Greek and Roman Myth Exam 2
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Polis
city/state in ancient Greece (included temples and government buildings and outer wall)
Didactic Poetry
Poetry that contains clear morals or message
Etemolgial Myth
origin story (creation/cosmogonic myth narrates origin of world)
Greek Archaic Colonization
development of the polis, larger community has priority over family and kinships
Poetic Ephithets
eph comes from greek word Epheton which is added or attributed literaly device that describes person place or object by replacing it with a describitve word or phrase. (Hera golden sandals)
Epic Poetry
lengthy narrative poem about the extraordinary/heroic deeds of character significant to culture of poet
Oral Composition
creation of organization verbal formulation without reliance of writing (most myths were oral compositions before they got written down and generalized)
Dactylic Hexameter
poetic rythem that Homer typically used (1 long and 2 short pattern —uu)
Nostos
a hero who is returning home after a long time away (usually for adventure or military reasons) (something that they wanted to achieve like Odysseus)
Kleos
greek word for renown or glory, it carries implied meaning of what others fear of you. Greek heroes wanted to achieve this Achilles
Xenia
hospitality or guest-friendship (Zeus-Xenios is the enforcer of it) ancient travelers relied on others’ hospitality and kindness, good xenia was providing food and a bed, not asking too many questions, and trading gifts.
Homophrosyne
like-minded, ex.) Odysseus and his wife Penelope both being clever and savvy.
Dionysia (the city)
large festival in 5th century ancient Athens to honor Dionysus, tragedy, comedy and drama performances were held throughout March. The playwrights would compete, each poet would have a day and do 3 tragedies and one satirical play.
Measure of Athenian Tragedy
typically 12 people consisted the chorus, 3 actors or less; began with the prologue and would use a lot of poetic language, monologues by themselves and dialogue with the chorus or another actor; always wore masks with hair sewn in, no women. no violent action is depicted onstage, messengers deliver speech of violent action.
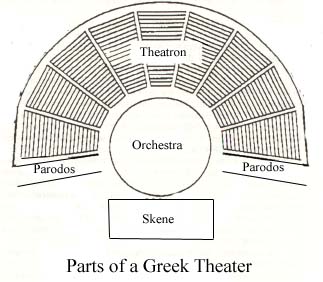
Parts of a Greek Theatre
the orchestra/ chorus of 12 people, the skene (a small building that served as backstage, with 2 doors for exit and entrance), theatron (the audience)
Chorus/Choral Ode
the 12 people singing in the play, change with each play, have special connections between them and the audience. physically between the actors and audience, interacts with actors but doesn’t contribute to action.
Dithyramb
a wild choral hymn of ancient Greece usually dedicated to Dionysus, a choral song or chant. strophe-turn, antistrophe-counter-turn, epode-added as bridge
Ekkyklema
wheeled platform that the Athenians rolled to push on stage or off stage, to roll off a dead body
Areopagus Court/ Athenian Jury System
500 jurors; men randomly selected, blood vengeance is no longer accepted and instead the jury system, individual grievances must be resolved within the framework of the larger political and social community
Bacchants
female worshipers of Dionysus, they prepared his wine, and used it (along with dancing and sex) to access a state of frenzied, divine madness and ecstasy. In this altered state, they were believed to be possessed by the god, imbued with gifts of prophecy and superhuman strength.
Aeschylus
greek tragedian, late 4th to 5th century, fought at Marathon and major battles of Persian wars. he’s the earliest major tragedian whose work survived. he created the orestia- Agamemnon, the libation bearers, the furies
Homer
wrote the iliad and the odyssey, at the very beginning of the archaic period. he was apparently blind
Hesiod
lived around 700 BCE, during the archaic period, wrote theogony (cosmogony) and works & days ‘wisdom’ poetry (didactic)
Euripides
4th century Classical Athens Greek Tragedian, Bacchae, and 2 other plays discovered after his death were produced by his son or nephew and won first prize. Bacchae, Hippolytus and Medea author.