CH. 5 Sleeping, waking, and circadian rhythms
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PSYC 305 Brain and Behavior
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Circadian rhythm
24-hour cycle that regulates our sleeping and waking phases
Zeitgebers
German time-givers
Are external cues that help us know the time (sunlight, temperature, sounds)
Superchiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
Uses light information to regulate our internal sense of time
Circadian factor
Our endogenous biological clock and external cues; control our circadian rhythm
Homeostatic factor
Our body’s natural attempt for homeostasis; control our circadian rhythm
Homeostasis
How body system regulates and maintains themselves
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Records the brain’s electrical activity (brain waves)
Electrooculogram (EOG)
Records eye movement using electrodes near the eyes
Electromyogram (EMG)
Records electrical activity from muscle fibers when muscles contract
Frequency
Number of cycles within a specific time frame
Amplitude
The height of each wave
Synchronized EEG
Neurons fire synchronously, producing brain waves with high amplitude and low frequency; happens when person is drowsy
Desynchronized EEG
Neurons fire asynchronously and produce brain waves with low amplitude and high frequency; happens when person is alert
Beta waves
Seen during alert wakefulness, desynchronization of EEG recordings
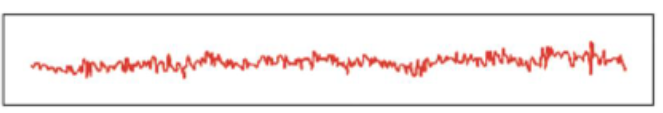
Alpha waves
Relaxation increases, and EEG shows increased amplitude
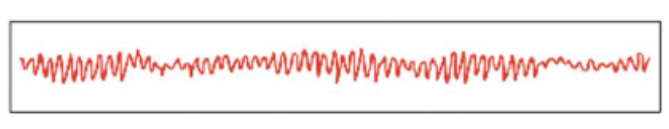
Stage 1 of sleep
Light sleep; transition between awake and asleep
Grouped with stage 2; slightly deeper
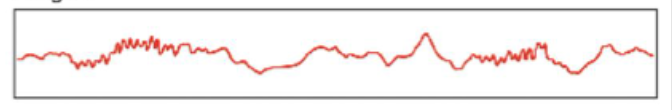
Stage 3
Delta waves
Deep sleep, slower frequency, and higher amplitude
Slow-wave sleep
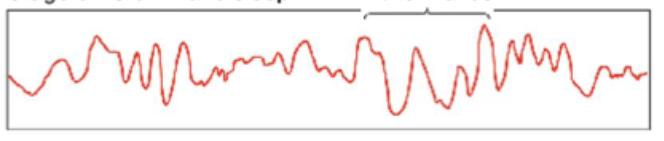
REM sleep
Dreaming occurs, sympathetic nervous system active, muscle atonia makes up temporarily paralyzed so we do not act out our dreams
The sleep cycle
We cycle through several times each nigh
Stage 3 is highest in 1st cycle, and decreases each additional cycle
REM sleep increases with each cycle
Each cycle lasts about 90 minutes
The fetus spends all its time in _____ before birth
REM sleep
REM sleep is only observed in ____ and _____
Birds; mammals
_____ do not exhibit REM sleep
Aquatic animals
_____ and ______ can sleep in one hemisphere while staying awake in the other
Killer whales; dolphins
Posterior cortical areas and the brainstem show _____ during REM sleep
Strong activation
Posterior parietal lobe
Attention, spatial and sensory integration
Frontal regions usually inactive, unless during:
Lucid dreaming
Thalamus job during waking
Generates by sending excitatory signals to the entire cortex
Deep brain stimulation:
Using electrodes to electrically stimulate the brain
Intralaminar nucleus
Region where minimal consciousness is exhibited by temporary alerts from stimulating the central thalamus
Neurotransmitters that promote wakefulness
Serotonin, norepinephrine, histamine, orexin, acetylcholine
Adenosine
This neurotransmitter accumulates during wakefulness to promote sleepiness and activation of “sleep-on” neurons
GABA
Released from the preoptic area to initiate sleep by inhibiting “waking-on” neurons
Stimulate drugs
Can enhance the activity of “waking-on” neurons (nicotine, amphetamines)
_____ blocks adenosine to stop the sleepy feeling
Caffeine
Clock gene
Molecular components for our internal clock
What did experiments using cat brains reveal about the brain stem during REM sleep
When the forebrain (cortex and thalamus) are disconnected from the pons, there is no REM sleep. If the cut was placed posterior to the pons, REM sleep was mostly normal.
When the ____ is lesioned muscle paralysis during REM sleep is lost
Pons
What causes sleep paralysis
Pons sends axons to the medulla, which inhibit spinal cord neurons
Insomnia
Inability to fall asleep and/or sleep through the night, caused by stress, anxiety, pain, caffeine, or enviromental factors
Medications for insomnia
Melatonin, antihistamines, hypnotics (benzodiazepines)
Benzodiazepines
Cause muscle relaxation and anti-anxiety effects
Target GABA-A receptors to inhibit waking-on neurons
Symptoms: Cataplexy (loss of muscle tone), sleep paralysis (inability to move upon waking or falling asleep), hypnagogic hallucinations (sensory hallucinations upon waking or falling asleep
Narcolepsy
Excessive, sometimes irresistible daytime sleepiness
May be a malfunction of REM sleep and orexin receptors
Medication(s) for narcolepsy
Stimulant drugs
Sleep apnea
Disruption of breathing during sleep
Loss of oxygen leads to poor sleeping and daytime fatigue
Snoring is a common symptom
REM sleep behavior disorder
Muscle paralysis does not occur
Likely related to a disruption in the pons
More likely to act out dreams
Treatment for sleep apnea
CPAP machine (continuous positive airway pressure)
Treatment for REM sleep behavior disorder
Options are limited