Low Vision Assessment
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
measuring visual function in visually impaired patients
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
why is it important to measure visual acuity?
to compare with ‘normal’ performance
to set a baseline for monitoring
quantify subjective impressions of visual performance
early detection + diagnosis
assess benefits of optical devices
refraction procedures and decision making
social-legal purposes
what should an ideal chart for low vision assessment involve?
moveable
variable illumination
high contrast
range of sizes
what are the common test charts used in the LVA?
snellen chart
logMAR chart
bailey lovie distance visual acuity chart
early treatment of diabetic retinopathy study (ETDRS)
keeler A chart
what are the advantages and disadvantages of snellen charts?
advantages:
cheap and readily available
measures baseline VA
predicts + verifies magnification for low vision aids
disadvantages:
no control over crowding - 6/60 line have one letter therefore no crowding, 6/36 has 2 letter etc.
non-uniformity in letter size progression
inability to easily score letter by letter acuity
due to non-uniform progression it is inaccurate for testing low vision patients
what are the advantages and disadvantages of logMAR charts?
advantages:
equal number of letters on every line
logarithmic progression of letter size
letter by letter acuity
more popular in research setting
disadvantages:
large size
cost
what are the corrections factors for the Bailey Lovie test chart?
designed to be used at 6m
3m: add 0.30
1.5m: add 0.60
0.75m: add 0.90
1m: add 0.80
what are the correction factors for the ETDRS chart?
designed to be used at 4m
2m: add 0.30
1m: add 0.60
0.5m: add 0.90
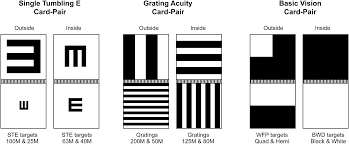
when and how is the Berkeley Rudimentary Vision Test used?
used when it is not possible to use a letter chart for VA
tested at 1m (100cm) and 0.25m (25cm)
consists of three card pairs, each containing 2×25cm square cards hinged together (4 panel faces/card)
single tumbling E: used for measuring VA with a single optotype and px has to identify the direction the legs are facing
grating acuity card pair: px has to identify if the strips are orientated horizontally or vertically
basic vision card test: tests 2 aspects of vision:
white field projection: 2 card faces are used (one black with white quadrant and one is divided into black and white halves) + px has to identify the location of the white area
black white discrimination: one card face is all black and one is all white and the px has to tell which one is black and which is white
what is the Freiburg Visual Acuity Test?
BRVT but computerised
uses Landolt’s C
how can distance VA be measured remotely?
using the home acuity test
developed by MEH
can be printed out and sent to px or ask them to print it out
carried out at 150cm/190cm - send a string to the px that is of this length
what is contrast threshold?
the smallest difference in luminance than an observer can detect
values vary from 0 to 1
can be expressed at a percentage
what is contrast sensitivity?
reciprocal of contrast threshold
what is contrast sensitivity function?
a plot of contrast sensitivity over a range of spatial frequencies
what are the four contrast sensitivity tests?
functional acuity contrast test (FACT)
Pelli-Robson letter chart
Mars letter contrast sensitivity test
Regan & Bailey-Lovie low contrast acuity chart
what does the functional acuity contrast chart look like?
spatial frequency increases as you go down
contrast decreases as you go across

how is the Pelli-Robson chart scored?
either record letter by letter - each letter being 0.05
or record the line if the px gets 2/3 on that line
why is it important to measure contrast sensitivity?
indicates what everyday tasks a px is likely to find difficult
correlates better than VA with the performance of daily tasks e.g. reading and mobility
poor contrast sensitivity means a px will likely not benefit so much from optical aids - electronic aids are more suitable
to determine whether to prescribe a monocular or binocular low vision aid
what are the three reading charts available and what do they measure?
they measure near VA and reading speed
Bailey Lovie reading test - unrelated words
MNREAD acuity chart - sentences
IReST - paragraphs
what are the different ways of recording near VA?
point system - one point is 1/72 inch
N notation - n is the point size of the print
sloan M - common in US
keeler A - A1 subtends an angle of 5 minutes of arc
jaeger notation - different depending on chart used
what is the MNREAD chart?
a near chart with each sentence having the same no. of characters and spacing between sentences + words
hence it can measure speed (in words/min.) and VA (in log)
done at 40cm
add a correction factor if done at a different distance
why is measuring reading ability important?
reading is the primary rehabilitation goal by most low vision individuals
what affects reading ability?
acuity reserve
contrast reserve
field of view
central scotoma
how many words per minute are needed for:
optimum reading
fluent reading (pleasure reading)
spot reading
optimum reading: 300wpm
fluent reading: 160wpm
spot reading: 40wpm
what are the requirements for fluent reading:
acuity reserve
contrast reserve
scotoma diameter
field of view
acuity reserve: 3:1 (needs to read N4 if wanting to reading N12 comfortably)
contrast reserve: 10:1
scotoma: 4 degrees
FoV: 4-6 characters
what are the requirements for optimum reading:
acuity reserve
contrast reserve
scotoma diameter
field of view
acuity reserve: 6:1
contrast reserve: 30:1
scotoma: 0 degrees
FoV: 4-6 characters
what are the requirements for spot reading:
acuity reserve
contrast reserve
scotoma diameter
field of view
acuity reserve: 1:1
contrast reserve: 3:1
scotoma: 30 degrees
FoV: 1 character
how are visual fields measured?
amsler chart for central vision
arc perimeter
scanning laser ophthalmoscope
microperimetry - allows compensation for poor fixation
automated perimetry
goldmann manual perimetry
why is measuring visual fields important?
it is a diagnostic test
allows for functional assessment of the extent, location and quality of areas of the best vision
help determine what LVAs and rehabilitation strategies will be useful
gives us information on how well the px is performing in real life conditions
how do you assess binocular vision?
cover test
stereopsis
titmus
frisby
TNO
what is the definition of QoL?
‘An individual’s perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards and concerns’ - World Health Organisation
what do QoL questionnaires assess?
functional capacity
social interactions
relationships
wellbeing
what are some examples of low vision QoL questionnaires?
Low Vision Quality of Life Questionnaire (LVQOL)
National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire (NEI-VFQ)
What observations should be made?
Postural abnormalities e.g. AHP
Mobility e.g. long canes, guide dogs
Appearance
what are halberg clips and when are they used?
Used when doing refraction over the patient’s current spectacles

what should be done if you cannot get a ret value and VA is poor?
estimate the sphere
estimate the cyl and cyl axis
refine using large steps (±2.00DS, ±1.50DC)
if the working distance for subjective is 3m, how would the prescription by adjusted to ensure DV is corrected?
minus around 0.25D
what can be recommended to px’s that don’t benefit from LVAs?
sensory substitutes
how do you measure magnification if a LogMAR chart is used?
(1.25)^n
n = number of steps
e.g. VA is 0.5 and 0.1 is required - this is 4 steps so (1.25)^4 = 2.5X
what are the distance magnifiers available?
telescope
monocular
binocular
what are the near magnifiers available?
spectacle mounted magnifiers
hand magnifiers
stand magnifiers
near vision telescope
bar magnifiers
what are useful contacts should you make the px aware of?
RNIB
Macular degeneration society
Social services department
Esme’s umbrella support group - for Charles Bonnet
History and symptoms ocular health questions?
diagnosis: length of time
treatment: discharged/active
spectacles
last eye exam
general description of how they see and how it affects them day to day
vision - can they see bus numbers, street signs, tv, reading etc.
mobility - walks alone or accompanied
glare - tinted sunglasses
activities e.g. cooking
flashing light
contrast
how do they get around the house
Charles Bonnet - do you ever notice objects that may not be there
History and symptoms general health questions?
co-morbidities
medications
how they manage other health conditions e.g. how they measure their glucose
any falls in the last 12 months
how they are in themselves
History and symptoms social questions?
what support is available at home
hobbies, activities
what they do for work or education
work requirements
does anyone depend on them e.g. children
registered as sight impaired
do they drive
have social services rehabilitation service visited them or offered any help
what is their accommodation like
are they managing their correspondence
History and symptoms aid questions?
what magnifiers, assistive tech and non optical aids do they already have
are they helpful
what do they use them for
are they in good working condition
what are they hoping we can help with