Chem
0.0(0)Studied by 3 people
Card Sorting
1/595
Last updated 5:52 AM on 1/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
596 Terms
1
New cards
State the method used to obtain sand from a mixture of sand and water
filtration
2
New cards
State the method used to obtain solid copper sulfate from aqueous copper sulfate
crystallisation
3
New cards
State the method used to obtain red food dye from a mixture of food dyes
paper chromatography
4
New cards
State the method used to obtain water from salt water
simple distillation
5
New cards
Draw a diagram to show equipment used in simple distillation
For what process is this equipment used?
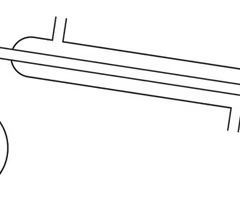
6
New cards
State the method used to obtain kerosene from a crude oil.
fractional distillation
7
New cards
Draw the equipment used in fractional distillation in the lab
For what process is this equipment used?
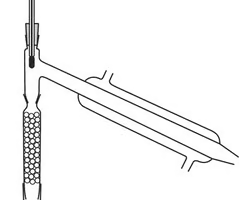
8
New cards
Explain how fractional distillation is used to separate a mixture of different liquids
The different liquids have different boiling points
9
New cards
State the method used to extract the red dye from a sample of rose petals
dissolving
10
New cards
Describe how pure salt can be obtained from rock salt
1) Grind rock salt into a fine powder. 2) Add powder to hot water and stir to dissolve salt. 3) Filter mixture. Salt solution passes through the filter paper leaving behind the sand. 4) Boil filtrate to evaporate some of the water. 5) Leave saturated solution to cool so that crystals of salt form. 6) Filter cold mixture to separate the crystals from the remaining solution.
11
New cards
Ethanol is a flammable liquid. Suggest how it could be heated safely
Use a water bath
12
New cards
Explain how a chromatogram shows that different dyes are different from each other
Each dyes has a different mixture
13
New cards
State the expression for calculating molar concentration
Molar concentration \= Amount (in moles)/volume (in dm^³)
14
New cards
Which cation gives a crimson red flame colour?
Li⁺
15
New cards
Which cation gives a orange flame colour?
Na⁺
16
New cards
Which cation gives a lilac flame colour?
K⁺
17
New cards
Which cation gives a brick red flame colour?
Ca²⁺
18
New cards
Describe how you would carry out a flame test
Put solid onto a wire. Put into a blue flame
19
New cards
How would you test for the ammonium ion?
Add sodium hydroxide. If ammonium ions were present
20
New cards
Describe how you would test for Cu²⁺ ions
Add sodium hydroxide and a blue precipitate will form
21
New cards
Give the formula of the blue precipitate formed when sodium hydroxide is added to a solution containing Cu²⁺
Cu(OH)₂
22
New cards
Describe how you would test for Fe²⁺ ions
Add sodium hydroxide and a green precipitate will form
23
New cards
Write a word equation for the reaction between sodium hydroxide and iron(II) sulfate
sodium hydroxide + iron(II) sulfate -\> iron (II) hydroxide + sodium sulfate
24
New cards
Describe how you would test for Fe³⁺ ions
Add sodium hydroxide and a brown precipitate will form
25
New cards
What 2 things are added to a solution to test for chloride ions? What is observed if they are present?
Add dilute nitric acid and silver nitrate. A white precipitate of silver chloride is formed.
26
New cards
Describe the test for bromide ions.
Add dilute nitric acid and silver nitrate. A cream precipitate of silver bromide is formed.
27
New cards
After adding nitric acid and silver nitrate to a solution containing iodide ions
what colour precipitate is formed?
28
New cards
Why is hydrochloric acid added before barium chloride solution in testing for sulfate ions?
To remove carbonate ions
29
New cards
Describe how you would test for sulfate ions
Add dilute HCl
30
New cards
Write an chemical equation for the reaction between barium chloride and lithium sulfate (Li₂SO₄). Include state symbols. Also
what would you see?
31
New cards
Describe how you would test for carbonate ions
CO₃²⁻
32
New cards
Describe the test for ammonia gas
Turns damp red litmus paper blue
33
New cards
State the expression for calculating % yield. (Triple science only!)
% yield \= (actual amount of products/theoretical amount of products) x100
34
New cards
Describe the chemical test for water
Add water to anhydrous copper(II) sulfate which will change from white to blue if water is present
35
New cards
What is the symbol for a reversible reaction?
36
New cards
The addition of water to anhydrous copper sulfate can be used to test for the presence of water. The reaction is reversible. What is the word equation? Describe the colour change.
anhydrous copper sulfate (white) + water
37
New cards
Ammonia and hydrogen chloride react together in a reversible reaction to produce a white solid. What are the word and symbol equations?
ammonia + hydrogen chloride
38
New cards
State two features of a reaction that is in dynamic equilibrium
1) The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the backward reaction. 2) There is no overall change in concentrations.
39
New cards
Predict what will happen to the equilibrium position in the following reaction when the pressure is increased. Give a reason for your prediction: CH₄(g) + H₂O(g)
Equilibrium will move to the left because there are fewer molecules on the left hand side
40
New cards
Predict what will happen to the equilibrium position in the following reaction when the temperature is increased. Give a reason for your prediction: CH₄(g) + H₂O(g)
Equilibrium will move to the right because the forward reaction is endothermic
41
New cards
Predict what will happen to the rate of reaction in the following reaction when the temperature and pressure is increased. Give a reason for your prediction: CH₄(g) + H₂O(g)
The rate will increase
42
New cards
Predict what will happen to the equilibrium position in the following reaction when the temperature is increased. Give a reason for your prediction: CO(g) + H₂O(g)
Equilibrium will move to left the because the reaction is exothermic
43
New cards
Predict what will happen to the equilibrium position in the following reaction when the temperature is decreased. Give a reason for your prediction: CO(g) + 2H₂(g)
Equilibrium will move to right the because the reaction is exothermic
44
New cards
Predict what will happen to the equilibrium position in the following reaction when the pressure is decreased. Give a reason for your prediction: CO(g) + 2H₂(g)
Equilibrium will move to left the because there are more molecules on the left hand side
45
New cards
State the raw materials used in the manufacture of ammonia
nitrogen from air and hydrogen from natural gas
46
New cards
State a use for N₂
making ammonia
47
New cards
The following reaction is used to manufacture ammonia in the Haber process: N₂ + 3H₂ -\> 2NH₃ ΔH \= -92KJ/mol. The reaction is carried out at 450⁰C but the reaction would be faster if a higher temperature were used. Suggest why a higher temperature is not used in the Haber process
Yield would decrease and energy costs would increase
48
New cards
State the temperature used for the manufacture of ammonia by the Haber process
450°C
49
New cards
State the pressure used for the manufacture of ammonia by the Haber process
200 atm
50
New cards
State the catalyst used for the manufacture of ammonia by the Haber process
Iron
51
New cards
How is ammonia separated from unreacted hydrogen and nitrogen in the Haber process?
The reaction mixture is cooled until the ammonia condenses into a liquid
52
New cards
What happens to the unreacted hydrogen and nitrogen in the Haber process?
Recycled
53
New cards
State the uses of ammonia
manufacture of nitric acid and fertilisers
54
New cards
Suggest the names of two elements
other than nitrogen
55
New cards
Write a chemical equation for the reaction between ammonia and nitric acid
NH₃ + HNO₃ -\> NH₄NO₃
56
New cards
State the raw materials used in the manufacture of sulfuric acid. (Triple science only!)
sulphur (from ores) and oxygen (from air)
57
New cards
Describe the manufacture of sulfuric acid by the contact process. (Triple science only!)
1) Making of sulfur dioxide: S + O₂ -\> SO₂
58
New cards
State the temperature used for the manufacture of sulfuric acid by the contact process. (Triple science only!)
450°C
59
New cards
State the pressure used for the manufacture of sulfuric acid by the contact process. (Triple science only!)
2 atm
60
New cards
State the catalyst used for the manufacture of sulfuric acid by the contact process. (Triple science only!)
Vanadium(V) oxide
61
New cards
State the uses of sulfuric acid. (Triple science only!)
manufacture of detergents
62
New cards
In Chemistry
what is the meaning of the word Group? What does that tell us about the electron configuration?
63
New cards
In Chemistry
what is the meaning of the word Period? What does that tell us about the electron configuration?
64
New cards
Where are the metals in the Periodic Table? Where are the Non-Metals?
Metals on the left of the Periodic Table. Non-Metals on the top-right
65
New cards
If an element conducts electricity
is it a metal or a non-metal?
66
New cards
If an element doesn't conducts electricity
is it a metal or a non-metal?
67
New cards
Are metal oxides acidic or basic?
Basic
68
New cards
Are non-metal oxides acidic or basic?
Acidic
69
New cards
Why do elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same chemical properties?
Elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same number of electrons in their outer shell
70
New cards
Explain
in terms of the arrangement of electrons in its atoms
71
New cards
Write the chemical equation for the reaction betweem sodium and water
2Na + 2H₂O -\> 2NaOH + H₂
72
New cards
State 5 observations when potassium reacts with water
1) fizzing occurs 2) potassium moves around 3) potassium melts 4) lilac flame is seen 5) potassium disappears 6) potassium floats
73
New cards
Complete the equation for the reaction by inserting the state symbols: 2Li(....) + 2H₂O(....) -\> 2LiOH(...) + H₂(....)
2Li(s) + 2H₂O(l) -\> 2LiOH(aq) + H₂(g)
74
New cards
State 4 observations when sodium reacts with water
1) fizzing occurs 2) sodium moves around 3) sodium melts 4) sodium disappears 5) sodium floats
75
New cards
How should group 1 elements be stored
Under oil
76
New cards
Describe the relative reactivities of the elements in Group 1
The reactivity increases as you go down the group
77
New cards
Explain
by referring to the electronic configurations of sodium and potassium
78
New cards
State the colour and physical state of chlorine at room temperature
Green gas
79
New cards
State the colour and physical state of bromine at room temperature
Orange brown liquid
80
New cards
State the colour and physical state of iodine at room temperature
Grey solid
81
New cards
Suggest how the reactivity of astatine compares to that of iodine. Explain your answer.
Astatine is less reactive because group 7 elements get less reactive with increasing atomic number.
82
New cards
State the most reactive element in group 7
Fluorine
83
New cards
Why does chlorine react with hydrogen bromide?
Chlorine is more reactive and so displaces the bromine.
84
New cards
Hydrogen bromide is reacted with chlorine to form bromine. Write a chemical equation.
2HBr + Cl₂ -\> 2HCl + Br₂
85
New cards
State the colour change observed when bromine is added to an aqueous solution of potassium iodide
Colourless to brown
86
New cards
Identify the element that is displaced in this reaction: 2HBr + Cl₂ -\> 2HCl + Br₂
Bromine
87
New cards
Why would there be no reaction when iodine was added to sodium bromide solution?
Iodine as it is less reactive than bromine
88
New cards
Name the substance with the brown colour that forms whem chlorine is added to potassium iodide solution
Iodine as it is less reactive than chlorine
89
New cards
Identify the species that is oxidised in the following reaction. Explain your answer: 2Br⁻ + Cl₂ -\> 2Cl⁻ + Br₂
Bromide. Loses electrons
90
New cards
Identify the species that is reduced in the following reaction. Explain your answer: 2Br⁻ + Cl₂ -\> 2Cl⁻ + Br₂
Chlorine. Gains electrons
91
New cards
When chlorine gas is bubbled into an aqueous solution of potassium iodide
the colourless solution turns brown. Complete the following ionic equation: Cl₂(g)+ \___I⁻(aq) -\> 2Cl⁻(aq) + \___(aq)
92
New cards
Describe the test for chlorine gas
Turns moist litmus paper white (bleaches)
93
New cards
Describe
in terms of electrons
94
New cards
Explain the term ionic bond
An ionic bond is the strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
95
New cards
Explain
in terms of structure and bonding
96
New cards
Explain
in terms of structure and bonding
97
New cards
Explain why magnesium oxide has a higher melting point than sodium chloride. (Triple science only!)
Mg²⁺ and O²⁻ ions have a higher charge than sodium and chloride therefore the electrostatic forces between the ions are much stronger. This requires more energy to break.
98
New cards
Describe the structure of an ionic compound
e.g NaCl. (Triple science only!)
99
New cards
Draw a diagram to represent the positions of the ions in a crystal of sodium chloride.
A - sodium ions. B - Chloride ions
100
New cards
Describe the formation of a covalent bond
The sharing of a pair of electrons between two nuclei