MIC 205 Exam 4: Chapter 16. Adaptive Immunity
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
Specific Defenses
Third line of Defense: lymphocytes, antibodies ( specific immune response)
AB is a another name for what?
Antibody
Characteristics of Specific Immunity
The body’s ability to recognize and defend itself against distinct invaders and their products
“Smart” system - memory function allow for rapid response to subsequent encoutners with familiar pathogens
Acquired over time as the body “teachs” its immune cells about differences between foreighn and self
What is an Antigen?
Any molecule or molecular fragment that triggers a specific immune response
What are included in antigens?
Components of bacterial cell walls
capsules
proteins of viruses, fungi, and protozoa
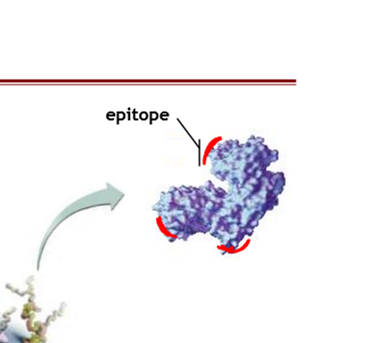
What is an Epitope?
A defined region or frageent of a molecule that has antigentic properties; note that a simple large molecule ( e.g. protein) may possess multiple epitopes
Food and dust also can contain antigentic particles
They are antigens, but they are a specific area of the protein ( which is also an antigen)
Induce a separate response ( subareas of the antigen)
Induce a strong response
Three different ways Antigens enter the body
1.) Through breaks in the skin and mucous membranes ( portal of entry / break in skin)
2.) Direct injection, as with a bite or needle ( vaccine)
3.) Through organ transplants and skin grafts
Do antigens have to be a certain molecule weight?
Yes, it has to be a big enough, or the immune system will ignore it
Example of an antigen the immune system ignores
Penicillin and other drugs due to their size
Other examples of Antigens
Lactose, Foods, Air molecules
Are proteins and molecules considered antigens?
Yes
Lymphatic System
A nework of organs, fluid-retun vessles, and clean-up cells that screen the tissues of the body for foreign antigens
Components of Lympathic System
Lymphoid Cells
Lymphatic Vessels
Lymph Nodes
Spleen, tonsils, etc
Lymph
Liquid similar in composition to blood plasma that arises from fluid leaked from blood vessels into surrounding tissues
Lymph is a ___ fluid?
immune
Lymph arises from where?
fluid leaked from blood vessels into surrounding tissues
Lymphoid Cells include:
Lymphocytes ( T-cells and B Cells)/ smallest of the WBCS
Where do lymphoid cells develop?
Stem cells in the red bone marrow
Lymphatic Vessels
One-ways system that collects lymph from tissues to the lymph nodes and returns it to the circulatory system
Lymph Nodes
House leukocytes that recognize and attack foreign antigens in lymph
Where are lymph nodes concentrated in?
Neck, groin, armpit,and abdominal regions
Third line of Defense mainly occurs where?
Lymphoid Cells, Lymphatic Vessels, and Lymph nodes
Any damaged/ cells bacteria are filtered into where?
The Lymphatic System
Spleen
similar in structure and function to the lymph nodes
Filters bacteria, viruses, toxins, and other foreign matter from the blood
Tonsils and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues (MALT)
physically trap foreign particles and microbes
Mucosal tissues include ( MALT)?
appendix
lymphoid tissue of the respiraotry tract
Peyer’s patches of the wall of the small intestine
Lymphocytes (Overview)
aries and mature in red bone marrow ( B cells) or thymus ( T-Cells)
Clonal Deletion
Found in the spleenand lymph nodes
Small percentage of them circulate in the blood
Activated ( Clonal Selection) by a single matching antigen will result in cell division
Produce memory cells for later response
B-lymphocytes ( B cells ) arise from where?
Red bone Marrow
T lymphocytes ( T cells ) arise from where?
Thymus
Where do majority of lymphocytes stay in?
Spleen, but a small percentage of them are in the blood
Clonal Deletion
Occurs with B and T Cells
Critcial that immune response directed against antigens derived from your “self” molecules ( autoantigens)
Body “edits” lymphocytes to eliminate all self-reactive cells
What cells in the bone marrow give rise to B cells?
Stem cells
B cells that respond to self Ag are
normally inactivated by Clonal Deletion ( self vs non-self)
Assortment of B Cells ( heterogenity)
During maturation, randomization of variable region receptors
Each cells has two matching receptors
Ag binds specifically to the antibody of the B cells ( specificity)
Activated B Cells Differentiate
Plasma cells synthesize/ secretes antibodies
Memory cells wait for restimulation by the same Ag later ( memory)
What is are antibodies?
Soluble proteins composed of polypeptides that are held together by covalent bonds
Where do antibodies circulate?
Blood and lymph where they find their counterpart antigen
What are antibodies secreted from?
Plasma cells which are B cells that are actively fighting antigens
Are antibodies considered part of the humoral immune response?
Yes, since bodily fluids like lymph and blood once were called humor
Structure of Antibodies
Four polypeptides
Covalent Bonds
Heavy ( large) chains and light ( small) chains
Two antigen-bind sites per antibody molecules
FC region
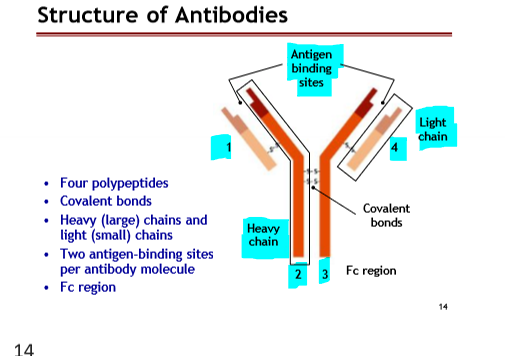
What is another name for the FC region?
The Constant Region
FC/ Constant region is more common among Antibodis
The Heavy and Light chains are bonded by what bond
Disulfate bonding, a type of Covalent bond
The Antibody class involved in the immune response depends on these factors:
Type of foreign antigen
Portal of entry
Antibody function
What are the five different classes of Antibodies?
IgA
IgD
IgE
IgG
IgM
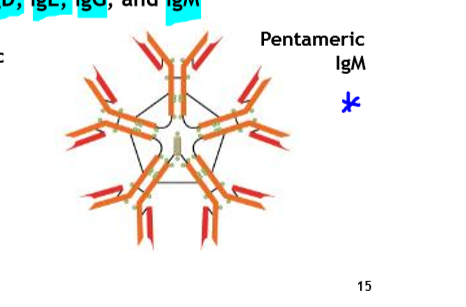
IgM
the primary antibody
shape: pentameric
First class of antibody in the humoral system
IgG
most prominnt in the immune system
shape: monomeric (Y-shaped)
IgA
Found in mucous membranes
Associated with breast milk, transferred from mom to baby, and they are protectory for the baby
shape: Dimeric
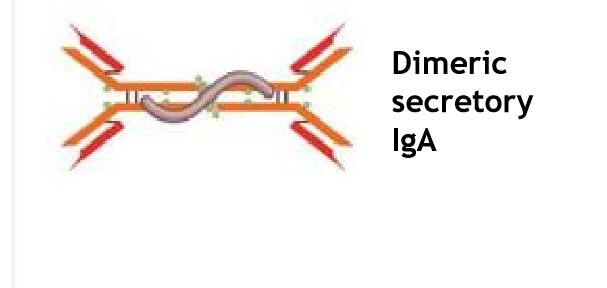
What is the class of antibody that is closely related with breast-milk/ breast feeding
IgA
IgG
Shape: Monomeric
Function: Allergic Reactions and other immune responses
IgD
Function: Not Known
Very first antibody that was produced by mammalians
Shape: Monomeric

Antibody Function
Form strong, noncovalent interactions with antigen
Binding occurs because antibody’s antigen-binding sites are complementary to antigeneic determinants ( epitopes)
Interactions involve hydrogen bonds and other attractions
What type of bonds are formed between an antigen and an antibody
Noncovalent bonds
What are the several roles of the Antibodies?
Activation of Complement System
Stimulation of inflammation
Agglutination
Neutralization
Opsonization ( phagocyte activation)
Activaton of Complement System and Stimulation of Inflammation ( Antibody Functions)
Chemicals signals tied back to 2nd line of defense for activation of complement system and stimulation of inflammation
Agglutination ( Antibody Function)
Crosslinking of antibodies to microbes —> removing of structures —> entice phagocyte to engulf the microbe —> Agglutination
Neutralization
Antibodies bind to glycoprotein spikes —> neutralizes the potential microbes by binding the glycoprotein spikes on the virus —> needs ligand to bind to receptor ( neutralizing)
Can toxins be neutralized by the antibody’s binding
yes, toxins can be neutralized by the antibody’s binding thus neutralizing the toxin
Opsonization
Performed by the complement system ( Complement protein binds to microbe —> signals immune system —> Phagocyte adheres to microbe for removal)
Process of Opsonization
Antibodies attach antibody to microbe —> Phagocyte comes in and attaches to antibody —> Phagocytosis can occur
Antigen receptors can recognize antigens which can cause it to?
Proliferate
Humoral Immune Response
Antibody-mediated responses mounted against exogenous pathogens
Components of the Humoral Immune Response
B cell activation
Clonal selections
Formation of plasma B Cells
Formation of memory B cells and immunological memory
When concerning humoral immune response, antibody-mediated responsed are mounted agains exogenous pathogens or endogenous pathogens?
Exogenous Pathogens
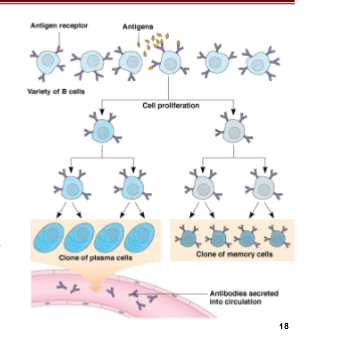
Plasma Cells only secrete ___?
Antibodies
Where are plasma cells located?
In the endoplasmic reticulum
What class of antibodies are secreted first?
IgM
When does the class switch of Antibodies occur?
It occurs when a mature B cells when activated by an antigen, changes the type of antibody it produces from IgM to antother antibody class ( typically IgG)
What happens to memory cells?
They are not used to remove the antigen, so they stay dormant
However, they are used again during a second response to the same antigen ( can take months or years to occur)
Plasma Cells
Make up the majority of cells produced during B cell proliferation
Plasma cells secrete only antibody molecules that are ___
complementary to the specific antigenic determinant
Are plasma cells short lived?
Yes, plasma cells are short lived they die within a few days of activation, through their antibodies and progency can persist
Do Memory B cells secrete antibodies?
They do not secret antibodies
Memory B cells display what on their membranes?
They display antibodies that are complimentary to the sepcific antigentic determinant that triggered their production
Are Memory B Cells long-lived?
Yes, they are long-lived cells that divide only a few times and then persist in the lymphoid tissue
Can memory B cells initiate antibody production if the same antigen is encountered again?
Yes, they are able to initiate antibody production
Truth about antigen binding to B Cells
It is rare that free Ag bind directly with B cells
Usually, Ag presented by antoher cell will produce a signal ( cytokines) to activate
Antigen Presenting Cell ( APC)
Display Ag on their surface to T-helper cell
T helper cell ( Th1 or Th2 cell)
Will direct the response via chemical signals such as interleukins ( IL)
Why do antigens present Ag on their surface to T-helper cells
To stimulate a more cell-mediated response with the assistance of T-Helper cells
T-helper cells with direct the response via chemical signals such as interleukins (IL)
Lysing
Needing more of the humoral response to kill everything after lysing cells
How many days does it take to seecrete IgM antibodies
5 days
IgM switches to IgG at appropximately at this day?
Roughly Day 6 or 7
What day is the peak amount of IgG during primary exposure?
Day 14
How many days does it take for the immune response to be fully activated?
10-14 days
What happens during a second exposure to a disease?
1.) Memory Cells become activated
2.) Memory cells make plasma cells
3.) Plasma cells make more antibdoies and memory cells
IgM 1st, IgG 2nd,
IgM produced at day 6
Max production of IgG at day 6
What is the difference between the second exposure and the first exposure to an antigen?
The immune response for the second exposure is more robust and happens faster
Are T-cells cell mediated immunity or humoral imuunity?
T-cells are cell mediated immunity
T Helper Cells (CD4)
Recognize MHC (safeguard signal)/ Ag complex from APC
Direct the specific immune response
T-cytotoxic Cells (CD8)
Triggers Apoptosis
Activated by Interleukin 2 produced by T helper cells
Attacks any cells carrying incorrect Ag/ MHC complex
Defense against cancer, virus-infected cells, tissue and organ transplant
T-cells serve protection against
Intercellular organisms, viruses, and cancer
What happens if you take away T-helper cells?
You are taking away the 3rd line of defense
What do T-helper cells recognize?
MHC
What T Cytotoxic Cells (CD8) do?
They tell cells to commite apoptosis
Where are Type T Lymphocytes ( T Cells) produced?
In the red bone marrow and MATURE in the thymus
Why must T-cells recognize MHC
This allows the immune system to remove foreign cells
examples: blood incompatibility, organ transplants
Where do T-cells circulate
Lymph, blood, and migrate to the lymph nodes, spleen, and Peyer’s patches
What percentage of B-cells are stored in the spleen?
10%
Are T-Cels part of the cell-mediated immune response?
Yes, because they act directly against various pathofens
They respond to intracellular pathogens and abnormal body cells
What are the most common intracellular pathogens
Viruses and intracellular bacteria