AP Psychology Unit 1.4 The Brain
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
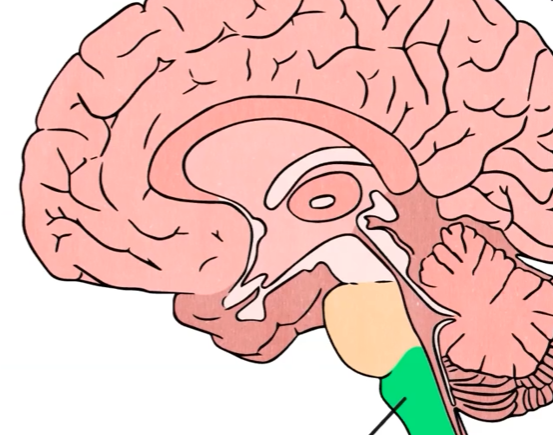
Medulla
Found in the Brain stem, plays a role in regulating heart rate, breathing, and Blood pressure. also involved in necessary reflexes ex. swallowing, vomiting, and sneezing
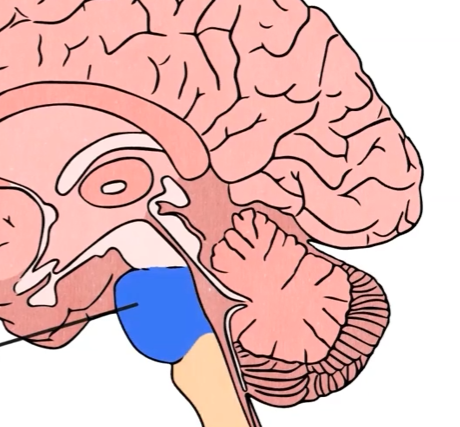
Pons
The bridge that connects the brainstem and the cerebellum, helps coordinate and integrate movements on each side of the body , plays a role in sleep function.
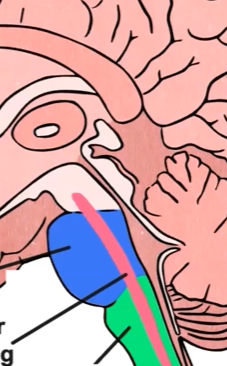
Reticular activation system (RAS)
A network of nerve fibers involved in attention, arousal, and alertness
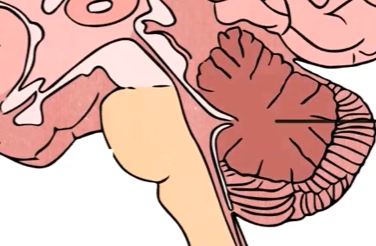
cerebellum
Balance and equilibrium, heavily involved in coordinative sequence of movement, plays a vital role in implicit memory’s
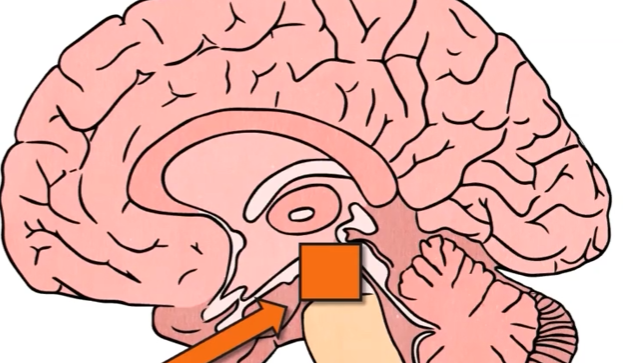
Mid Brain
Is a part of the brain that connects its upper and lower sections. It sends information between the brain, ears, and eyes.
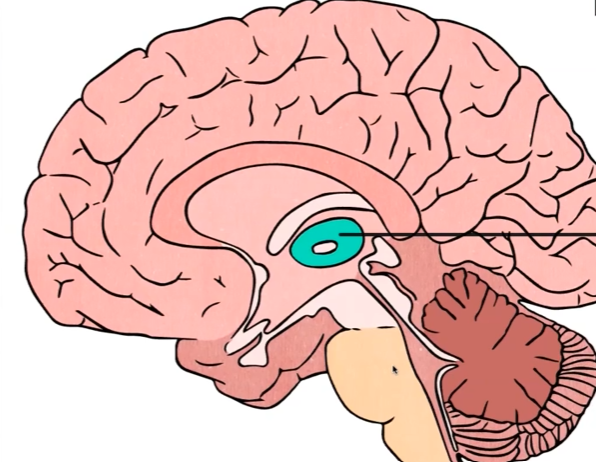
Thalamus
Receives and sorts sensory information (except smell) than sends it to the cortex for further interpretation
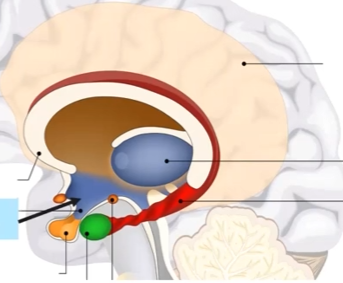
Hypothalamus
Regulates sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system(Fight or Flight)
initiating motivation to eat and when you had enough to eat (feeding)
sexual motivation (Fornication)
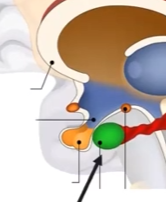
Amygdala
Anger Aggression and Afraid response emulates from this part, also helps highly emotional memory
Hippocampus
Converts short term memory to long term memory, involved in processing and retrieving declarative (facts and events) memories. plays a role in spatial memories
Frontal lobe
Consists of two parts
prefrontal cortex: involved in cognitive functions such as thinking, planning, and decision making, Massive changes happen when you turn 18 - 25 years old.
Motor cortex: involved in initiating voluntary movements, its contralateral(left hemisphere controls right side of your body), body areas that are more diverse and precise movements get more space on this strip of the brain
Partial lobe
Somatosensory cortex: the strip of tissue represents your sense of touch, contralateral, the parts of your body that are more more sensitive have more tissue devoted to them on this strip
Occipital lobe
Primary visual cortex: Visual perception, Significant damage to this part might cause blindness.
Temporal lobe
Primary auditory cortex: Your primary sense of hearing
Auditory association cortex: help ingrate somethings that your perceiving in sound.
Broca’s area
Found in the LEFT frontal lobe, is involved in expressive speech, damage to it is called Broca’s aphasia inability to express the speech your trying to explain.
Wernicke’s area
Found in the LEFT temporal lobe which is involved in understanding and comprehending language. damage to it is called Wernicke’s aphasia which might cause the inability to understand language
Corpus collosum
A massive bundle of nerves connecting the two hemispheres, Allows constant communication between the right and left hemisphere.
Brain Lateralization
Some functions are lateralized to the left hemisphere and other functions are lateralized to the right hemisphere, for most people language functions are lateralized to the left hemisphere, and the ability to recognize faces is primarily lateralized as a right hemisphere function.
Neuroplasticity
The ability of the brain to change as a result of experience or injury
Neurogenesis
the creation of new cells, Exercise seems to increase it and social isolation seems to decrease it.
Long-term potentiation
When a network of neurons fires together repeatedly, that neural pathway becomes smoother and more efficient. It may represent the biological base of learning.
functional plasticity
The brain can shift functions from damaged areas to undamaged areas
fMRI (functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
an imaging scan that shows the structure and function of the brain, measures changes in oxygen levels as brain areas activate/deactivate.
EEG (Electroencephalograph)
Measures electrical activity coming off the surface of the brain, can be used to identify issues such as epilepsy or various sleep disorders.