3.1.1.3 Factors driving change in the magnitude of these stores over time and space, including flows and transfers at plant, sere and continental scales. Photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, combustion, carbon sequestration in oceans and sediments, weathering.
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are transfers in carbon cycles, and why are they important?
transfers are processes which move carbon between stores; this may include a change in state
The size of transfers controls the size of
stores
What are the main transfers operating in the carbon cycle?
1- photosynthesis
2- respiration
3- decomposition
4- combustion
5- burial and compaction
6- carbon sequestration
7- weatheringDescribe how photosynthesis acts as a carbon flow [4 marks]
bonus: positive or negative feedback?
Equation: “Carbon dioxide + water + light energy = glucose + oxygen
Photosynthesis transfers carbon stored in the atmosphere to biomass. During photosynthesis: light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll - a green substance found in chloroplasts in the palisade cells in the leaf. Plants and phytoplankton use energy from the sun to change water and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen, allowing them to grow. Carbon is passed through the food chain and released through respiration and decomposition.
BONUS: This is a negative feedback loop as it removes CO2 from the atmosphere helping to regulate Earth’s climate.
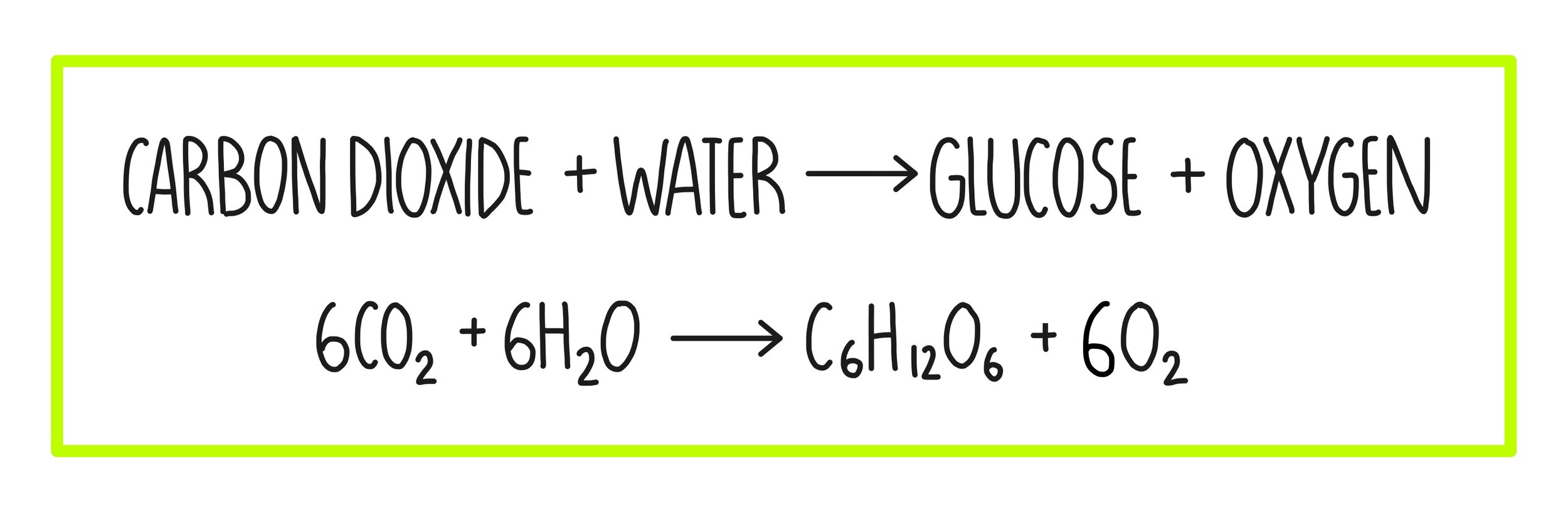
Describe how respiration acts as a carbon flow [4 marks]
Respiration transfers carbon from living organisms to the atmosphere.
Both plants and animals break down glucose during respiration to produce energy in the form of ATP.
As glucose is broken down, carbon dioxide is released as a byproduct into the atmosphere.
This carbon dioxide can be taken up by plants during photosynthesis to produce glucose again, completing the cycle. In animals, it is released into the atmosphere through exhalation.
Describe how decomposition acts as a carbon flow [4 marks]
Decomposition transfers carbon stored in dead biomass to the atmosphere and soil. When organisms die, they are consumed by decomposers such as bacteria, fungi and earthworms. This releases carbon dioxide in the process. Some carbon is transferred to the soil in the form of humus. The rate of decomposition is reliant on temperatures (higher temperatures normally leads to higher rate of decomposition
Describe how combustion acts as a carbon flow [4 marks]
Combustion is basically the burning of material. An example of combustion is burning fossil fuels to produce energy. Combustion releases carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere as a byproduct. The carbon emitted during combustion can be absorbed by carbon sinks such as forests and oceans, where it is stored temporarily, influencing the balance of carbon within these reservoirs.
Describe how sequestration acts as a carbon flow [4 marks]
Carbon sequestration is an umbrella term used to describe the transfer of carbon from the atmosphere to carbon sinks such as forests, oceans, and soils
Carbon sequestration helps to mitigate climate change by reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. However, carbon is sequestered until it is burnt (combustion).
CCS stands for Carbon Capture and Storage, which is a type of carbon sequestration. CCS is a recent term used to describe the technological ‘capturing’ of carbon emitted from power stations
Advantages of carbon capture storage
Can be fitted to existing coal power stations.
Captures 90% of CO₂ produced and has the potential to capture half the world's CO₂ emissions.
Disadvantages of carbon capture storage
High cost is the main restriction to the growth of CCS.
Increases energy demand of power stations.
May not be space to fit it to existing power stations.
Describe how weathering acts as a carbon flow [4 marks]
Chemical weathering transfers carbon from the atmosphere to the hydrosphere and biosphere. Carbonation weathering occurs when CO ₂ in the air mixes with rainwater to create acid rain which aids erosion of rocks such as limestone. The carbon is moved through the water cycle and enters the oceans. Marine organisms use the carbon in the water to build their shells.
What is a carbon source
Carbon source - A store that emits more carbon than it absorbs
E.g. a damaged rainforest
What is a carbon sink
Carbon sink - A store that absorbs more carbon than it emits.
E.g. a virgin rainforest
Summarise carbon cycle of a tree
tree acts as a carbon sink- wood is about 50% carbon
flows include photosynthesis, leaf litter, decomposition, respiration by decomposers and general plant respiration