bio 12: digestive system
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/123
Last updated 11:41 PM on 2/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
1
New cards
ingestion meaning
intake of food by mouth
2
New cards
propulsion meaning
movement of food by peristalsis; “wave like” muscle contractions that move food through digestive tract
3
New cards
digestion meaning
mechanical breakdown of food into smaller pieces
4
New cards
absorption meaning
passage of digested nutrients from gut into blood or lymph to distribute throughout body
5
New cards
defecation meaning
removal of indigestible waste from body
6
New cards
where does absorption take place
small intestine
7
New cards
what are lymphs
wbc’s that attack bacteria in blood or body tissue
8
New cards
proteins >
(sugar) carbohydrates >
fat >
nucleic acids >
(sugar) carbohydrates >
fat >
nucleic acids >
peptides
glucose
fatty acids and glycerol
nucleotides
glucose
fatty acids and glycerol
nucleotides
9
New cards
what is the gut
a tube that runs from mouth to anus
10
New cards
where does digestion happen first
mouth
11
New cards
what is the pH of the mouth
pH 7
12
New cards
what does the mouth start to digest
starch
13
New cards
what is the hard palate and the soft palate of the mouth consist of
hard palate: roof of mouth; several bones
soft palate: tonsils, uvula; muscle tissue
soft palate: tonsils, uvula; muscle tissue
14
New cards
what do tonsils do
stop germs from entering body thru mouth or nose
15
New cards
how many teeth does a normal adult mouth have
32
16
New cards
what are the different teeth types
8 incisors for biting
4 canines for tearing
8 flat premolars for grinding
12 molars for crushing
4 canines for tearing
8 flat premolars for grinding
12 molars for crushing
17
New cards
what are the three sets of salivary glands that produce saliva?
name location, and what it contains
name location, and what it contains
parotid - below ears, contains serious acini and makes watery saliva
\
sublingual - below tongue, contains serious acini and mucous
\
submandibular - below lower jaw, contains serious acini and mucous
\
sublingual - below tongue, contains serious acini and mucous
\
submandibular - below lower jaw, contains serious acini and mucous
18
New cards
what does saliva contain
water, mucus, and a salivary amylase which is a hydrolytic enzyme that breaks down STARCH in the presence of water
19
New cards
why is mucus important
lubricant to keep tissues (or other) from dying out
20
New cards
what does starch get broken into
maltose then glucose
21
New cards
whats a bolus
when food is chewed up
22
New cards
steps of what happens when swallowing
\
(3)
\
(3)
1. soft palette moves back to cover nose opening
2. trachea moves up under a flap called EPIGLOTTIS, blocking its opening
3. opening to larynx (voice box) is called the GLOTTIS and is covered when trachea moves up by EPIGLOTTIS as well
23
New cards
what is the epiglottis
a flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe
24
New cards
review time!
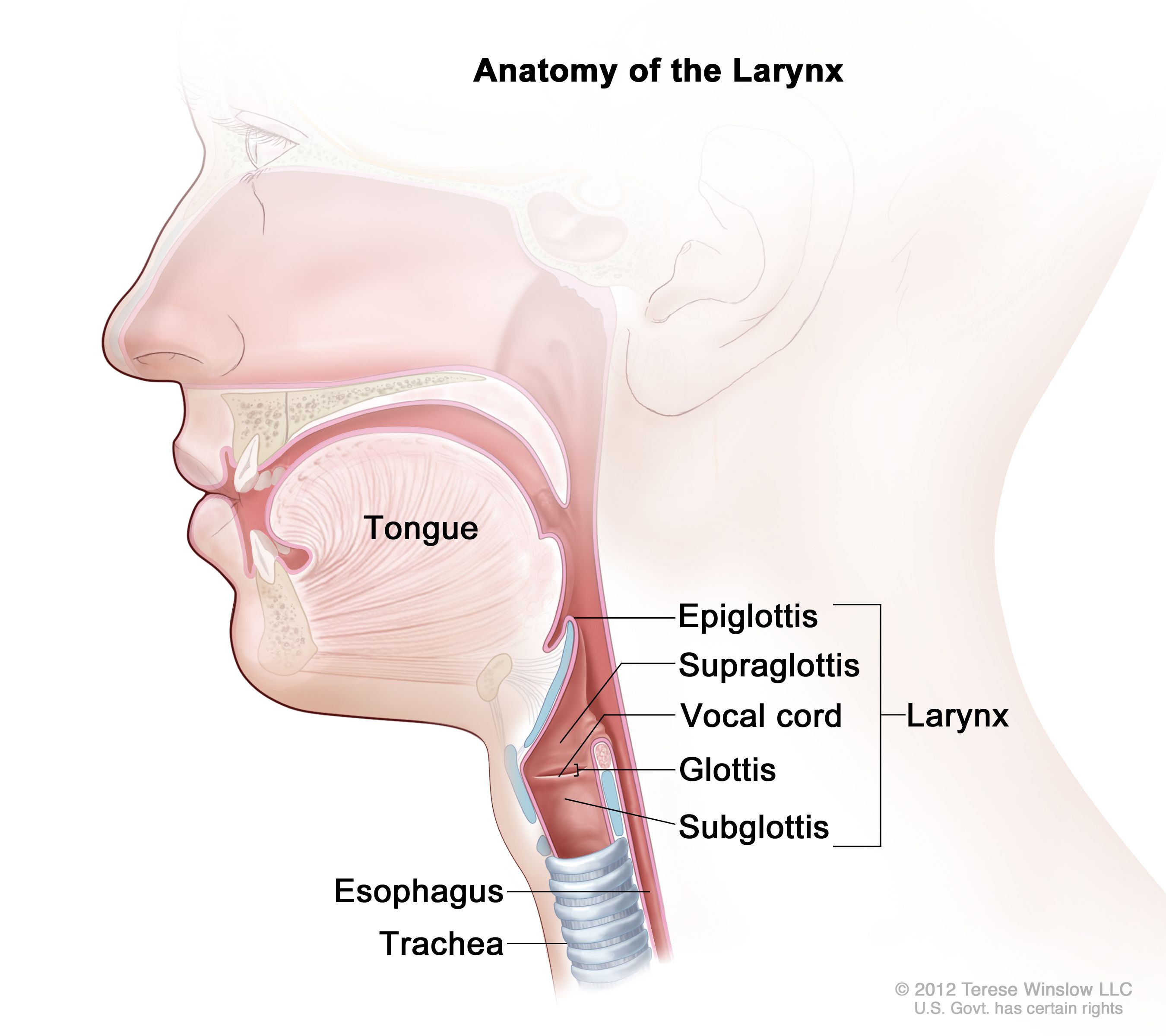
25
New cards
what is the esophagus
a long tube that goes from pharynx to stomach
26
New cards
what is the pharynx also called
the throat
27
New cards
where is the pharynx located in between
mouth and esophagus
28
New cards
how does food move through the esophagus
thru peristalsis
29
New cards
what are sphincters
muscles that encircles tubes; open when relaxed and closed when contracted/tense
30
New cards
what is the cardiac sphincter
a valve between esophagus and stomach; where bolus reaches
31
New cards
structure and location of stomach
its thick and J-shaped, and is on the left side of the body beneath the diaphragm
32
New cards
how many layers of muscle does the stomach have and what does it do
3 layers and it contracts to churn and mix the contents of a bolus
33
New cards
how much solid/liquid can a stomach take
2 liters
34
New cards
what is the rugae and what does it do and why is it important
folds in stomach lining
\
it increases the SA of the stomach; more SA allows greater intake of food and efficient absorption
\
it increases the SA of the stomach; more SA allows greater intake of food and efficient absorption
35
New cards
what is the pyloric sphincter
a valve between the stomach and small intestine
36
New cards
what does the mucus lining of the stomach contain
contains inner gastric glands which produce GASTRIC JUICE that contains HCl and pepsinogen.
\
when both combine it becomes PEPSIN which is a hydrolytic enzyme that breaks down proteins into peptides
\
when both combine it becomes PEPSIN which is a hydrolytic enzyme that breaks down proteins into peptides
37
New cards
whys the HCl in the stomach important
HCl gives the stomach a pH of 3 which helps kill bacteria in food and breaks food down
38
New cards
what is the inner wall of the stomach protected by
a thick layer of mucus secreted by mucosal cells
39
New cards
what happens when HCl penetrates the stomach
pepsin starts to digest the STOMACH LINING which forms an ulcer
\
too much GASTRIC JUICE can cause ulcers (and too much stress as well)
\
too much GASTRIC JUICE can cause ulcers (and too much stress as well)
40
New cards
what are ulcers and what can cure it
open sores in stomach lining
\
from bacterial infections that impair the ability of cells to produce mucus and it can be cured by antibiotics
\
from bacterial infections that impair the ability of cells to produce mucus and it can be cured by antibiotics
41
New cards
what is acid chyme and where does the stomach empty first
when the food gets turned into semi-liquid food after 2-6 hours
\
the stomach empties into the first part of the small intestine called the duodenum and is controlled by the PYLORIC SPHINCTER
\
the stomach empties into the first part of the small intestine called the duodenum and is controlled by the PYLORIC SPHINCTER
42
New cards
what makes the small intestine stay basic
sodium bicarbonate /NaHCO3 from the pancreatic juice makes the small intestine basic as it enters the duodenum
43
New cards
small intestine function
absorbs nutrients and some water from food
\
chemical digestion
\
propulsion and breakdown of chyme
\
chemical digestion
\
propulsion and breakdown of chyme
44
New cards
what are the three parts of the small intestine
duodenum - connects to stomach
jejunum - middle of small intestine
ileum - connects to colon
jejunum - middle of small intestine
ileum - connects to colon
45
New cards
how long is the duodenum
around the first 25 cm of the small intestine
46
New cards
how long is the small intestine
6 meters
47
New cards
what does the duodenum do
secretions sent from liver and pancreas break down fat and peptides and secretions from duodenum itself break down nutrients
48
New cards
where in the small intestine does most of the absorption of nutrients and vitamins
ileum
49
New cards
what do the walls of the S.I. consist of
interstitial glands that produce juices containing enzymes that FINISH the digestion of protein and starch
\
peptidases digest peptides > amino acids
maltase digests maltose > glucose
\
peptidases digest peptides > amino acids
maltase digests maltose > glucose
50
New cards
whats the structure of the small intestine like
\
3 points
\
3 points
long with complex walls to increase SA
\
SA is further increased by finger-like projections called villi and interstitial glands are at the base of each villus
\
villi are lined with columnar cells coated with microvilli and each villus contains blood and lymph vessels (lacteal)
\
SA is further increased by finger-like projections called villi and interstitial glands are at the base of each villus
\
villi are lined with columnar cells coated with microvilli and each villus contains blood and lymph vessels (lacteal)
51
New cards
what do villi do
it absorbs fat and increases SA
52
New cards
where is villi
small intestine
53
New cards
where in the small intestine does absorption take place in
across the wall of each villus
54
New cards
absorption; where do they go and how do they go?
\
1. fatty acids and glycerol
\
2. sugar and amino acids
hint: epithelial, lymphatic, capillary
\
how is the hepatic portal vein created
\
1. fatty acids and glycerol
\
2. sugar and amino acids
hint: epithelial, lymphatic, capillary
\
how is the hepatic portal vein created
1. absorbed across the villi and combined into fat molecules in the EPITHELIAL cells of the villus then move into the lacteal of each villus and enter the LYMPHATIC system
\
2. enter the blood through capillary network
\
its created by the merging of blood vessels from the villi
55
New cards
what do the blood vessels from the villi in the S.I. merge?
the hepatic portal vein which leads to the liver
\
(blood vessel that carries blood from liver to intestines, pancreas, etc.)
\
(blood vessel that carries blood from liver to intestines, pancreas, etc.)
56
New cards
what do the pancreas do
creates juice/enzymes to break down food
57
New cards
what is the location and structure of the pancreas
located behind the stomach and it is near the liver and gallbladder. the head of the pancreas lie in the curve of the duodenum and the body and tail are covered by the stomach
58
New cards
what juice does the pancreas make and what does it contain and do
it makes pancreatic juice; sends it into the DUODENUM through the pancreatic duct
\
juice contains hydrolytic enzymes and NaHCO3 which makes the juice highly alkaline (basic) pH 8. it neutralizes the acid thyme and makes pH basic in the S.I.
\
enzymes include pancreatic amylase (starch > maltose), trypsin (protein > peptides), lipase (fat droplets > glycerol + fatty acids)
\
juice contains hydrolytic enzymes and NaHCO3 which makes the juice highly alkaline (basic) pH 8. it neutralizes the acid thyme and makes pH basic in the S.I.
\
enzymes include pancreatic amylase (starch > maltose), trypsin (protein > peptides), lipase (fat droplets > glycerol + fatty acids)
59
New cards
what does lacteal take
fats
60
New cards
what is a duct
a tube or passageway
61
New cards
what does an exocrine and endocrine function mean
exocrine: makes substances like juice or saliva and releases it thru a duct
\
endocrine: makes and releases hormones
\
endocrine: makes and releases hormones
62
New cards
what hormones do pancreas produce
insulin and glucagon
63
New cards
what do the two hormones that pancreas produce do
insulin - lowers blood glucose concentration and is produced by beta cells
\
glucagon - raises blood glucose concentrations and is produced by alpha cells
\
glucagon - raises blood glucose concentrations and is produced by alpha cells
64
New cards
steps if you’re hyperglycemic
1. beta cells of the pancreas release insulin into the blood
\
2. some of the insulin goes to the liver and the liver takes up glucose (insulin) and stores it as glycogen
\
3. other insulins goes into body cells; body cells take up more glucose
\
4. blood glucose level declines to set point
65
New cards
steps if you’re hypoglycemic
1. alpha cells of the pancreas release into the blood
\
2. glucagon is introduced and the liver breaks down glycogen and releases glucose to the blood
\
3. blood glucose level rises to set point
66
New cards
how does diabetes occur
people who dont produce enough insulin or lack insulin receptors on target cells
67
New cards
liver structure and location
located above the stomach and in the upper right spot in the abdominal area. consists of 2 main lobes (large right and small left) that are both made up of 8 segments that have 1000 small lobes called LOBULES
68
New cards
liver functions
1. keeps blood concentrations of nutrients, hormones, etc constant (e.g. converts glucose > glycogen then back to glucose)
\
2. interconversions of nutrients (e.g. carbo to fat, A.A to carbo or fats)
\
3. detoxification from blood (by converting toxins to a water-soluble form so it can be removed as urine)
\
4. production of bile
\
5. destroys old RBC’s
\
6. production of urea (breakdown of protein)
\
7. manufacture of plasma proteins (e.g. albumin) which maintains intravascular volume
\
8. manufacture of cholesterol
\
9. storage or iron and vitamins
\
10. in embryos, the liver makes RBC’s
69
New cards
what happens if bile is reduces
bile breaks down cholesterol and fat so if its removed or reduced, cholesterol cannot be broken down equals higher cholesterol
70
New cards
what is bile
a thick green liquid (green from byproducts of hemoglobin) and is a digestive fluid
71
New cards
what organ produces bile and where is bile stored
produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder
72
New cards
bile function
carries away waste in the form of digestive fluid
\
smaller parts of bile called bile salts break fat into fat droplets and SA is increased
* an increase in SA allows lipase to break fat further
\
breaks down fat and turns it into energy
\
smaller parts of bile called bile salts break fat into fat droplets and SA is increased
* an increase in SA allows lipase to break fat further
\
breaks down fat and turns it into energy
73
New cards
how does bile go to liver > gallbladder
thru a duct called common bile duct which sends bile to the duodenum
74
New cards
what is trypsin? where is it and what does it do
an enzyme that helps digest proteins
\
found in the small intestine
\
created by pancrea
\
found in the small intestine
\
created by pancrea
75
New cards
what does amylase do
break down carbohydrates
76
New cards
is the pH of large intestine acidic or basic
basic
77
New cards
is the pH of small intestine acidic or basic
basic
78
New cards
what does the stomach break down
proteins into peptides
79
New cards
if the liver wasnt working how would that affect the villi
it would affect the absorption of fats
80
New cards
components of intestinal juice
hormones, digestive enzymes, mucus, and neutralizing substances released from the glands from both intestines
81
New cards
what does intestinal juice do and where is it produced
neutralizes HCl in the stomach
\
releases hormones in the bloodstream
\
has digestive enzymes that help with absorption
\
the pancreas produce it
\
releases hormones in the bloodstream
\
has digestive enzymes that help with absorption
\
the pancreas produce it
82
New cards
where is glycogen produced and stored
liver
83
New cards
where is lipase created and released
pancreas to duodenum
\
through pancreatic duct
\
through pancreatic duct
84
New cards
what is a reactant in the chemical digestion of food
water
85
New cards
where is starch digested
mouth and small intestine (from pancreatic enzymes)
86
New cards
where are peptides produced
pancreas, stomach, small intestine
87
New cards
what is jaundice
a condition that gives a person yellow skin
88
New cards
how is yellow skin caused (from jaundice)
due to the build up of BILIRUBIN in blood
89
New cards
what is bilirubin
breakdown of RBC’s
90
New cards
what is the cause of bilirubin
\
what happens if u have it
\
what happens if u have it
when the body breaks down too many RBC’s too fast
\
liver damage or blockage of bile duct
\
liver damage or blockage of bile duct
91
New cards
what are gallstones made out of
cholesterol and CaCO3
92
New cards
what can gallstones do to the body
can block bile ducts
93
New cards
what is the cause of viral hepatitis
jaundice AND liver damage
94
New cards
what is type A hepatitis
infectious; caused by unsanitary food
95
New cards
what is type b hepatitis
serum; spread thru blood contact like transfusions
96
New cards
what is cirrhosis caused by
an over consumption of alcohol
97
New cards
what happens to the liver if you drink too much alcohol over time
liver fills up with FAT DEPOSITS and SCAR TISSUE
98
New cards
what does alcohol break down into
lots of fatty acids
99
New cards
what are the 3 main functions of the large intestine
breaks down some indigestible food
\
produces vitamins like B and K (e.g. convert food into energy AND makes proteins for bone building and blood clotting)
\
abosrbs water and salt to make food dehydrated
\
produces vitamins like B and K (e.g. convert food into energy AND makes proteins for bone building and blood clotting)
\
abosrbs water and salt to make food dehydrated
100
New cards
what does feces consist of (5)
dead bacteria, indigestible material, inorganic substances, bile pigments, cell debris