F5 Investments, Statement of Cash Flows, and Income Taxes
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
What are some examples of financial assets?
Cash
Ownership interest in an entity
Contract to receive cash/financial instrument or exchange other financial instruments on potentially favorable terms
What is a financial liability?
Contract to either:
deliver cash or another financial instrument
exchange other financial instruments on potentially unfavorable terms
What is a fair value option?
Ability to measure eligible (i.e. recognized) financial instruments at fair value
Unrealized gains and losses reported in earnings
Irrevocable and applied individually
Which financial instruments are not eligible for fair value option?
Investments in subsidiaries or VIEs
Pension benefit assets or liabilities
Financial assets or liabilities under leases
Deposit liabilities of financial institutions
Financial instruments classified as equity
What is the treatment of financial liabilities other than derivative liabilities under the fair value option?
Portion of change in fair value related to change in instrument-specific credit risk is recognized in OCI
Upon derecognition of liability, any accumulated gains/loses in OCI is recognized
When can fair value option be elected?
Date when:
entity first recognizes eligible financial instrument
investment becomes subject to equity method of accounting
entity ceases to consolidate investment in subsidiary/VIE
What is a debt security?
Any security representing creditor relationship with entity (e.g. corporate bonds, redeemable preferred stock, convertible debt)
What is not included in debt securities?
Options, futures, or forward contracts
Lease contracts
Accounts and notes receivable
What are the three categories that debt securities can be classified into?
Trading securities
Available-for-sale debt securities
Held-to-maturity debt securities
What are trading securities?
Debt securities bought and held for purpose of selling in near-term (within 12 months of purchase date)
Objective is to generate profits in the short-term
Recorded at fair value and generally reported as current assets
What are available-for-sale debt securities?
Securities that do not meet the definition of trading or held-to-maturity securities
Reported as either current or non-current asset
What are held-to-maturity debt securities?
Debt securities that entity has positive intent and ability to hold until maturity
Reported as current or non-current asset depending on time to maturity
When can held-for-maturity classification not be used?
If intent to hold security for indefinite period but not to maturity
If security can be paid or settled such that the holder can not recover substantially all of its investment
How are available-for-sale and trading debt securities reported?
Reported at fair value
Changes in fair value result in unrealized gains or losses
Presented on balance sheet in one net amount
Realized gains/losses recognized when sold
Loss recognized if AFS security is impaired
What is the accounting for unrealized gains and losses of trading securities?
Recognized in net income

What is the accounting for unrealized gains and losses of available-for-sale debt securities?
Recognized in OCI

How are held-to-maturity debt securities reported?
Reported at amortized cost
Unrealized gains/losses are not recognized
What is the accounting for reclassification of debt securities?
Occur only when justified, generally rare
Accounted for at fair value
Any unrealized gain/loss depends on category
What is the accounting for unrealized gain/loss reclassifying from trading category?
Unrealized gain/loss already recognized in earnings and shall not be reversed
What is the accounting for unrealized gain/loss reclassifying to trading category?
Unrealized gain/loss at date of transfer recognized in earnings immediately
What is the accounting for unrealized gain/loss reclassifying from held-to-maturity to available-for-sale?
Unrealized gain/loss at date of transfer reported in OCI (i.e. difference in amortized cost versus fair value)
What is the accounting for unrealized gain/loss reclassifying from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity?
Unrealized gain/loss at date of transfer already reported in OCI
Unrealized gain/loss should be amortized over remaining life in income statement as interest revenue/payment
What is the accounting for interest income from investment in trading/available-for-sale securities?
Reported on the income statement

What is the accounting for available-for-sale and held-to-maturity debt securities under the CECL model?
Reported at expected amount to be collected net of allowance for expected credit losses
Credit loss recognized as current period expense offset by allowance for credit loss
Changes in expected credit loss reflected in period incurred
What is the accounting for impairment of held-to-maturity securities?
If all amounts due will not be collected (i.e. if amortized cost > present value to be collected):
Report at present value of principal and interest expected to be collected
Credit loss is difference between present value and amortized cost
What is the accounting for impairment of available-for-sale debt securities?
Impairment if fair value < amortized cost:
Credit loss recognized in income statement and limited to amount of present value below amortized cost (i.e. purchase price)
Any additional loss reported as unrealized loss in OCI
What is the accounting for sale of trading security?
Realized gain/loss is difference between adjusted cost (original cost plus unrealized gains or minus unrealized losses) and selling price

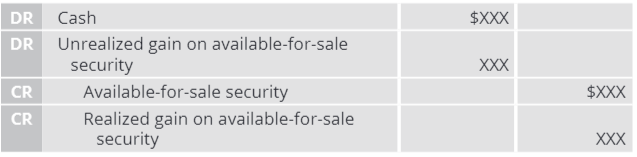
What is the accounting for sale of available-for-sale security?
Realized gain/loss difference between selling price and original cost
Any unrealized gains/losses accumulated in OCI must be reversed
What is an equity security?
Ownership interest in an enterprise or right to acquire/dispose of ownership interest in an enterprise (e.g. common stock, stock warrants, put options)
How are equity securities reported?
At fair value through net income
Unrealized gains/losses included in earnings immediately in the period incurred

What is the practicability exception?
If equity investment does not have a readily determinable fair value:
measured at cost less impairment, plus/minus observable price changes of identical or similar investments from the same issuer
What is accounting for dividend income of a non-liquidating dividend?
Recognized in net income

What is accounting for dividend income of a liquidating dividend?
Portion of dividend not in excess recognized as dividend income
Return of capital decreases investor’s basis in investment

What is the qualitative impairment assessment for equity securities without a determinable fair value?
Heightened concerns regarding investee’s ability to continue as going concern
Significant and adverse changes in investee’s environment
Significant decline in earnings, business prospects, asset quality, or credit rating of investee
Offers to buy from investee same or similar investment less than carrying value
What is the accounting for impairment of equity investment without determinable fair value?
Cost basis of security written down to fair value
Amount of write-down accounted as realized loss and included in earnings
What is the accounting for sale of equity security?
If all changes in fair value have been reported as unrealized gains or losses:
No gain or loss (DR cash, CR equity security)
If changes in fair value were not reported:
Gain/loss equal to difference between adjusted cost (original cost plus unrealized gains or minus unrealized losses) and selling price
DR cash, CR equity security, DR/CR loss/gain
What must be disclosed for available-for-sale and held-to-maturity securities?
Aggregate fair value
Gross unrealized gains/losses
Amortized cost basis
Information about contractual maturities
What must be disclosed for equity securities?
Portion of unrealized gains/losses

How are financial assets and liabilities disclosed?
On balance sheet or in notes
Grouped by measurement category
What must be disclosed for fair value information?
Classification level of measurement hierarchy
If measured at amortized cost, fair value should be disclosed in accordance with exit price
Exceptions:
Payables and receivables due within one year
Deposit liabilities with no defined maturities
Equity investments reported under practicability exception
What must be disclosed if practicability exception is elected?
Carrying amount of investments without determinable fair values
Any impairment charges
Upward or downward adjustments to carrying amount
What are concentrations of credit risk?
Possibility of loss due to failure of another party to perform according to terms of contract
Occurs when entity has contracts of material value with one or more parties in same industry/region or having similar economic characteristics
Must be disclosed
What is market risk?
Possibility of loss from changes in market value due to changes in economic circumstances
Not required to disclose
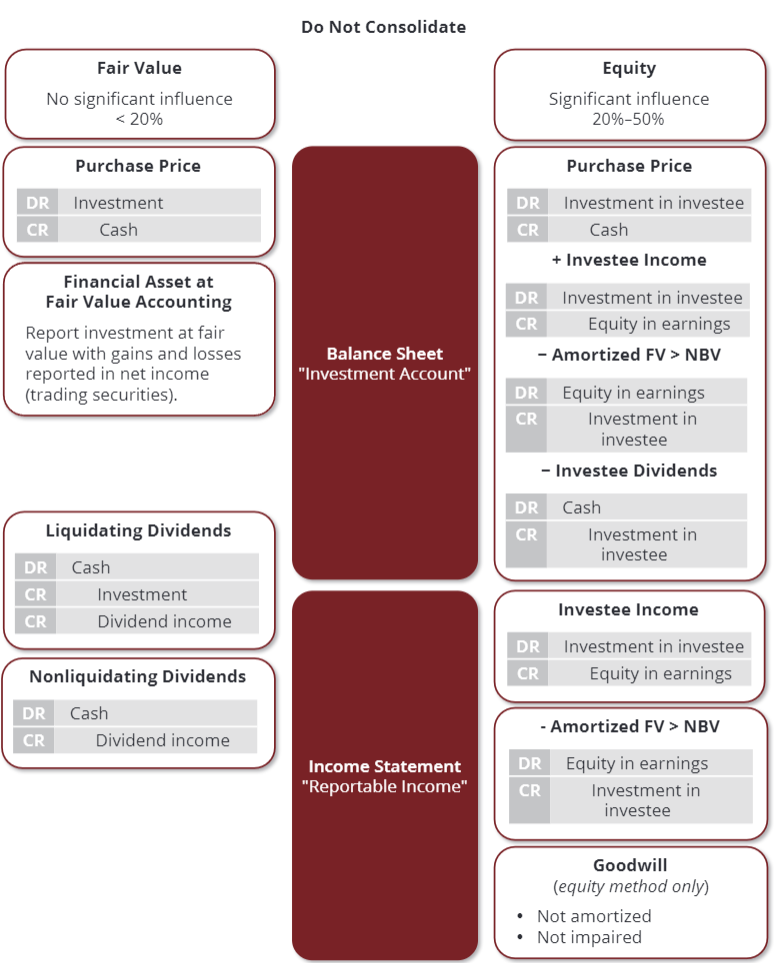
When should equity method be used?
If significant influence can be exercised by investor over investee
When should consolidated statements be presented under the equity method?
If ownership is greater than 50% and there is control over investee
What is significant influence in regards to the equity method?
Parent company owns 20% - 50% of voting stock of another investee
Must use equity method in consolidated financial statements not of that investee or unconsolidated parent financial statements
When is the equity method not appropriate?
Bankruptcy of subsidiary
Investment in subsidiary is temporary
Lawsuit or complaint is filed
“Standstill agreement” (i.e. investor surrenders significant rights)
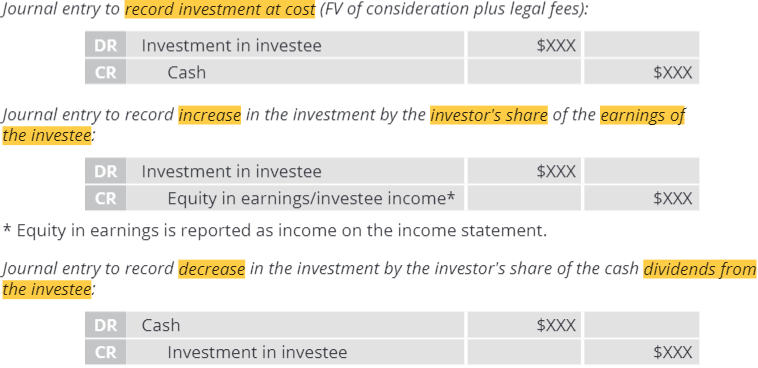
What is the accounting for the equity method?
Investment is originally recorded at price paid to acquire investment
Investment account is increased by share of earnings of the investee
Investment account is decreased by cash dividends from the investee
Under the equity method, what happens if investor owns both common and preferred stock?
“Significant influence” test is used on common stock only
Consolidated income statement of subsidiary will include subsidiary’s:
Preferred stock dividends
Earnings available to common shareholders (Net Income - Preferred Dividends)
How is the difference between purchase price of investment and net book value of investee’s net assets accounted for?
Excess of asset’s fair value over book value is amortized (except land), causing investment to decrease
Any excess fair value (i.e. goodwill) is not amortized
Total equity method must be annually tested for impairment
Which conditions must occur for equity method investment to be impaired?
Fair value of investment falls below carrying value
Decline in fair value is not temporary
How is impairment loss in equity method investment reported?
Recorded on income statement
Carrying value is reduced to lower fair value
Impairment reversal is not permitted
Illustrate the difference between fair value and equity method
What must be done when changing from fair value to equity method?
Add cost of acquiring additional interest to carrying value of investment
Adopt equity method as of date when investment qualifies for equity method. No retroactive adjustments required
In transitioning from either fair value or equity method, how are equity securities without readily determinable fair values handled?
If transitioning to equity method:
Investment remeasured immediately before transition
If transitioning from equity method:
Investment remeasured immediately after transition
In a parent-subsidiary relationship, when must consolidated financial statements be prepared?
Parent has control over investee; or
parent owns more than 50% of voting stock
What is the difference between controlling vs noncontrolling interest?
Controlling interest owns more than 50% and has controlling interest
Noncontrolling interest is portion of subsidiary’s equity not attributable to parent
What are the two distinct accounting characteristics under the acquisition method?
100% of net assets acquired are recorded at fair value with excess creating goodwill
Subsidiary’s entire equity is eliminated (not reported)
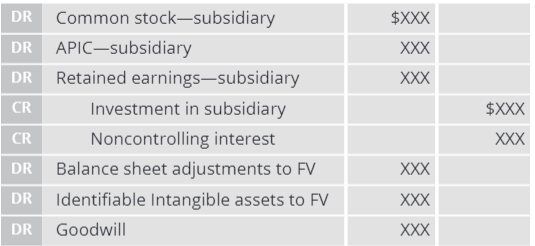
What must be adjusted in consolidation? (CAR IN BIG)
Common stock - eliminated
APIC - eliminated
Retained earnings - eliminated
Investment - eliminated
Noncontrolling interest - created
Balance sheet - adjusted to fair value
Intangible assets - adjusted to fair value
Goodwill - any excess of fair value of subsidiary over net assets creates goodwill
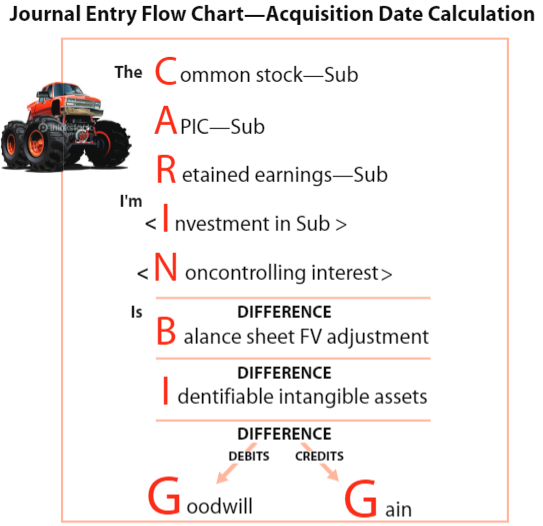
What is year-end consolidating journal entry?
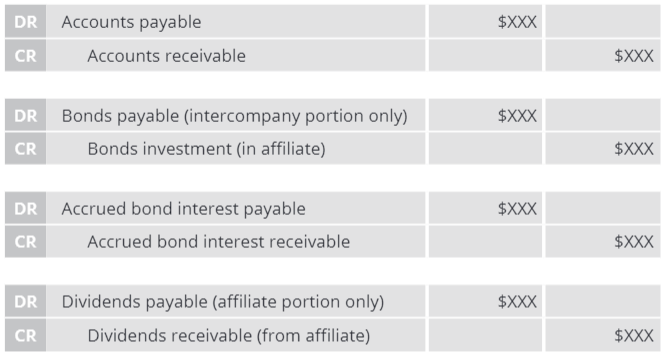
What are the balance sheet intercompany eliminations?
What are the income statement eliminations?
Interest expense/Interest income
Gain on sale/Depreciation expense
Sales/Cost of goods sold
What is the journal entry for eliminating intercompany merchandise transactions?
Eliminate intercompany sale (debit sales, credit COGS)
Eliminate intercompany profit (allocated in ending inventory [sales/ending inventory] and COGS [1 - sales/ending inventory])
![<ul><li><p>Eliminate intercompany sale (debit sales, credit COGS)</p></li><li><p>Eliminate intercompany profit (allocated in ending inventory [sales/ending inventory] and COGS [1 - sales/ending inventory])</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7f0a1bec-d318-4697-a32b-31bdceb5f728.png)
How are intercompany bond transactions accounted for?
Gain/loss on extinguishment of debt is recognized via an elimination entry
Eliminate intercompany interest expense, interest income, interest payable, and interest receivable
Elimination amortization of discount/premium and unamortized discount/premium
Elimination for realized but unrecorded gains/loss adjusted to retained earnings
How are intercompany sale of land accounted for?
Gain/loss unrealized until land is sold to a third-party (selling price - original cost)
Eliminate intercompany gain/loss and adjust land to original cost
Retained earnings debited and land credited
How are intercompany profit on sale of depreciable fixed assets accounted for?
Gain/loss unrealized until sold to third-party
Eliminate intercompany gain/loss, adjust asset to original balance and, depreciate as if the sale had not occurred
What is included in a consolidated balance sheet?
100% of parent’s and subsidiary’s assets and liabilities (after eliminating intercompany transactions) included but subsidiary’s equity not included
Subsidiary’s PP&E must be reported at net book value (fair value - accumulated depreciation); subsidiary’s accumulated depreciation is zeroed out
If non-wholly owned, portion of subsidiary’s net income attributable to noncontrolling interest reported in retained earnings
What is included in consolidated income statement?
100% of parent’s revenues and expenses and all of subsidiary’s revenues and expenses after date of acquisition
Subsidiary’s pre-acquisition revenues and expenses not included
Separately stated consolidated net income. net income attributable to noncontrolling interests, and net income attributable to parent company
What is included in consolidated comprehensive income?
Consolidated comprehensive income
Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest
Comprehensive income attributable to parent company
What is included in consolidated statement of changes in equity?
Reconciliation of beginning-of-period and end-of-period carrying amount of total equity
Equity attributable to parent
Equity attributable to noncontrolling interest
How to prepare consolidated statement of cash flows?
Net cash spent or received in acquisition must be reported in investing section
Assets and liabilities of subsidiary on acquisition date must be added to parent’s assets and liabilities at beginning of the year to determine change in cash
In subsequent periods, how is consolidated statement of cash flows prepared?
Present cash inflows and outflows of consolidated entity except cash flows between parent and subsidiary
When reconciling net income to net cash from operating activities, total consolidated income should be used
Financing section should report dividends paid by subsidiary to noncontrolling interest only
Investing section may report acquisition of additional subsidiary shares by parent if acquisition was open-market purchase
What is the journal entry on the partnership books for the purchase/sale of an existing partnership interest?
No journal entry except for change of name on capital account
How are contributions to a partnership recorded?
Assets at fair value
Liabilities at present value
Equity is difference between fair value of assets and present value of liabilities
What is the ‘exact method’ regarding partnerships?
When purchase price is equal to book value, no goodwill or bonuses are recorded
What is the ‘bonus method’ regarding partnerships?
When purchase price is more or loss than book value, bonuses are adjusted between old and new partners’ accounts and do not affect partnership assets
If interest is less than amount contributed, difference as bonus to old partner(s)
If interest is more than amount contributed, difference as bonus to new partner and capital balances of old partner(s)’ needs to be adjusted downwards
How is goodwill recognized regarding partnerships?
Determine implied total capital of the partnership (new partner’s contribution divided by interest share)
Difference in implied total capital and actual total capital is goodwill
Goodwill is adjusted upwards to old partner(s) according to old partnership profit ratios
How are profit and loss distributed regarding partnerships?
Accordance with agreement
If agreement is absent, profit and loss is shared equally
All payments for interest on capital, salaries, and bonuses deducted prior to distribution
What is the accounting for a withdrawal of a partner under the bonus method?
Difference between balance of withdrawing partner and amount that partner paid is the bonus
Bonus is allocated among remaining partners in accordance with remaining profit and loss ratios
Withdrawing partner’s assets may be revalued at fair value but goodwill is not recorded
What is the accounting for a withdrawal of a partner under the goodwill method?
Record the implied goodwill and allocate to all partners in accordance with profit and loss ratios
Balance in withdrawing partner’s capital account should equal amount that person is expected to receive in final settlement
What is the order of preference regarding distribution of assets in liquidating a partnership?
Creditors
Partners’ capital
How are losses accounted for in liquidating a partnership?
Do not distribute any cash until maximum potential losses have been taken into consideration
Losses are charged to partners in accordance with agreement; absent an agreement, losses are shared equally
What is a capital deficiency?
A debit balance in a partner’s capital account that the partnership has a claim against for that amount
What is the right of offset regarding capital deficiency?
If partner with a capital deficiency has a loan account, the partnership can use the payable to offset the deficiency
What happens if a capital deficiency still exists?
Remaining partners must absorb deficiency according to profit and loss ratios
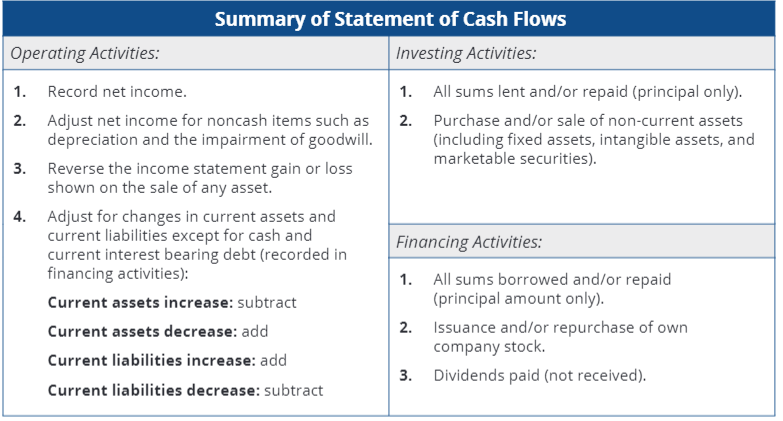
What do each of the cash flows (i.e. operating, investing, and financing) provide infromation about?
Cash receipts and disbursements of:
Operating: income statement transactions and current assets and liabilities
Investing: non-current assets
Financing: debt
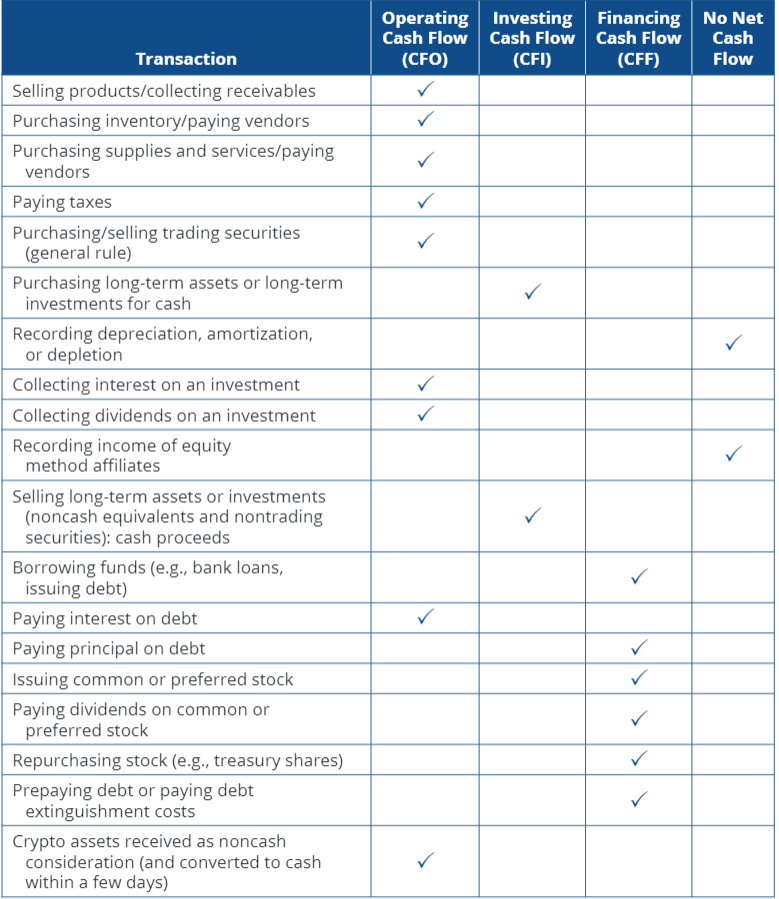
What is the indirect method for preparing the statement of cash flows?
Report operating net cash flows indirectly by adjusting net income

How is net income adjusted under the indirect method? (CLAD)
Current assets and liabilities (change in debit = inverse; change in credit = direct)
Losses and gains (gains subtracted, losses added)
Amortization and depreciation (added)
Deferred items (subtract)
What is included in the supplemental disclosure regarding the indriect method?
Cash used to pay income tax and interest
Illustrate the segments of the statement of cash flows
What is allocated in intraperiod tax allocation? (IDA-PUFI)
Income/loss from:
Income from continuing operations
Discontinued operations
Accounting principle change (retrospective)
Pension funded status change
Unrealized gain/loss on AFS debt securities
Foreign translation adjustment
Instrument-specific credit risk
How do we calculate the amount of income tax expense/benefit allocated to continuing operations?
Tax effect of pretax income/loss from continuing operations plus/minus tax effects of changes in tax laws or rates, expected realization of a deferred tax asset, or tax status of the entity
What are the characteristics of permanent tax differences?
Do not affect deferred tax computation
Only affect current tax computation
Affect only the period in which they occur
Do not affect future financial or taxable income
What are the characteristics of temporary tax differences?
Will affect deferred tax computation
Eventually will be recognized for GAAP purposes (or vice versa)
Temporary differences affect future period(s) and require:
Liability (for future taxable)
Asset (for future deductible)
Should be recognized until difference turns around completely
What is the asset and liability method (AKA balance sheet approach)?
For comprehensive allocation
Interperiod tax allocation applied to all temporary differences
Either income taxes payable or deferred tax liability be recorded for all tax consequences of current period
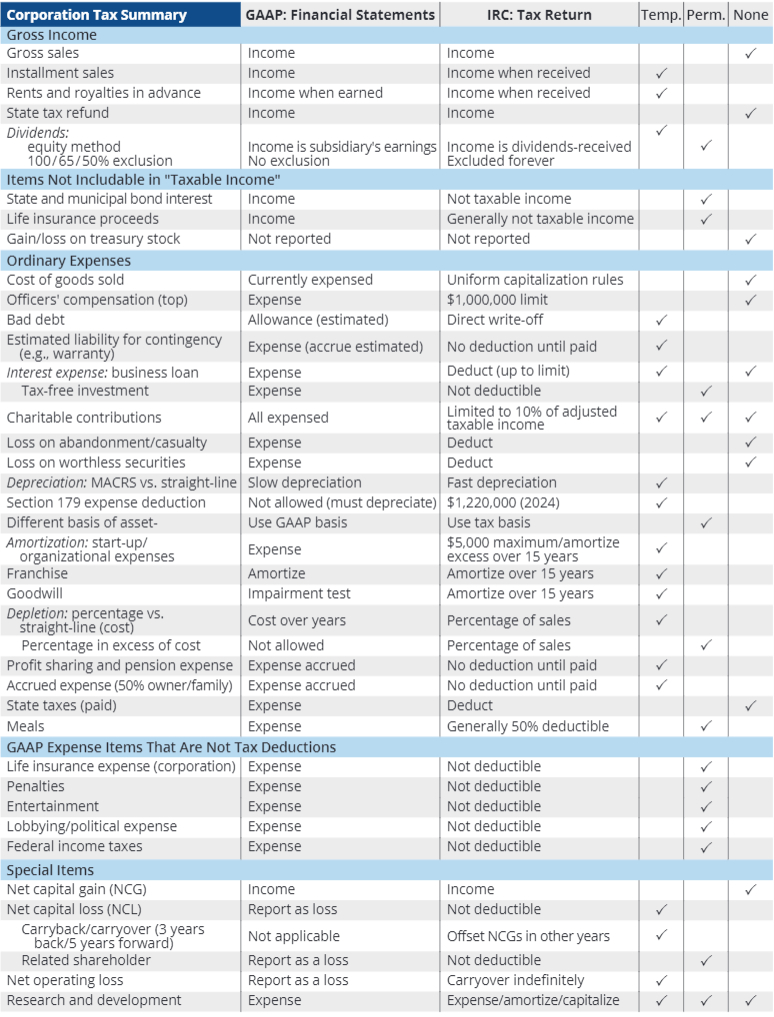
How is total income tax expense calculated?
Sum of:
Current income tax expense/benefit; and
Income taxes payable or refundable
Deferred income tax expense/benefit
Change in deferred tax liability or asset from beginning to end of period

What are some examples of permanent tax differences?
Tax-exempt interest
Nondeductible portion of meal and entertainment expense
Life insurance proceeds on officer’s key person policy
What results in a deferred tax liablity?
Revenues/gains included in financial statement income before taxable income
Expenses/losses deducted from taxable income before financial statement income

What results in a deferred tax asset?
Revenues/gains included in taxable income before financial statement income
Expenses/losses deducted from financial statement income before taxable income

When will a valuation allowance be recognized?
More likely than not (more than 50%) that part or all of deferred tax asset will not be realized
Net deferred tax asset should equal portion of deferred tax asset that is more likely than not to be realized