OIA1012 PHENOLS, ETHERS, ESTERS
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Definition of Phenols
Aromatic compounds with one or more hydroxyl groups attached to the benzene ring.
Phenol Acidity
More acidic than alcohols due to resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion.
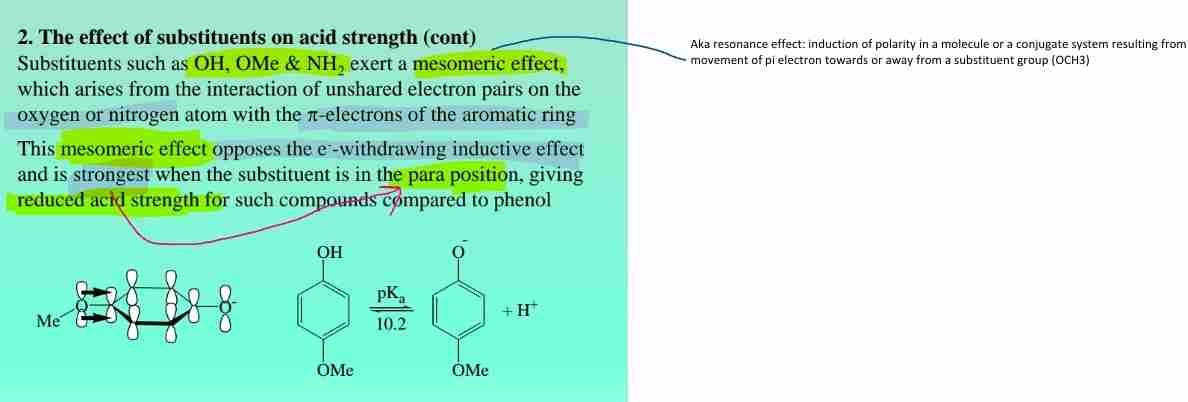
Substituent Effects on Phenol Acidity
- Electron-withdrawing groups stabilise phenoxide ion → increase acidity.
- Electron-donating groups destabilise phenoxide ion → decrease acidity.
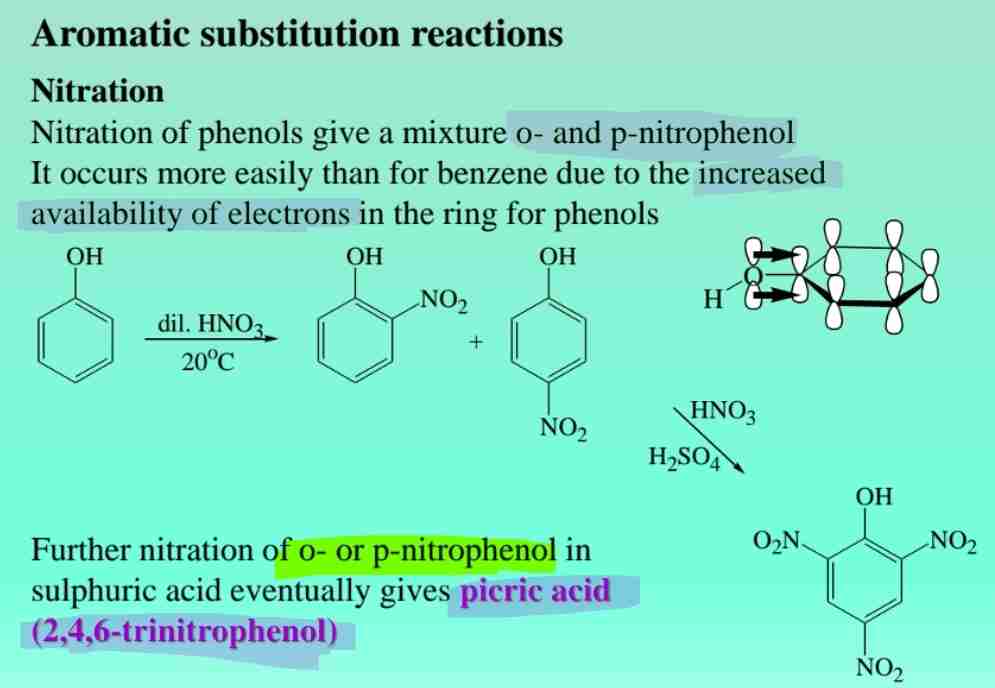
Nitration of Phenols
Produces ortho- and para-nitrophenols, enhanced by electron-rich aromatic rings.
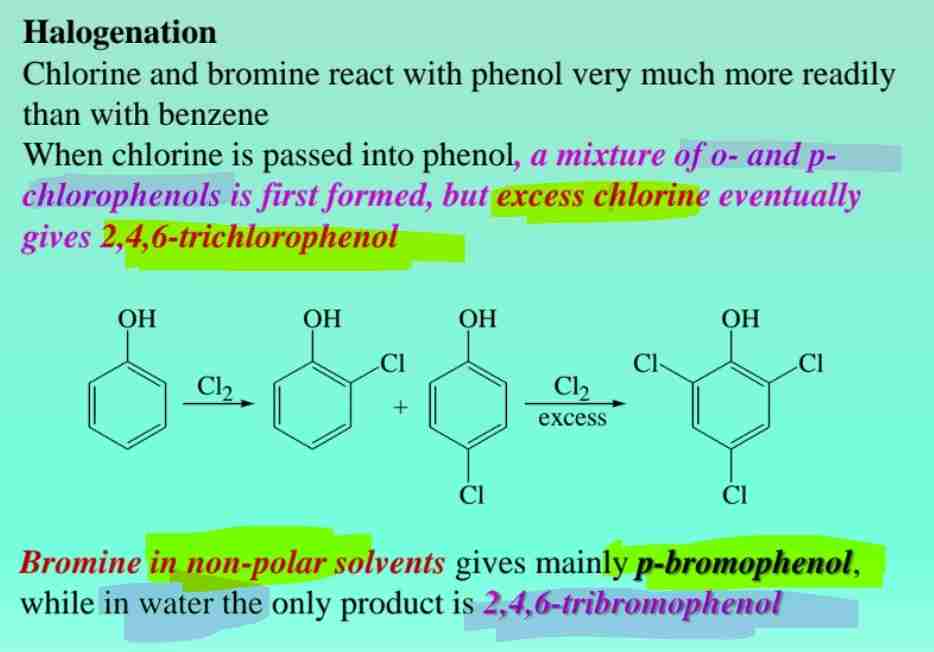
Phenol Halogenation
Phenols react readily with halogens to produce halogenated derivatives (e.g., trichlorophenol).
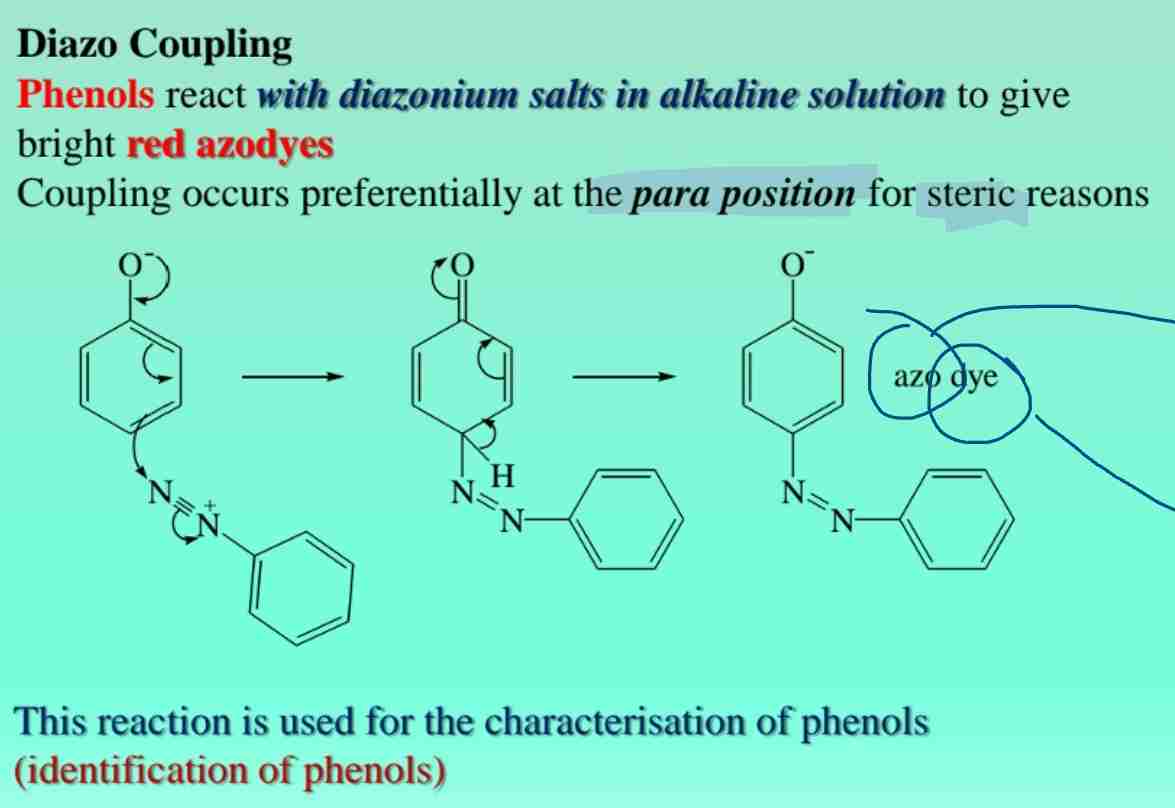
Diazo Coupling
Phenols react with diazonium salts to form azo dyes, useful in characterization.
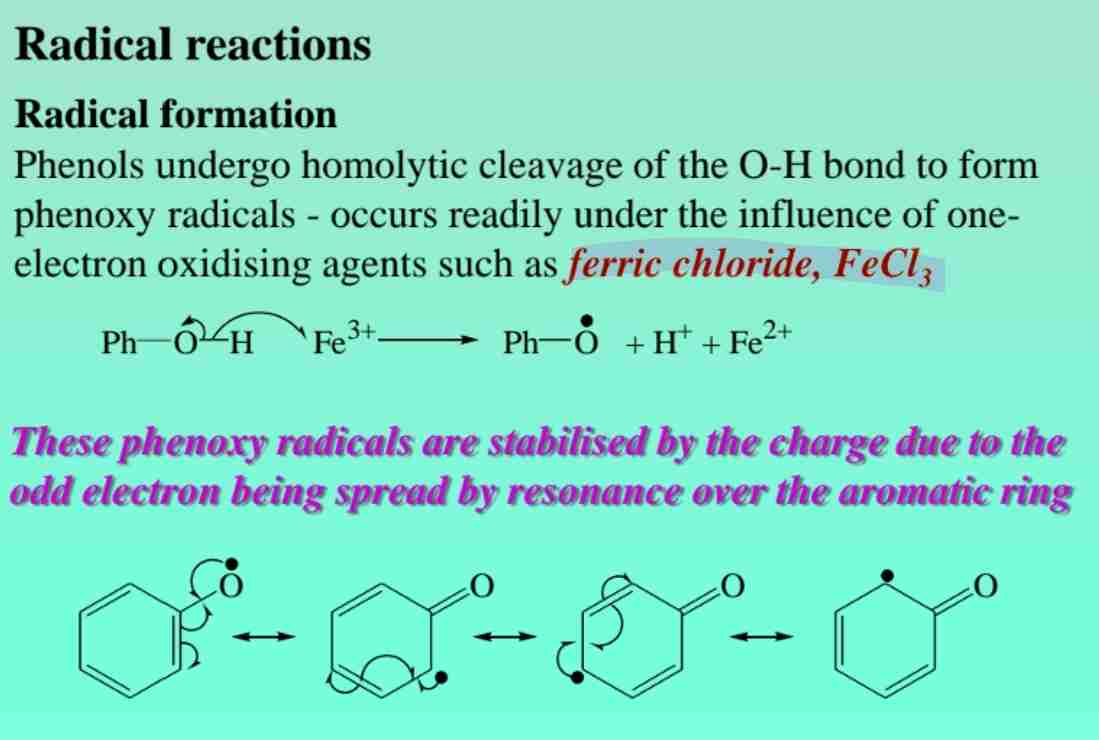
Phenol Radical Reactions
Forms phenoxy radicals, stabilized by resonance.
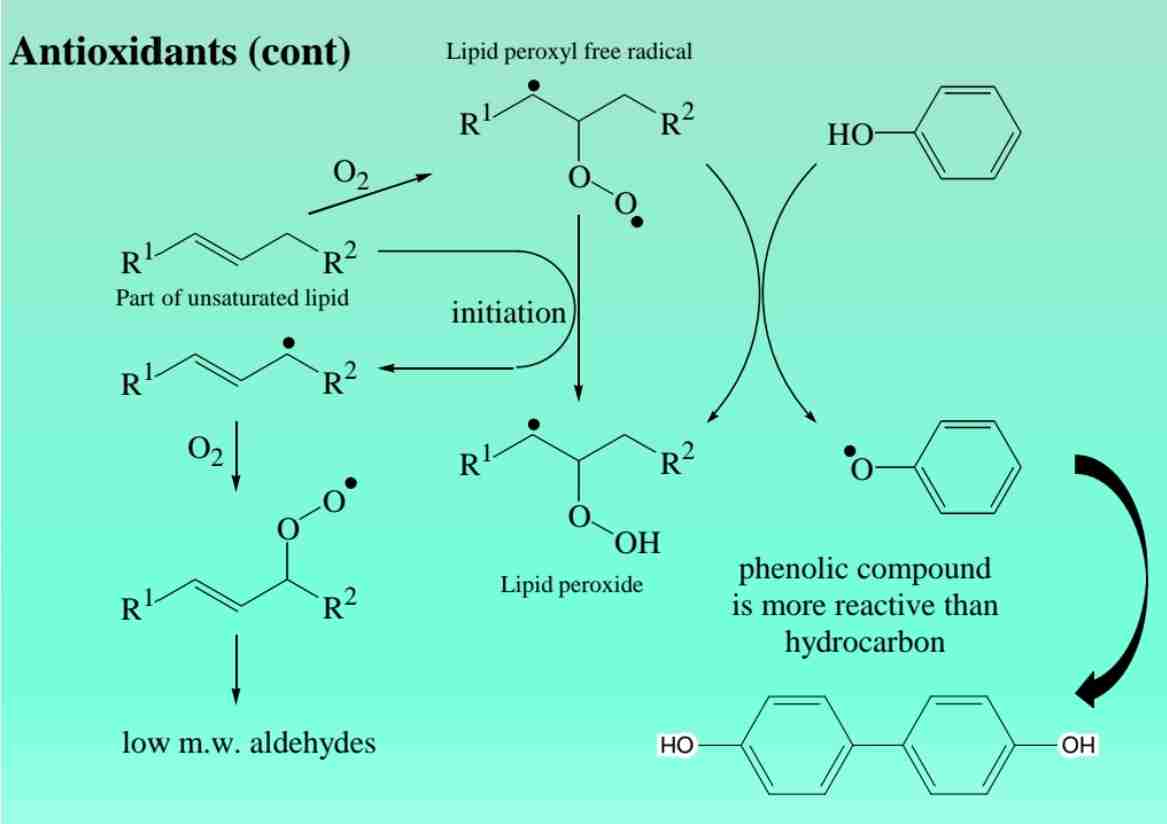
Phenols as Antioxidants
Phenolic compounds like BHA prevent oxidation in pharmaceutical formulations.
Ethers Definition
Compounds with an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups.
Physical Properties of Ethers
Low boiling points, poor water solubility, chemically inert.
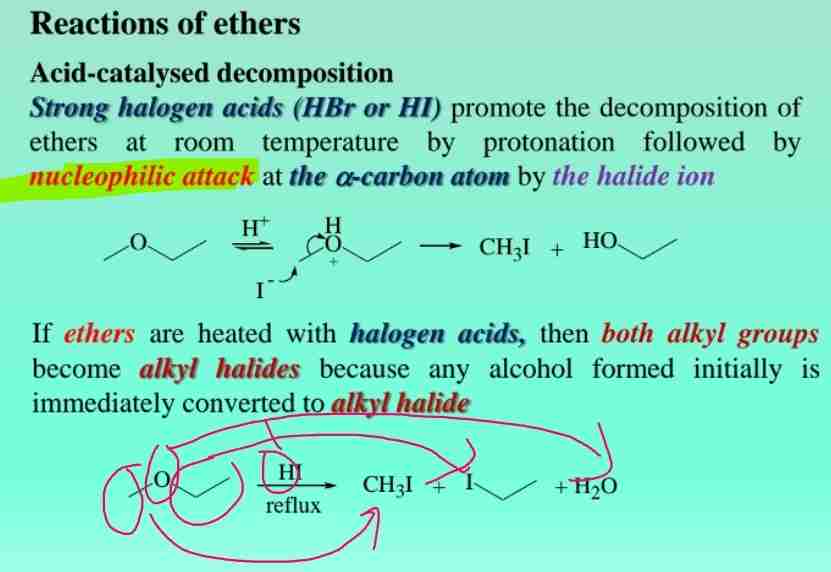
Ether reactions: Acid-catalyzed decomposition
React with strong halogen acids (HBr/HCl) to promote decomposition of ethers at room temperature followed by nucleophilic attack at the a-carbon atom by halide ion.
If ethers are heated with halogen acids, both alkyl groups become alkyl halides
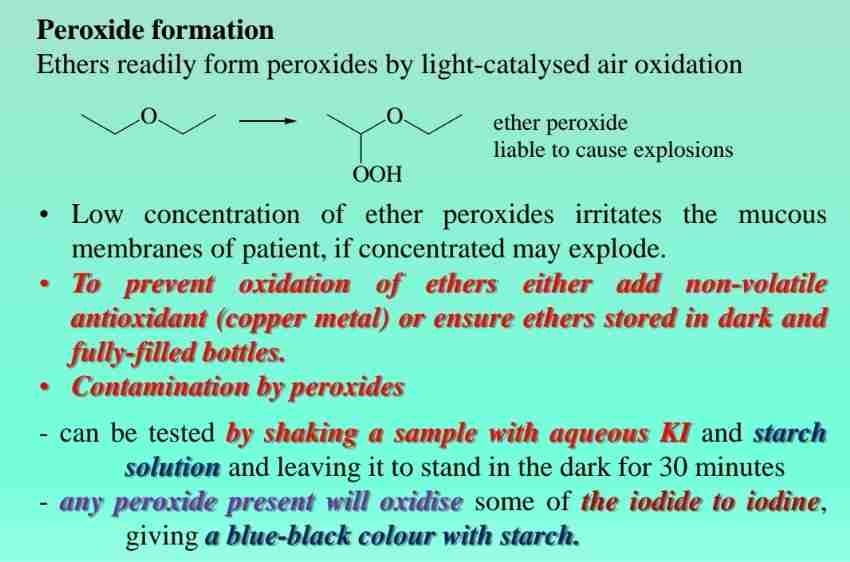
Ether reactions: Peroxide formation
Ethers readily form peroxides by light-catalyzed air oxidation
Ethers in Pharmaceuticals
Used as solvents and anesthetics (e.g., diethyl ether).

Epoxides Reactivity
Highly reactive three-membered cyclic ethers, used in sterilization (e.g., ethylene oxide).
Epoxide Reactions
React with alcohols or amines to form glycol ethers or alkanolamines.

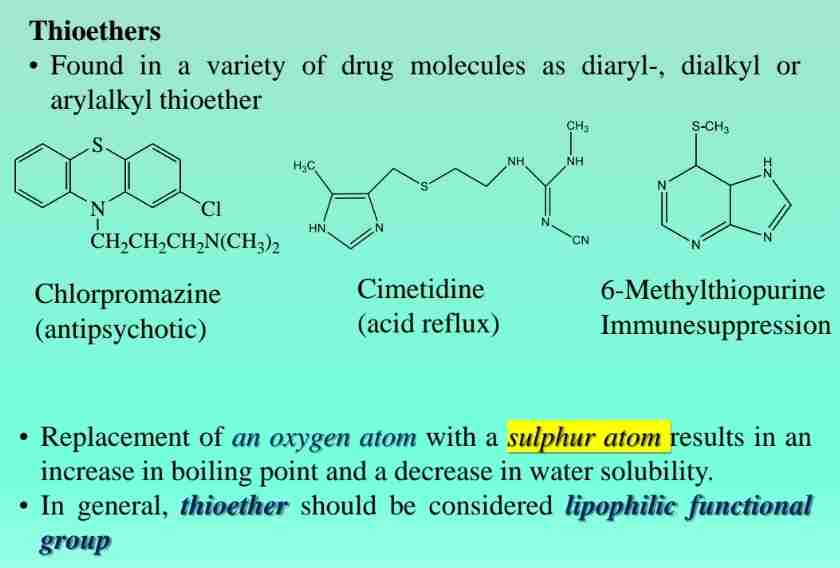
Thioethers
Sulfur analogs of ethers, found in drugs like chlorpromazine.
Esters Definition
Derived from carboxylic acids and alcohols.
Ester Physical Properties
- Low molecular weight esters have fruity odors.
- Lipophilic nature increases drug solubility.
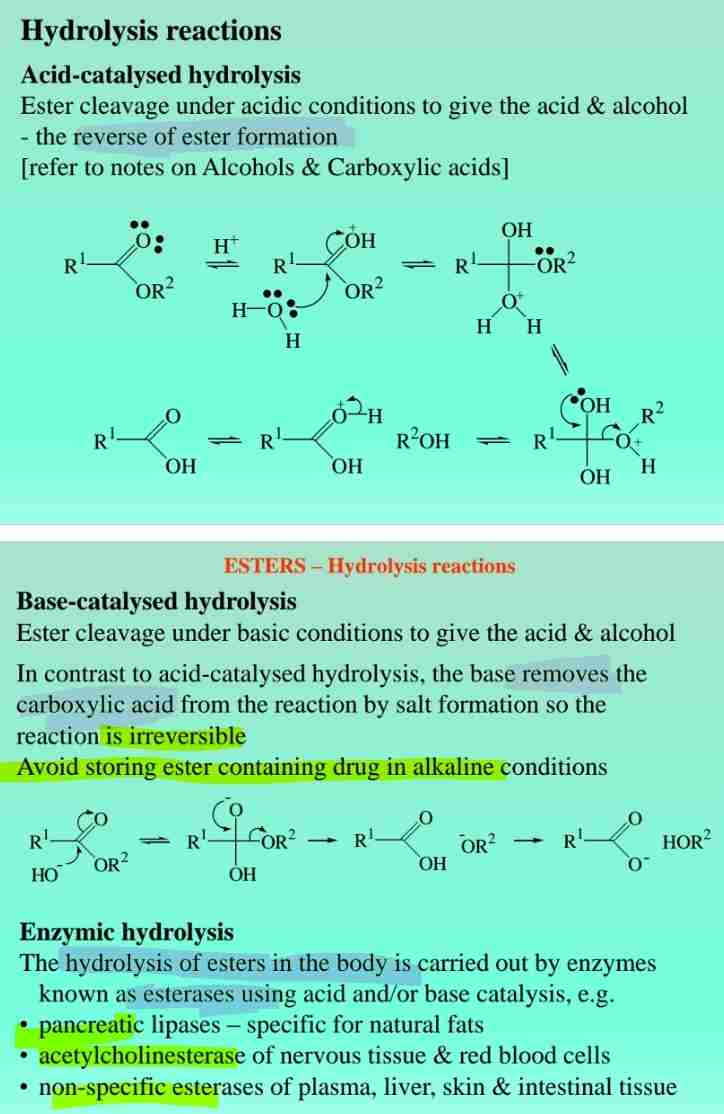
Hydrolysis of Esters
- Acid hydrolysis: Produces alcohol and carboxylic acid.
- Base hydrolysis (saponification): Produces carboxylate salt.
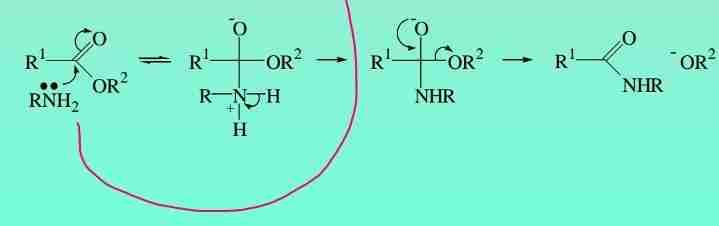
Aminolysis
Esters react with ammonia & amines to give amides
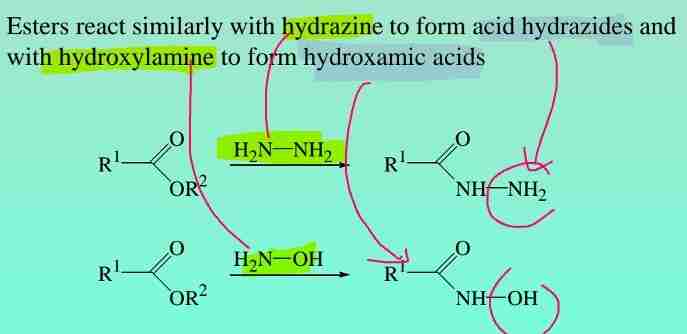
Other reactions of esters
Esters react with hydrazine to form acid hydrazides & with hydroxylamine to form hydroxamic acids
Esterases
Enzymes that hydrolyze esters in the body (e.g., acetylcholinesterase).
Lipid Esters
- Fats: Saturated glycerol esters. Fluids at room temperature.
- Oils: Unsaturated glycerol esters. Solid or semi-solid at room temperature.
Waxes
Mixture of esters of long-chain carboxylic acids and alcohols (sterols), used in ointments and tablet coatings. Hard, brittle, non-greasy solids at room temperature
Phospholipids
Glycerol-based esters, key components of cell membranes.
Sphingolipids
Found in nerve tissue, derived from sphingosine.

Ester in Drug Formulations
Prodrugs like chloramphenicol palmitate mask unpleasant tastes.
Trans Fats
Partially hydrogenated vegetable oils containing trans isomers, linked to heart disease.

Ester Reductions: Hydride reduction
Hydride reduction with LiAlH4 produces primary alcohol

Ester Reductions: Catalytic reduction
Catalytic hydrogenation of esters produces alcohols (e.g., lauryl alcohol from coconut oil).
