bio 1111 || lab 3 exam
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
genes
units of heredity and are made up of segments of DNA
gametes
sperm and eggs
46
humans have __ chromosomes in their somatic cells
locus
a gene’s specific position along a chromosome is called the _______
asexual reproduction
a single individual passes all of its genes to its offspring without the fusion of gametes
clones
a group of genetically identical individuals from the same parent
sexual reproduction
two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combinations of genes inherited from the two parents
life cycle
the generation-to-generation sequence of stages in the reproductive history of an organism
23
human somatic cells have __ pairs of chromosomes (one set from mom, one set from dad)
homologous chromosomes / homologs
two chromosomes in each pair
diploid cell
2n has two sets of chromosomes
sex chromosomes
determines the sex of the individual, are called X and Y
female
which sex is this? XX
male
which sex is this? XY
autosomes
remaining 22 pairs of chromosomes
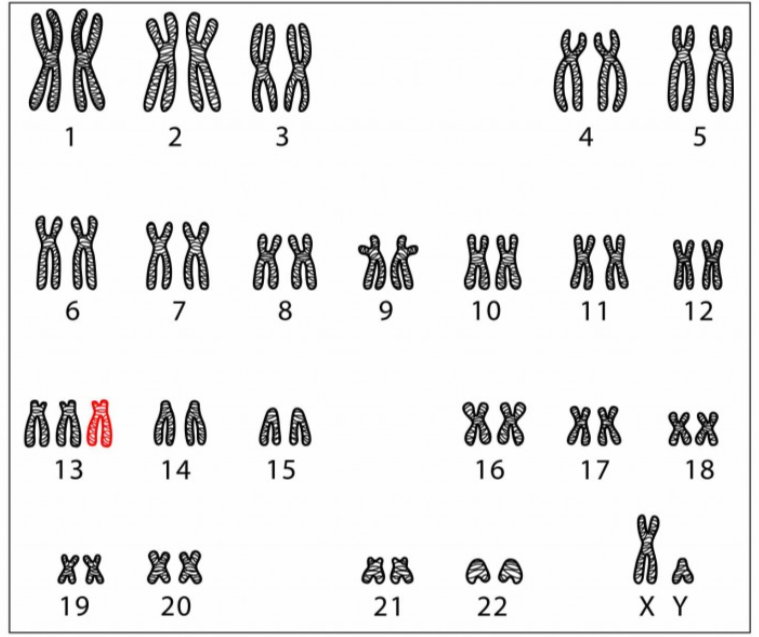
karyotype
an ordered display of the pairs of chromosomes from a cell
nonjisdunction
pairs of homologous chromosomes do not separate normally during meiosis &, as a result, one gamete receives two of the same type of chromosome, and another gamete receives no copy
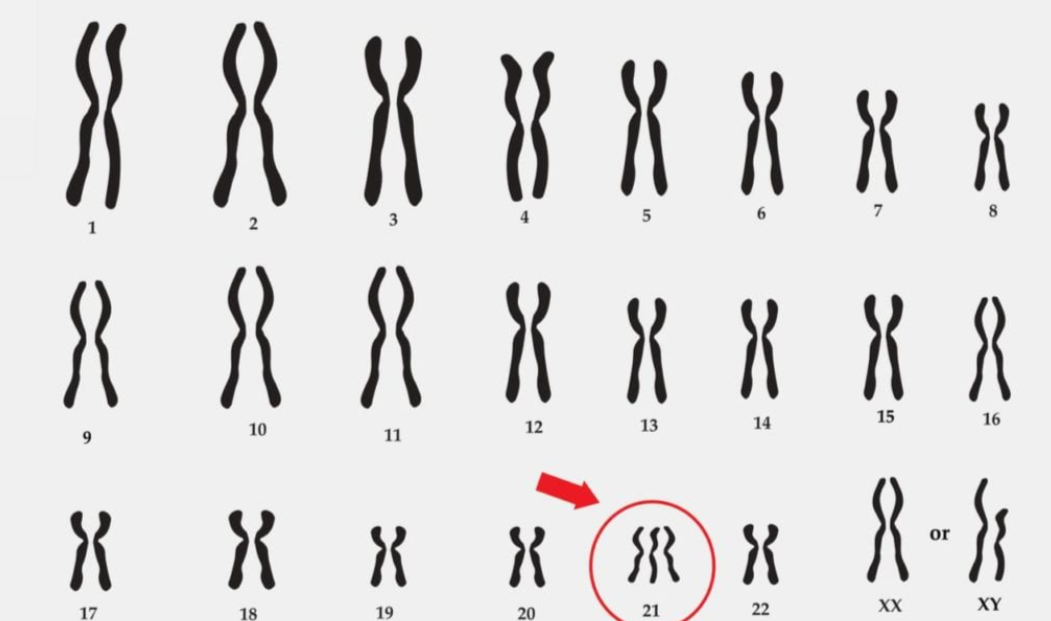
trisomy 21
what disorder does this represent?
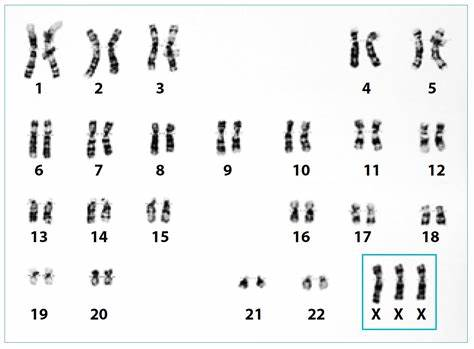
triple x syndrome
what disorder does this represent?
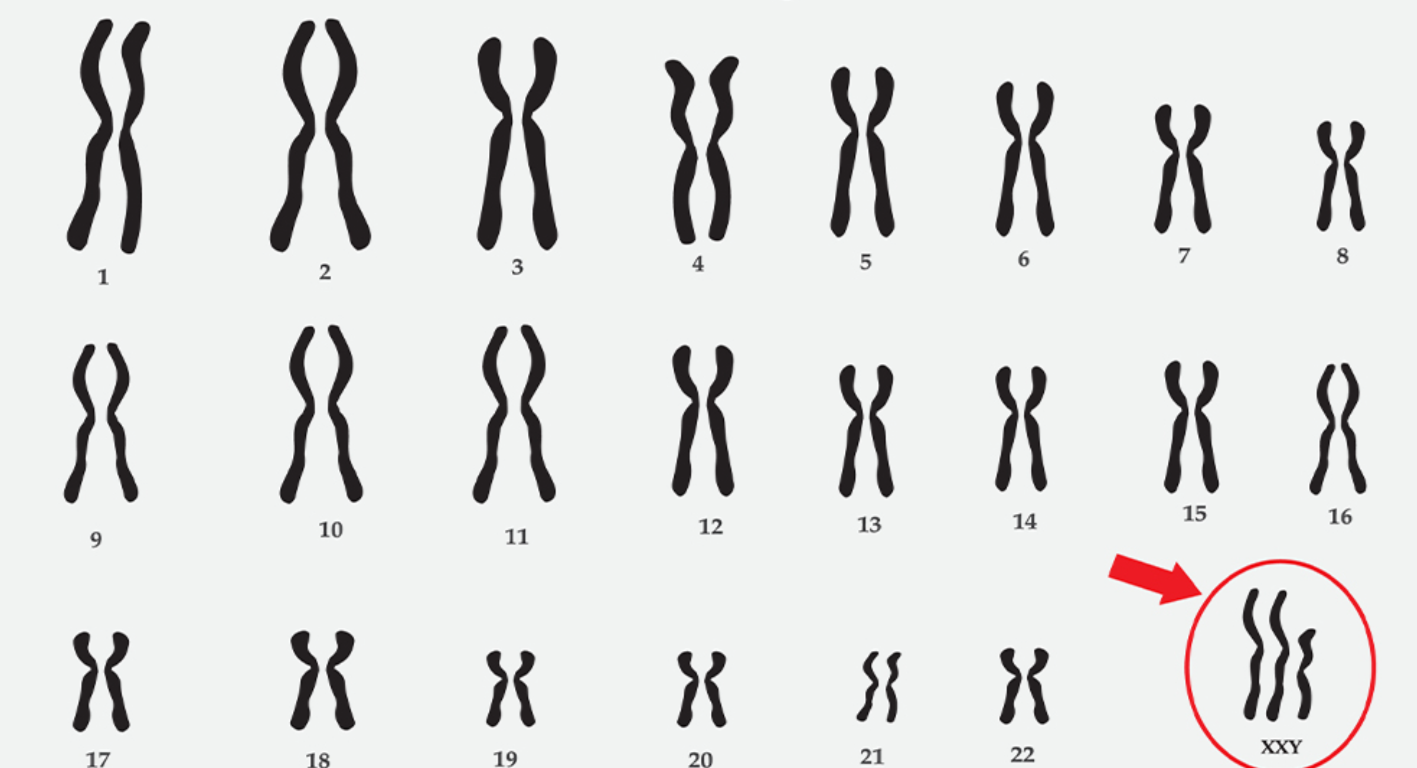
klinefelter syndrome
what disorder does this represent?
XYY syndrome
what disorder does this represent?

trisomy 18
what disorder does this represent?
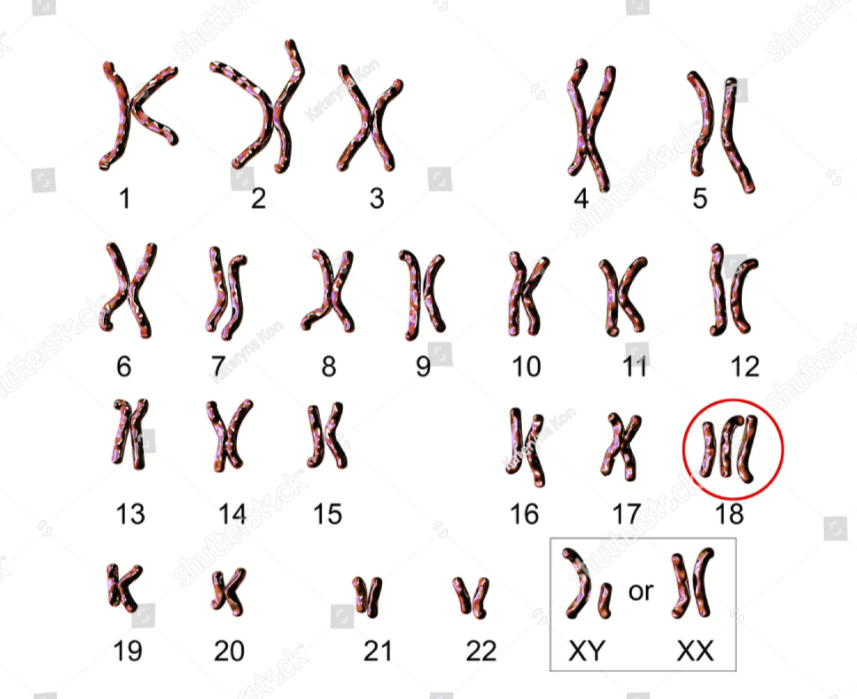
trisomy 13
what disorder does this represent?
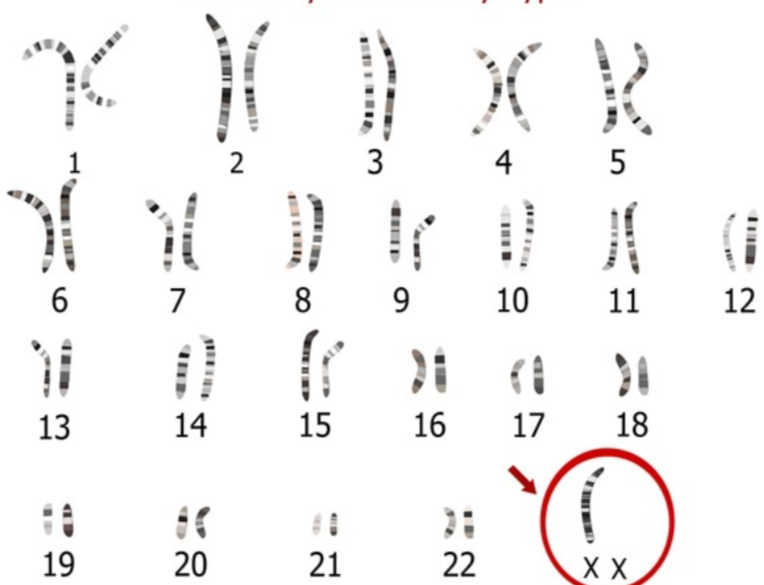
tuner syndrome
what disorder does this represent?
probability equation
# of ways event “A” can occur / total # of possible outcomes
false - always between 0-1 (as fraction/percentage)
true or false:
probability can exceed 0 and 1 — it never is between 0 and 1
rule of multiplication (the “and” rule)
determining the probability of two independent events, multiply the probabilities for each event
rule of addition (the “or” rule)
determining the probabilities of two dependent events, add the probability
heredity
the transmission of traits from one generation to the next
genetics
the scientific study of heredity
phenotype
the PHYSICAL aspect/expression of a trait
genotype
the genetic makeup of a trait
true-breeding
result when self-fertilization produces offspring all identical to the parent
hybrids (aka genetic cross)
cross-fertilization = the offspring of two different varieties
P generation
true-breeding parental plants
F1 generation
hybrid offspring
F2 generation
cross of F1 plants results in __
monohybrid cross
follows a single gene
punnett square
a physical chart that shows the potential outcomes of a cross
Mendel’s law of independent assortment
states that alleles of a pair segregate independently of other allele pairs during gamete formation
DNA structure
phosphate, sugar, and nitrogenous base
gel electrophoresis
detects the PRESENCE of DNA in a sample & the NUMBER OF NUCLEOTIDES in a fragment of DNA
electrical current
a sample which contains fragments of DNA is forced by an _______ ________ through a firm gel which is really a sieve with small holes of a fixed size
more nucleotides
will longer fragments have more or less nucleotides than short fragments?
short fragments
are able to pass through and move farther along the gel
gel
agarose
anode
positive
cathode
negative