Chapter 9: Pure Competition
Pure competition - A very large number of firms producing a standardized product; easy market entry/exit
Pure monopoly - 1 firm is sole seller of good/service; no market entry
Monopolistic competition - Relatively large number of sellers producing differentiated products; non-price competition
Oligopoly - Only a few sellers of a standardized or differentiated product; mutual interdependence
Pure competition characteristics
- Large # of independent sellers
- Identical product
- Price taker - Cannot change market price, can only adjust to it
- Free market entry/exit
Purely competitive demand
- Perfectly elastic at market price
- All firms can simultaneously increase price by reducing output
Average revenue - Revenue per unit
Total revenue - Price * corresponding quantity firm can sell
Marginal revenue - Change in total revenue (or the extra revenue) that results from selling one more unit of output
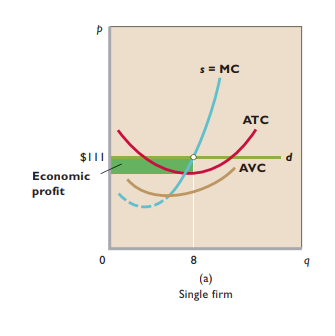
Profit maximization in short run
- Break-even point - Firm makes normal profit but not economic profit
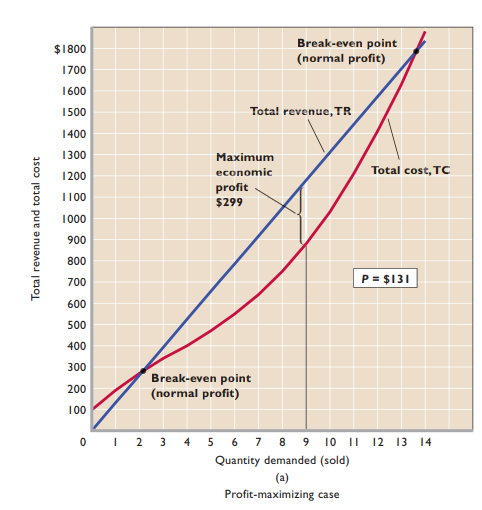
- MR = MC rule - In the short run, the firm will maximize profit or minimize loss by producing the output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost (as long as producing is preferable to shutting down).
- Applies only if producing preferred to shutting down
- Accurate guide no matter the firm type
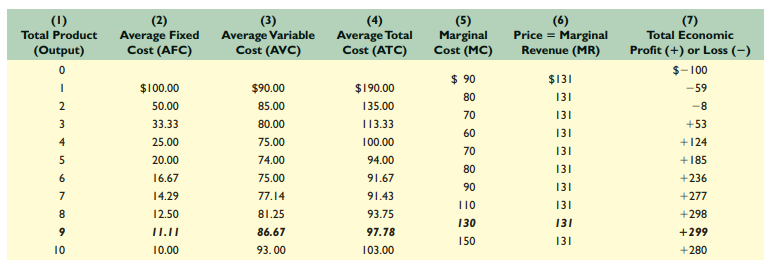
Economic profit = Total revenue - total cost
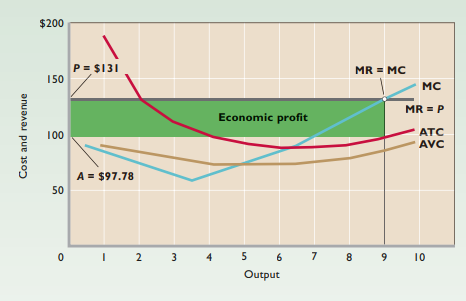
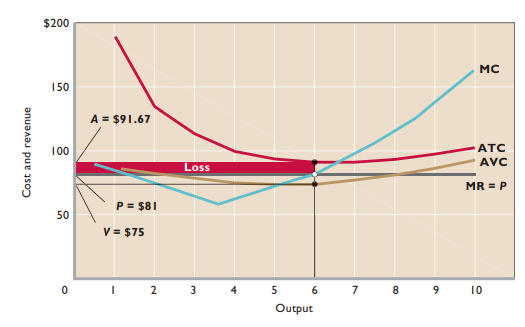
Price < Average variable cost → Shutting down more profitable than continuing to produce
Short-run supply curve - Solid segment of marginal cost curve
Higher product prices + marginal revenue → Purely competitive firm will expand output
Wage increase → Shifts supply curve right
Profit maximization in long run
- Only long-run adjustment is entry/exit of firms
- Identical cost curves
- Constant-cost industry
Long-run equilibrium
- MR = MC
- Economic profit of 0
- Firms enter → Market supply increases → Price decreases → Economic profit decreases
- Firms exit → Market supply decreases → Price increases → Economic profit increases
Long-run supply curve - Effect that changes in number of firms in industry will have on costs of individual firms in industry
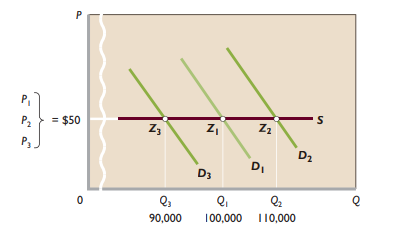
Constant cost industry - Industry expansion or contraction will not affect resource prices and therefore production costs
- Entry/exit of firms doesn’t shift long-run ATC curves
Decreasing cost industries - Industry expands → Firms experience lower costs
- Supply increases more than demand → Price decreases
Firm will only earn normal profit by producing with MR = MC rule
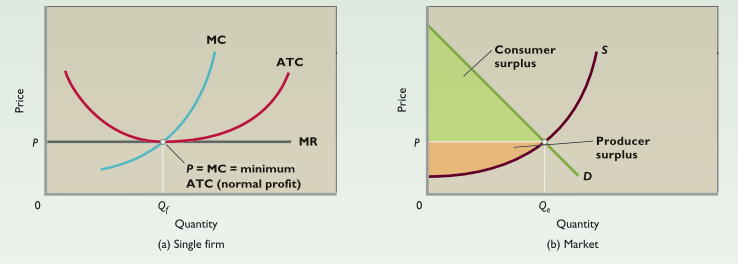
Productive efficiency - Goods being produced in least costly way
- P = minimum ATC
Allocative efficiency - Resources apportioned among firms + industries to yield mix of goods/services most wanted by society
- P = MC
- Producing beyond P = MC → Sacrifice alternative goods with greater value
Consumer surplus - Difference between the maximum prices that consumers are willing to pay for a product (as shown by the demand curve) and the market price of that product
Producer surplus - Difference between the minimum prices that producers are willing to accept for a product (as shown by the supply curve) and the market price of the product
Change in consumer tastes, resource supplies, technology → Automatic realignment of resources
Invisible hand - Businesses seek to further self-interest → Unconsciously benefits entire society