defects causing stenosis/regurg
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
valvular anomalies
abnormal cusp #, abnormal cusp, annulus or supporting structure malformation can cause both stenosis and regurg
pulmonary stenosis is _____ common as a congenital defect than degenerative pulmonary stenosis
more
in all of the valves except pulmonary, _____ stenosis is more common
acquired
bicuspid aortic valve
valve composed of 2 cusps intead of 3, most commonly results from fusion of rt and left coronary cusps w larger anterior/smaller posterior
which cusp do the coronary arteries originate from in bicuspid aorta
anterior cusp
most common congenital heart defect found in adulthood
bicuspid aorta
how does a bicuspid aortic valve sound
systolic ejection click immediately after s1 sound
may be followed by a crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur if stenosis is present
in bicuspid av, how do the leaflets look in systole
doming of leaflets (concave)
in bicuspid av, how do the leaflets look in diastole
hammock shaped (convex)
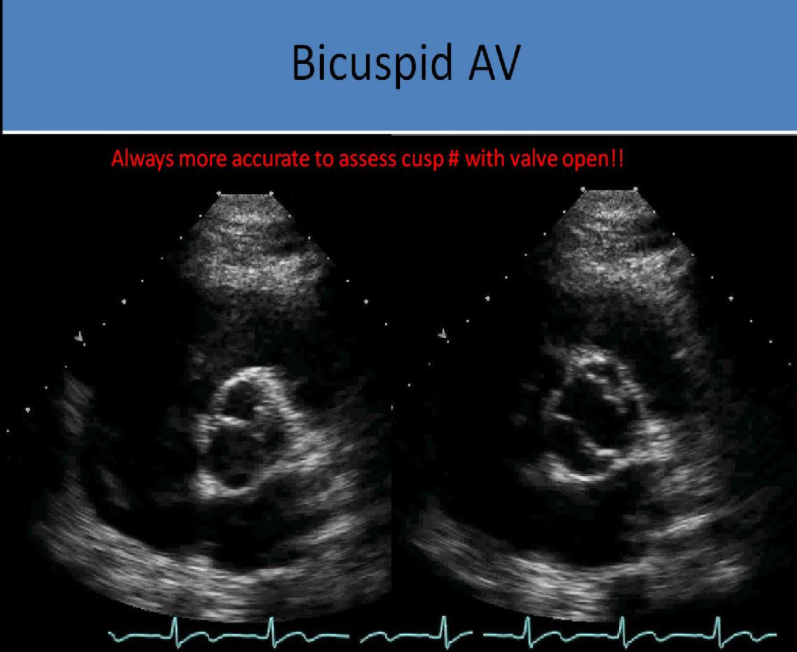
when must leaflet number be evaluate for bicuspid av
in systole, the valve may appear normal in diastole and fused raphe cannot be detected without the valve open
what is bicuspid av associated with
ai
coarctation
dilated aorta
marfan syndrome
what does screening look like for bicuspid av
patients screened annually when asymptomatic, biannually w aortic dilation
first degree family members should be screened for the defect
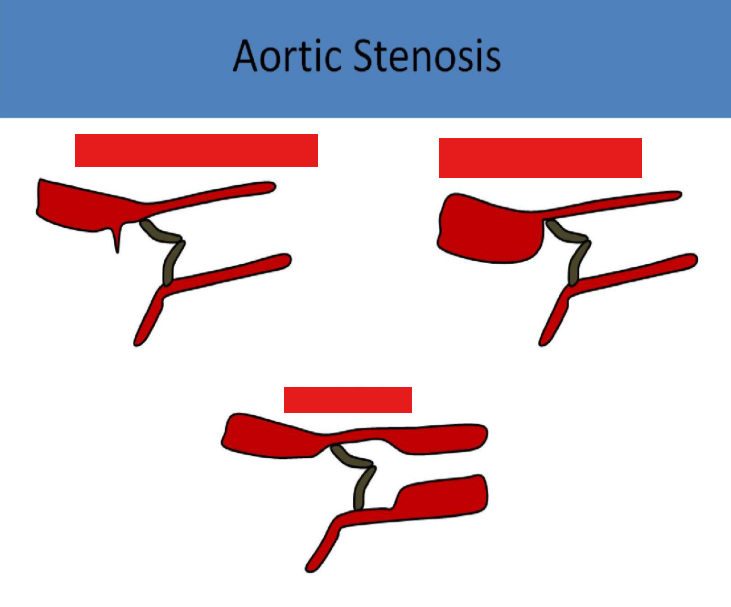
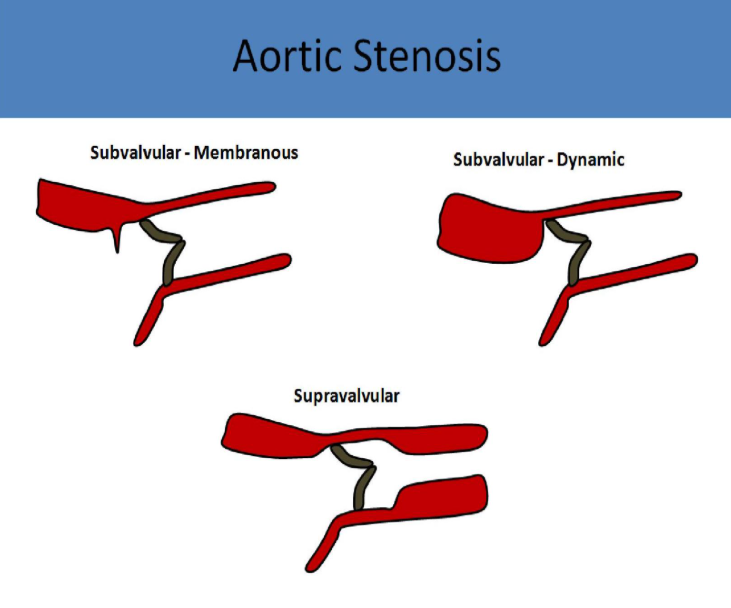
membranous subvalvular aortic stenosis
membranous band of tissue located in the lvot near the aortic valve, obstructing left ventricular ejection of flow and simulating aortic valve stenosis
membranous subvalvular stenosis is best evaluated in what view
apical 5 chamber
why can’t the continuity equation provide an accurate valve area
bc the obstruction is in the lvot
how is membranous subvalvular aortic stenosis best demonstrated
using pw doppler to demonstrate the increasing velocity as the cursor is moved along the lvot
cw doppler may be used for peak velocity at the defect once location has been documented w pw
what can membranous subvalvular stenosis cause in the heart
compensatory left ventricular hypertrophy
early systolic closure of the aortic valve that can be demonstrated on m mode
how is m mode used to differentiate the difference between subvalvular from valvular aortic stenosis
elevated velocity + normal valve opening + early systolic closure = subvalvular
elevated velocity + restricted valve opening = valvular
supravalvular aortic stenosis
narrowed aortic root
t/f: supravalvular aortic stenosis is uncommon
true, results from a congenital condition such as williams syndrome
what is supravalvular stenosis typically caused by in adults
abnormal fibrous tissue accumulation/inflammation (takayasu arteritis)
how does supravalvular stenosis appear on us
increased velocity in the affected segment w normal aortic valve motion
why won’t the continuity equation not provide the correct valve area
obstruction is in the aortic root and valve can demonstrate normal motion
what imaging modalities are useful in making a diagnosis for supravalvular aortic stenosis
ct/mr bc of the limited sonographic windows of the ascending aorta in some patients
types of aortic stenosis
aortic valve prolapse
normal aortic cusps coapt approximately halfway between the aortic annular base and the sinotubular junction, prolapse is diagnosed if a cusp demonstrates downward displacement below this level
aortic valve prolapse is most commonly seen in patients with
bicuspid av
aortic valve prolapse is also associated with
aortic root dilation
mitral valve prolapse
severe mitral regurgitation
outlet vsd
what will be present in cases of aortic prolapse
ai
cleft mitral valve
split or tear in one or both of the mitral valve leaflets, psax view most often shows a divison of the anterior leaflet, sometimes making the valve appear as though it has 3 leaflets
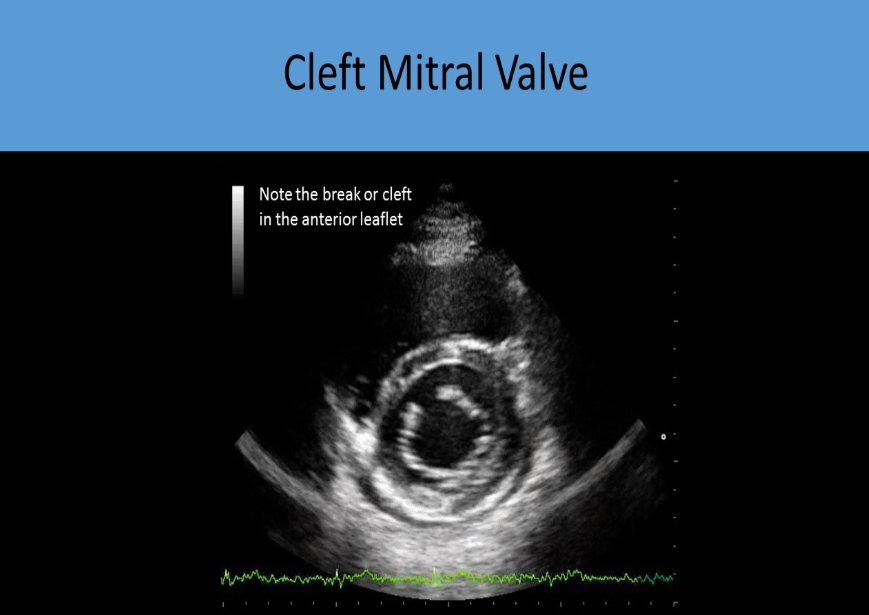
what is cleft mitral valve associated with
partial atrioventricular septal defect
primum asd
cleft mitral valve results in
mr
with cleft mitral valve, plax view will show
anterior mitral doming during systole, but there is no stenosis of the valve
parachute mitral valve
congenital anomaly
one papillary muscle attached to both sets of chordae
usually the posteromedial muscle is the only one present
presents like mitral stenosis on echo/doppler
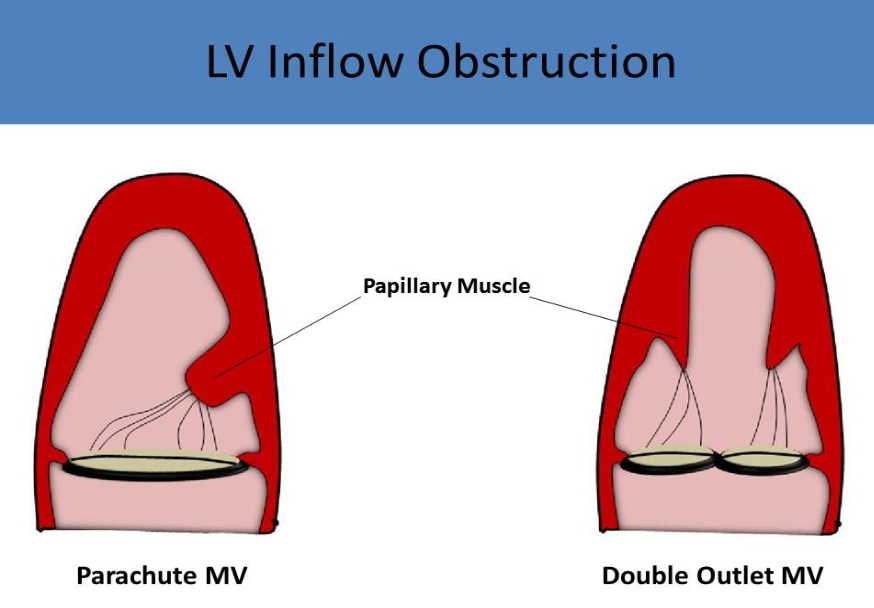
double orifice mitral valve
accessory orifice
psax best to visualize
flow eval may be normal or appear w signs of stenosis/regurg
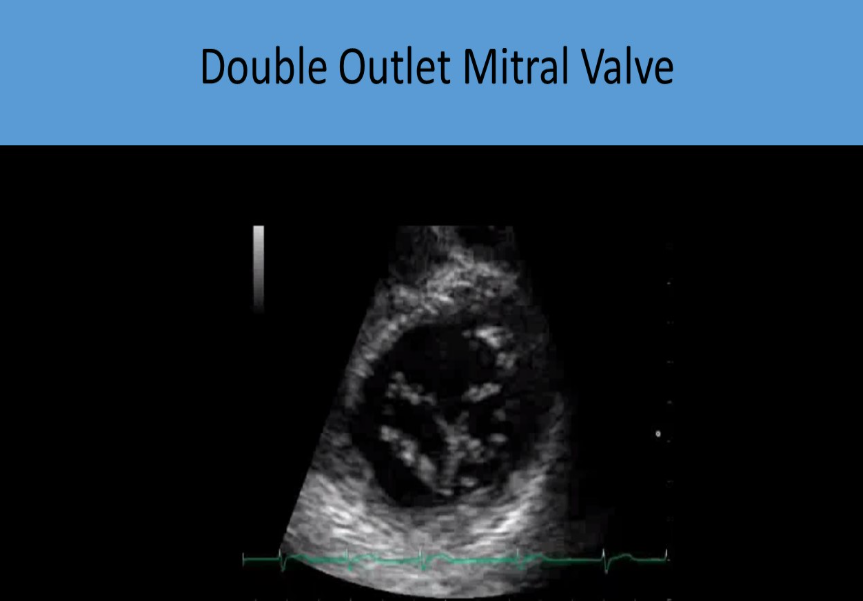
how can a mitra-clip device and double outlet mv be differentiated from each other
note the echogenicity of the clip to differentiate
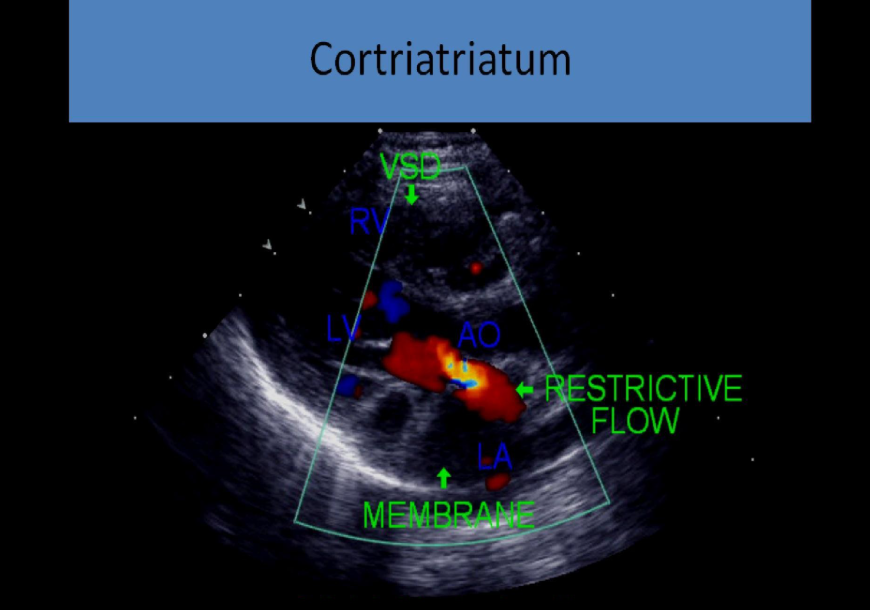
cor triatriatum
membrane across the mid portion of the left trium disrupts flow from atrium through mitral valve, membrane usually above the level of the fossa ovalis
how does cor triaatriatum look on us
suggests presence of 3 atrial chambers on 2d
can cause supravalvular stenosis
mimics mitral stenosis w turbulent flow, increased psv and ppg
dilated pulmonary veins
80% also have asd
can form in the right atrium as well but this is less common
supravalvular mitral stenosis
membrane or tissue thickening located at the level of the mitral annulus obstructs left ventricular inflow
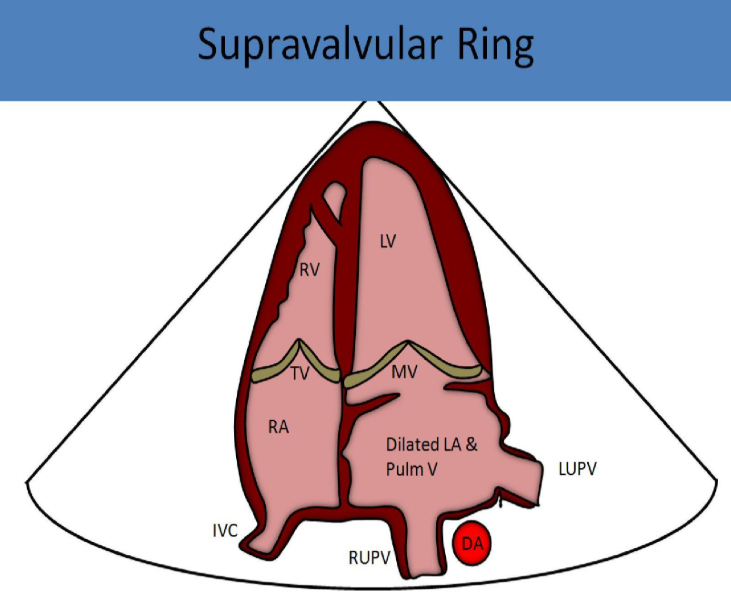
what is supravalvular mitral stenosis associated with
asd
vsd
coarctation
persistent left svc
shone complex
mitral valve prolapse most often occurs as a _____ disorder
congenital
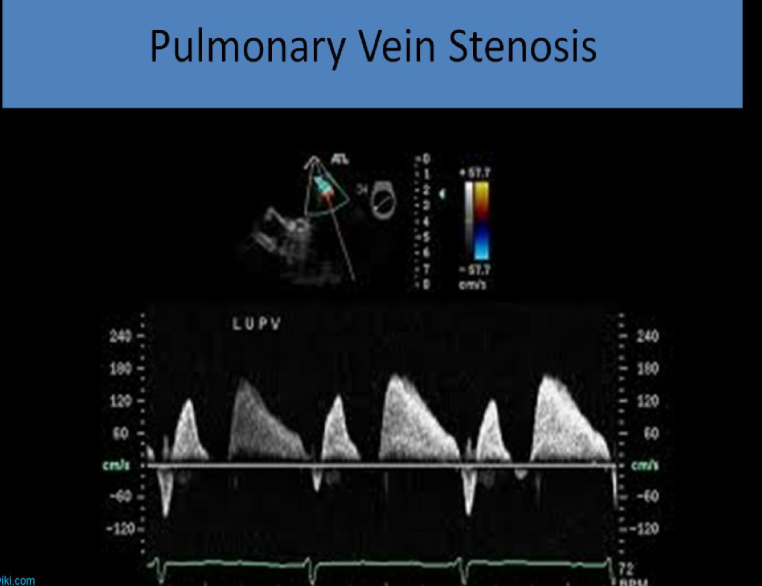
pulmonary vein stenosis
narrowing of one or more pulmonary veins at their connection with the left atrium
usually congenital
difficult to diagnose w tte
what is seen w pulmonary vein stenosis
pulmonary htn
right ventricular hypertrophy
right ventricle and atrial dilation
how does pulmonary vein stenosis look on doppler eval
peak systolic velocity (s) and peak diastolic velocity (d) both increased
flow reveral between systole and diastole