Aquatic Botany Quiz
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What distinguishes algae from higher plants?
lack of true stem, leaves, and roots
What is the kingdom name of prokaryotic algae?
monera
What is the kingdom name of eukaryotic algae?
protista
What is the kingdom name of eukaryotic angiosperms?
plantae
SAV means
submerged aquatic vegetation
HABs mean
Harmful algal blooms
What are some examples of SAVs?
pond weeds and sea grasses
Uses of algae and aquatic plants
supplemental nutrition, pest control, food, etc.
Phylum =
~phyta
class =
~phyceae
order =
~ales
family =
~aceae
genus =
genus
species =
species
What type of cell wall do prokaryotic cells have?
the same cell wall as gram negative bacteria (peptidoglycan layer)
Plasmalemma
a cell membrane in eukaryotic algae
What do prokaryotic algae have instead of plastids?
thylakoids and phycobilisomes
What stores nitrogen in a prokaryotic cell?
cyanophycin
What stores phosphorus in a prokaryotic cell?
polyphosphate bodies
Is photosystem II cyclic?
No
Is photosystem I cyclic?
Yes
Which comes first: photosystem I or II?
II
What color wavelength of light is absorbed first?
red
Eutrophic
high nutrients
mesotrophic
moderate nutrients
oligotrophic
low nutrients
What is the most ancient algae?
cyanobacteria
What is found in diatom cell walls?
silica
Dinoflagellates contain 2 flagella. (true/false)
true
What phytoplankton causes marine snow?
coccolithophores
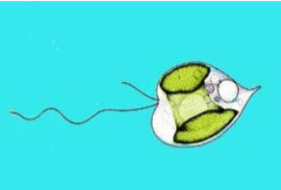
What phytoplankton is this?
Chrosophytes
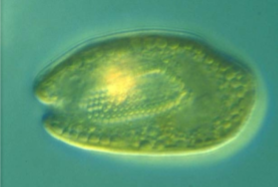
What phytoplankton is this?
cryptophytes
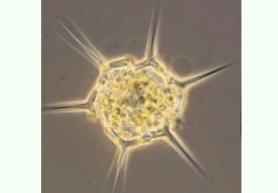
What phytoplankton is this?
silicoflagellates

What phytoplankton is this?
coccolithophores
What causes HABs?
dinoflagellates
What can make HABs dangerous to humans and other terrestrial life?
Toxins can build up in food and the contaminated water can aerosolize
What stores lipids and proteins in eukaryotic algae?
pyrenoid
What are polyglucans in prokaryotes?
complex carbohydrates that can easily be degraded and synthesized (these processes do not change osmotic pressure)
Where does photosynthesis take place?
thylakoid membrane
What chlorophyll pigment is found in all photosynthetic algae?
Chlorophyll a
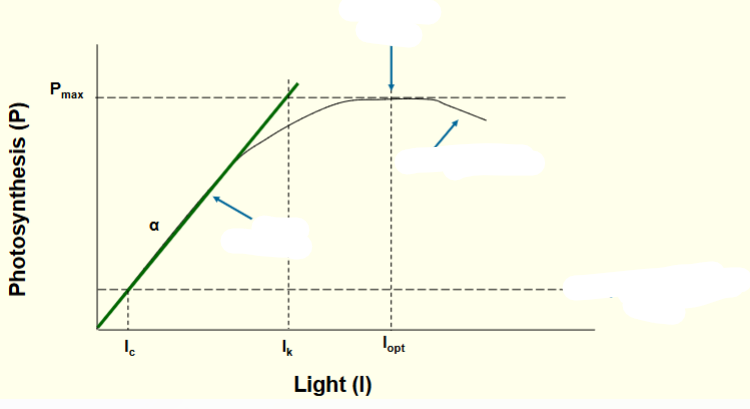
Where is the optimum light curve?
Where the curve meets maximum photosynthesis
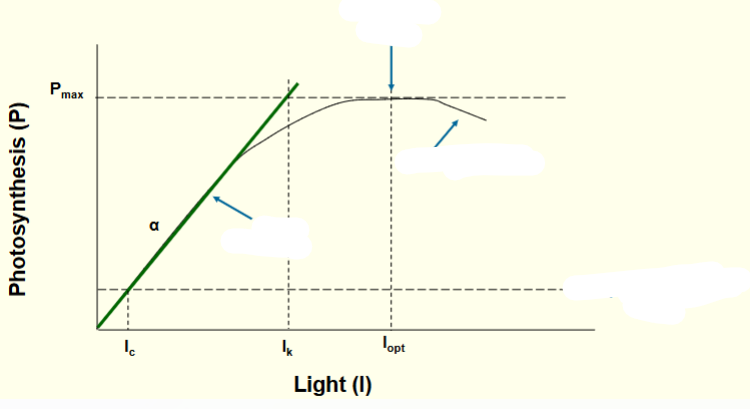
What does is mean when photosynthesis is occurring at the green line?
implies that the process is light-limited
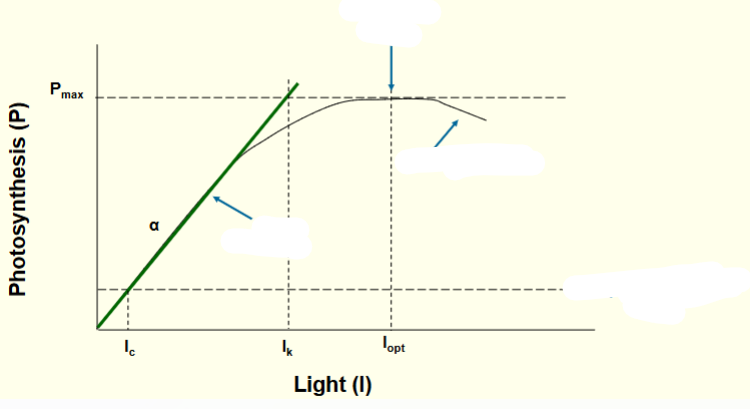
What does it mean when photoinhibiton occurs?
When too much photosynthesis causes a negative effect (too many oxidizing electrons)
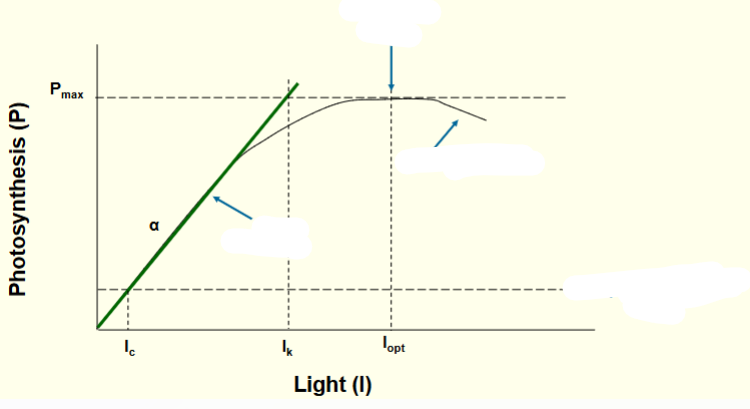
What does compensation point mean?
when the amount of photosynthesis equals respiration
Where is peridinin found?
Only in dinoflagelletes