Genetics Exam 3
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Paralogs are…
DNA sequences that are similar to one another due to duplication.
functional redundancy
two identical genomic loci that have the same function causing immediate gain of function
solution to functional redundancy
Ohno’s Model and the DDC Model
Ohno’s Model has three fates:
neofunctionalization, pseudofunctionalization, retention of same ancestral function
DDC Model
Duplication Degeneration Complementary model
DDC leads to…
subfunctionalization
3 types of RNA produced during transcription and the specific polymerases
RNA polymerase I transcribes ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes.
RNA polymerase II transcribes all structural genes (mRNA).
RNA polymerase III transcribes transfer RNA (tRNA) and the 5S RNA genes.
RNA polymerase I
transcribes ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes
RNA polymerase II
transcribes all structural genes (mRNA).
RNA polymerase III
transcribes transfer RNA (tRNA) and the 5S RNA genes.
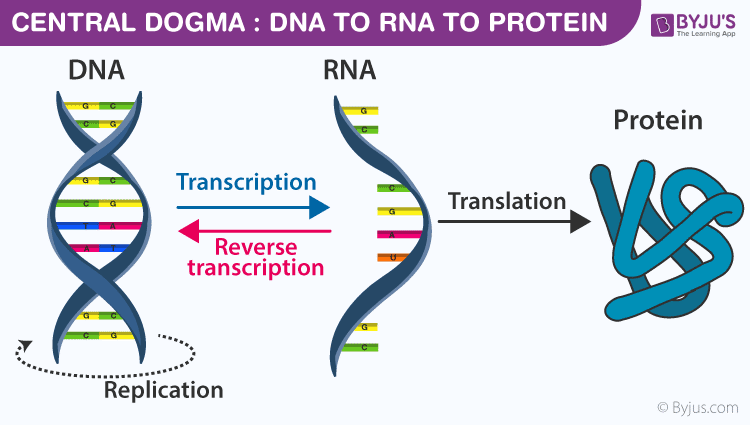
Central Dogma
How many Hox genes do humans have?
39
Hox clusters exhibit which two types of collinearity
temporal and spatial collinearity
Spatial Colinearity
Hox gene position in cluster matches relative position of Hox transcription/expression along
the primary Anterior-posterior axis.
Temporal collinearity
position of a Hox gene in the cluster determines timing of expression in
embryonic life.
processed pseudogene
mRNA molecules reverse transcribed by a special reverse transcription
polymerase, forming double stranded RNA/DNA hybrid that cannot be translated and can
integrate anywhere in the genome.
The wobble rule
The first codon of any protein in any organism is ‘AUG’. The tRNA with an anticodon ‘UAC’ carries the amino acid Methionine. Thus the first amino acid of any protein in any organism is Methionine. The start codon (AUG) defines the beginning of the open reading frame (ORF), a sequence of codons that defines the sequence of the polypeptide.

Exon skipping
spliceosome removes exon along with introns during mRNA splicing causing exon to be left out of final mRNA transcript
Cis mutation
A genetic alteration on the same DNA, chromosome, gene as the gene it affects
Trans mutation
Concept describing the evolutionary change of species into another
Pseudogenization
Paralog accumulates a LOF mutations eg deletion, nonsense,etc that makes it nonfunctional
Neofunctionalization
The extra paralog that is freed from constraints takes on a new function by cis and/or trans mutations
Retention of ancestral function
The second pardlog retains the same ancestral function.
The production of gene families, such as the goblin genes, is the result of
gene duplication
homologous genes with in a single species are said to be
paralogs
Activator proteins bind to what type of DNA sequence
enhancers
What is the result when the core histones are acetylated via histone acexyltransferase
The DNA becomes less associated with the core
Combination control of transcription factors refers to …
The combination of many factors determines the expression of any given
splicing joins together
two exons