MCAT Physics and Math - Waves and Sound
1/64
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
sinusoidal waves
individual particles oscillate back and forth with a displacement that follows a sinusoidal pattern; transverse or longitudinal
Transverse waves
the direction of particle oscillation is perpendicular to the propagation of the wave
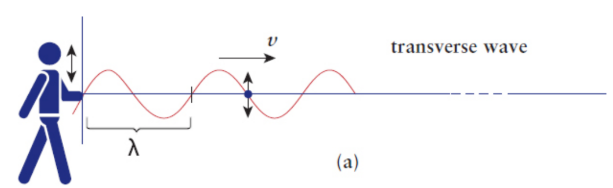
propagation
movement
Longitudinal waves
the particles of the wave oscillate parallel to the direction of propagation
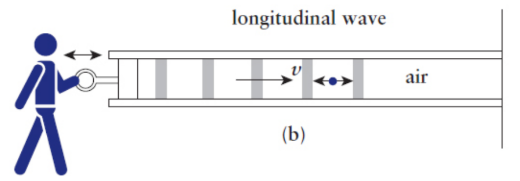
compression
particles closer together
rarefaction/decompression
partices farther apart
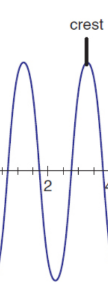
crest
maximum of a wave
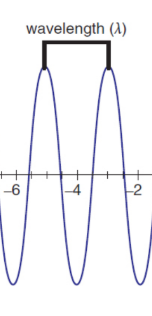
wavelength (λ)
distance from a specific point in the phase of a wave to the next in the same phase, often using the crest/trough
unit: distance (m/cm/nm)
frequency (f)
the number of wavelengths passing a fixed point per second
unit: Hertz (Hz = s-1)
propagation speed (ν)
ν = fλ
period (T)
number of seconds per cycle
T = 1/f
angular frequency (ω)
scalar measure of the angle per unit time
ω = 2πf
unit: radian/s
equilibrim position.
Waves oscillate about a central point
displacement (x)
describes how far a particular point on the wave is from the equilibrium position, expressed as a vector quantity
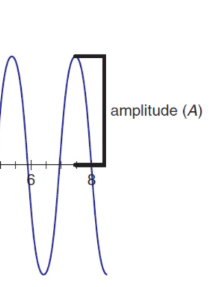
amplitude (A)
maximum magnitude of displacement in a wave; measured from the equilibrium position
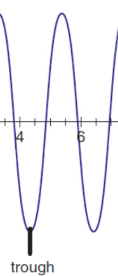
trough
minimum of a wave
phase difference
how well the toughs and crest of two waves that have the same frequency, wavelength, and amplitude and that pass through the same space at the same time align
in phase
crests and troughs coincide; fully constructive interfernece
phase difference = 0
coincide
line up with each other
out of phase
the crests of one wave coincide with the troughs of the other; fully destructive interference
phase difference = λ/2 or 180°
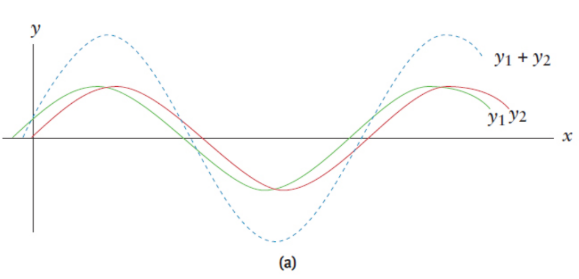
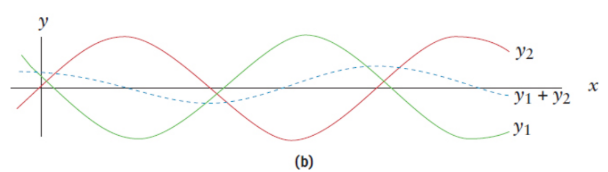
principle of superposition
when waves interact with each other, the displacement of the resultant wave at any point is the sum of the displacements of the two interacting waves
construcive interference.
displacements in the same direction add together; the amplitude of the resultant is equal to the sum of the amplitudes of the two waves
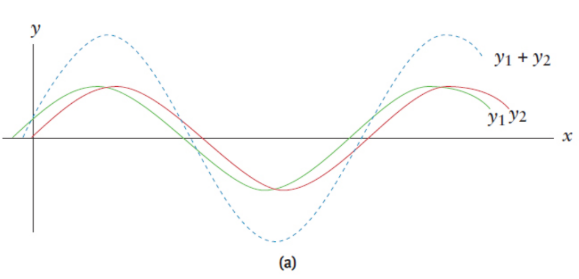
destructive interference
displacements in opposite directions counteract each other; amplitude of the resultant wave is the difference between the amplitudes of the interacting waves
ex. noise-cancelling headphones
traveling wave
move through a medium, transferring energy from one place to another; continuous movement of crests and troughs; no confinement
ex. ocean, sound, light
standing wave
stationary with the only apparent movement of the string is fluctuation of amplitude at fixed points; two waves of same frequency and amplitude travel from opposite directions/reflect back and forth; confined space
ex. instruments with strings, open pipes
nodes
Points in the wave that remain at rest; amplitude is constantly zero
antinodes
Points midway between the nodes fluctuate with maximum amplitude
natural/resonant frequencies
Any solid object, when hit, struck, rubbed, or disturbed in any way will begin to vibrate;can be changed by changing some aspect of the object itself
ex. musical instruments
timbre
quality of the sound; determined by the natural frequency(ies) of the object
noise
resonant frequencies that we do not find particularly musical
fundamental pitch
main resonant frequency
overtones
additional complementary resonant frequencies, related to each other by whole number ratios, producing a richer, more full tone
HUman audible range
frequencies between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz to healthy young adults, and high-frequency hearing generally declines with age
forced oscillation
periodically varying force is applied to a system, the system will then be driven at a frequency equal to the frequency of the force
force frequency
nearly identical to the swing’s natural frequency
resonating
frequency of the periodic force is equal to a natural (resonant) frequency of the system
damping/attenuation
decrease in amplitude of a wave caused by an applied or nonconservative force
Sound
longitudinal wave produced by the mechanical disturbance of particles in a deformable material along the sound wave’s direction of propagation
speed of sound
v = sqrt(B/ρ)
where B is the bulk modulus, a measure of the medium’s resistance to compression (gas < liquid < solid), and ρ is the density of the medium
spped of sound in air @ 20°C
343 m/s
vocal cords
pair of thin membranes stretched across the larynx, vibrates to make sound
Adult male vocal cords are often larger and thicker than those of adult females; thus, male voices are commonly lower in pitch
pitch
perception of the frequency of sound; proportional
infrasonic
Sound waves with frequencies below 20 Hz
ex. dog whistle
ultrasonic
Sound waves with frequencies above 20,000 Hz
ex. ultrasound
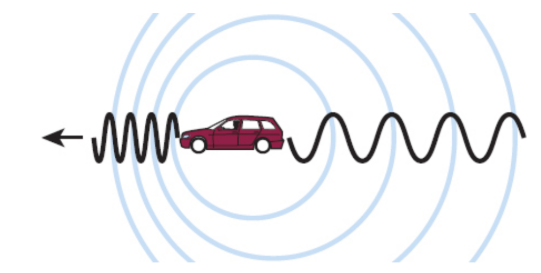
Doppler effect
describes the difference between the actual frequency of a wave and its perceived frequency when the source of the wave and the wave’s detector are moving relative to one another; closer, higher/bluer
Doppler equation
where f′ is the perceived frequency, f is the actual emitted frequency, ν is the speed of sound in the medium, νD is the speed of the detector, and νS is the speed of the source
the upper sign should be used when the detector or source is moving toward the other object; the lower sign should be used when the detector or source is moving away from the other object
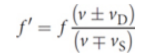
echolocation
the animal emitting the sound (usually a dolphin or bat) serves as both the source and the detector of the sound; how long it takes for the sound to return and the change in frequency of the sound can be used to determine the position of objects in the environment and the speed at which they are moving
shock wave
while traveling at or above the speed of sound; highly condensed wave front; cause physical disturbances as it passes through other objects
sonic boom
passing of a shock wave creates very high pressure, followed by very low pressure
Mach 1
point at which the speed of sound is exceeded
loudness/volume
the way in which we perceive its intensity
Intensity
average rate of energy transfer per area across a surface that is perpendicular to the wave; power transported per unit area
I = P/A
where P is the power and A is the area
I ∝ Amplitude2
units: W/m2
softest audible sound: 10-12 W/m2
loudest audible sound: 10 W/m2
Instant perforation: 104 W/m2
sound level (β)
logarithmic scale of sound intensity
β = 10 log I/I0
where I is the intensity of the sound wave and I0
is the threshold of hearing
βf = βi + 10 log I/I0
units: decibels (dB)
Beat Frequency
When two sounds of slightly different frequencies are produced in proximity, as when tuning a pair of instruments next to one another, volume will vary at a rate based on the difference between the two pitches being produced
fbeat = |f1 - f2|
Closed boundaries
do not allow oscillation and that correspond to nodes
Open boundaries
allow maximal oscillation and correspond to antinodes
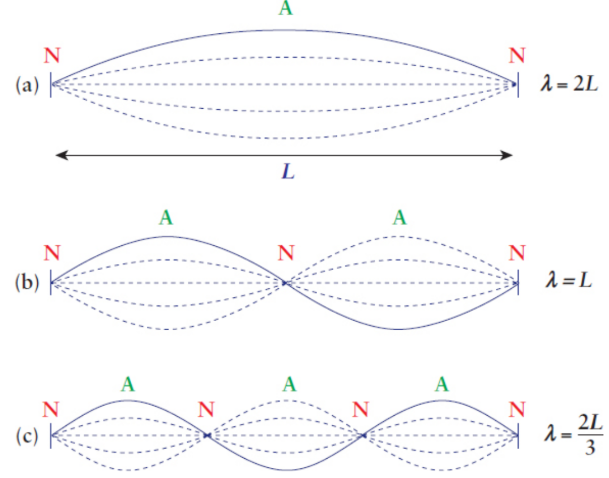
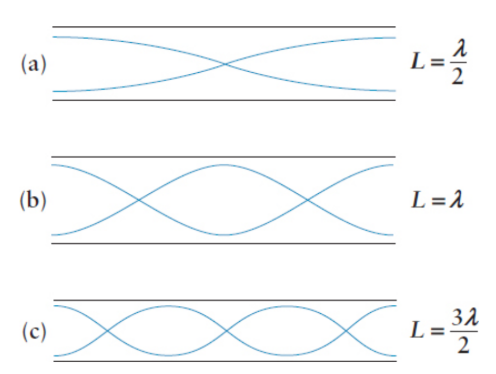
String waves
equation that relates the wavelength λ of a standing wave and the length L of a string
λ = 2L/n
where n is a positive nonzero integer (n = 1, 2, 3, and so on) called the harmonic.
harmonic
corresponds to the number of half-wavelengths
supported by the string
f = nv/2L
fundamental frequency (first harmonic)
lowest frequency (longest wavelength) of a standing wave that can be supported in a given length of string
first overtone or second harmonic
frequency of the standing wave given by n = 2; one-half the wavelength and twice the frequency of the first harmonic
harmonic series
All the possible frequencies that the string can support
open pipes
pipes open on both ends
same harmonics as string
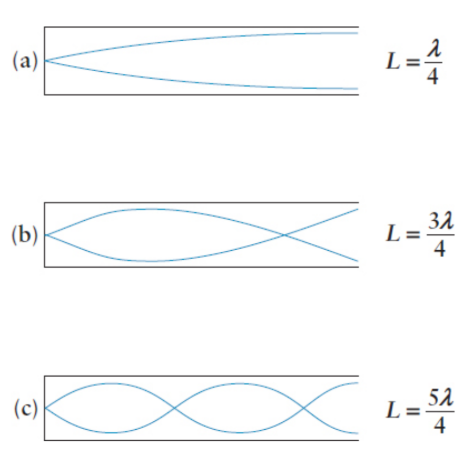
closed pipes
pipes closed at one end
λ = 4L/n
f = nv/2L
Ultrasound
uses high-frequency sound waves outside the range of human hearing to compare the relative densities of tissues in the body
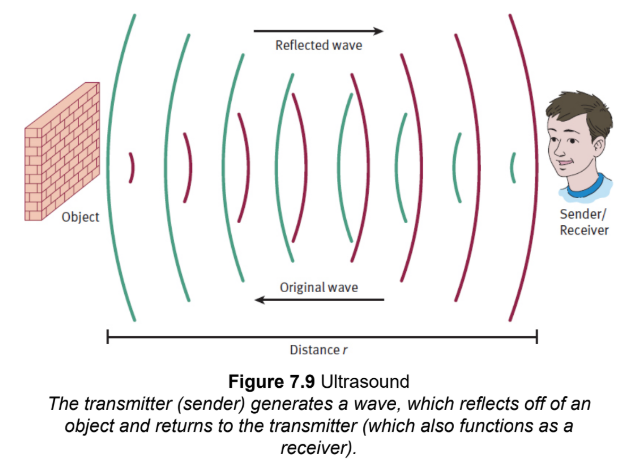
Doppler ultrasound
used to determine the flow of blood within the body by detecting the frequency shi that is associated with movement toward or away from the receiver.