Mucogingival Deformities and Conditions Around Teeth
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What are Mucogingival Deformities and Conditions
Any defect associated with deviation from normal anatomic/morphologic relationship between gingiva and alveolar mucosa
All age groups susceptible
Can affect any tooth or implant and can occur in presence or absence of periodontal disease
What are examples of mucogingival deformations or condition
Gingival/soft tissue recession
Lack of keratinized gingiva
Decreased vestibular depth
Aberrant frenum/muscle position
Gingival excess
Abnormal color
What are Periodontal biotypes
Features of periodontium influenced by genetic and environmental factors
What are the 3 Periodontal biotypes
Gingival biotype
Bone morphology
Tooth dimension of any given tooth
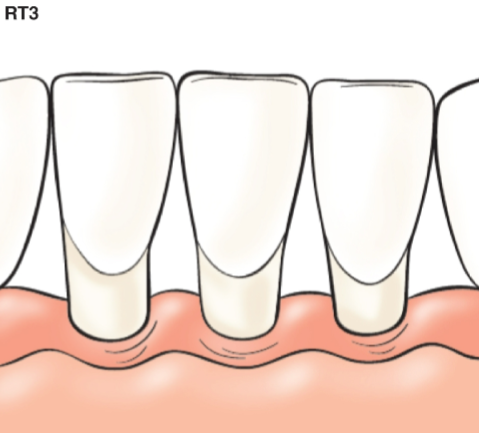
What is a thin-scalloped gingival biotype
Slender, triangular-shaped crown
Thin, delicate, friable soft tissue with thin alveolar bone
Narrow zone of keratinized tissue
Accentuated scalloped gingival margin contour
Greater tendency for onset, progression of mucogingival deformity
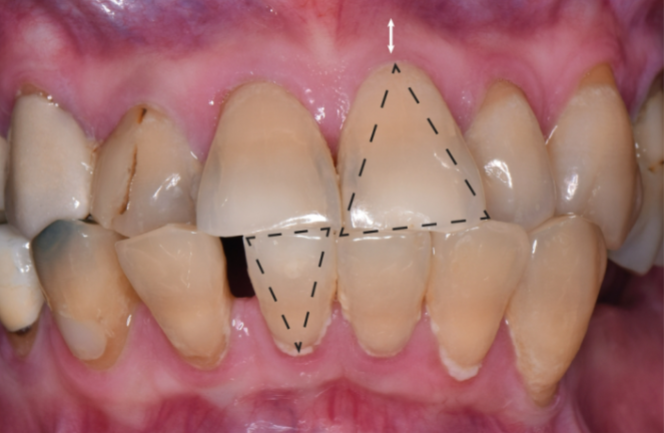
What is a thick-scalloped gingival biotype
Slender, triangular-shaped crown
Thick, fibrotic gingiva
Narrow-to-moderate zone of keratinized tissue
Accentuated scalloped gingival margin contour
Prone to development of mucogingival deformity
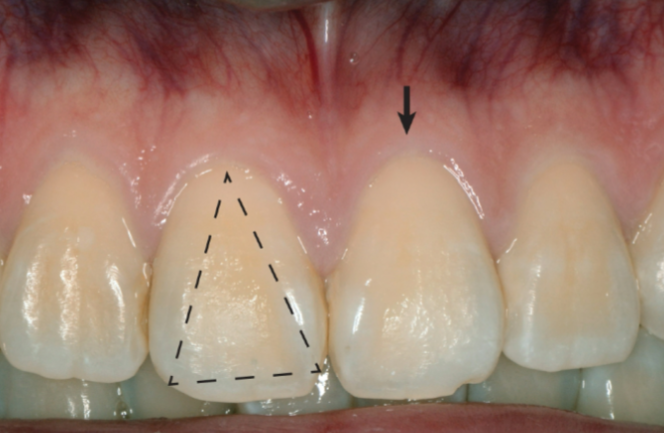
What is thick-flat biofilm
Wide, square-shaped crown
Thick, dense, and fibrotic tissue
Wide band of keratinized tissue
Flat gingival margin contour
More resilient and less susceptible to inflammation and trauma than thin- and thick-scalloped biotypes
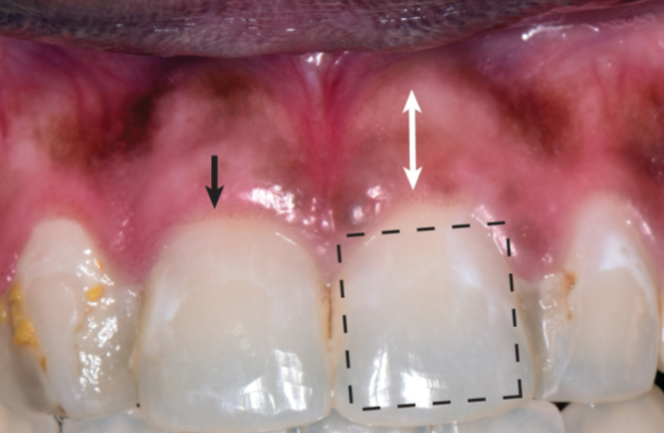
Can Periodontal biotype vary among different teeth within same individual
yes
Describe recession of gingival margins
Movement of gingival margin to point apical to cementoenamel junction
Most common mucogingival deformity
Can affect any age group
Corresponds to attachment loss that exposes rootsurface to oral environment
What is the Miller classification system for recession
Most widely used for nearly four decades
Based on level of gingival margin with respect to mucogingival junction and underlying alveolar bone
Consists of four recessions categories
What is class 1
Marginal tissue that does not extend to mucogingival junction (MGJ)
What is class 2
Marginal tissue recession that extends to or beyond MGJ with no periodontal loss in interdental area
What is class 3
Marginal tissue recession that extends to or beyond MGJ with interdental bone or soft-tissue loss and/or malpositioning of teeth
What is class 4
Marginal tissue recession that extends beyond MGJ with severe loss of interdental bone to level corresponding to most apical extent of marginal tissue recession
What is the Cairo classification system
Uses objective identifiable criterion (clinical attachment level) to classify extent and severity of soft tissue recession
More reliable; can be used in clinical practice
Identifies three gingival recession types
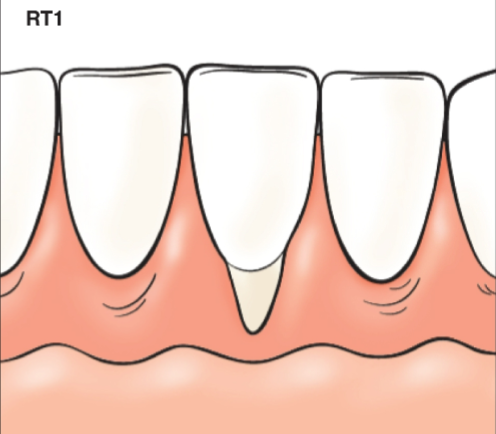
Cairo recession type 1
Gingival recession with no loss of interproximal attachment
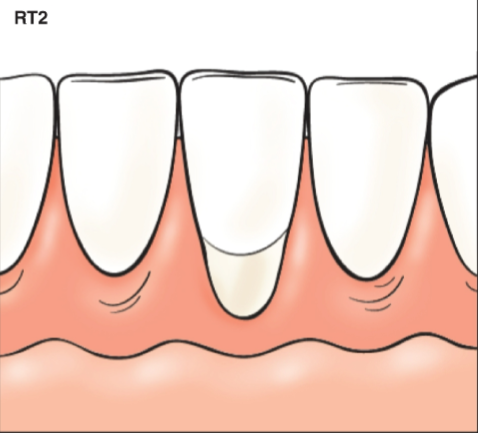
Cairo recession type 2
Gingival recession with loss of interproximal attachment
Amount of interproximal attachment loss less than or equal to buccal attachment loss
Cairo recession type 3
Gingival recession with loss of interproximal attachment
Amount of interproximal attachment loss greater than buccal attachment loss