Microbiology Lab Midterm
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
ubiquity
present nearly everywhere
Normal flora
microorganisms associated with animal body tissue
Nosocomial infections
infection originate in hospital environments
Colony
visible cluster of bacteria growing on solid medium, presumably cultured from a single cell
Colony formation
when one microorganism is deposited on an agar surface and the nutrients provided allow a cell to start dividing
Sterile
free of any living organism
Contamination
introduction of any unwanted organisms
TSA
Trypticase Soy Agar
TSB
Trypticase Soy Broth
Environmental sampling procedure
obtain sample of microorganism using cotton swab
zigzag inoculation
dispose of cotton swab into biohazard bin
Label date, initials, and sampling location on agar side of plate
place agar side up in incubator
Why are plates stored upside down?
to prevent condensation on the agar
What should all be found on a correctly labeled dish
organism, date, initials, temperature
Where should the label be placed on a dish
around the outside edge on the agar side
For a tube, where should the label not be placed
near the lips of the tube
Colony morphology
Shape
edge
elevation
Primary purpose of agar plate
isolation
Primary purpose of agar slant
storage
Primary purpose of agar deep
test oxygen requirement and motility
Primary purpose of agar broth
grow large amounts of cells
What does TSA have that TSB does not
agar
Aseptic technique
ability to transfer cells from one place to another without contaminating the original culture, the new medium, or the environment
Aseptic technique procedure
flame the instrument between before and after each use and flame the top of the tube
where should media tubes be placed when not in use
in a rack
Which two bacteria were used for lab 2 aseptic technique
E. coli and Bacillus subtilis
E. coli is a facultative
anaerobe
B. subtilis is an obligate
aerobe
What growth patterns can be identified on slants
filiform
arborescent
beaded
effuse
rhizoid
echinulate
Bacterial growth in broth
pellicle
sediment
turbid
floculent
Bacterial growth in deep
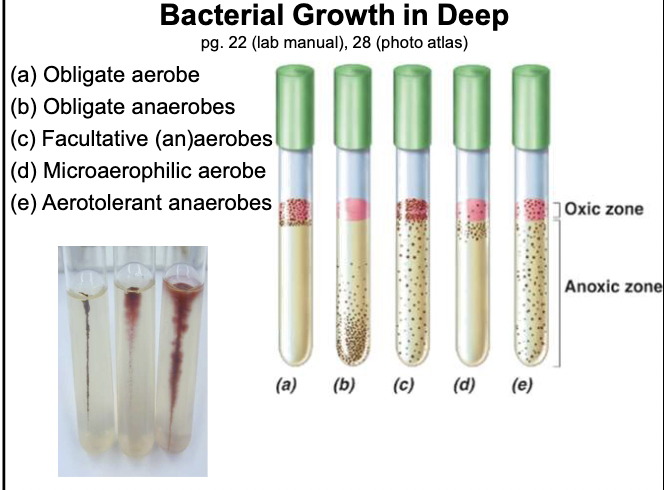
Who developed pure culture
Robert Koch
Mixed culture
a culture of many cells
Pure culture
one type of cell
Isolation streak procedure
Flame between each streak, inoculate plate, streak four times
Carrying microscope
use two hands and report any problems
How are images viewed in a microscope
reversed and inverted
Overal magnification
ocular lens x objective lens
What is the magnification for the ocular lens
10x
What are the magnifications of the objective lens
4x
10x
40x
100x
Resolution
the ability to distinguish between two points in an image
Contrast
the ability to distinguish between the sample and the background
Parfocal
the ability for a microscope to stay relatively in focus from one objective to the next
Storing microscope
4x objective lens in place
oil should be cleaned from lens
lower stage
wrap cord
slides removed
place microscope on desk
Four eukaryotic microbes examined in Lab 4
Protozoa
fungi/yeast
algae
helminths
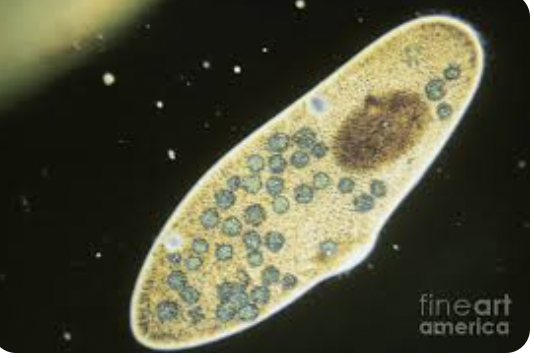
Protozoa
Paramecium
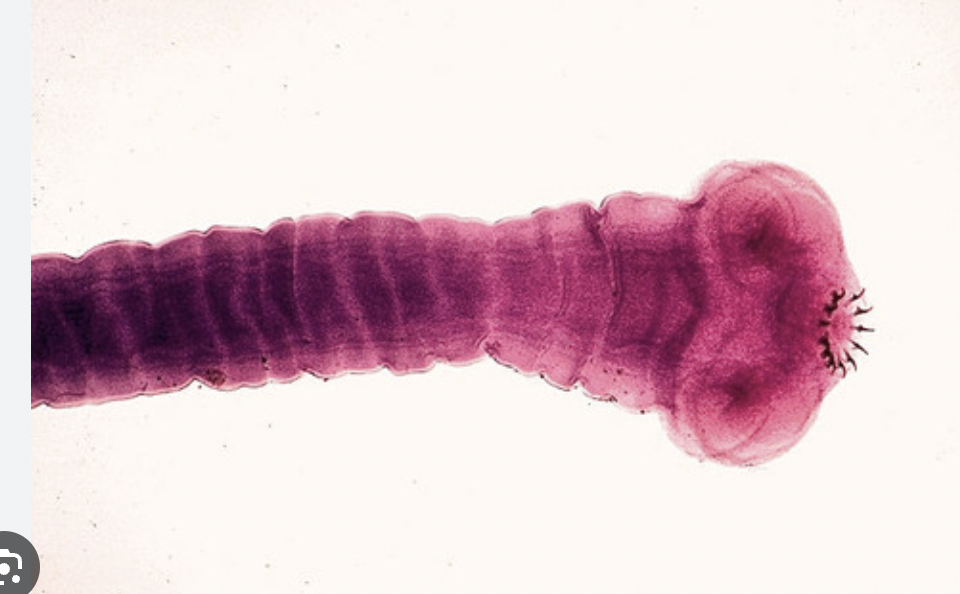
Helminth
scolex
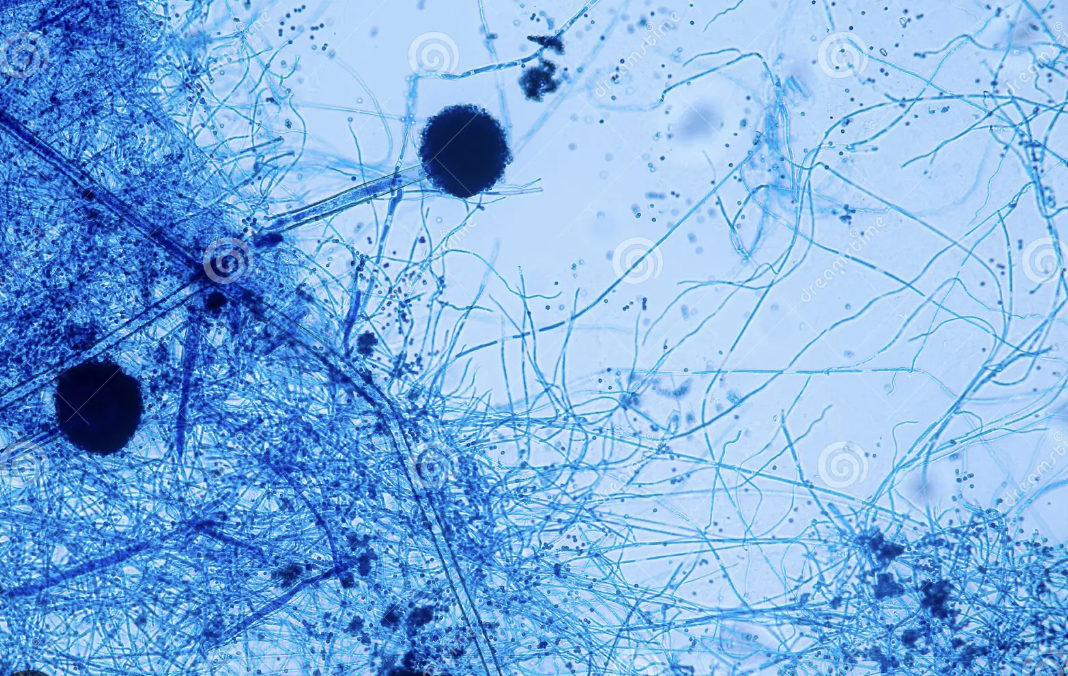
Fungi
Aspergillus
Algae
volvox
all cells have a ___ charge
negative
A basic stain stains the ___ and an acidic stain stains the ___
cell; background
Chromophore
a colored ion
Basic stain means ___ chromophore
positive
simple stain means ___ chromophore
one
Bacterial smear preparations
small drop of water on slide
aseptically add and mix bacteria
allow smear to air dry
heat fix
Simple stain preparation
begin with heat fixed emulsion
cover with methylene blue
rinse with water
blot using bibulous paper
Which dye was used in the simple stain
methylene blue
A negative stain is acidic and therefore stains the
background
Steps to negative stain
Add nigrosin to slide
aseptically add organisms
use second slide to pull then push the dye
air dry
Which dye was used in the negative stain
nigrosin
what is the purpose of gram staining
differentiate between gram positive and gram negative organisms
Crystal violet
primary stain
Iodine
mordant
Ethanol
decolorizer
Safranin
counterstain
Gram staining steps
start with heat fixed sample
cover with crystal violet for one minute
rinse with water
cover with iodine for one minute
rinse with water
decolorize with alcohol for ~20 seconds
rinse with water
counterstain with safranin for one minute
rinse with water
blot with bibulous paper
Gram negative stains
pink
Gram positive stains
purple
Why is oil immersion needed for 1000x objective
to help focus the light by reducing refraction
What color does E. coli stain in gram staining
red
What color does micrococcus luteus stain
purple
E. coli is gram
negative
M. luteus is gram
positive
Defined media
exact chemical composition
Complex media
easy to use
selective media
selectively inhibit/foster growth
differential media
indicator dye to distinguish species
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA)
selective for gram + and fermented mannitol turns plate yellow
Which organisms grew on the MSA
SA and SE
Which organism did not grow on the MSA
EC
Which organism turned the MSA plate yellow
SA
Which indicator dye is used in MSA
phenol red
Phenylethyl Alcohol Agar (PEA)
selective for gram + and used for isolation
Which indicator dye is used in PEA
none
Which species grew the best of PEA
SA and SE
Eosin Methylene Blue agar (EMB)
selective for gram -, ferments lactose, and recognize coliforms
What indicator dye is used in EMB
Eosin Y and Methylene Blue
Color of EC in EMB
metallic green
Color of PV in EMB
Pink
Color of EA in EMB
Pink
Color of SE in EMB
none
Is E. coli a coliform?
yes
MacConkey agar (MAC)
selective for gram -, fermentation of lactose cause change from colorless to red
What inhibits the growth of gram + in MAC
Bile salts
What is the indicator dye used in MAC
neutral red
Which two organisms grew on MAC
EC and EA
What color were EC and EA in MAC
pink
What instrument of sterilization have we used in most labs
Bunsen burner
____ ____ is a method used to transfer bacterial cultures from one place to another without contaminating yourself, the source, culture, or the destination culture
aseptic technique
Which medium did you inoculate with an inoculating needle
TSA deep
What is the purpose of the streak plate method
to get isolated colonies
What does it mean to heat fix a slide
to run the slide through the bunsen burner several times to stick the bacteria to the slide and kill it