Chapter 34: Pulmonary Structures and Mechanics
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is Dalton’s Law of partial pressures?
the pressure of gases in a space is the sum of the individual partial pressures of the gases in that space.
What is the ocnductive zone?
The part of the respiratory system that is responsible for moving air to the respiratory zone, no gas exchange occurs here.
What is the respiratory zone?
The part of the lungs that actually participates in gas exchange.
What are, in order, the segments of the conducting zone?
Trachea → bronchi → bronchioles → terminal bronchioles
What are, in order, the segments of the respiratory zone?
respiratory bronchioles → alveolar ducts → alveolar sacs
What is the difference in effort between inhalation and exhalation?
Inhalation is an active process, expiration is a passive process.
What is the intrapulmonary pressure compared to atmospheric pressure during inhalation?
Intrapulmonary pressure is less than atmospheric, promoting inhalation of air into lungs.
What alveolar cells secrete surfactant? What is it’s purpose?
secreted by Type II Alveolar cells
prevents alveolar collapse due to surface tension of water
What does Laplace’s Law state?
The smaller the radius, the larger the pressure required to prevent collapse.
What is the difference between a volume and a capacity?
Capacities must be calculated, volumes are just values.
What is inspiratory reserve volume?
The extra amount of air that can be inhaled after a normal tidal inhalation
What is tidal volume?
The amount of air inhaled in a normal breath, approximately 500 mL of air.
What is expiratory reserve volume?
How much air can be expelled beyond the air in a normal breath (the amount of air that can be expelled after a tidal exhale)
What is residual volume?
The amount of air in the lung that remains after all the air has been forcefully expelled.
What is inspiratory capacity?
total amount of air that can be inhaled
What is the vital capacity? How do we determine it?
The vital capacity is the capacity of the lungs when you inhale as much as possible and then exhale as much as possible.
What is the total lung capacity?
All of the air in the lungs at once at max capacity:
includes the inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and residual volume.

What is the answer to this question?
Option C is the correct answer.
What occurs when the diaphragm and external intercostals contact?
Inspiration occurs due to an increase in thoracic volume
What muscles are responsible for expiration?
diaphragm and internal intercostals
What is the difference between physiologic and anatomic dead space?
Anatomic dead space is where no gas exchange occurs due to a lack of gas exchange surfaces, its supposed to be that way.
Physiological dead space is when areas that should conduct gas exchange become damaged or otherwise disabled from disease or infection
not supposed to happen
How do you calculate the alveolar ventilation rate?
(Tidal volume - Dead Space) X Respiratory Rate

What is the answer to this question?
Option D.
Minute volume is tidal volume X respiratory rate.
What effect do bronchodilators have on alveolar CO2?
Increased alveolar CO2 (increased gas exchange)
What effect do bronchoconstrictors have on alveolar CO2?
Decreased alveolar CO2 (less gas exchange)
What parasympathetic impulses are responsible for bronchoconstriction?
Parasympathetic stimulation via M3 receptors results in bronchoconstriction.
acetylcholine
Histamines
How is hyperventilation defined in terms of the alveolar pressure of CO2?
PACO2 that is less than 40 is considered hyperventilation (too much carbon dioxide removed)
What is the fick principle?
The amount of a substance taken into an organ per unit of time is equal to the difference between the arterial and venous concentration of the substance times the blood flow rate.
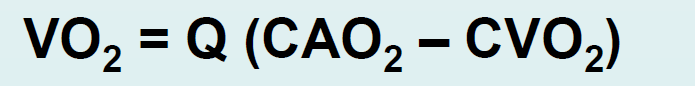

What is the answer to this question?
Option A.
increases in membrane thickness directly correlate to a decrease
What is the normal PO2 in the atmosphere?
Atmosphere is 158 mmHg oxygen
What is the PCO2 in the atmosphere?
~0.4 mmHg
What is the PO2 in the alveoli?
100 mmHg
What is the PCO2 in the alveoli?
40 mmHg
What is the PCO2 in expired air?
32 mmhg
What is the PO2 in expired air?
116 mmHg
What is the PCO2 of venous blood?
46 mmHg