Chapter 20: Income Inequality, Poverty, and Discrimination
Income inequality - How income is distributed around the average
- Distribution by income category
- Distribution by quintiles (fifths) - Dividing into 5 equal groups + examining % of total personal income of each quintile
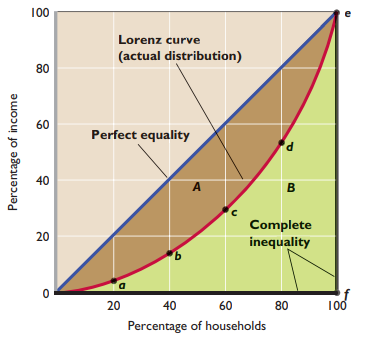
Lorenz curve - Displays quintile distribution of personal income
- % of households on horizontal, % of income on vertical
- Diagonal line represents perfectly equal distribution of income
- Gini ratio - Numerical measure of the overall dispersion of income
Income mobility - Movement of individuals + households between income quintiles
- Change time period measured → Significant differences in income inequality
Effect of gov’t redistribution
- Non-cash transfers - Provide goods/services rather than cash
- Gov’t redistributes income from high to low income households
Causes of income inequality
- Different mental, physical, aesthetic abilities
- Education + training
- Discrimination - Practice of according people inferior treatment (for example, in hiring, occupational access, education and training, promotion, wage rate, or working conditions) on the basis of some factor such as race, gender, or ethnicity
- Different preferences for market work
- Unequal distribution of wealth
- Rigging market power on one’s own behalf
- Luck, connections, misfortune
Income inequality over time
- More unequal distribution over time
- Causes of growing inequality
- Greater demand for highly skilled workers
- Demographic changes
- International trade, immigration, decline in unionism
Equality vs. efficiency
- Case for equality - Income equality maximizes total consumer satisfaction (utility) from any particular level of output and income
- Yields greater combined total utility
- Case for inequality - Income distribution determines amount of output/income produced + available to distribute
Equality-efficiency trade-off - Greater income equality (achieved through redistribution of income) comes at the opportunity cost of reduced production and income
- Society must choose how much distribution it wants
Poverty - Condition in which a person or a family does not have the means to satisfy basic needs for food, clothing, shelter, and transportation
- Poverty rate - Percent of population living in poverty
US income-maintenance system
- Entitlement programs - Social insurance + welfare; eligible persons ensured to benefits in programs
- Social insurance programs - Partially replace earnings that have been lost due to retirement, disability, or temporary unemployment; they also provide health insurance for the elderly
- Social Security - Federal pension program that replaces part of the earnings lost when workers retire, become disabled, or die
- Medicare - Federal insurance program that provides health insurance benefits to those 65 or older and people who are disabled
- Unemployment compensation - Social insurance program that makes income available to workers who are unemployed
Public assistance programs - Provide benefits to people who are unable to earn income because of permanent disabling conditions or who have no or very low income and also have dependent children
- Supplemental Security Income (SSI) - Provides a uniform nationwide minimum income for the aged, blind, and disabled who are unable to work and who do not qualify for Social Security aid
- Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) - Basic welfare program for low-income families in the United States
- Food stamp program - Federal program (financed through general tax revenues) that permits eligible low-income persons to obtain vouchers that can be used to buy food
- Medicaid - Federal program (financed by general tax revenues) that provides medical benefits to people covered by the SSI and TANF (basic welfare) programs
- Earned income tax credit (EITC) - Refundable Federal tax credit provided to low-income wage earners to supplement their families’ incomes and encourage work
Taste for discrimination model - Views discrimination as resulting from a preference or taste for which the discriminator is willing to pay. The model assumes that, for whatever reason, prejudiced people experience a subjective or psychic cost—a disutility—whenever they must interact with those they are biased against
- Discrimination coefficient - Amount of disutility
- Suggests that competition will reduce discrimination in very long run
Statistical discrimination - People are judged on the basis of the average characteristics of the group to which they belong, rather than on their own personal characteristics or productivity
Occupational segregation - Crowding of women, African Americans, and certain ethnic groups into less desirable, lower-paying occupations
- Minorities unable to move into occupations with higher wages
- Loss of output for society
- Removal → More efficient allocation of resources