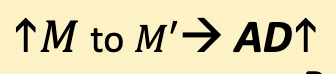Things that will actually help me during exam ECON 402
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Investment is ______ than GDP
much more
Consumption is _____ volatile than GDP
much less
Basic Business Cycle Facts: Expenditures
Consumption
Volatility: ____
Co-movement: _____
Phase shift: _____
Less volatile
Pro-cyclical
Neither
Basic Business Cycle Facts: Expenditures
Investment
Volatility: ____
Co-movement: _____
Phase shift: _____
More volatile
Pro-cyclical
Neither
Basic Business Cycle Facts: Inputs
Hours per worker
Volatility: ____
Co-movement: _____
Phase shift: _____
Less volatile (1/3)
Pro-cyclical
Neither
Basic Business Cycle Facts: Employment
Hours per worker
Volatility: ____
Co-movement: _____
Phase shift: _____
Less volatile (2/3)
Pro-cyclical
Slight Lag
Basic Business Cycle Facts: Employment
Capital
Co-movement: _____
Phase shift: _____
Pro-cyclical,
1 year lag
Basic Business Cycle Facts: Employment
Output per worker
Co-movement: _____
Phase shift: _____
Pro-cyclical
Neither
Capital lags output:
It takes time to build factories/machinery.
Employment Lag Explained
• Firms seem to respond to an increase in demand
by first asking existing workers to work longer
hours.
• After about three months, they hire more worker
Real wages co-movement
Acyclical (neither pro nor counter cyclical
Unemployment co-movement
Counter cyclical
The “Long Run”
• All inputs are flexible
• All prices are flexible
• Capital accumulation
• Technological progress
Short Run:
• Only labor is flexible
• Capital and technology are fixed
• Some prices (wages) are fixed
Quantity of Money in the economy is related to
number of dollars exchanged in transactions
“Equation of Exchange”:
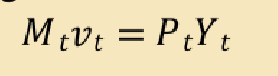
Mtvt = PtYt
Where M
money supply
Mtvt = PtYt
Where P
aggregate price level
Mtvt = PtYt
Where Y
real output
Mtvt = PtYt
Where v
velocity of money: average number of times each dollar is spent
The Quantity Theory of Money
The price level(P) and the rate of inflation(\pi) are ultimately determined by changes in the level and growth rate of the money (M)supply
The central bank controls the money supply, has ultimate control over the rate of inflation.
The Quantity Theory of Money: Assumptions
Real GDP is independent of M and P
Velocity is constant
The Quantity Theory is a good theory of inflation for ____ run but NOT ____ run
long, short
Hyperinflation is when inflation is greater than __
50
What causes hyperinflation?
• Hyperinflation is caused by excessive money
supply growth.
• When the Central Bank prints money, the price
level rises.
• If it prints money rapidly enough, the result is
hyperinflation.
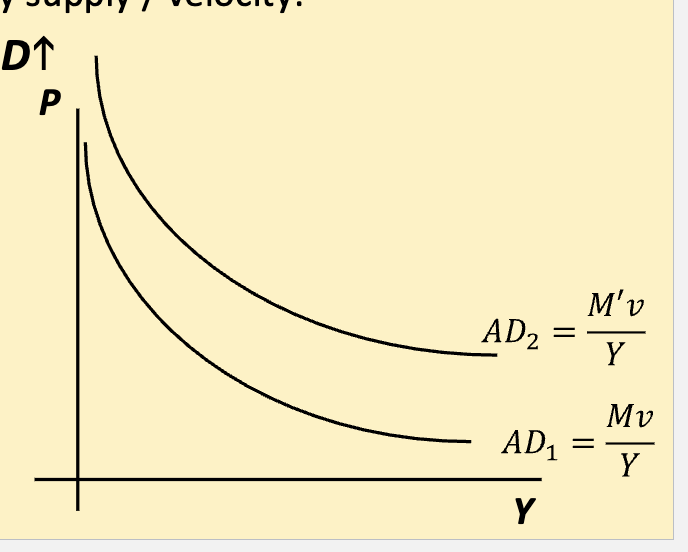
Aggregate Demand (AD
relationship between
quantity of output demanded and the aggregate
price level
Aggregate demand formula
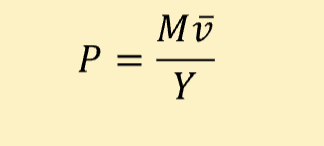
Shifts in Aggregate Demand:
Changes in money supply / velocity:
• Increase M or Increase V𝑣→ AD
• ↓ 𝑀 or ↓ 𝑣→ AD↓