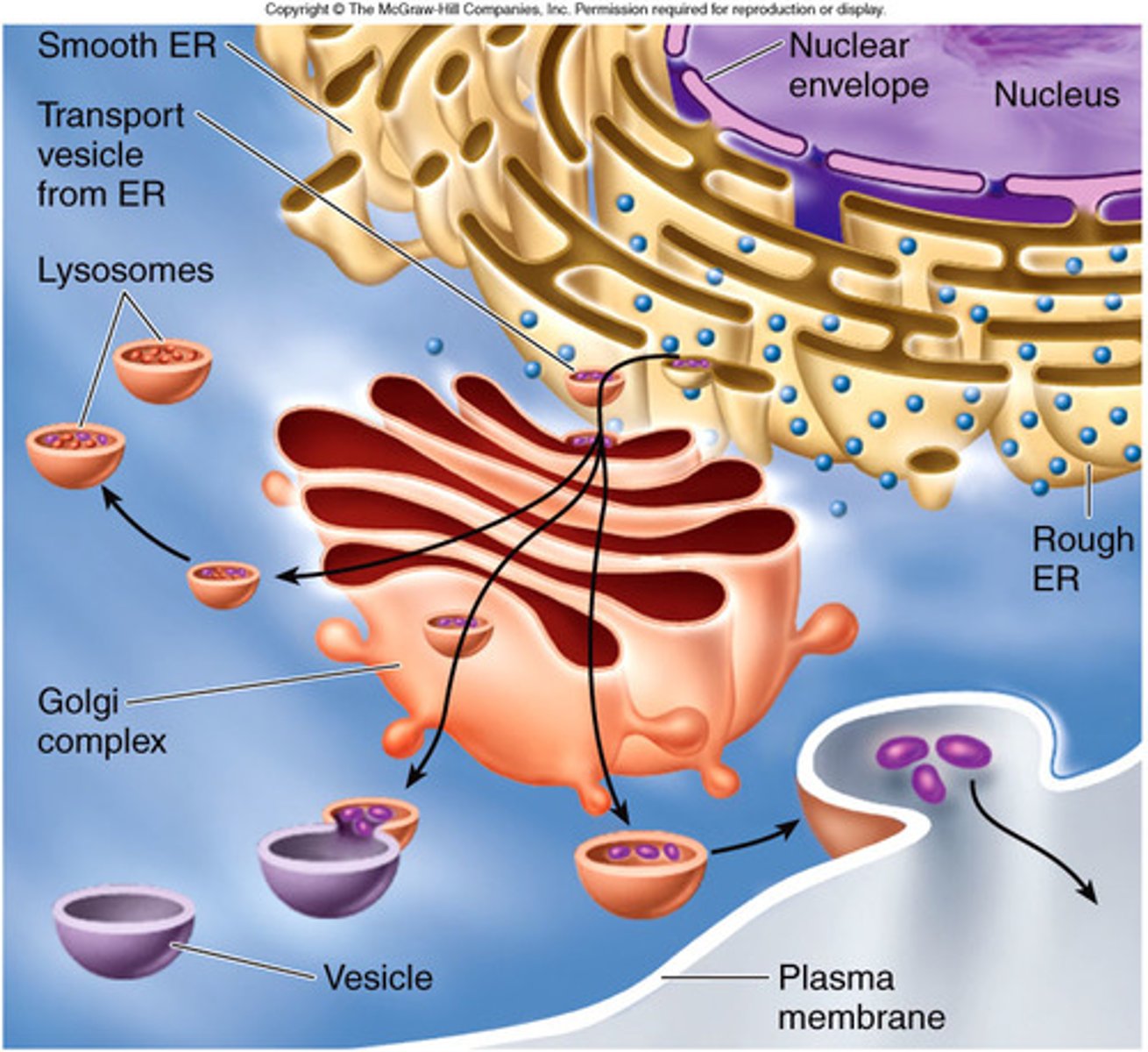
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER)
Extends beyond the nuclear envelope as a series of membranes without ribosomes attached. Functions in making lipids and detoxing the cell from toxic substances.
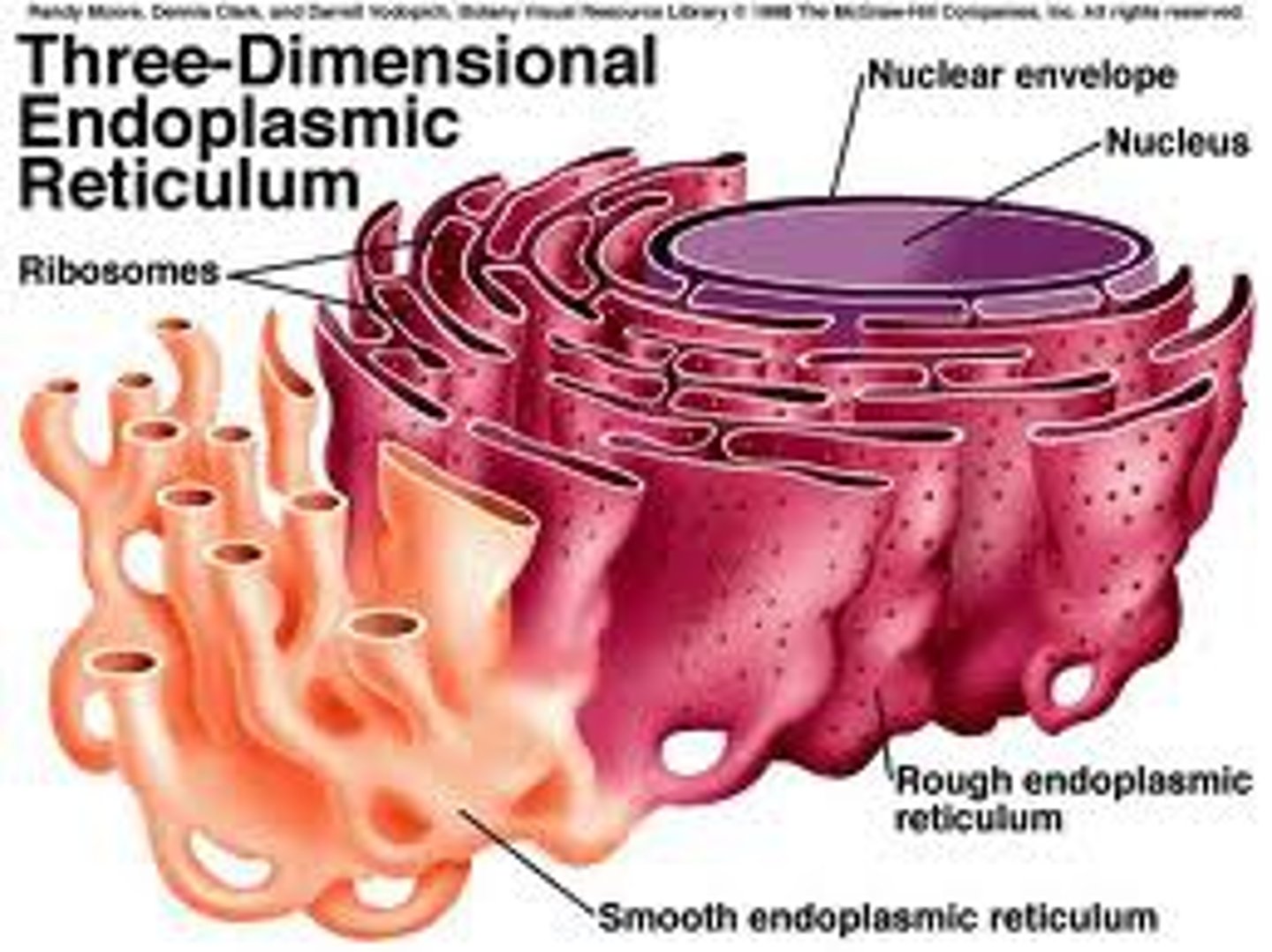
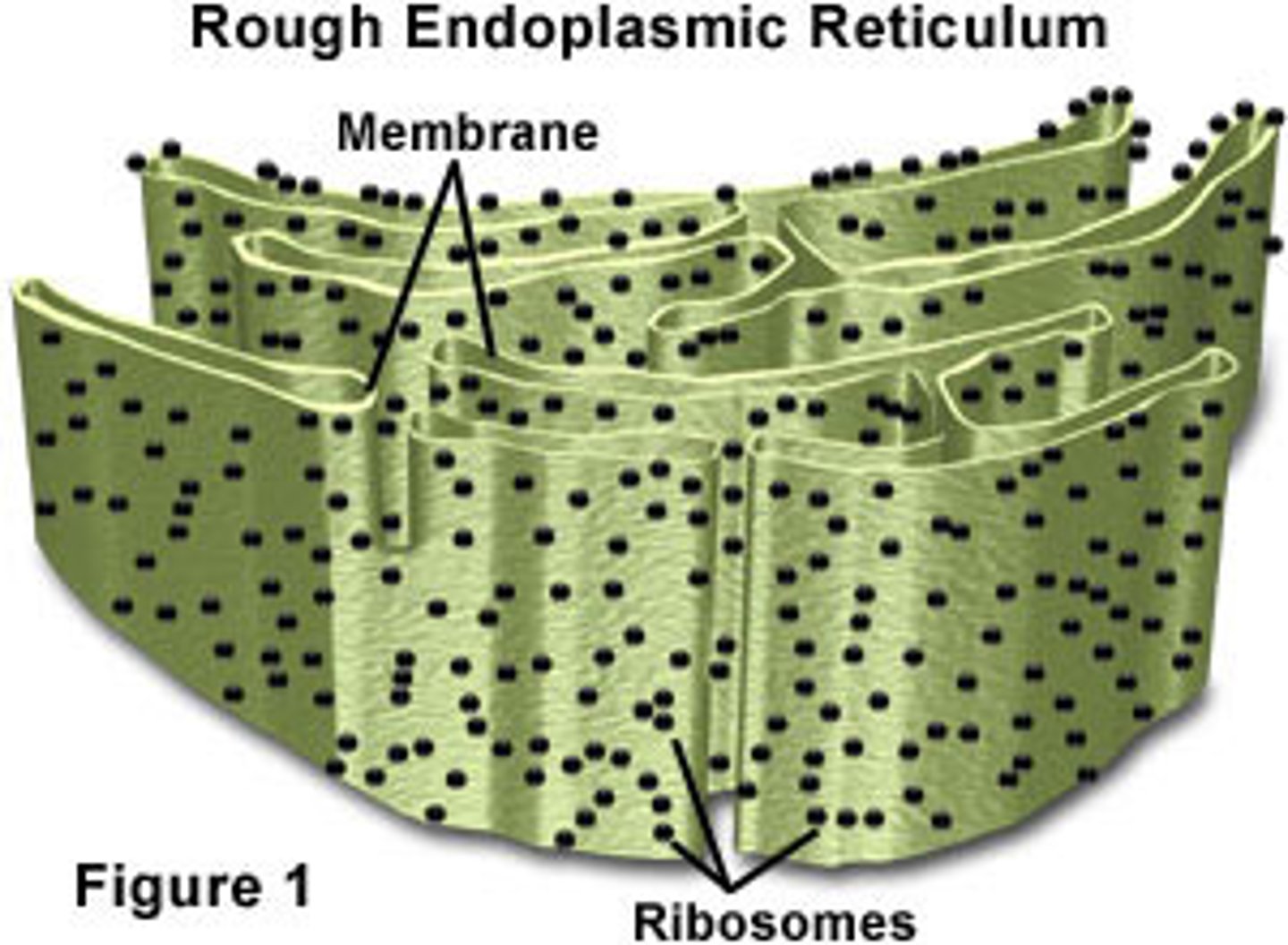
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER)
Extends from the Smooth ER as a series of membranes with ribosomes attached. Proteins are made by the ribosomes and are transported by the rough er and vesicles to the Golgi complex to be shipped out of a cell.
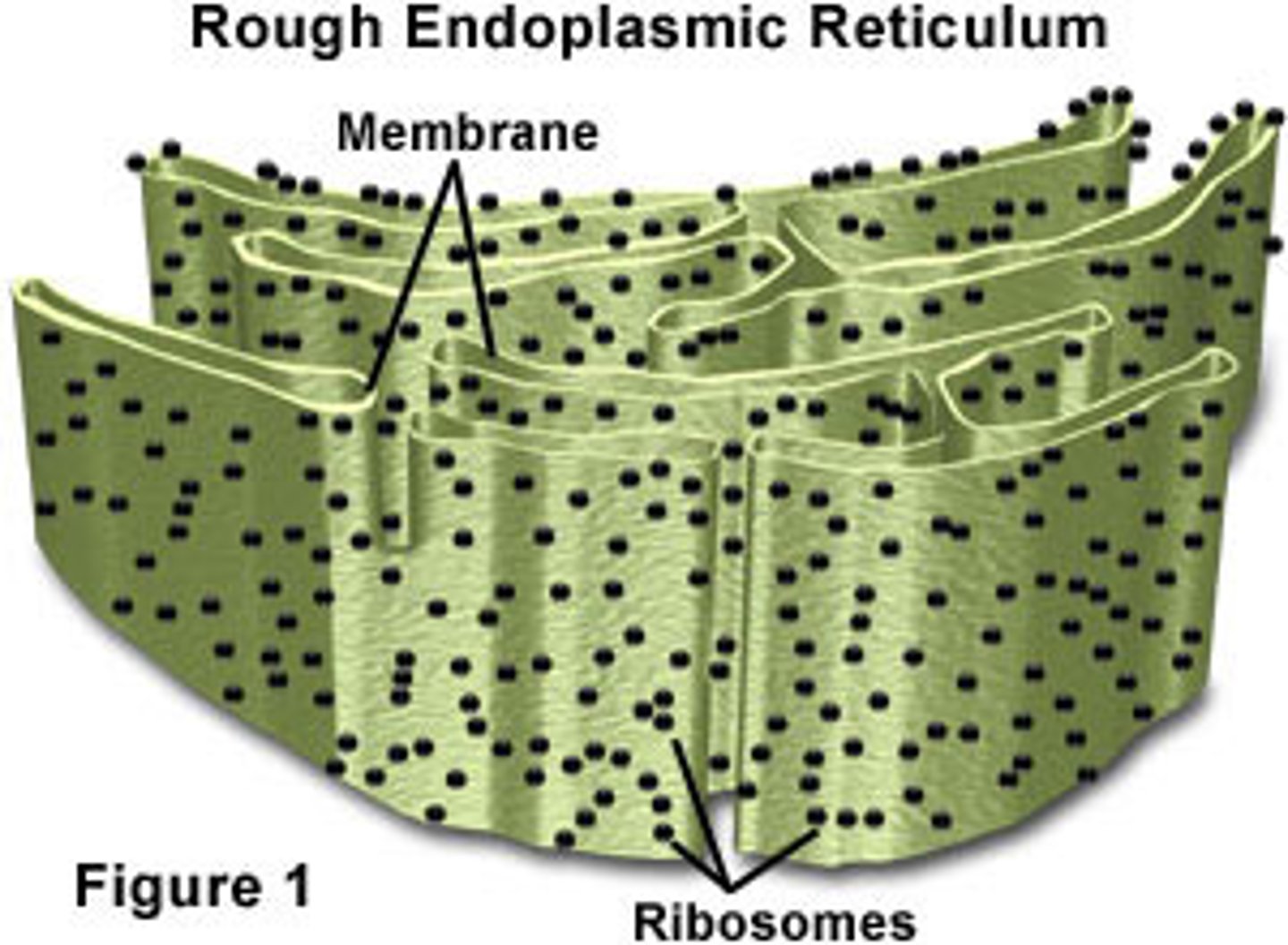
Ribosomes
Made by the nucleolus and are not membrane bound or part of the endomembrane system (not considered a true organelle). Made up of ribosomal RNA and proteins. Function in producing proteins for the cell (free ribosomes in the cytoplasm) or export from the cell (attached to the rough ER).
Vesicle
A membrane bound sac that contains materials involved in transport of the cell.

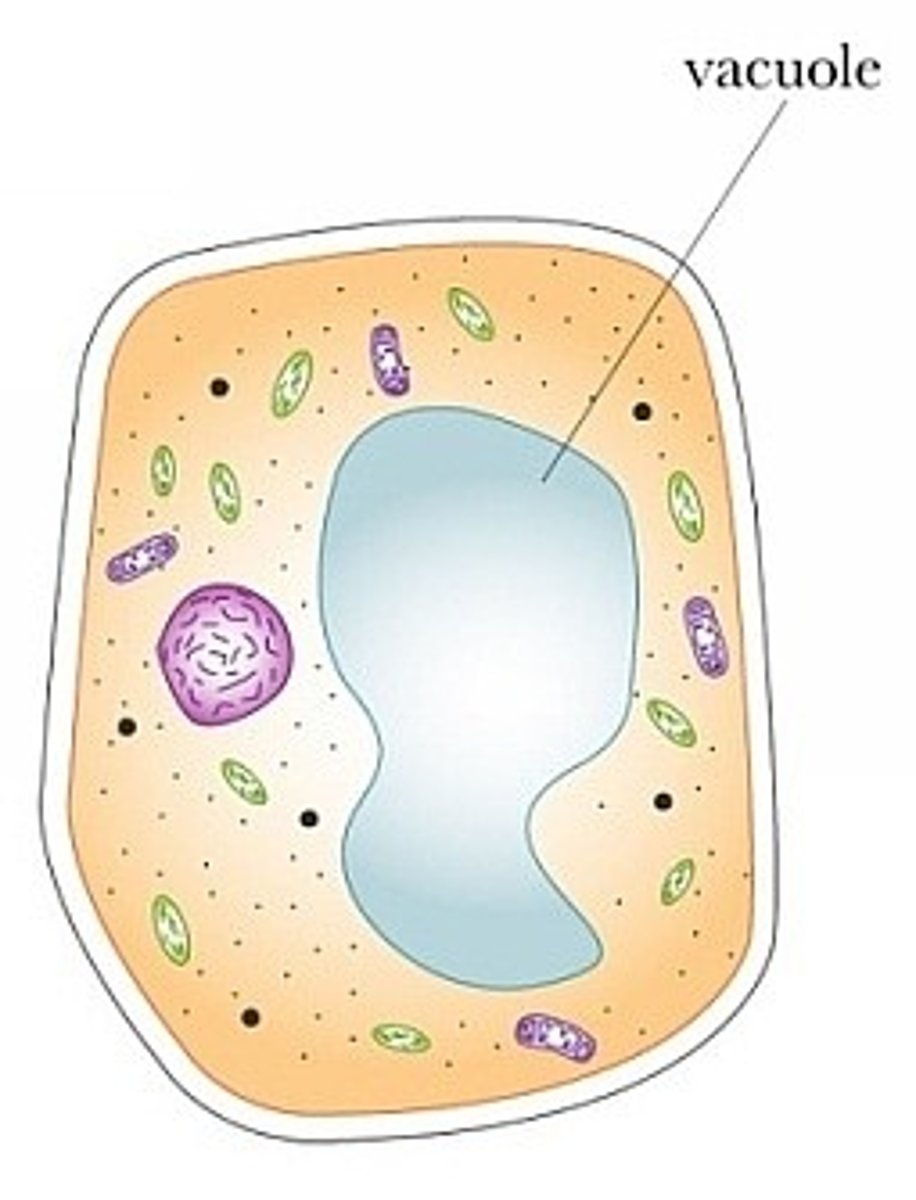
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates. Can also store food or function in pumping water out of a single celled organism.
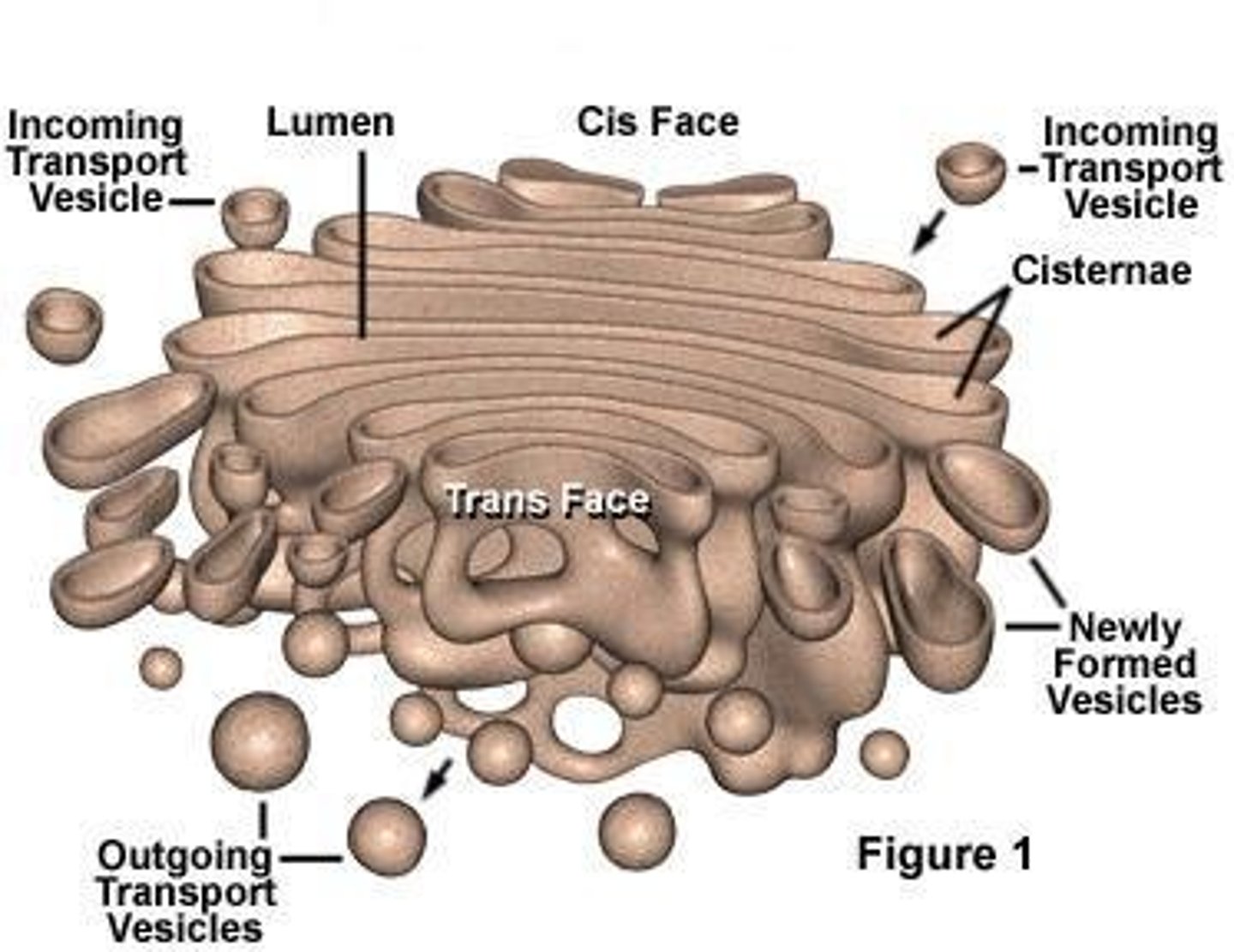
Golgi Complex
Accepts materials enclosed in a vesicle from the rough ER. Packages and processes substances for export from the cell. Has a sidedness - the cis face accepts materials and the trans face ships materials out.
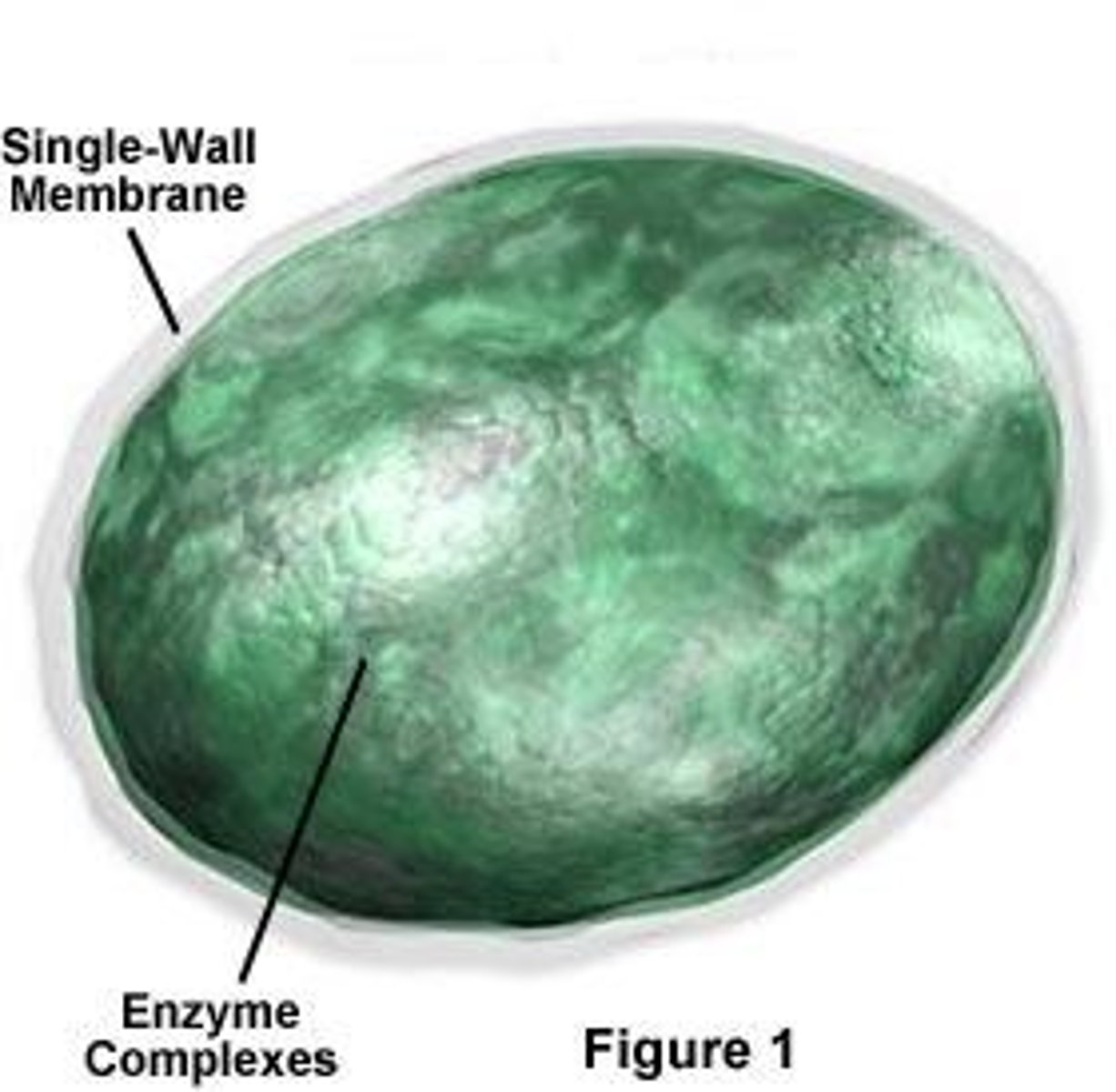
Lysosome
A membrane bound organelle containing hydrolytic enzymes used to digest macromolecules. The enzymes function best in an acidic environment.
Hydrolytic
cleavage of bonds by the addition of water
Intracellular
within the cell
Extracellular
outside the cell
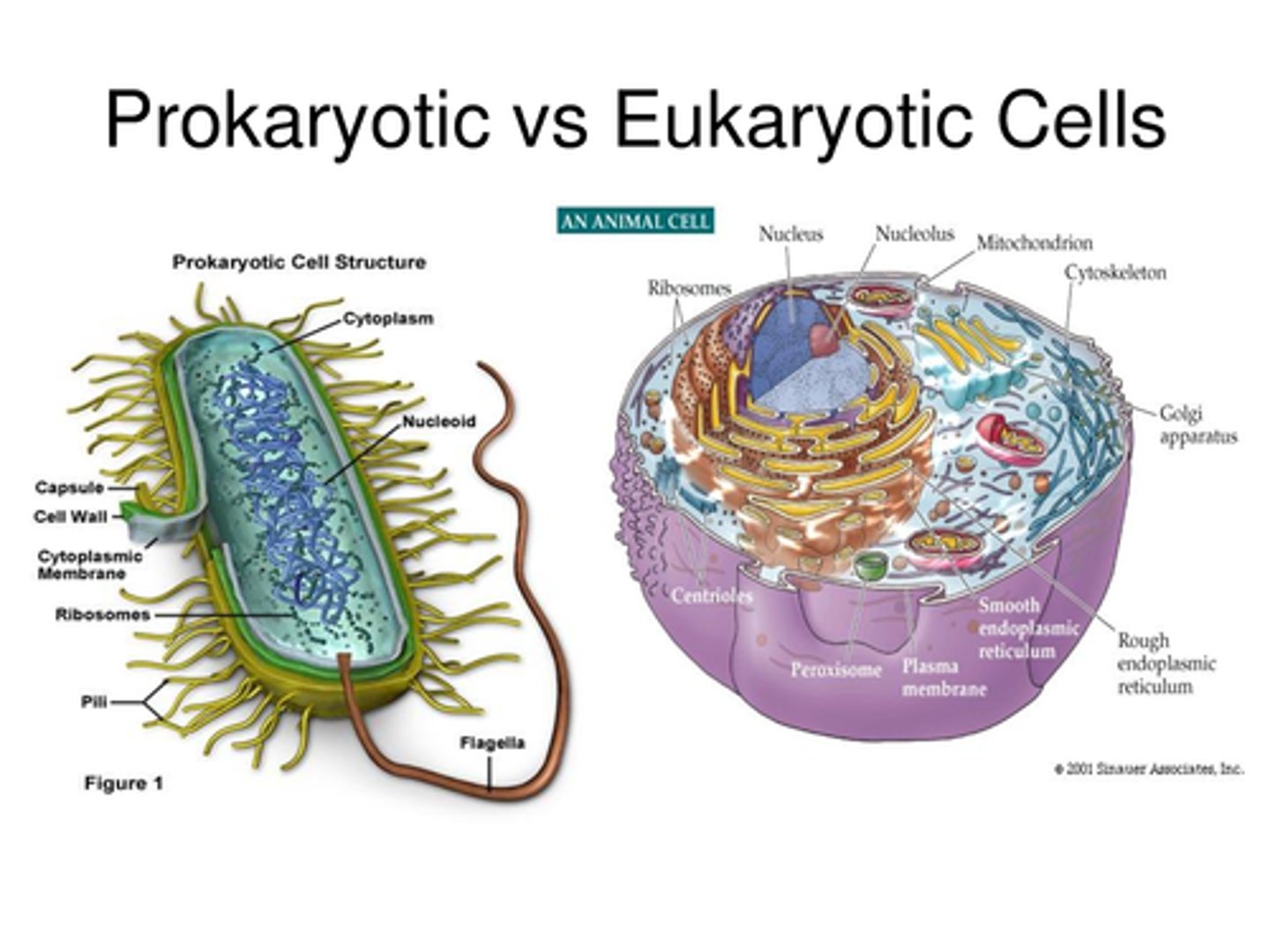
Eukaryotic
A cell characterized by the presence of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can be unicellular (protists) or multicellular (fungi, plants and animals).
Cell
smallest unit of life
Nucleus
Subcellular organelle that contains DNA and a nucleolus
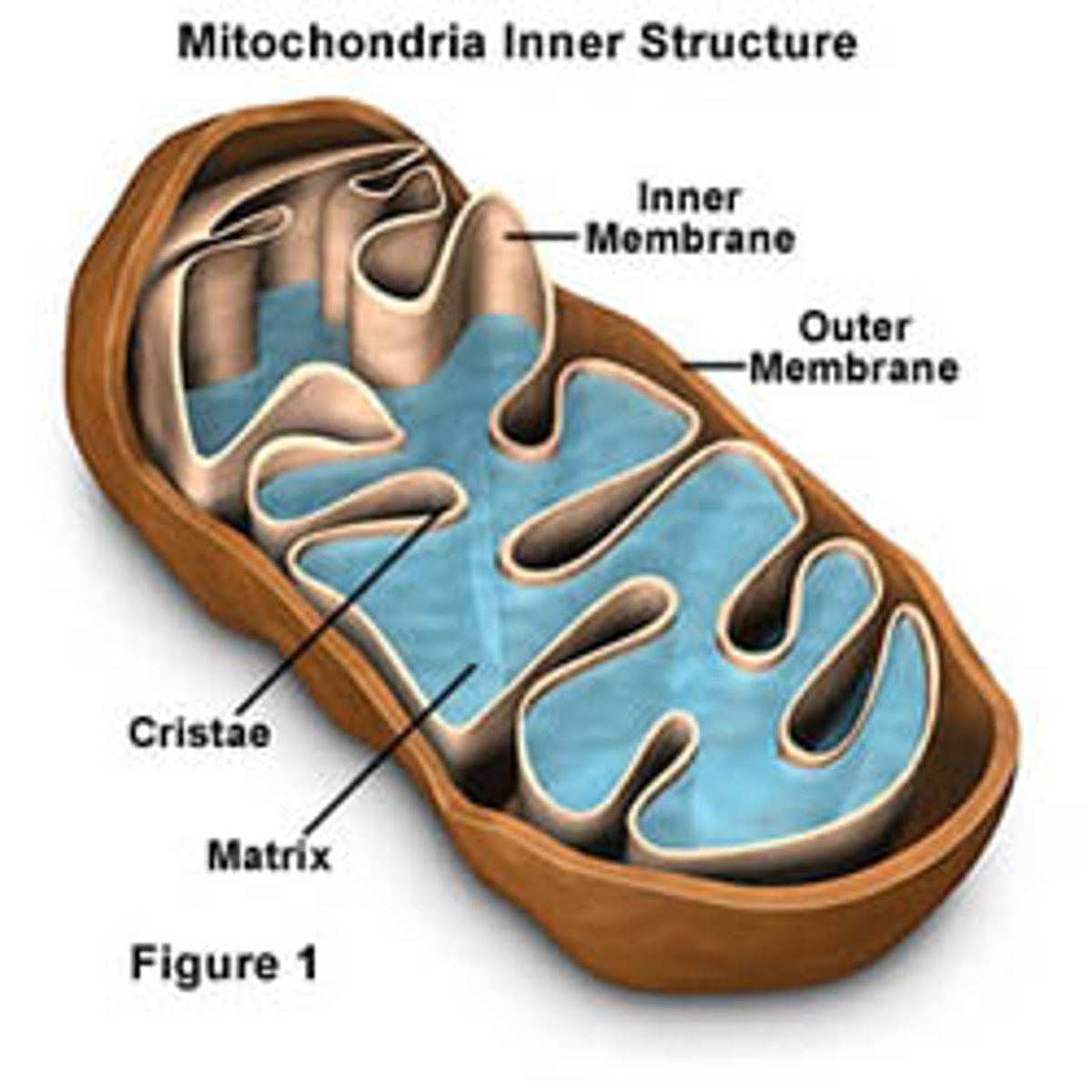
Mitochondria
Membrane bound organelles that are the sites of cellular respiration. They produce ATP from sugars, fats, and other fuels. Found in all eukaryotic cells. Made up of an outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane with folds called cristae, and a matrix in the middle. Have their own DNA and ribosomes.
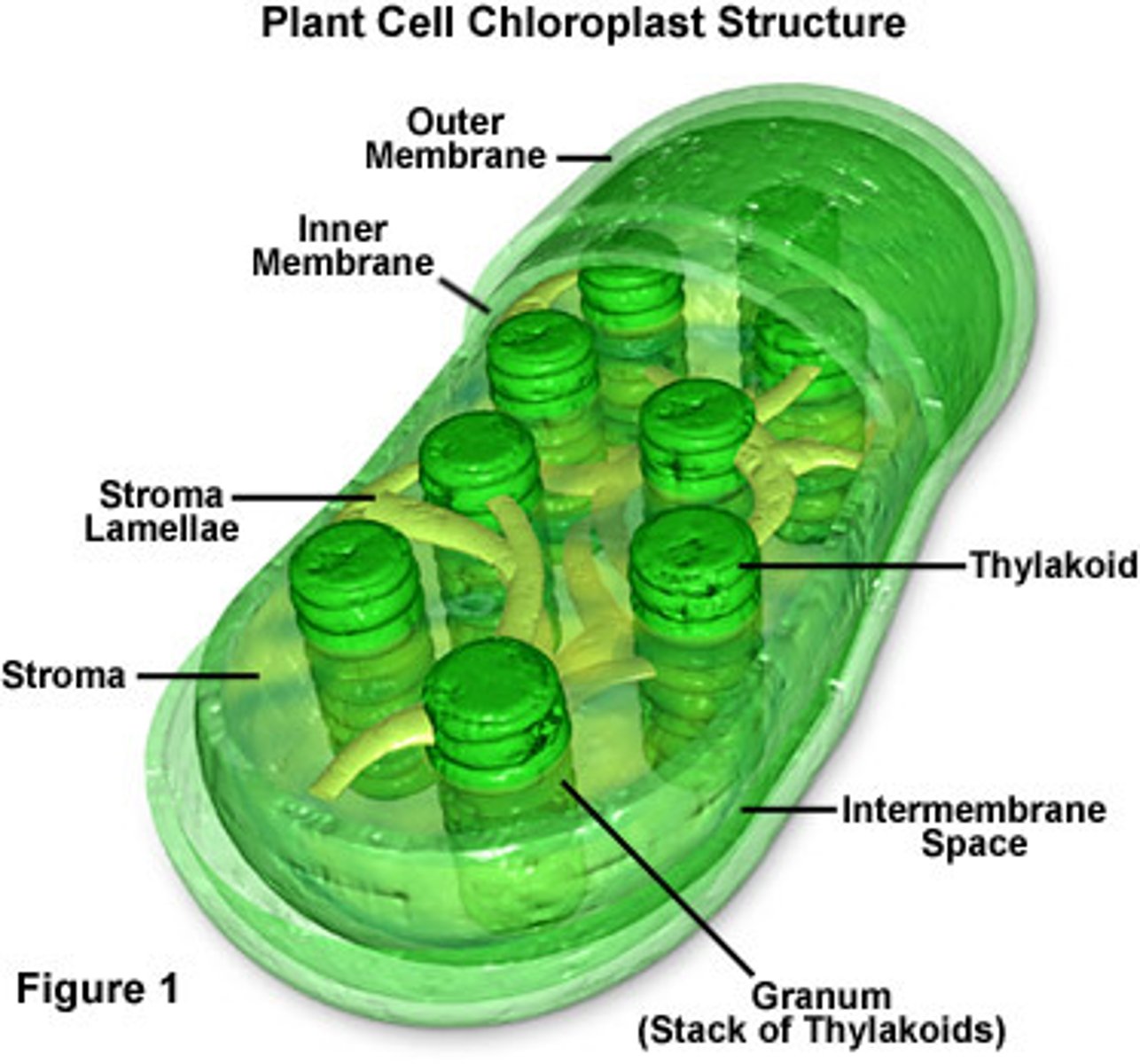
Chloroplasts
Membrane bound organelles that are the sites of photosynthesis. They use carbon dioxide to produce sugars and other compounds. They contain chlorophyll and enzymes for photosynthesis. Chemical reactions are compartmentalized by the membranes. There's an outer double membrane, flattened discs called thylakoids that contain chlorophyll and organize to form stacks called grana. Thylakoids are suspended in the fluid filled stroma. Have their own DNA and ribosomes.
Compartmentalization
seen in eukaryotes; consequence of organelles being membrane-bound. - keeps functions and raw materials or chemical reactions separated
Form fits function
How something works is related to its structure
Enery
the ability to do work
Surface Area
The measurement of the outer surface of an object.
Volume
The amount of space an object takes up
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Ratio of a cell's outside area to its internal volume.
Examples of Cell Adaptation to Increase the Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Root Hairs in Plant Cells, Guard Cells Surrounding Stomata, Epithelial Cells of the Small Intestine
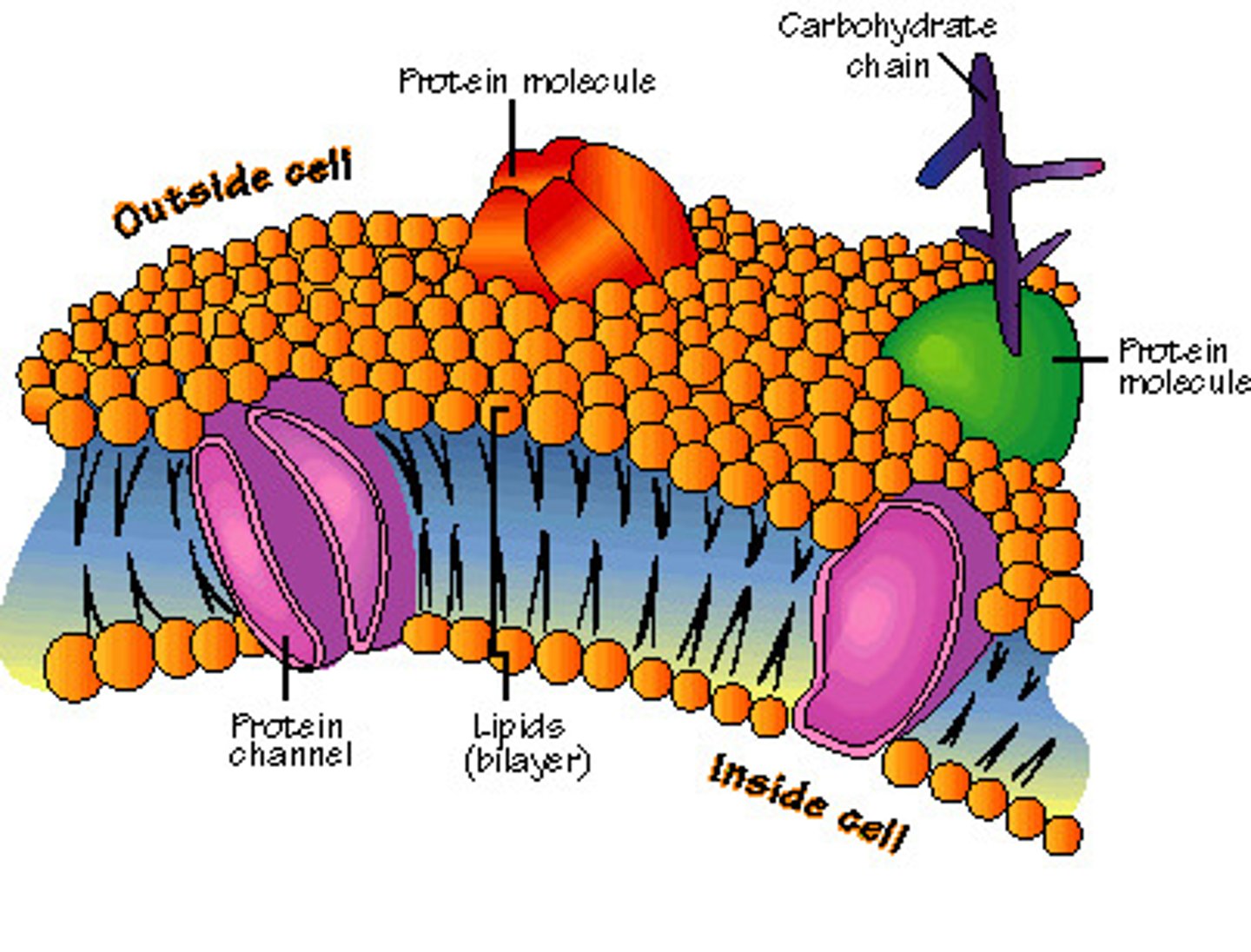
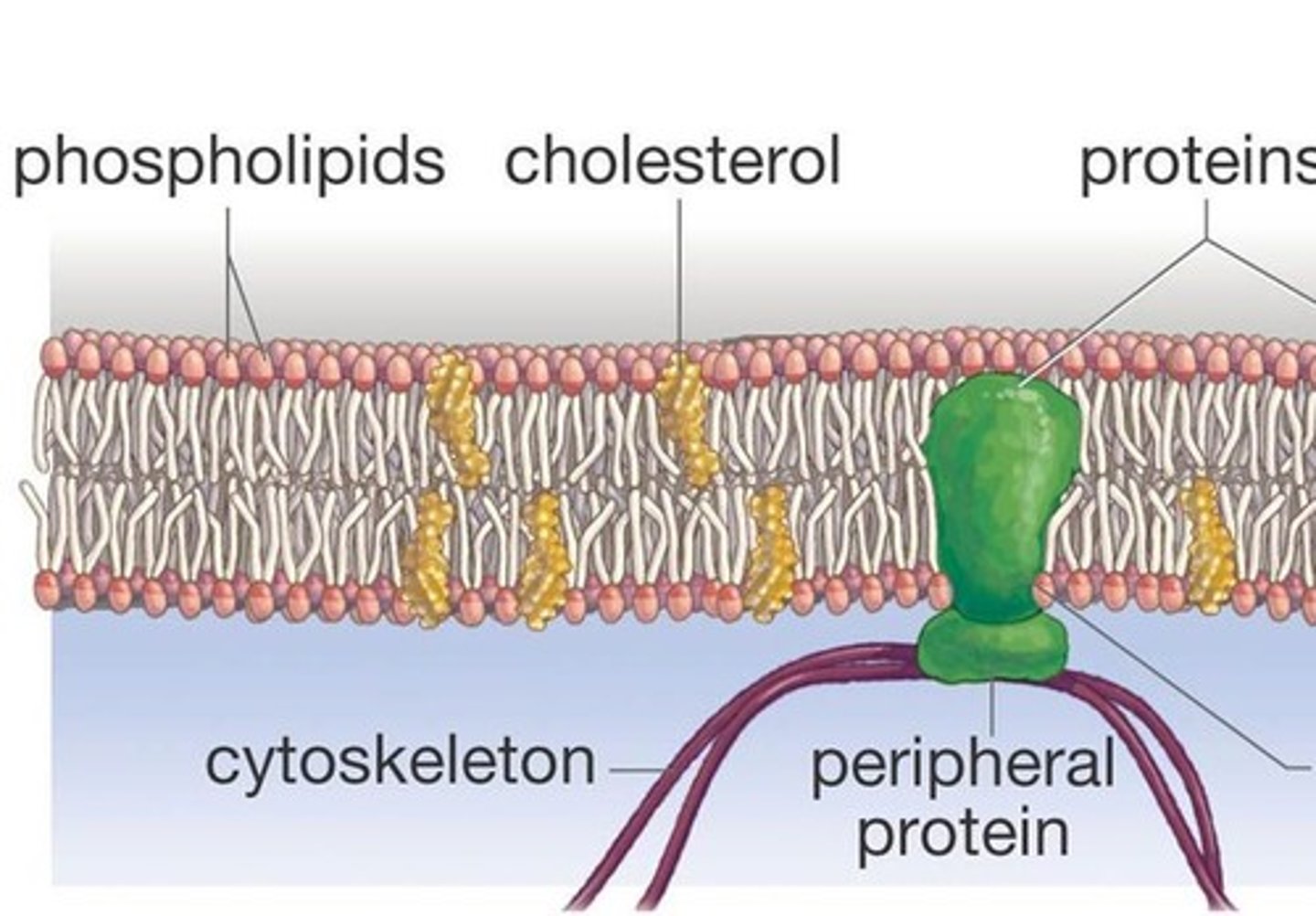
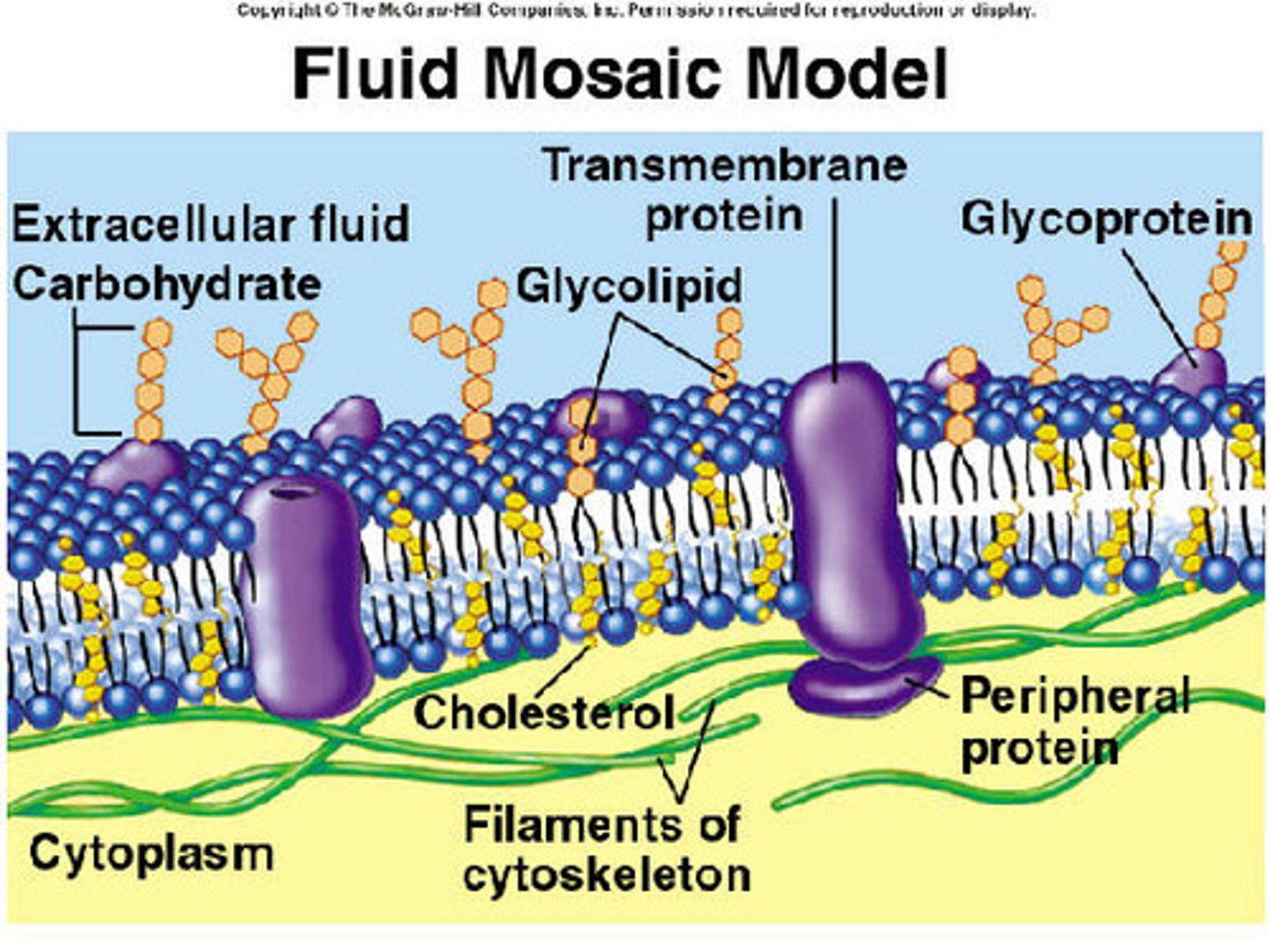
Plasma Membrane
a microscopic membrane of lipids and proteins that forms the external boundary of the cytoplasm of a cell or encloses a vacuole, and that regulates the passage of molecules in and out of the cytoplasm.
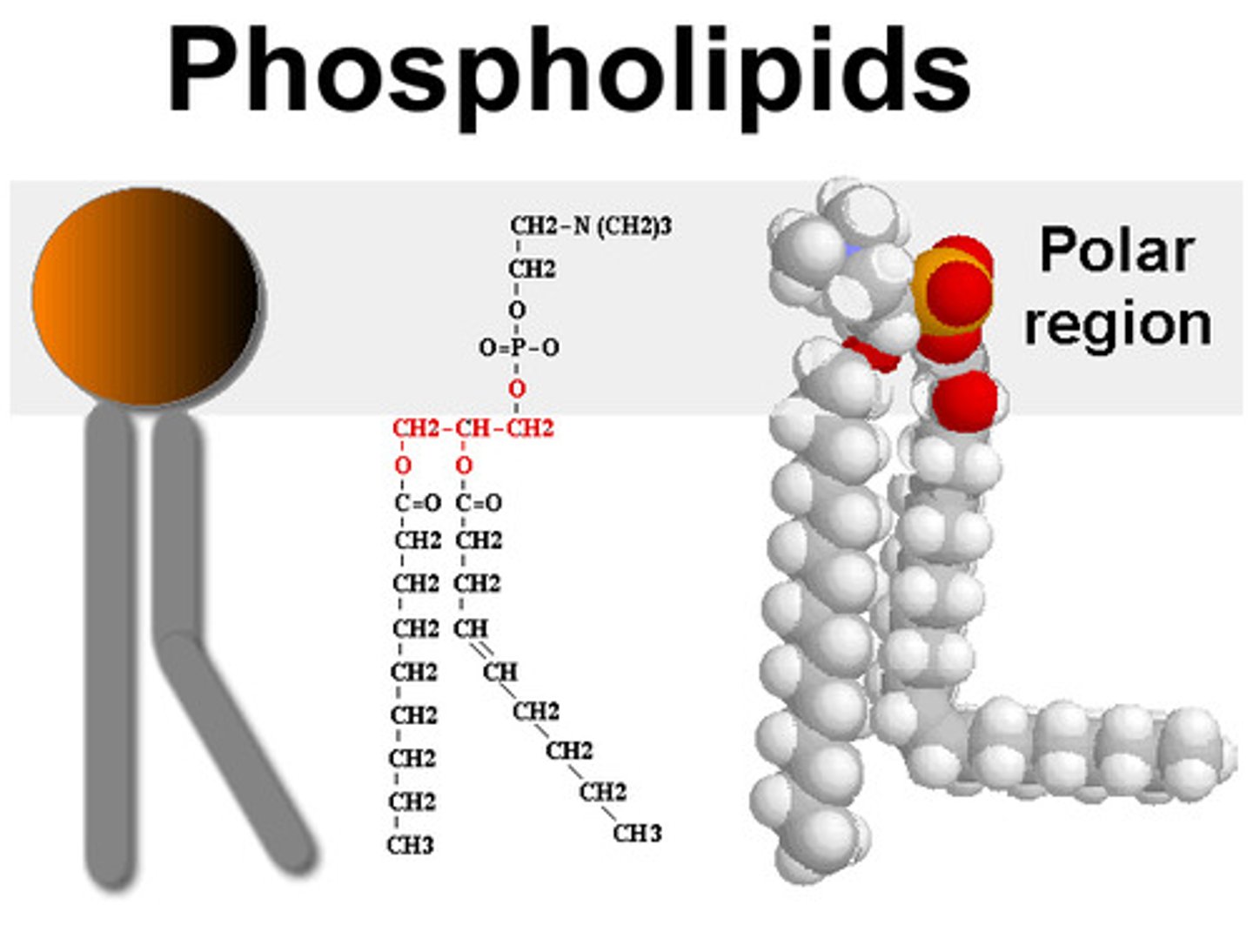
Phospholipid
a lipid that contains phosphorus and that is a structural component in cell membranes
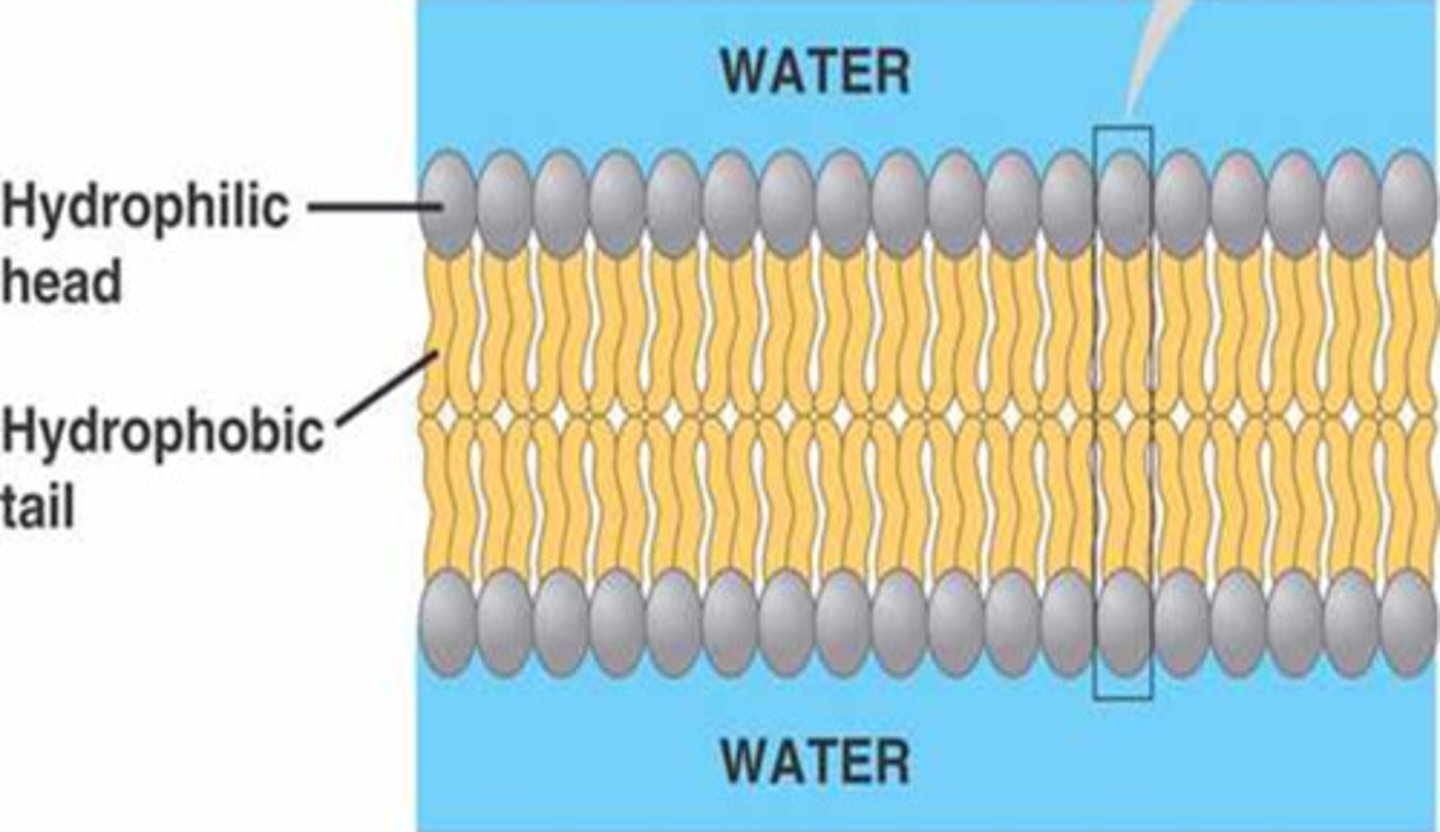
Phospholipid Bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up plasma and organelle membranes.
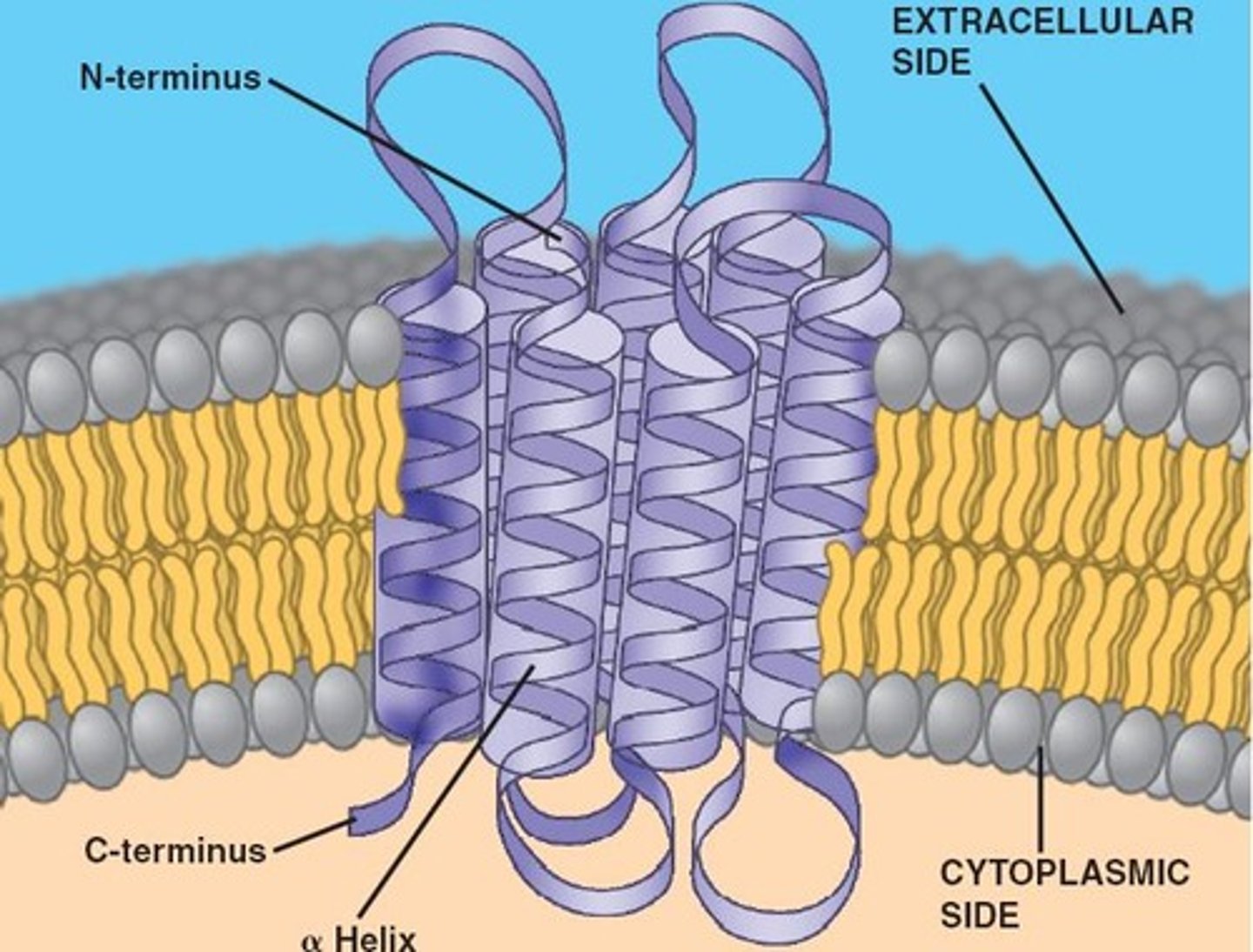
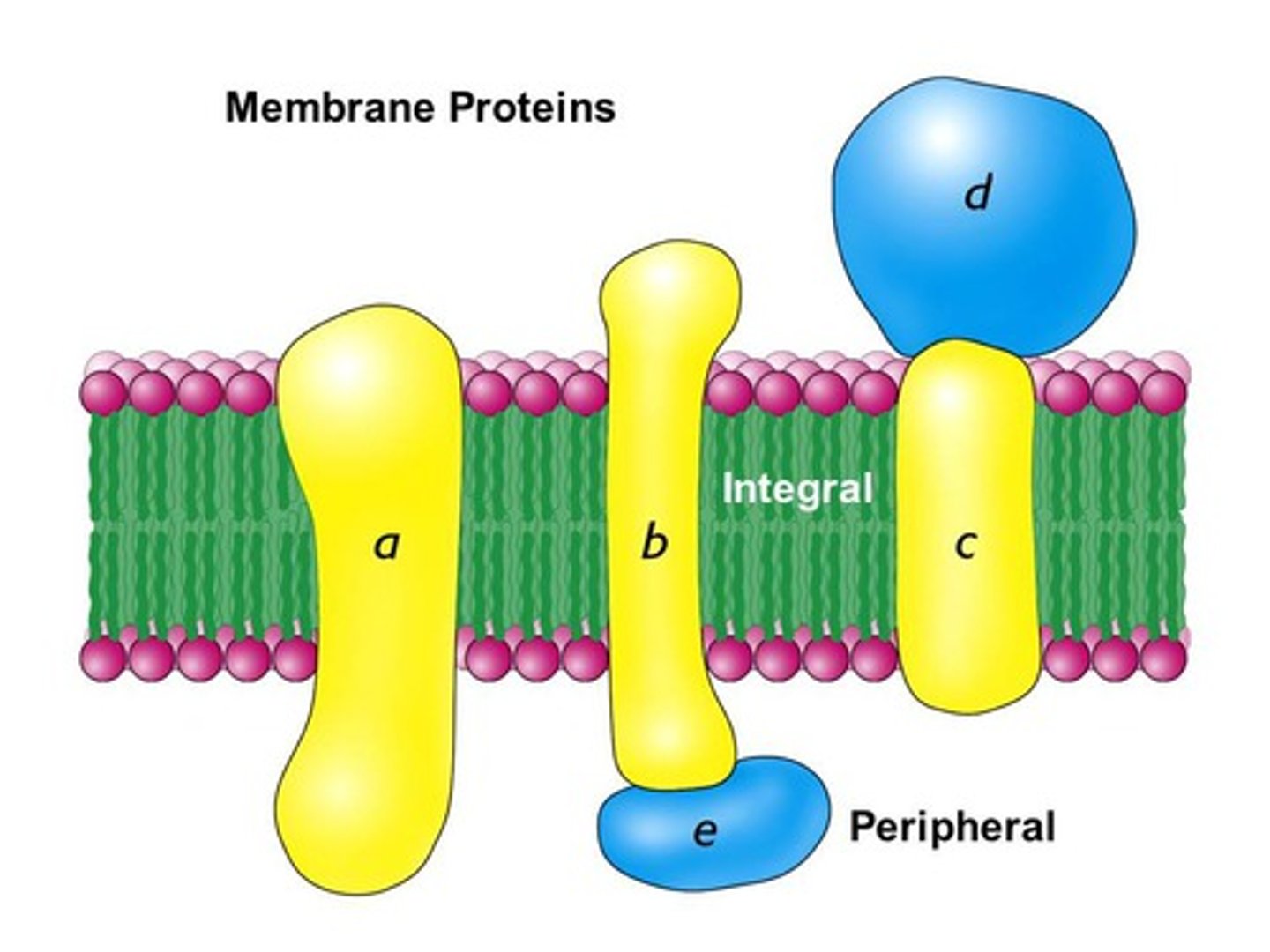
Transmembrane Protein
An integral membrane protein that spans the phospholipid bilayer.
Peripheral Protein
A protein loosely bound to the surface of a membrane or to part of an integral protein and not embedded in the lipid bilayer.
Steroid
lipid molecule with four fused carbon rings
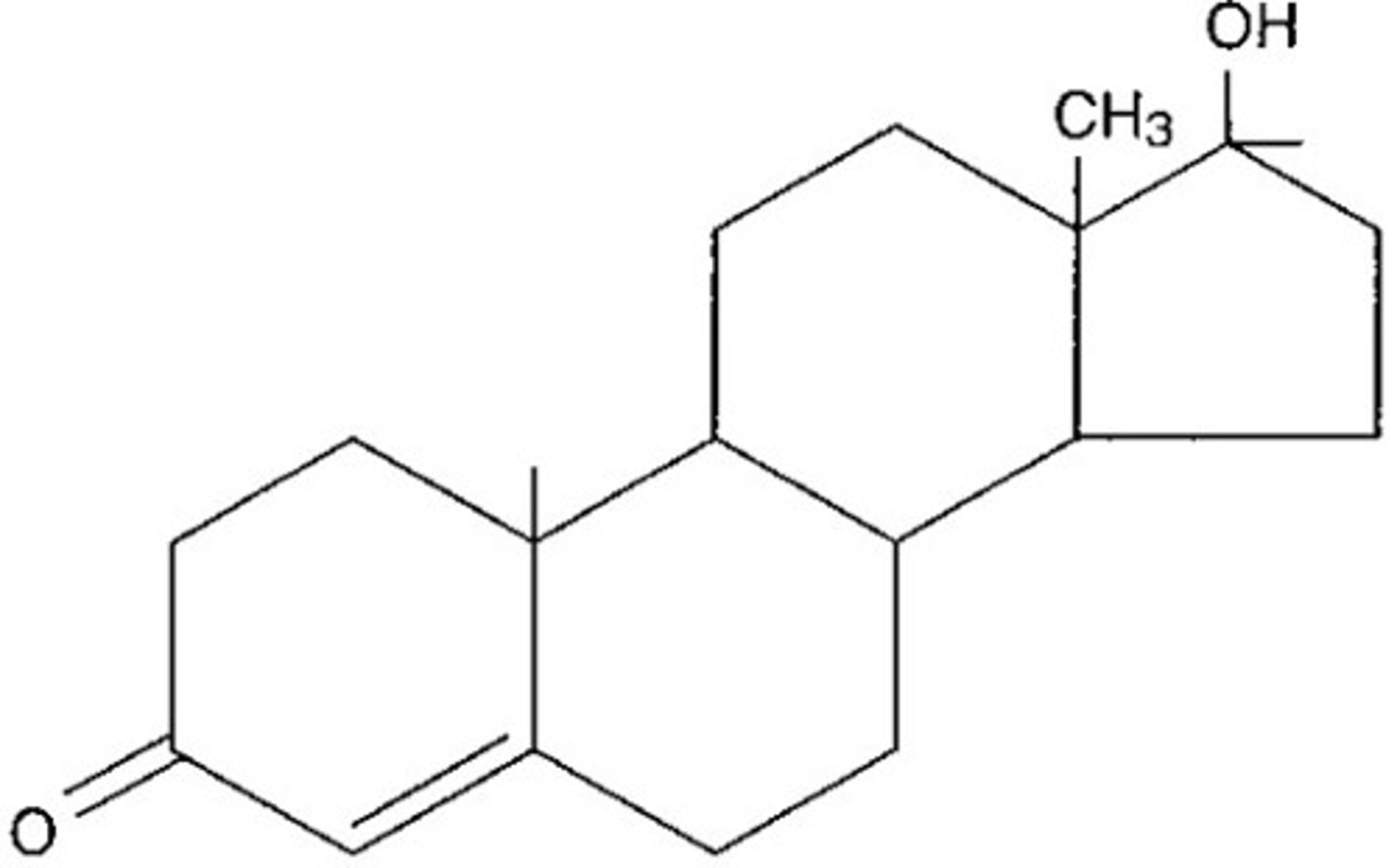
Cholesterol
A lipid that forms an essential component of animal cell membranes and acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of other biologically important steroids.
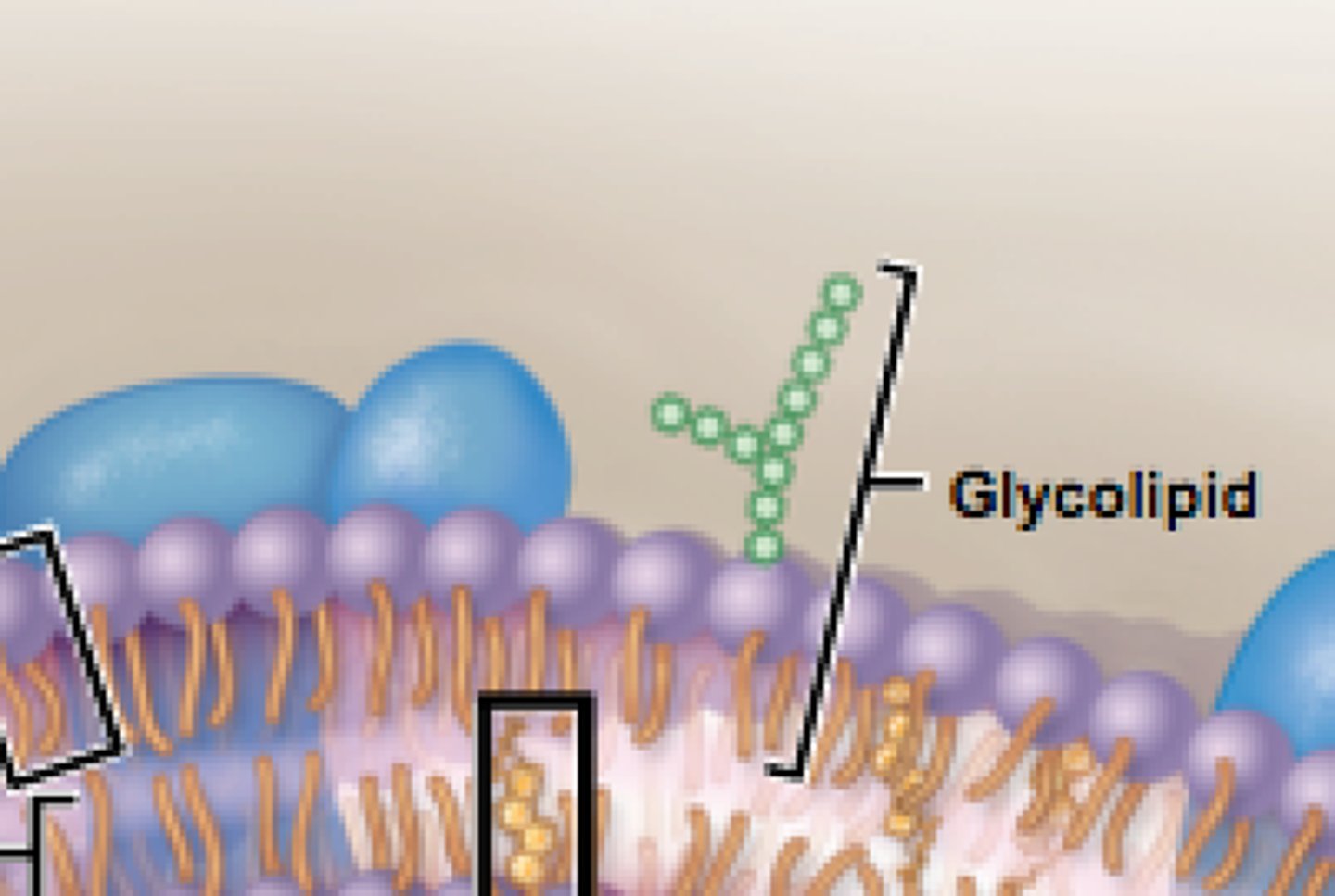
Glycolipid
a lipid with one or more covalently attached carbohydrates
Glycoprotein
A protein with one or more carbohydrates covalently attached to it.
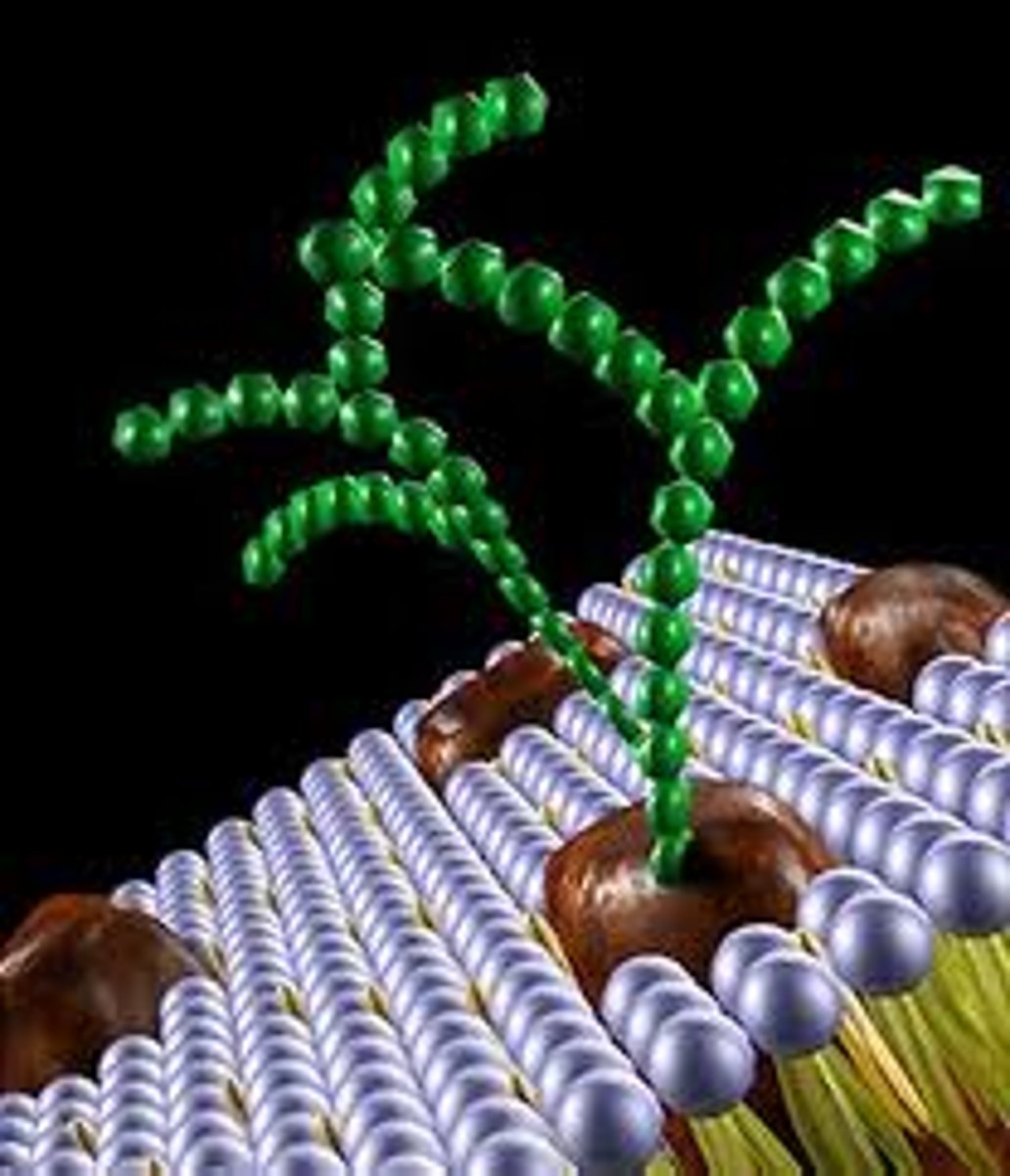
Fluid Mosaic Model
Structural model of the plasma membrane where molecules are free to move sideways within a lipid bilayer.
Aqueous
watery

Cell Wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants, prokaryotes, and fungi
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Selective Permeability
A property of biological membranes that allows some substances to cross more easily than others.
Passive Transport
The net movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration without the direct input of metabolic energy. (Down the concentration gradient) - Plays the primary role in the import of materials and the export of wastes
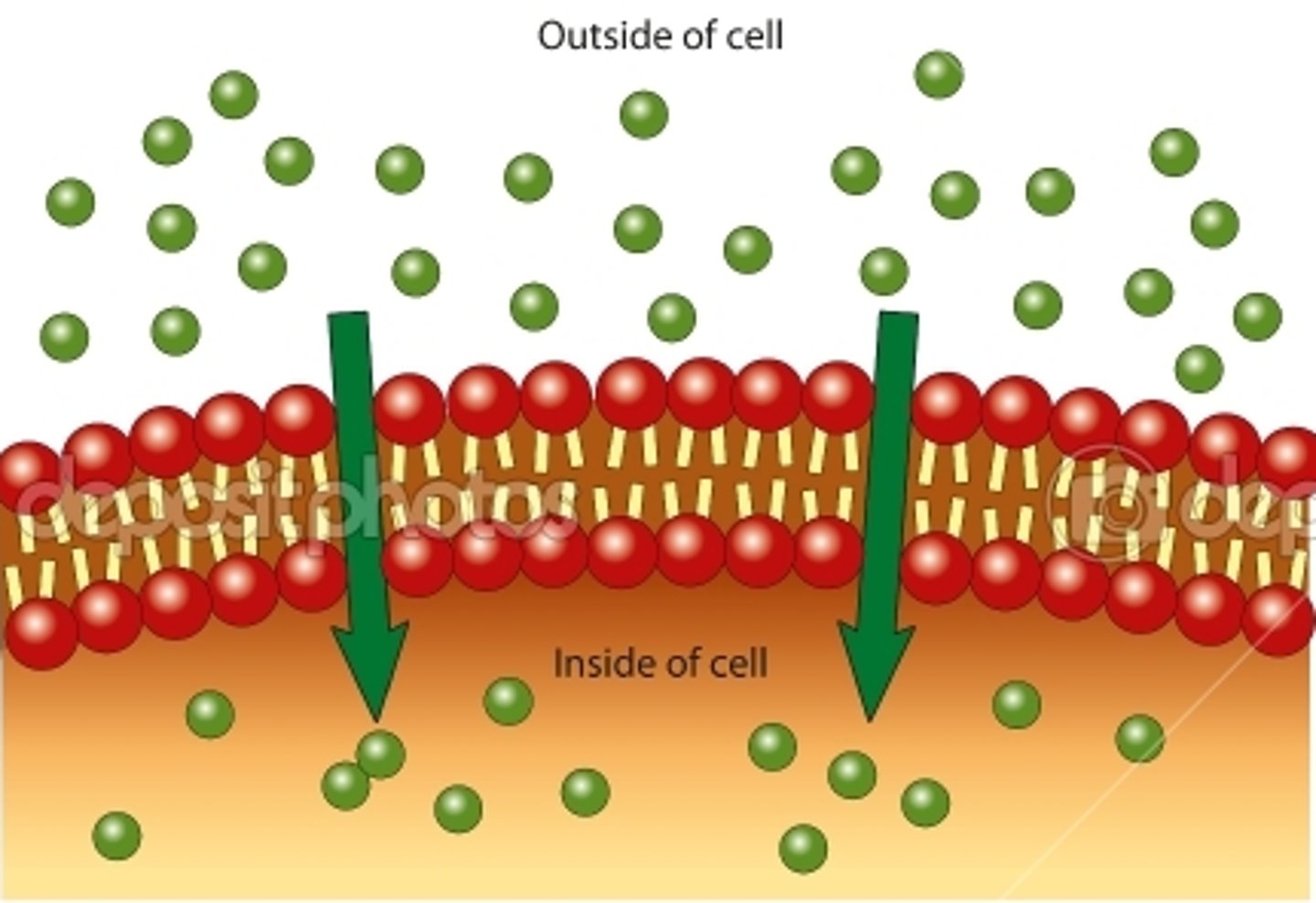
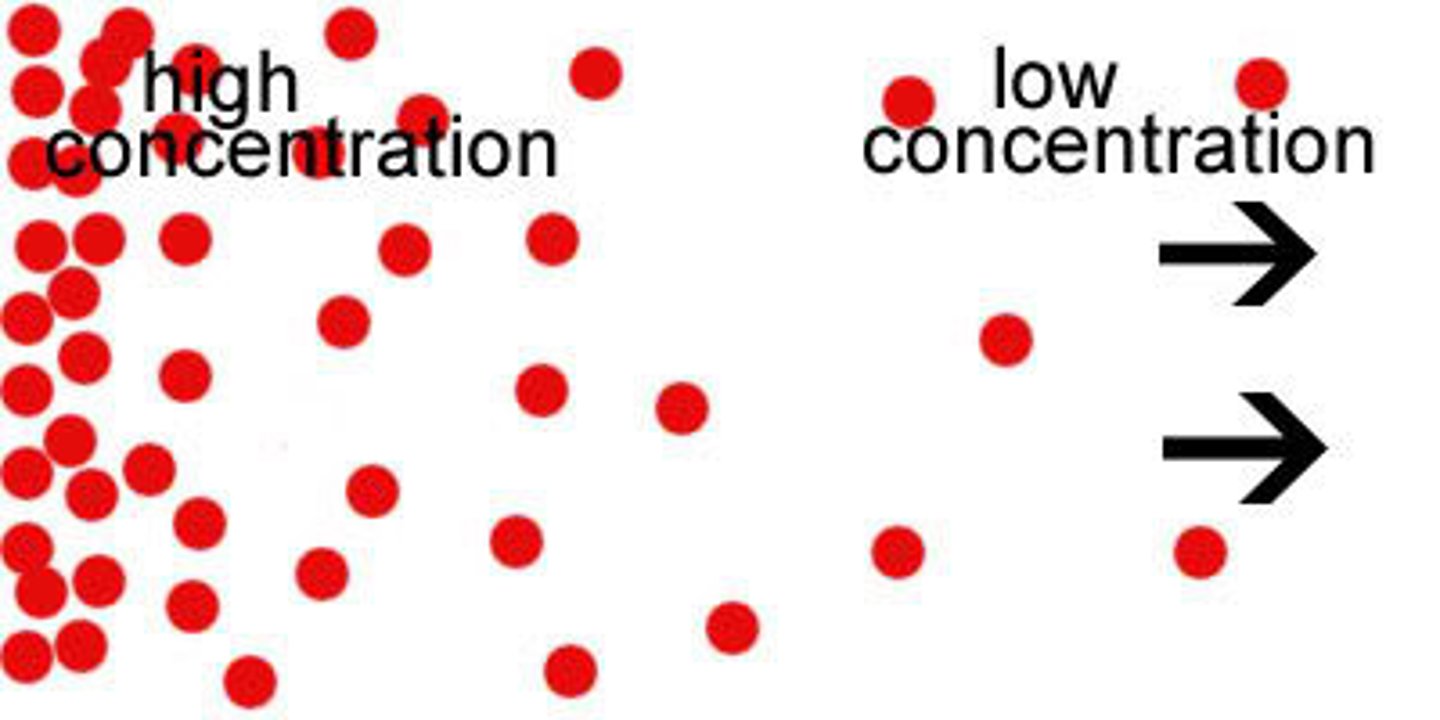
Concentration Gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance across space.
What type of molecules pass freely through the cell membrane?
Small, non polar molecules (N2, O2, CO2) - pass between the lipids.
What type of molecules use transport or channel proteins for passive transport?
Hydrophilic substances such as large, polar molecules and ions.
Channel Protein
A membrane protein, specifically a transport protein, that has a hydrophilic channel that certain molecules or atomic ions use as a tunnel.
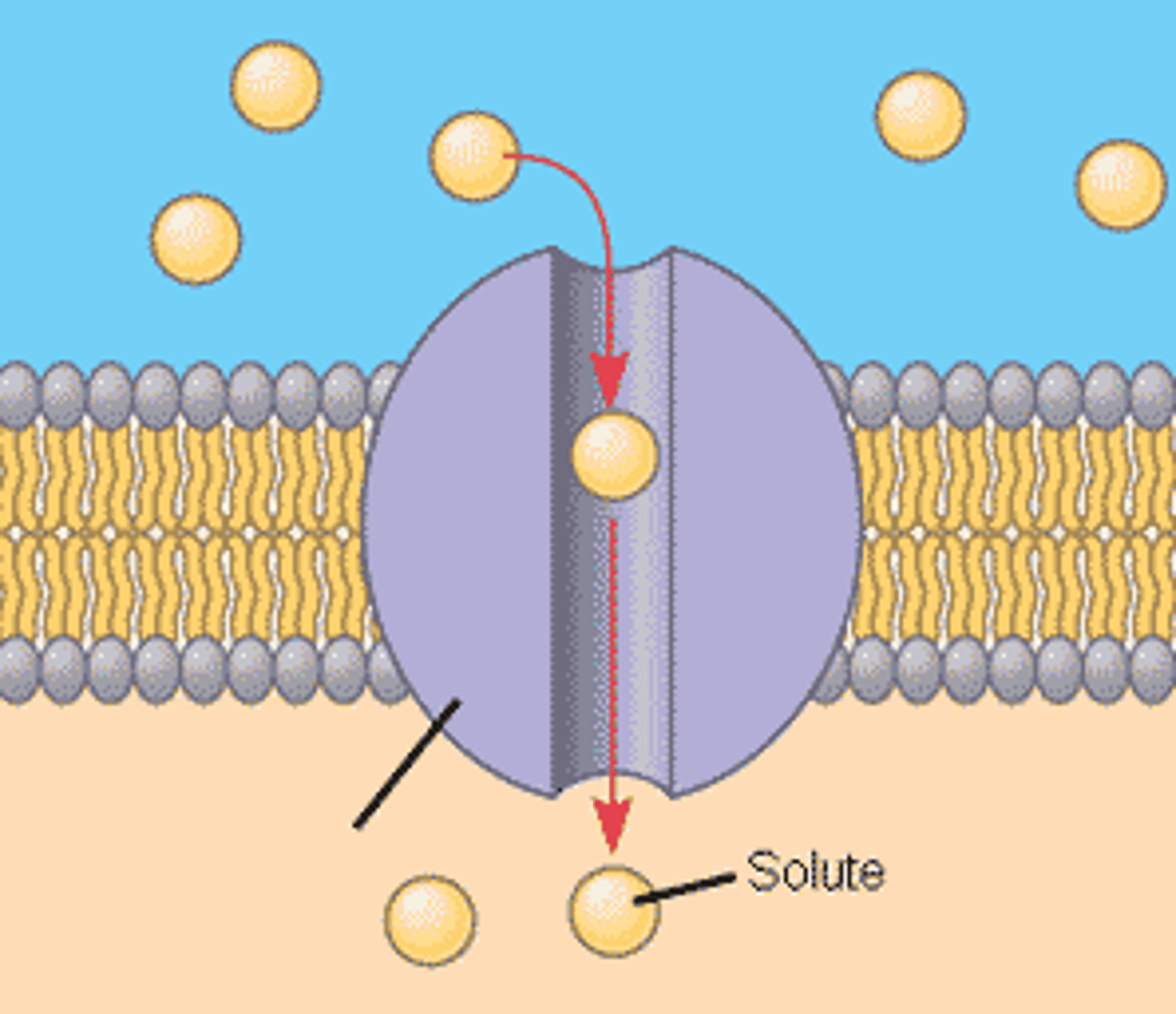
Transport Protein
A transmembrane protein that helps a certain substance or class of closely related substances to cross the membrane.
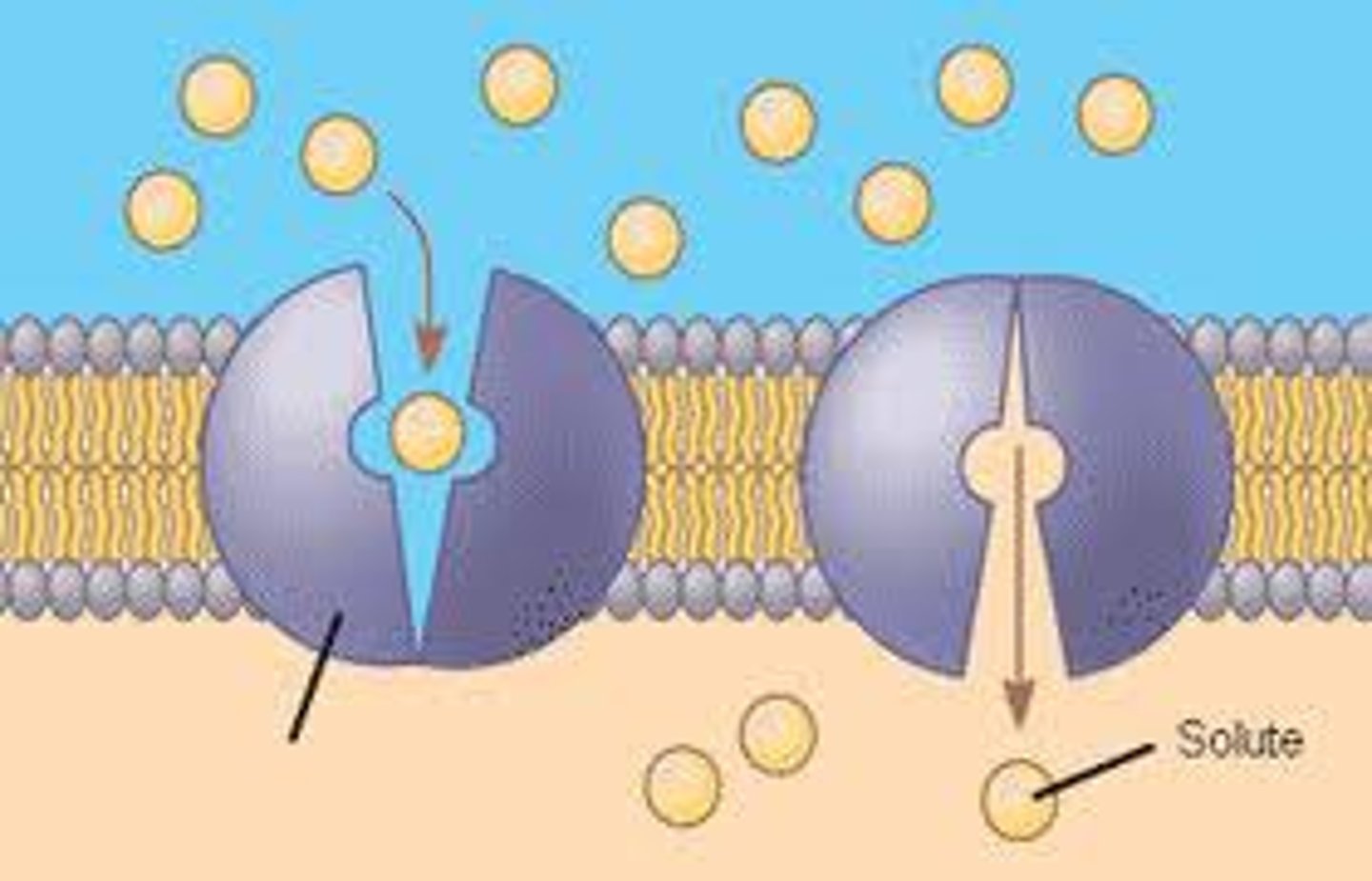
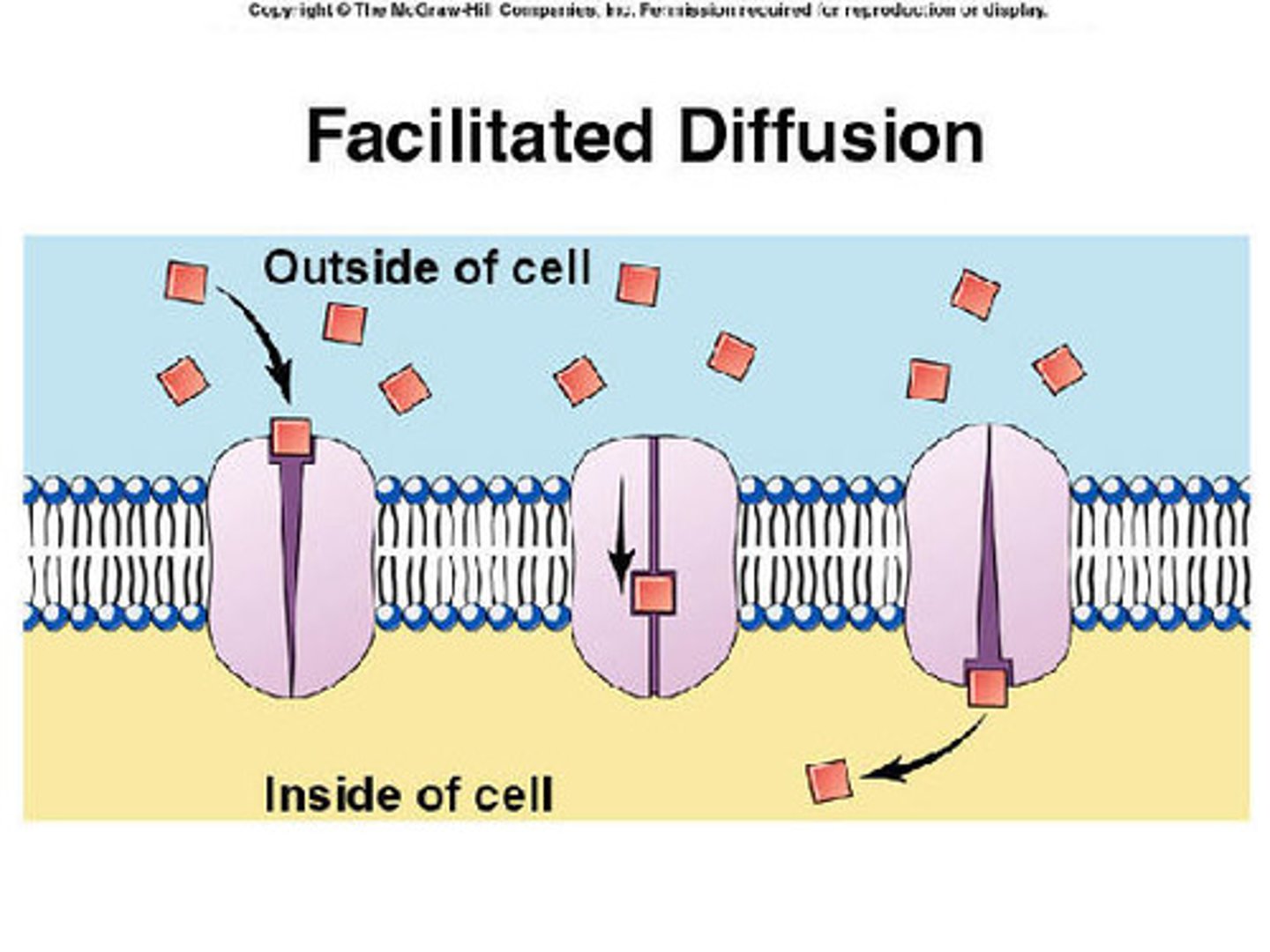
Facilitated Diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels/transport proteins (High concentration to low concentration)
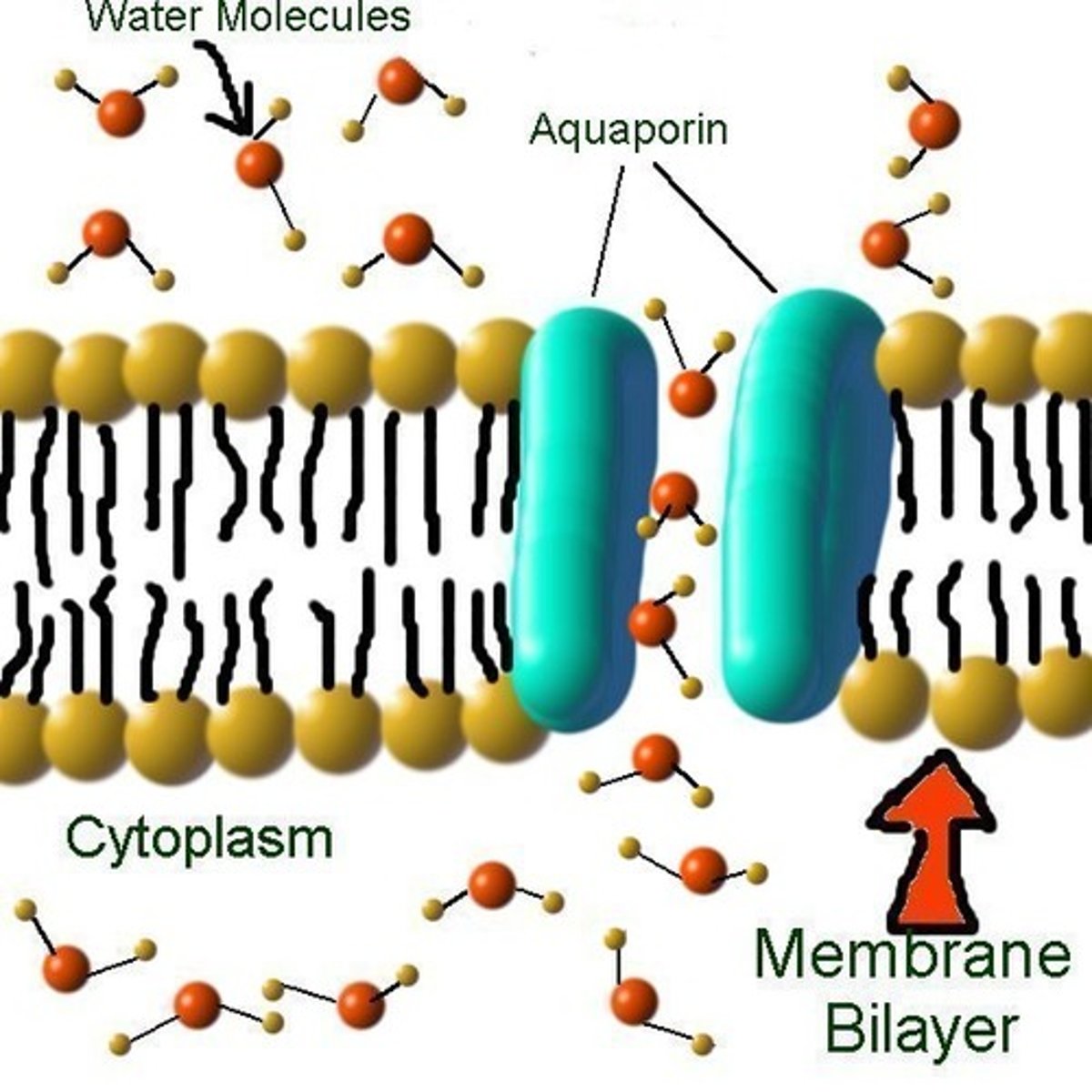
Aquaporin
water channel protein in a cell
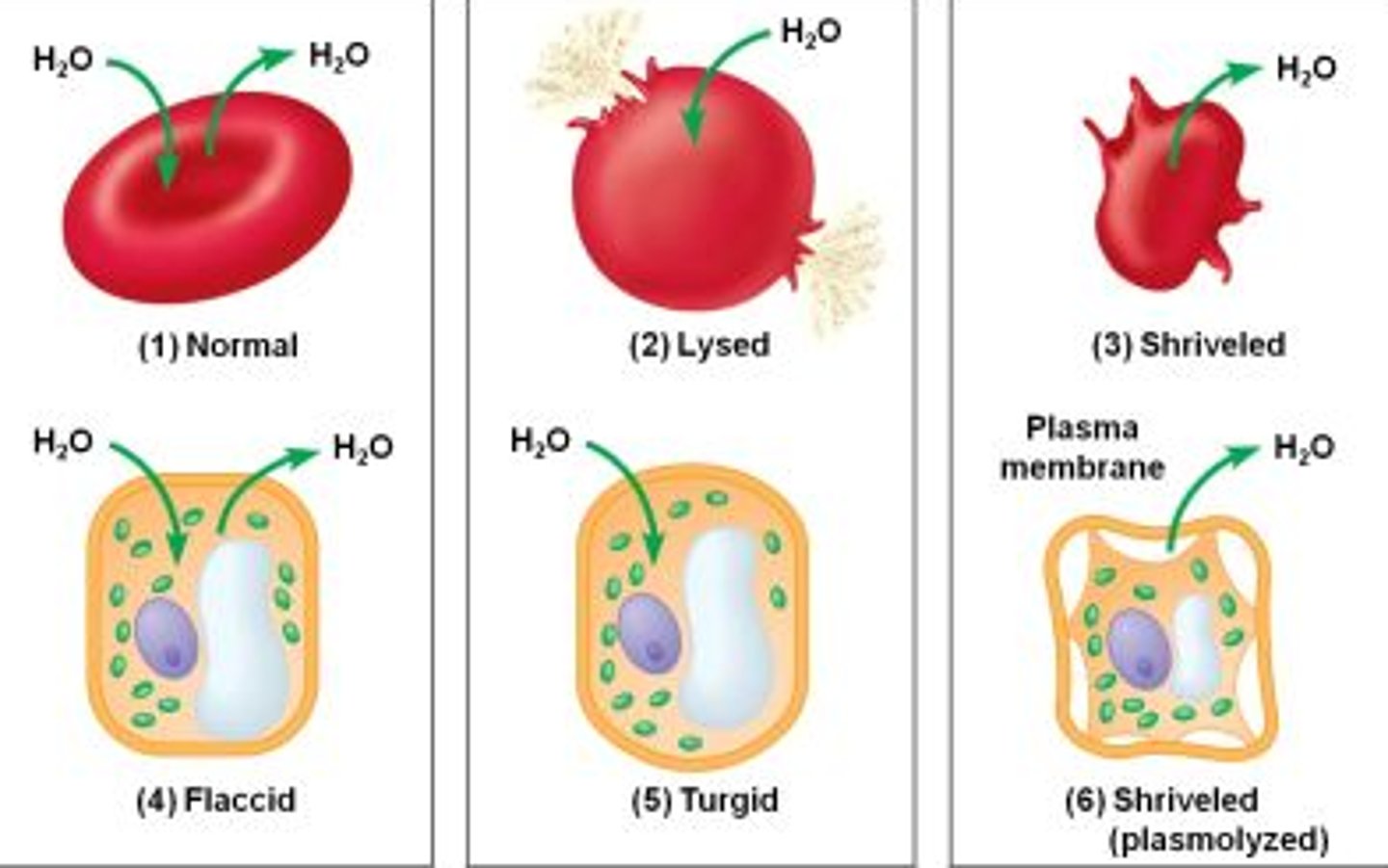
Tonicity
The ability of a solution surrounding a cell to cause that cell to gain or lose water.
Osmolarity
total concentration of all solute particles in a solution
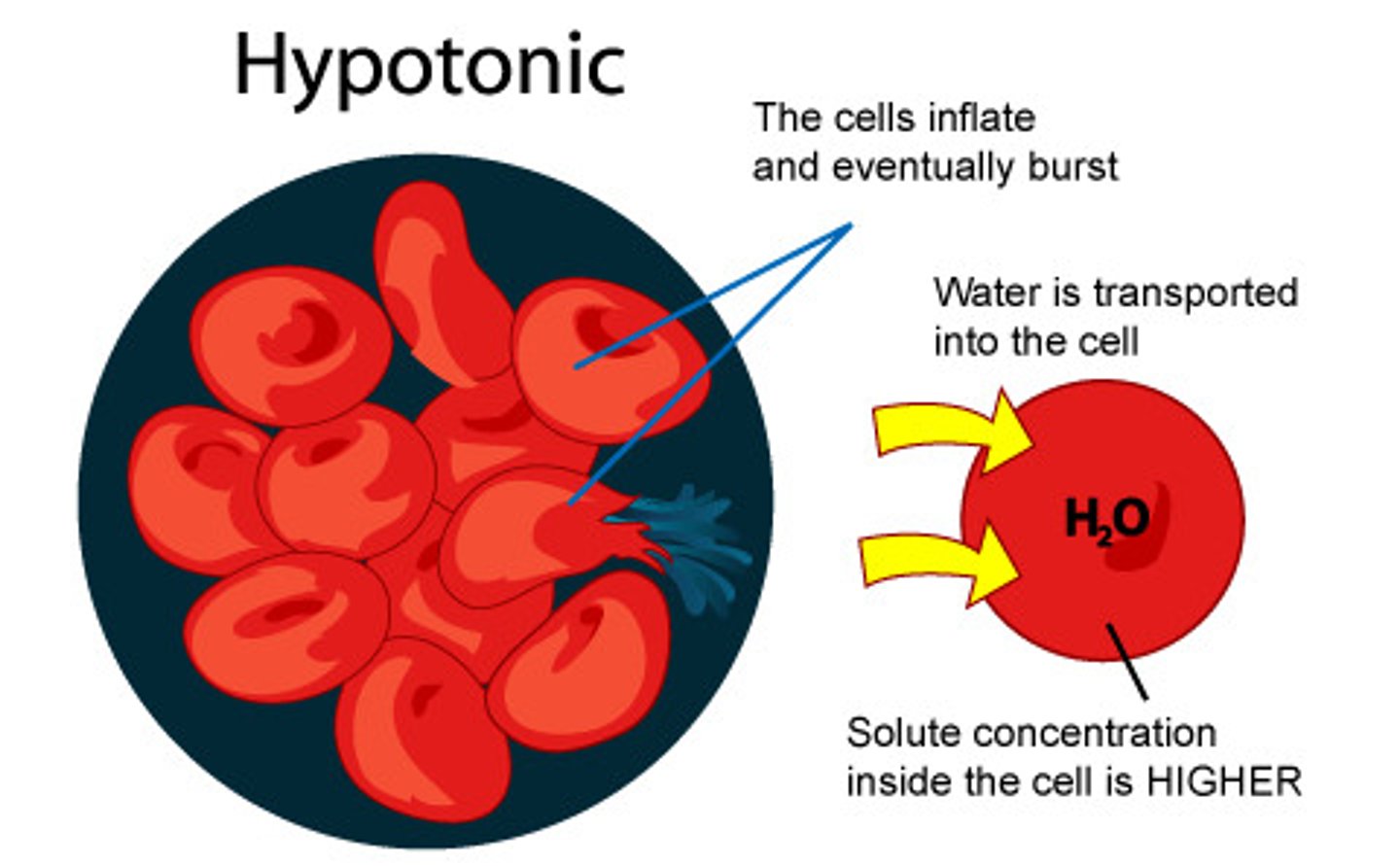
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
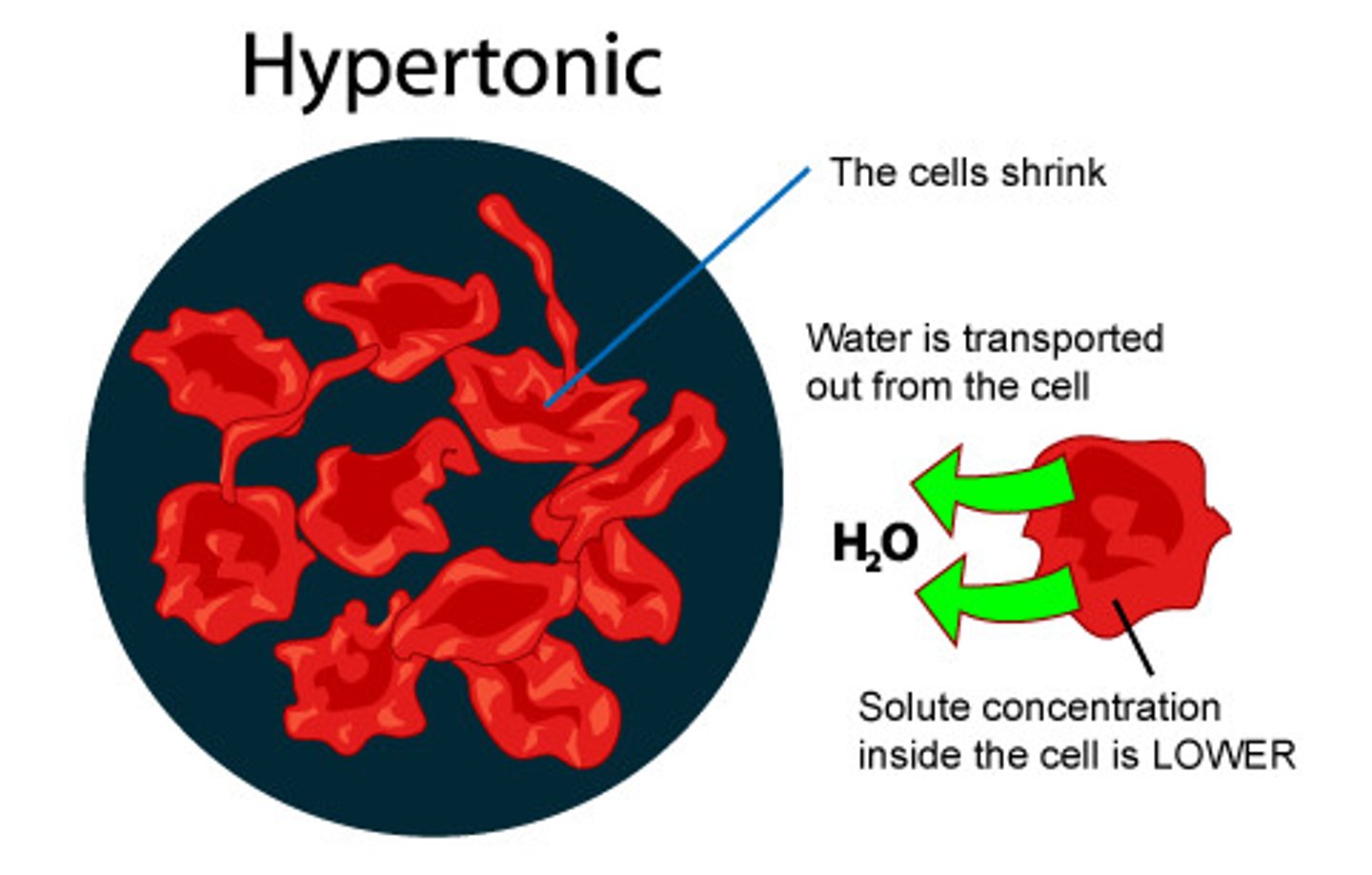
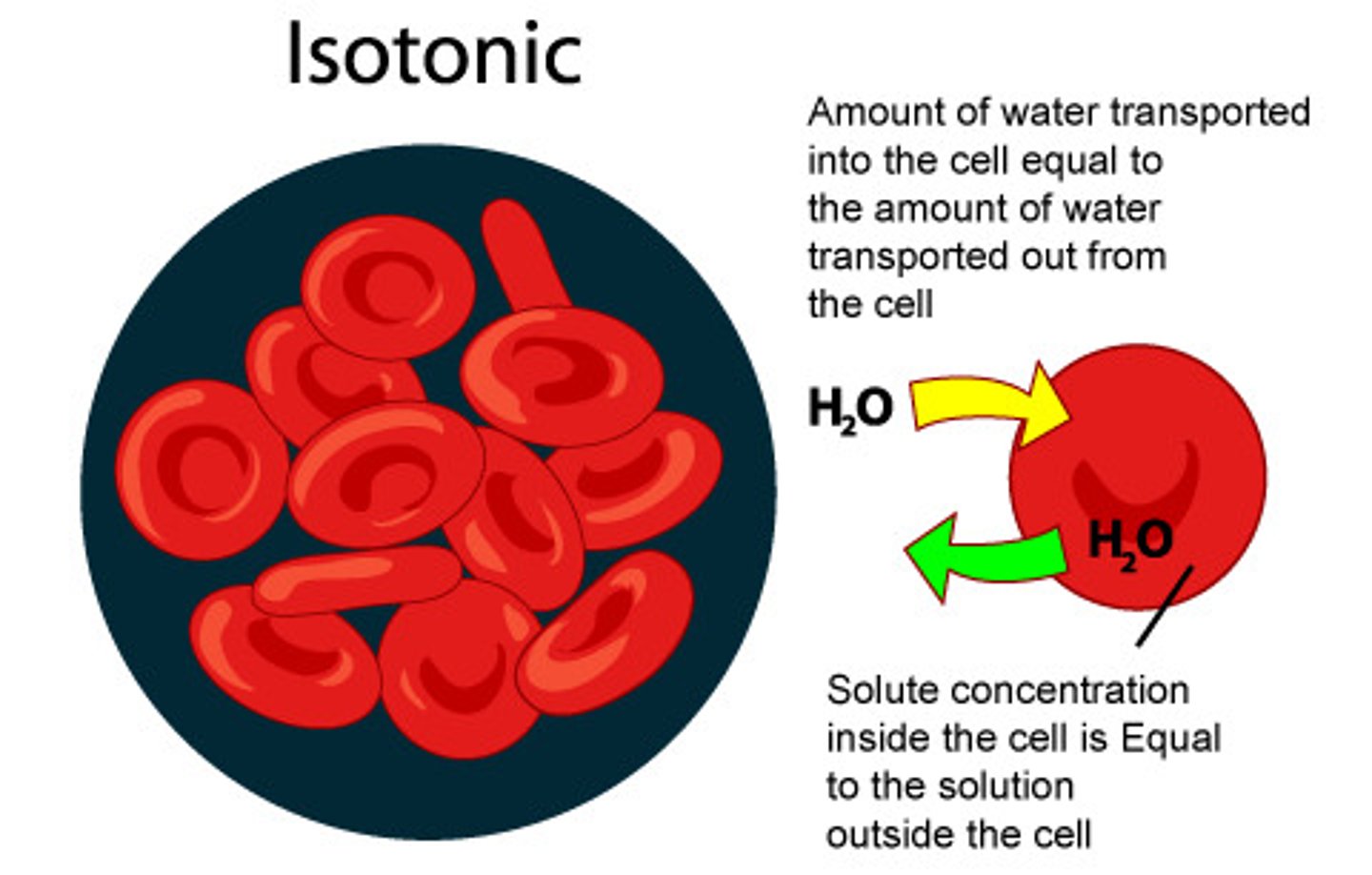
Isotonic
Having the same solute concentration as another solution.
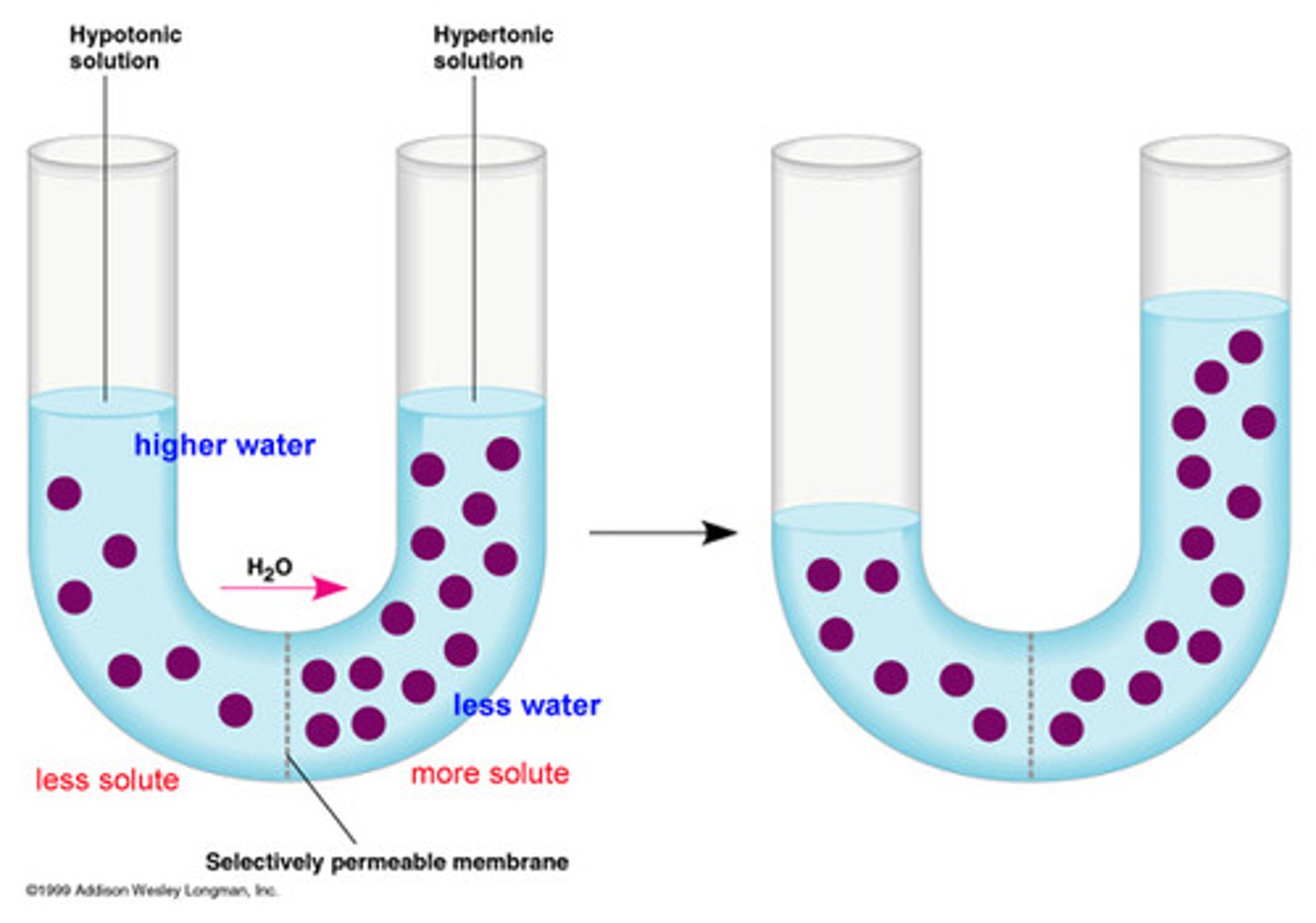
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
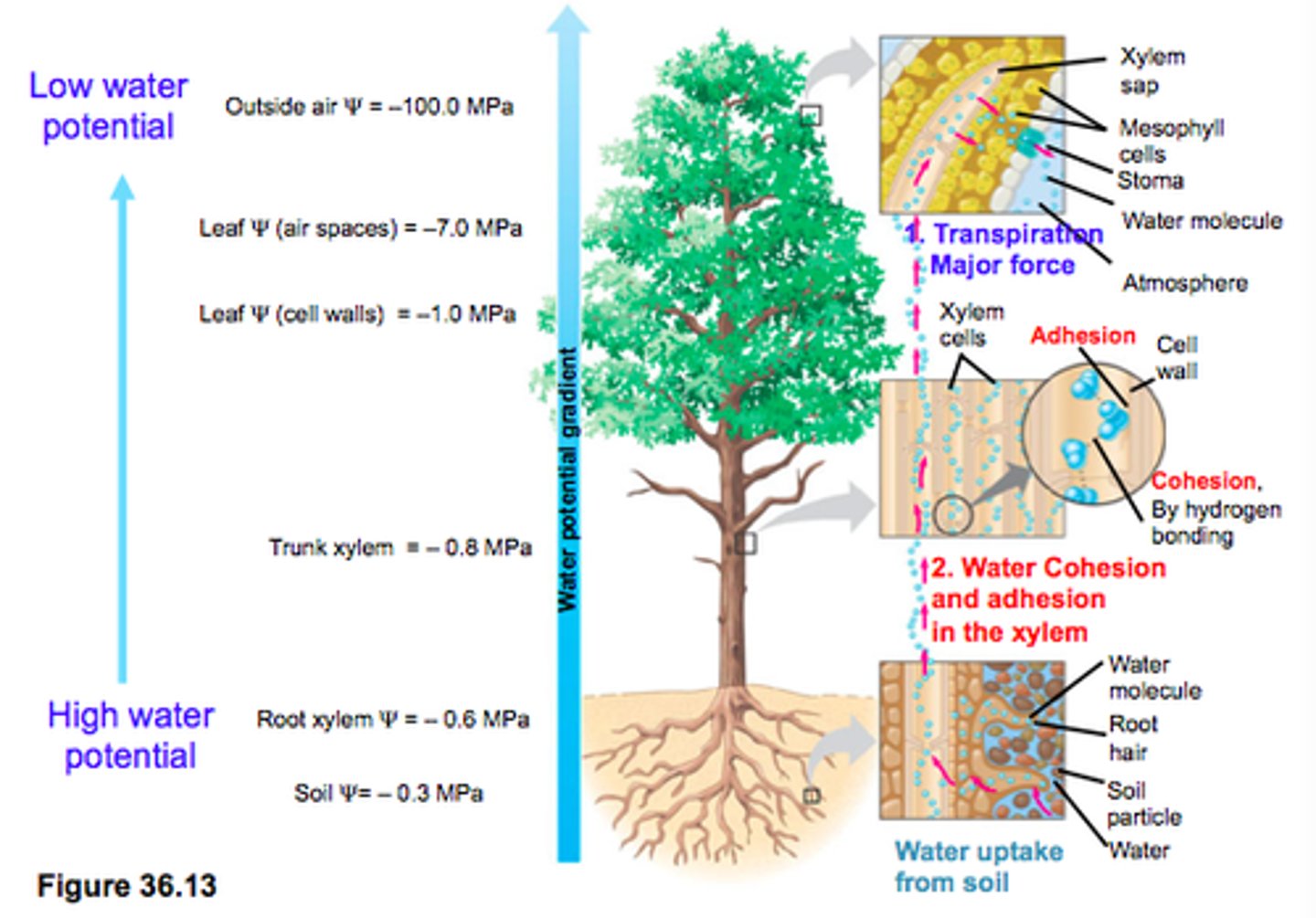
Water potential
The physical property predicting the direction in which water will flow, governed by solute concentration and applied pressure, gravity, or capillarity (difference in potential energy between a given water sample and pure water)
Active Transport
The movement of molecules from low concentration to high concentration with a direct input of energy.
Carrier Protein
A membrane protein, specifically a transport protein, that holds onto molecules and changes their shapes in a way that shuttles them across the membrane.
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
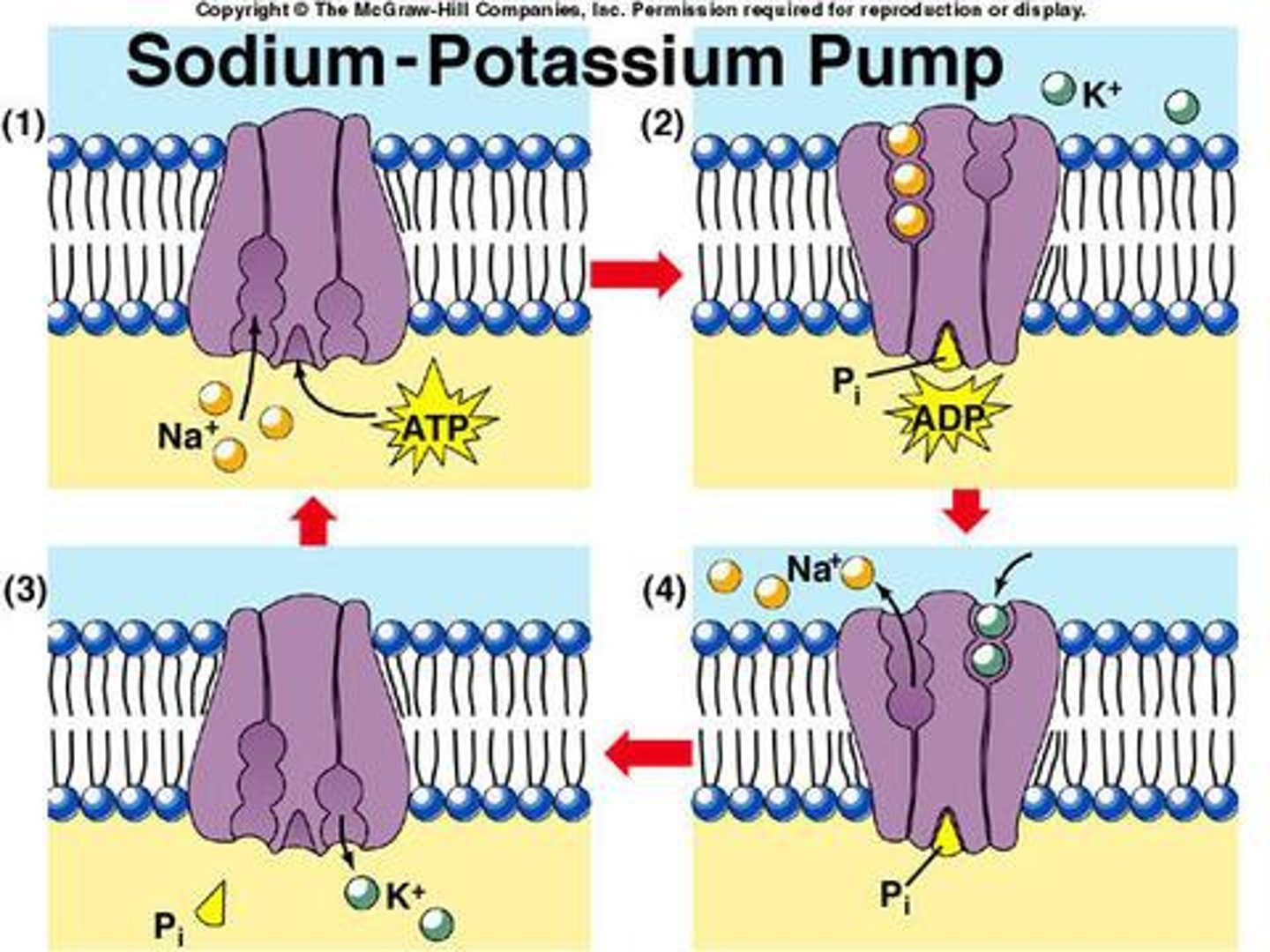
sodium-potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell
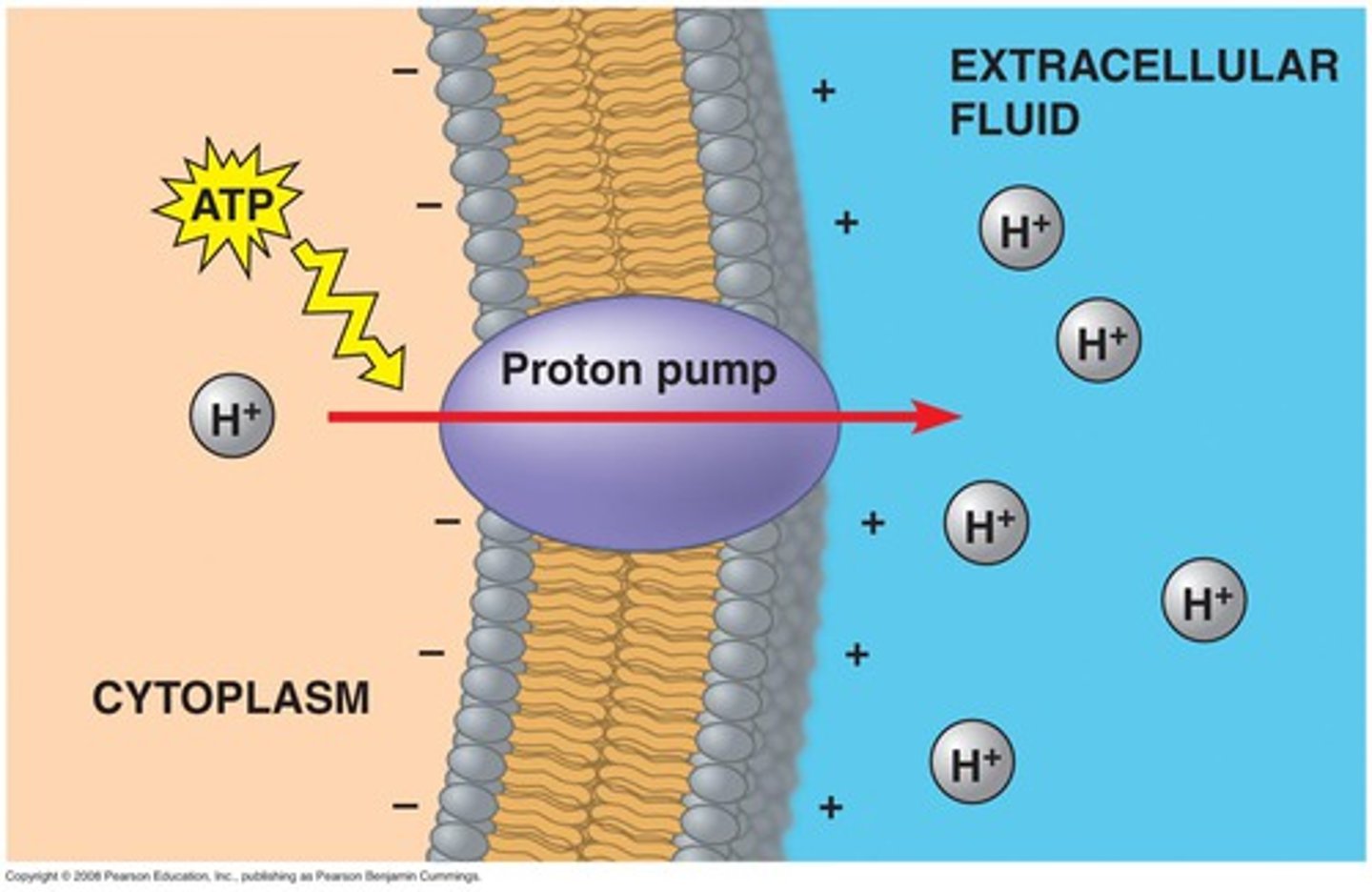
proton pump
An active transport protein in a cell membrane that uses ATP to transport hydrogen ions out of a cell against their concentration gradient, generating a membrane potential in the process.
electrochemical gradient
The diffusion gradient of an ion, which is affected by both the concentration difference of an ion across a membrane (a chemical force) and the ion's tendency to move relative to the membrane potential (an electrical force).
Membrane potential
The voltage across a cell's plasma membrane.
Cotransport
The coupling of the "downhill" diffusion of one substance to the "uphill" transport of another against its own concentration gradient.
Bulk transport
The process by which large particles and macromolecules are transported through plasma membranes. Inc. exocytosis and endocytosis
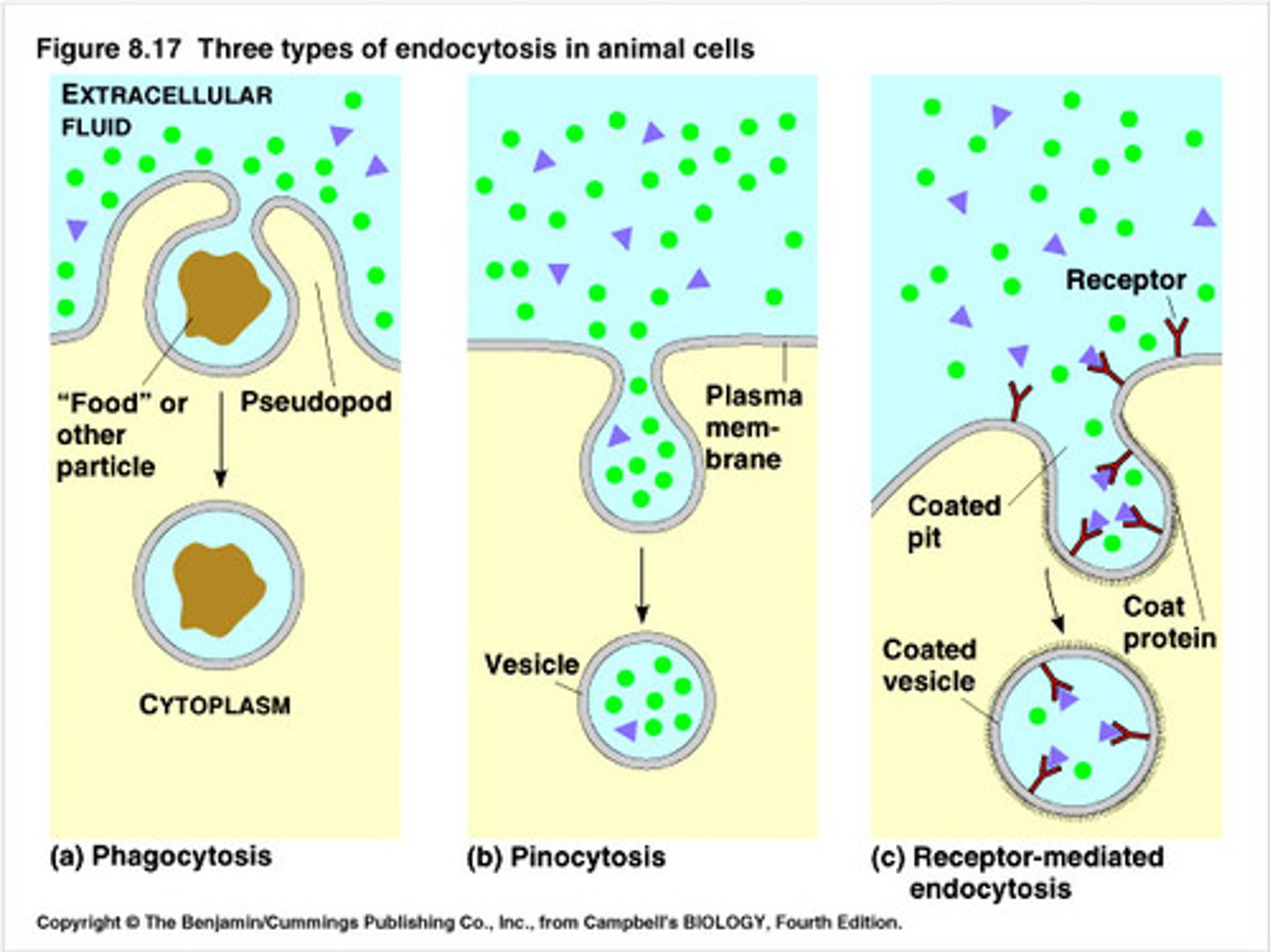
Endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
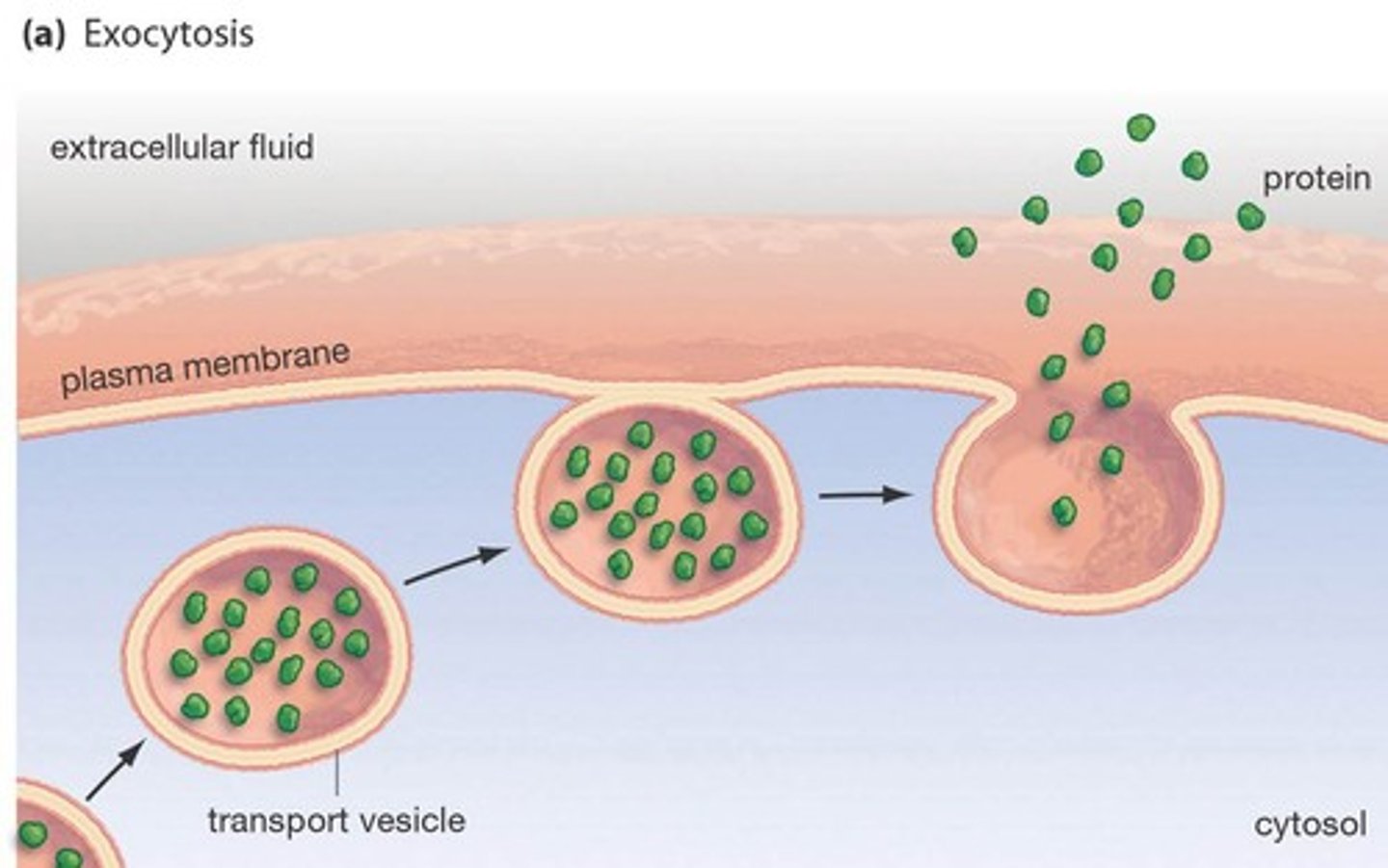
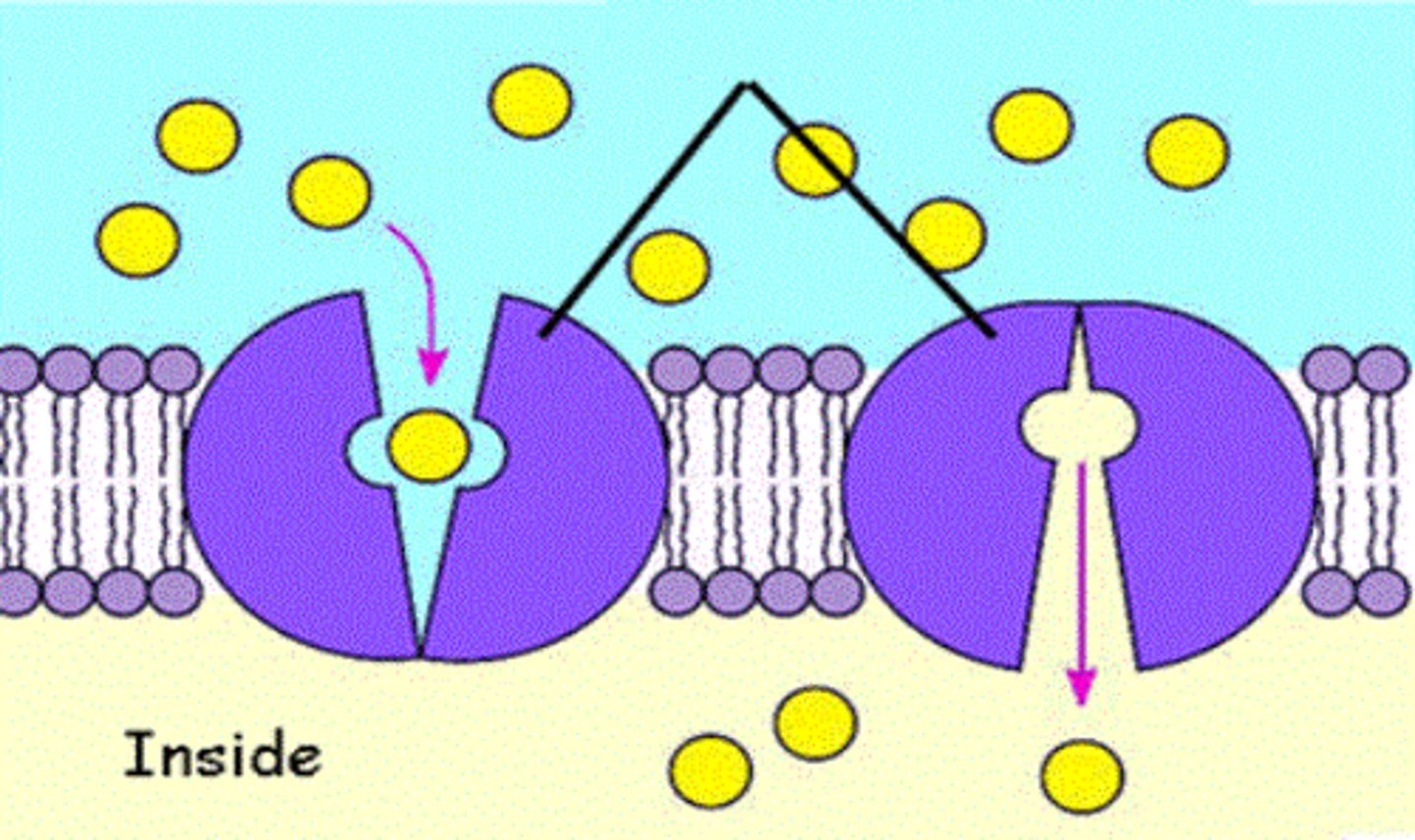
Exocytosis
release of substances out a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane.