Anaphy Lab: 1st Practical Exam
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
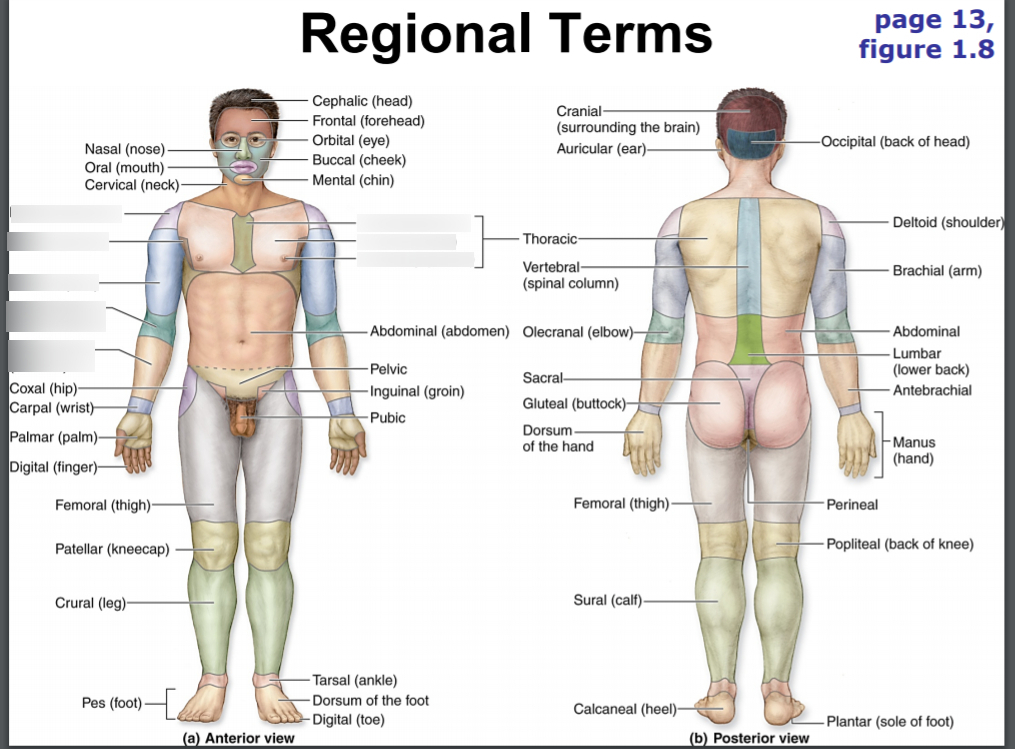
cephalic
head
frontal
forehead
orbital
eyes
nasal
nose
oral
mouth
cervical
neck
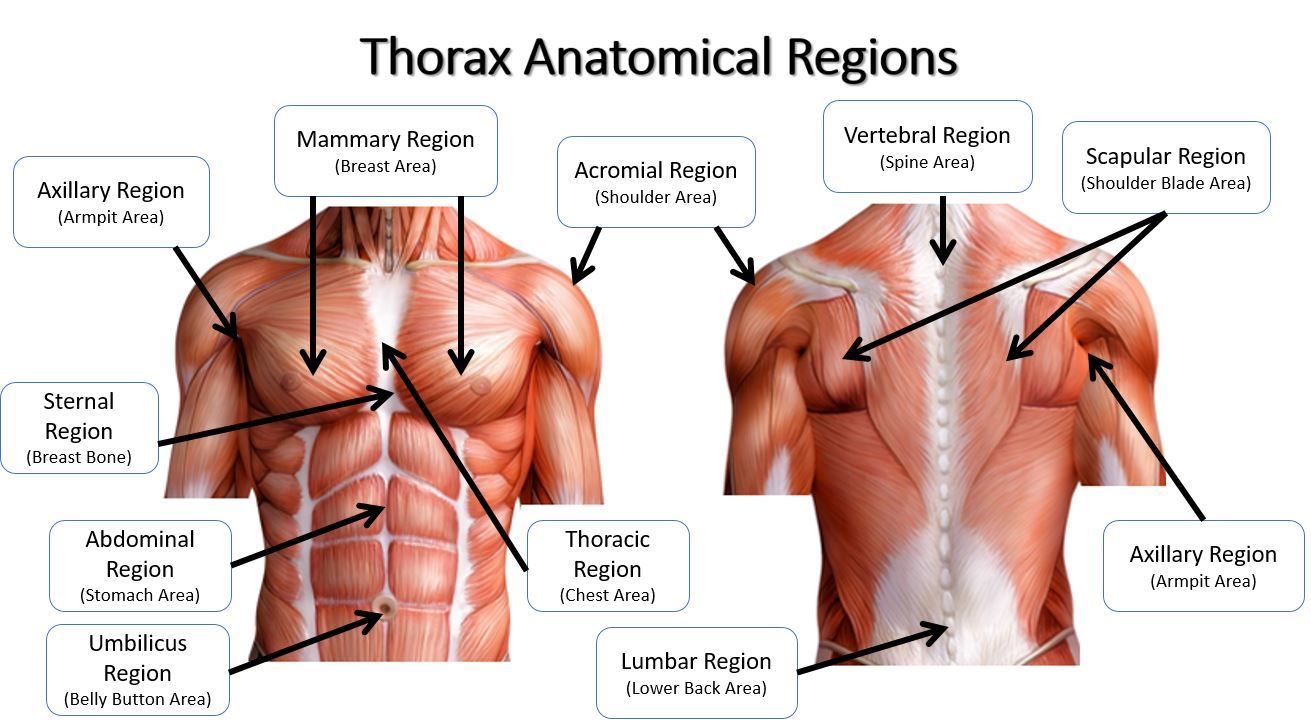
thoracic
thorax
pectoral
chest
sternal
breastbone
mammary
breast
abdominal
abdomen
umbilical
navel
pelvic
pelvis
inguinal
groin area
pubic
genital area
otic
ear
buccal
cheek
mental
chin
clavicular
clavicle/ collarbone
axillary
armpit
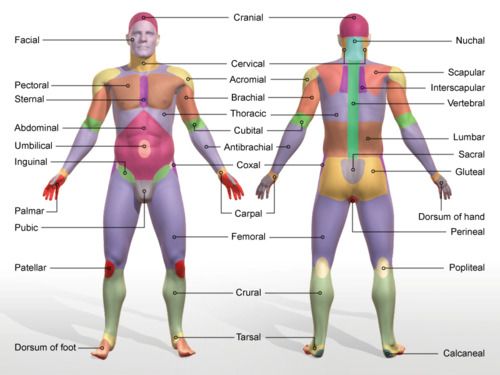
brachial
arm
antecubital
front of elbow
carpal
wrist
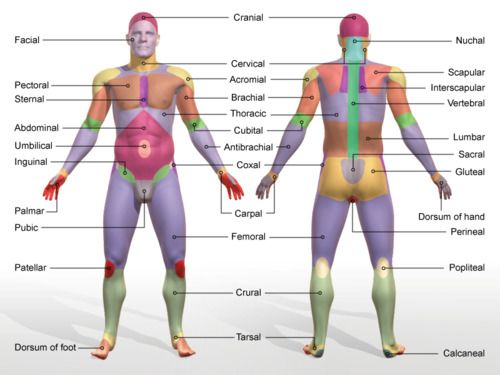
manual
hand
palmar
palm
digital
fingers/ toes
coxal
hip
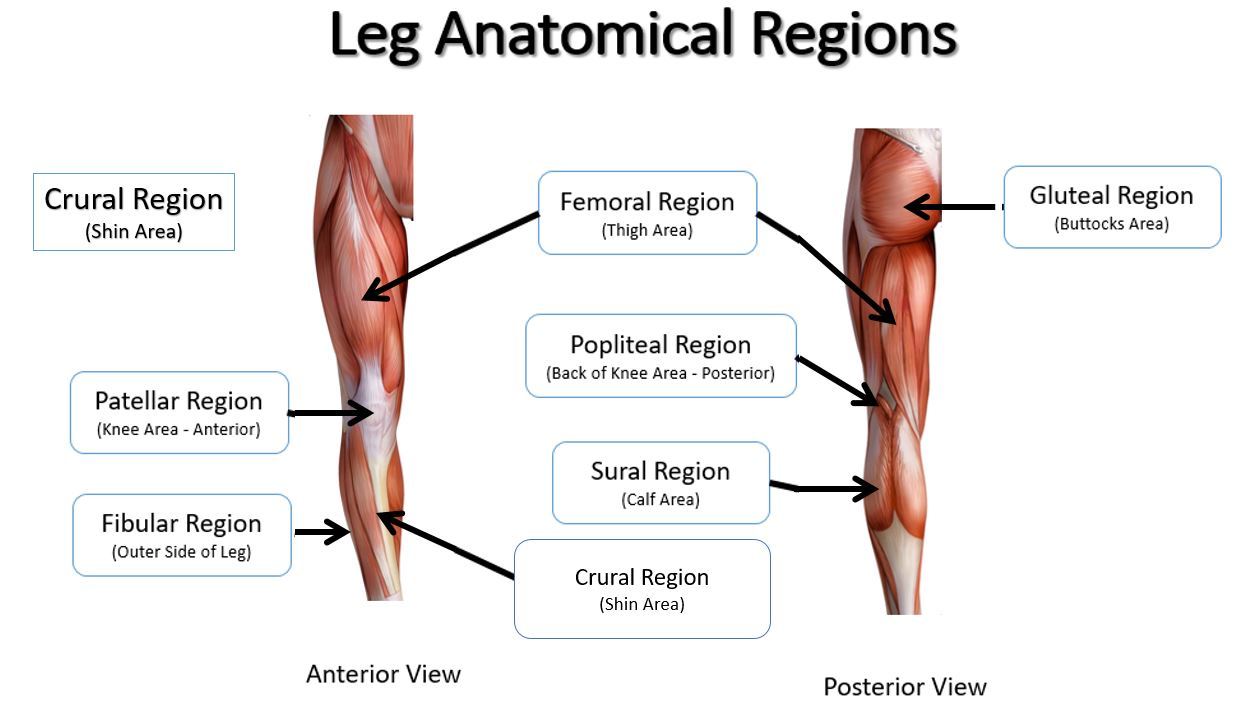
femoral
thigh area
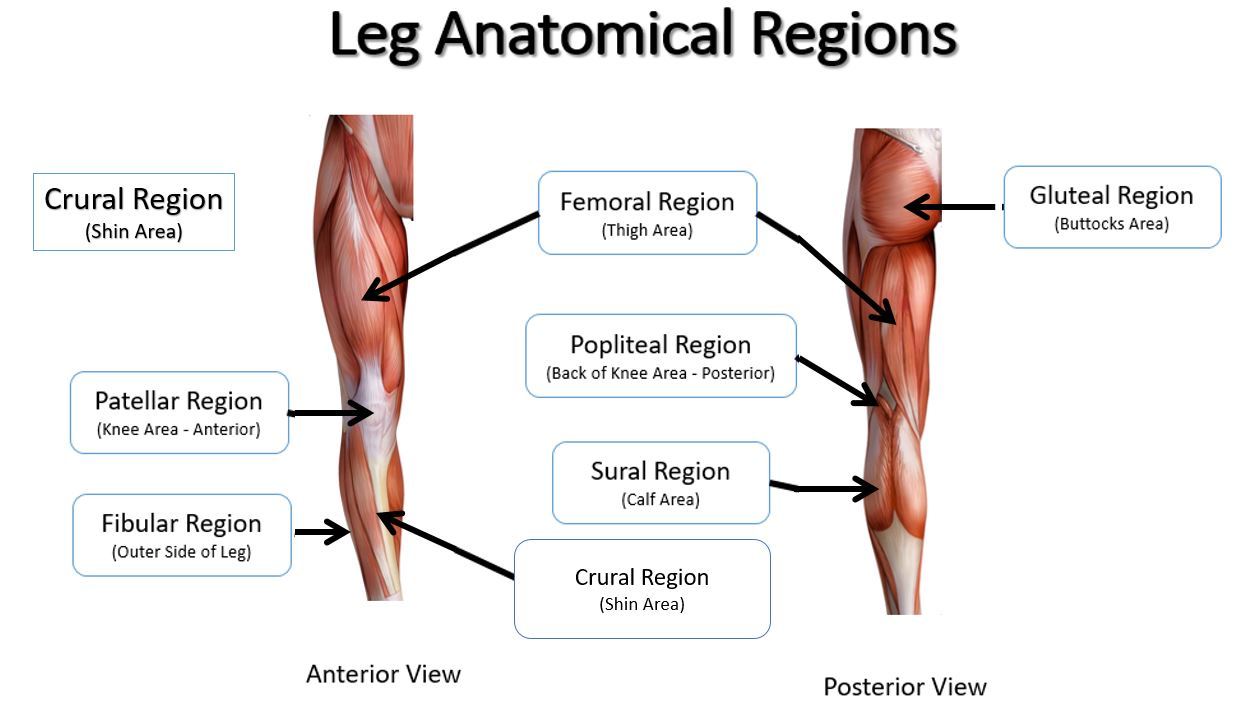
patellar
kneecap
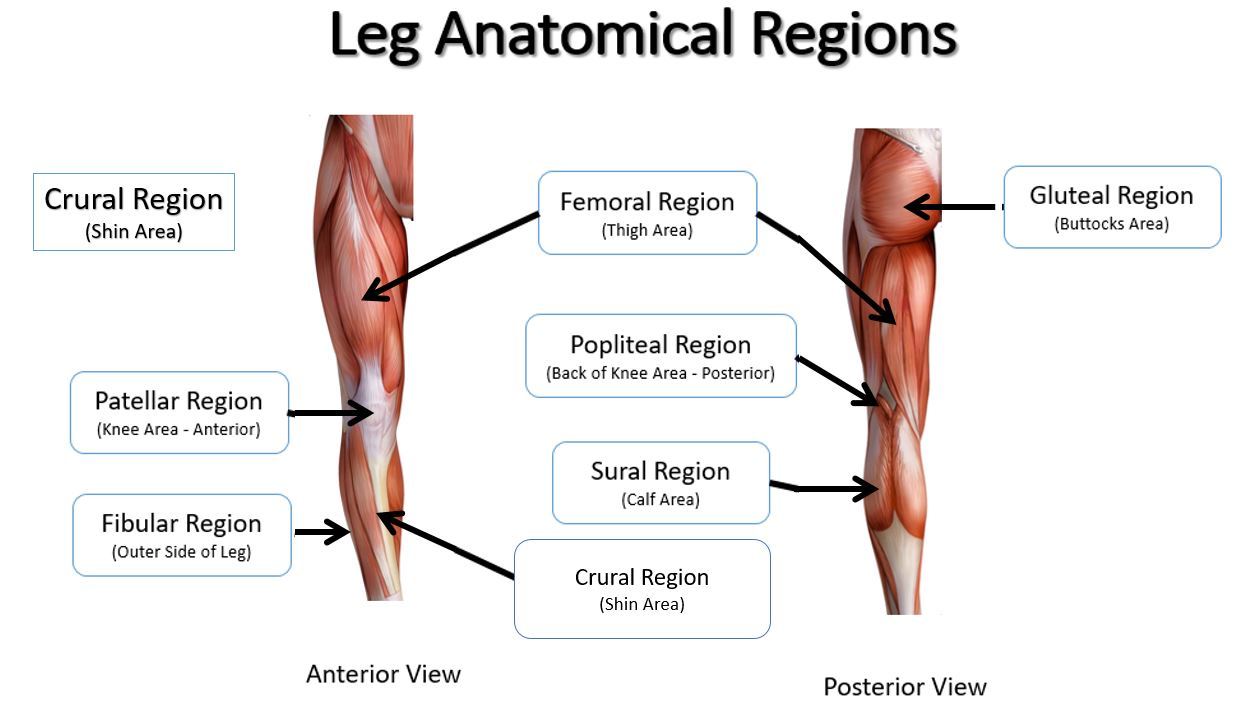
crural
leg; shin area (anterior)
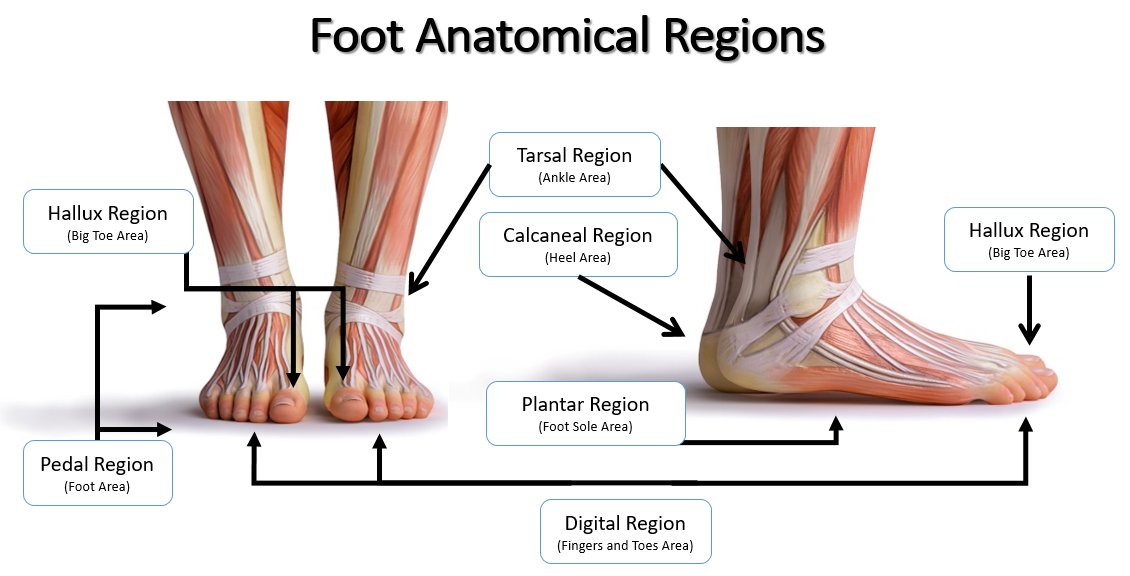
pedal
foot
talus
ankle
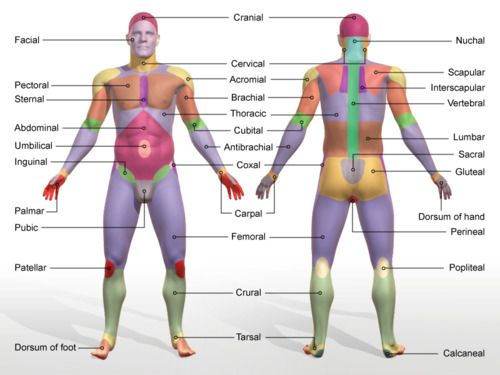
dorsum of foot
upper surface of foot
dorsal
back
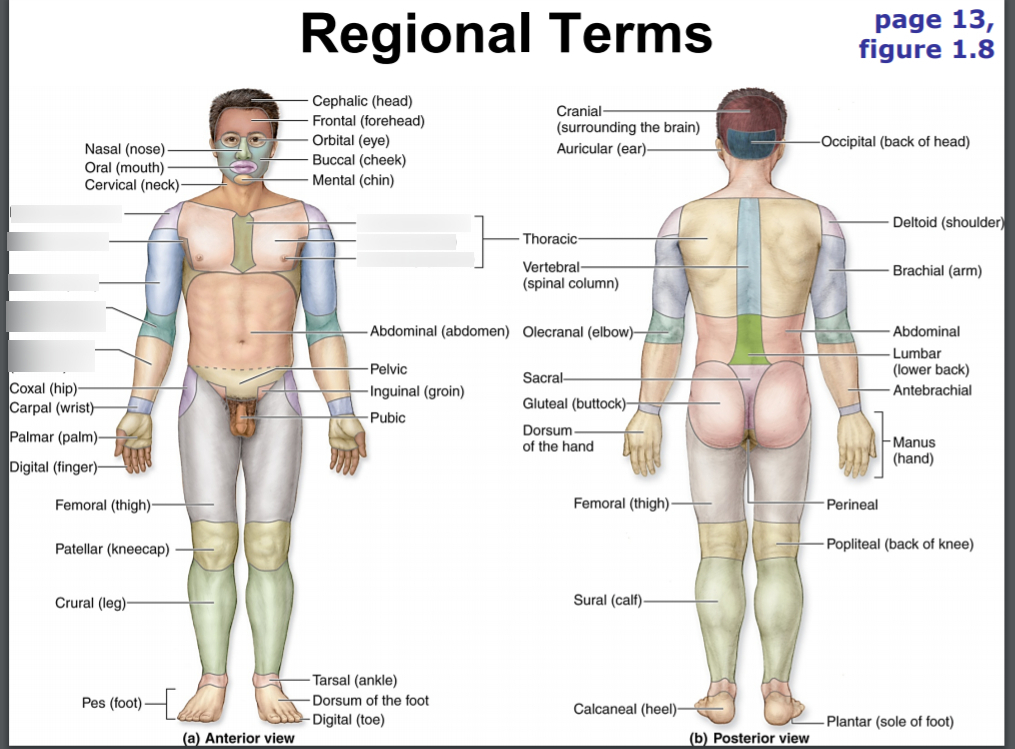
occipital
base of skull
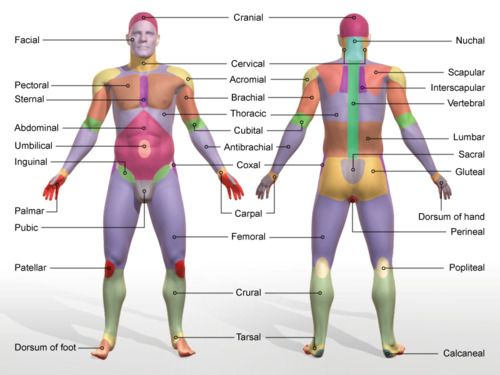
nuchal
back of neck
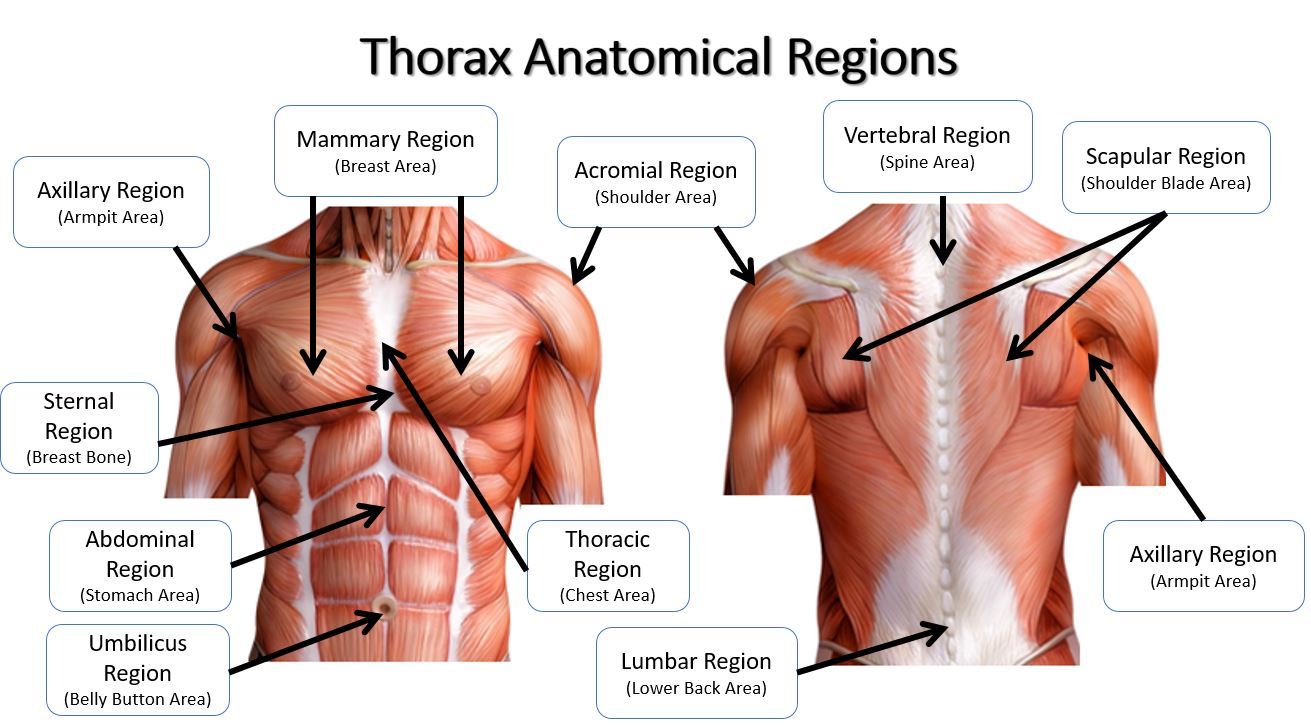
scapular
shoulder blades
vertebral
spinal column
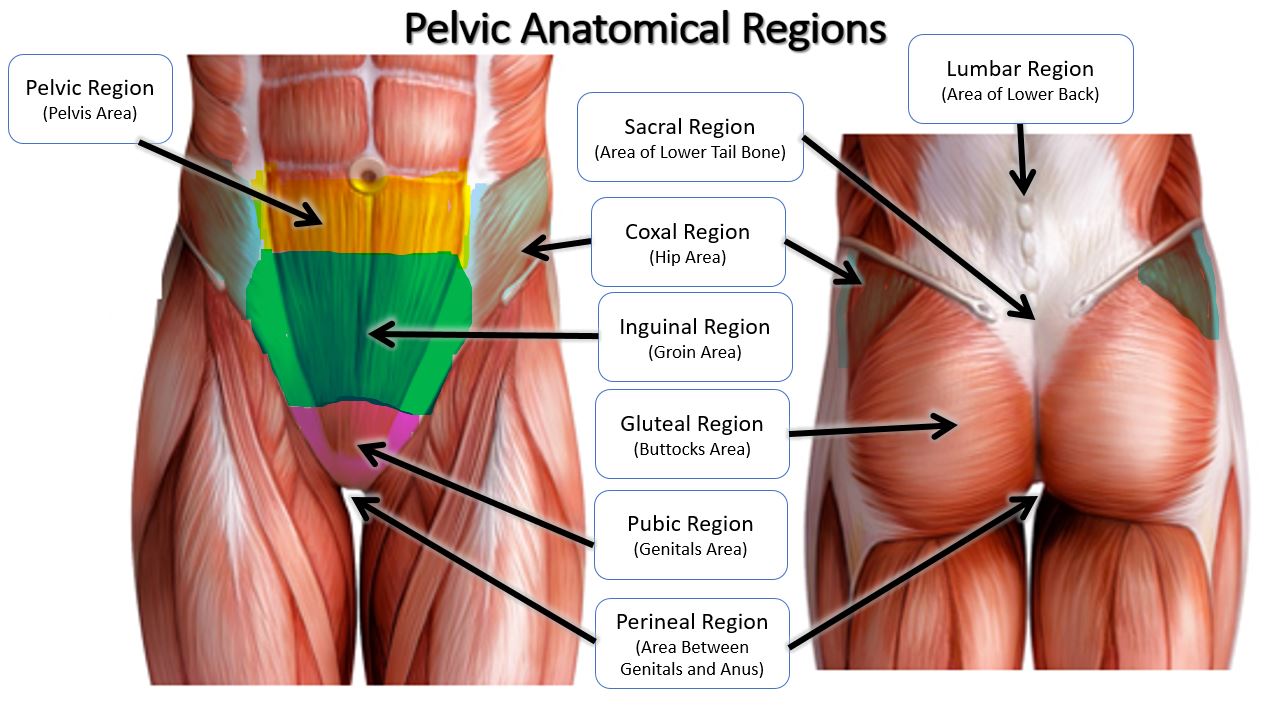
lumbar
loin
sacral
between hips/ area of lower tailbone
gluteal
buttocks
perineal
perineum; surface region in both males and females between the pubic symphysis and the coccyx
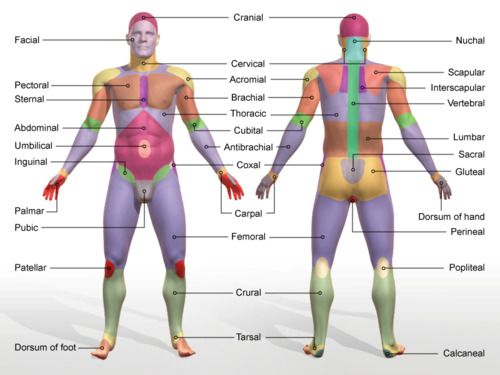
cranial
skull
acromial
point of shoulder
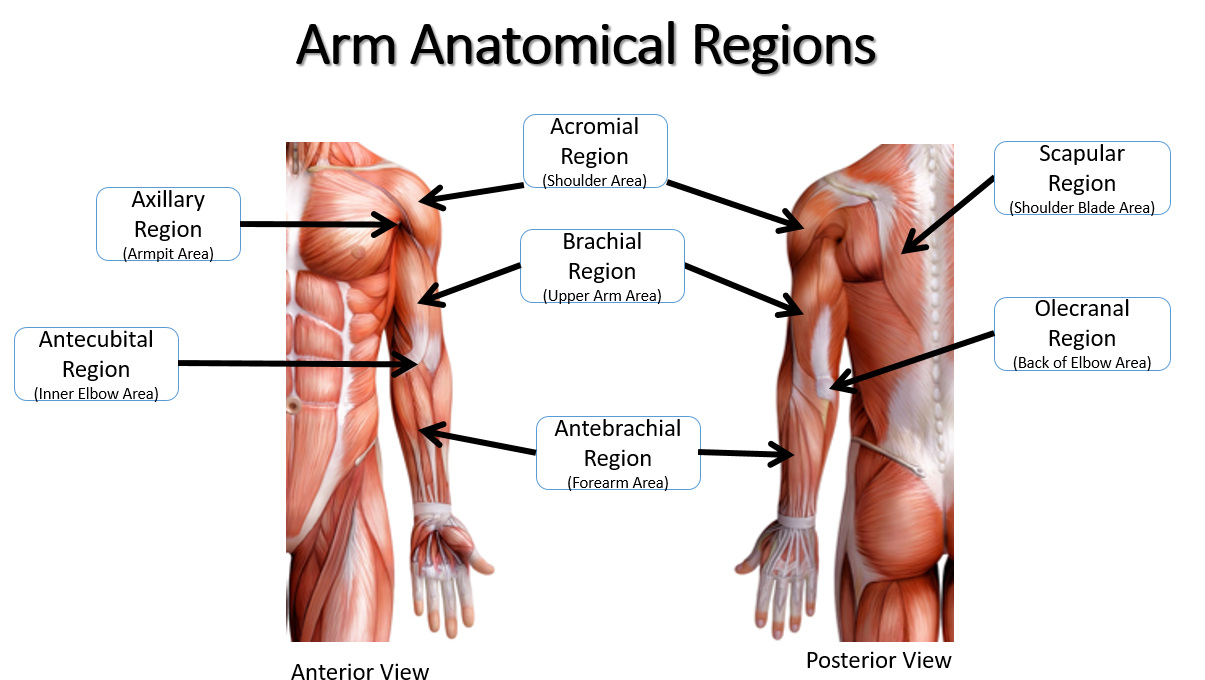
olecranon
point of elbow
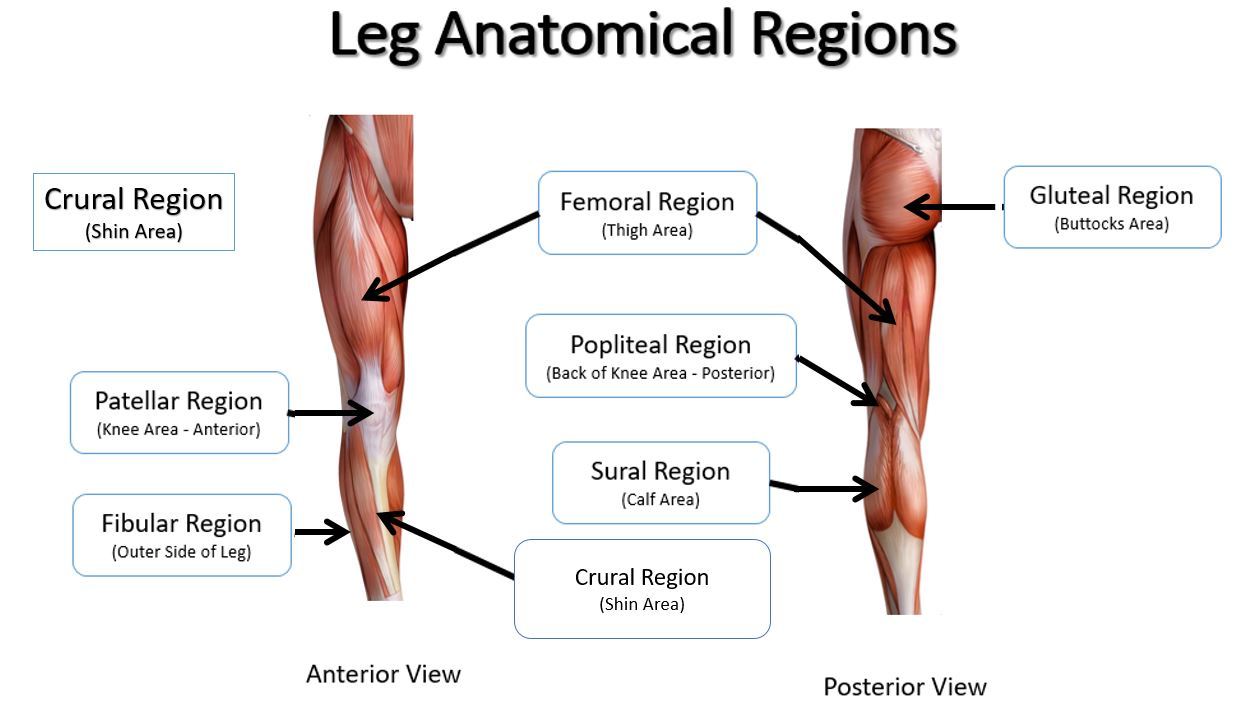
popliteal
hollow/ back of knee
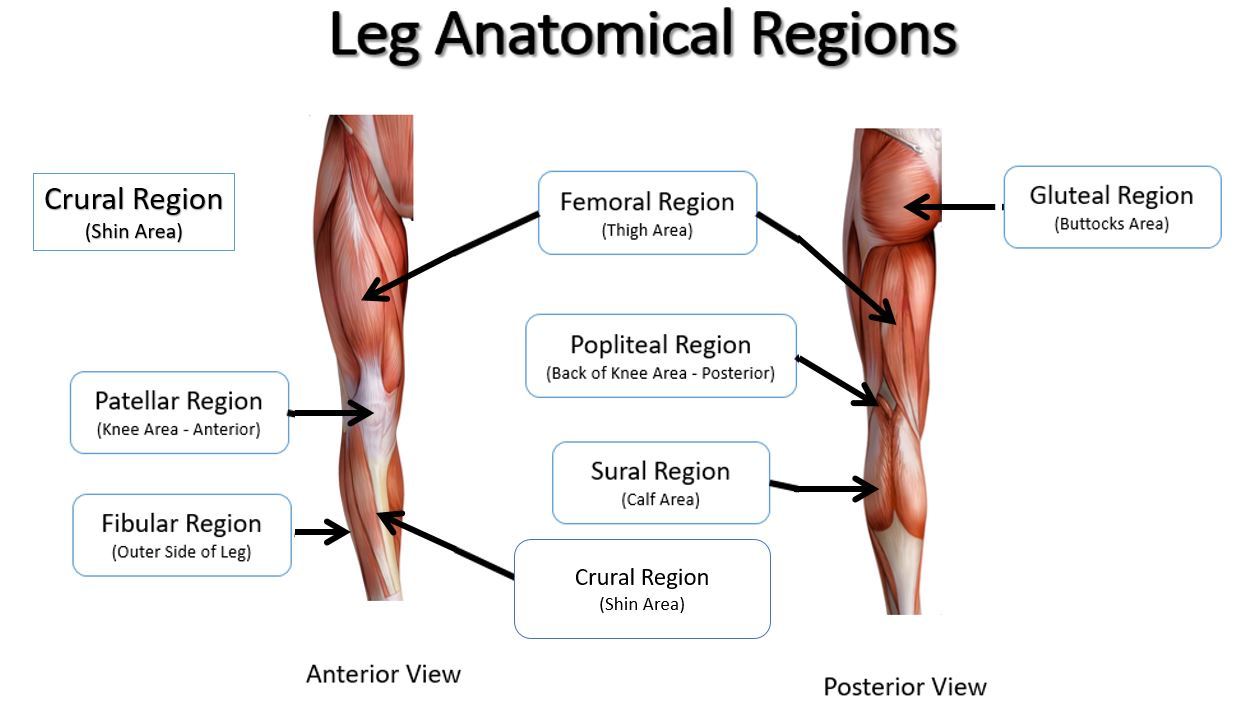
sural
calf area
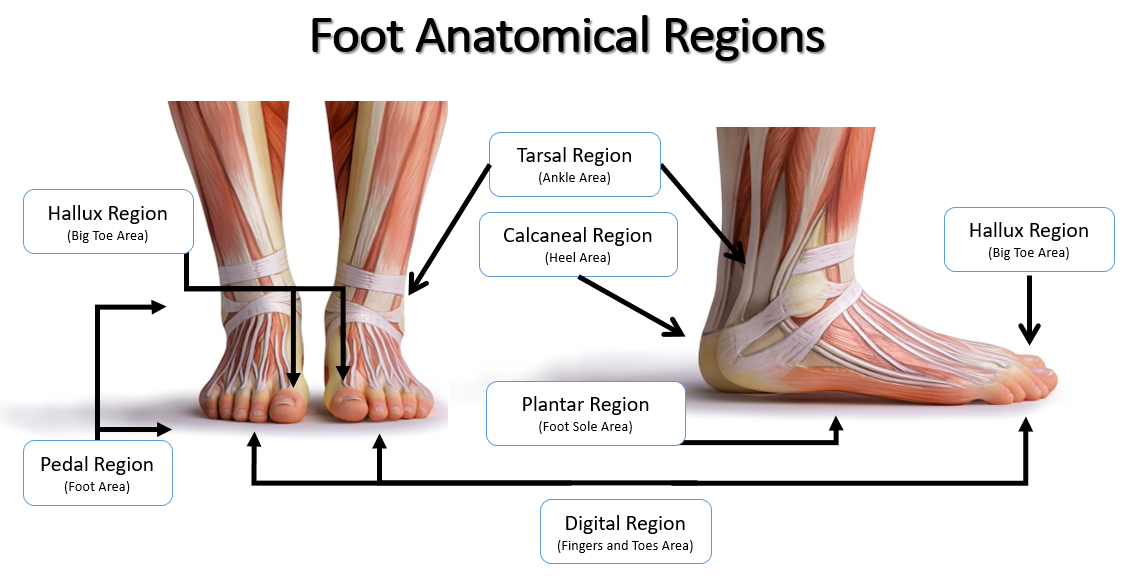
plantar
sole of foot
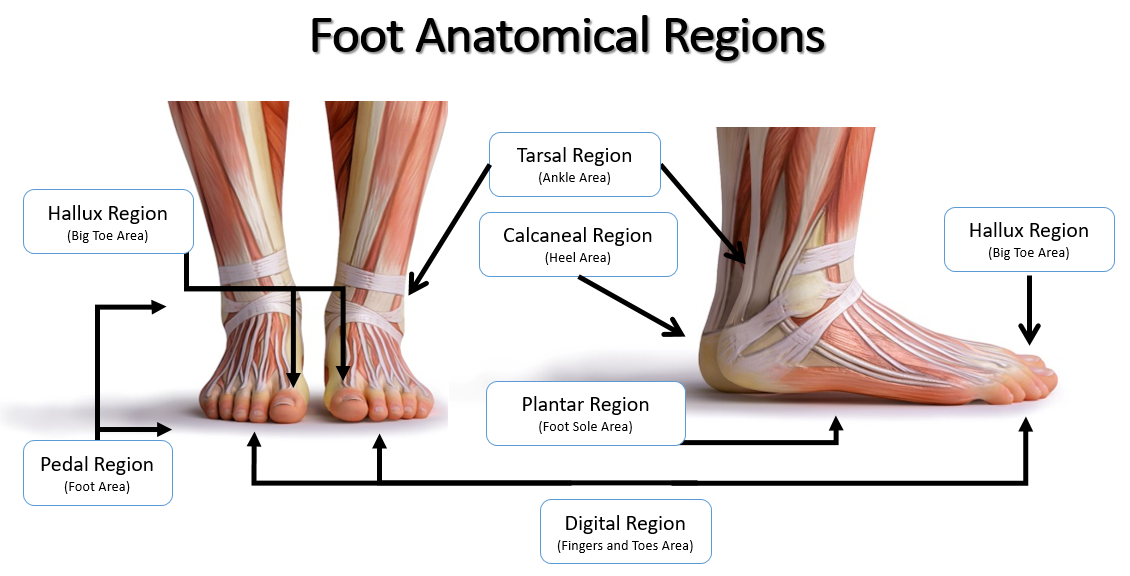
calcaneal
heel
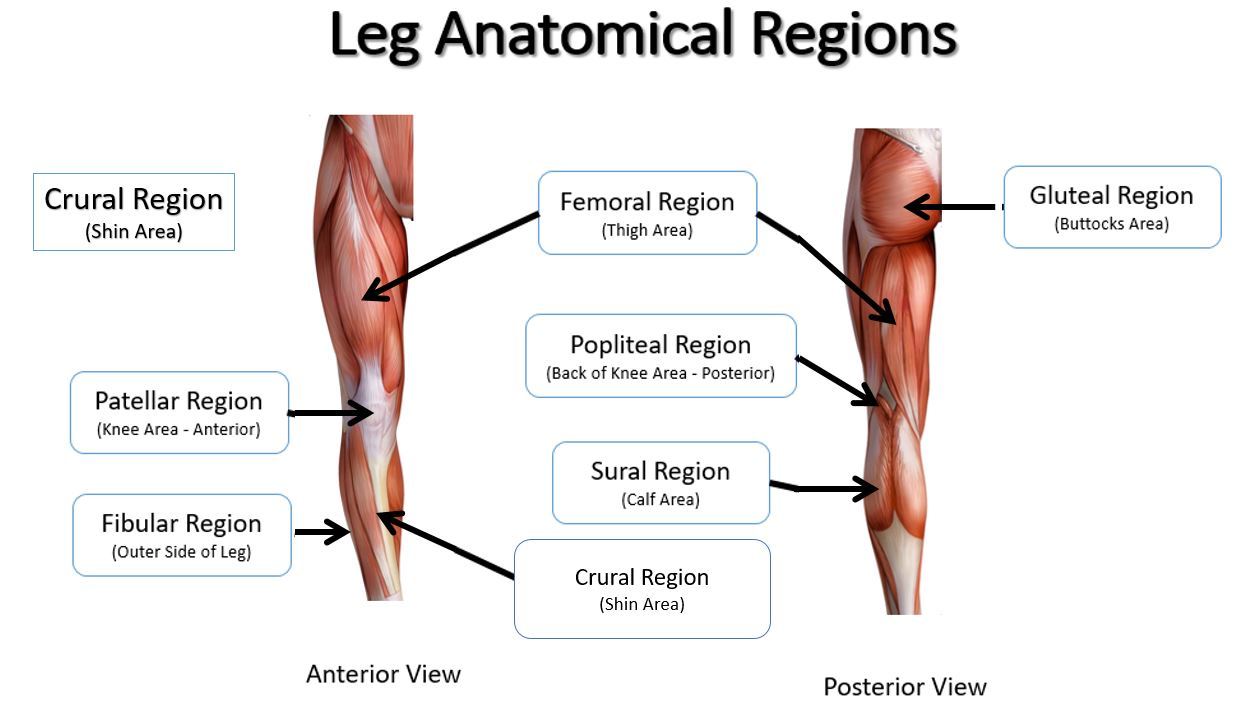
fibular
outer side of leg (anterior)
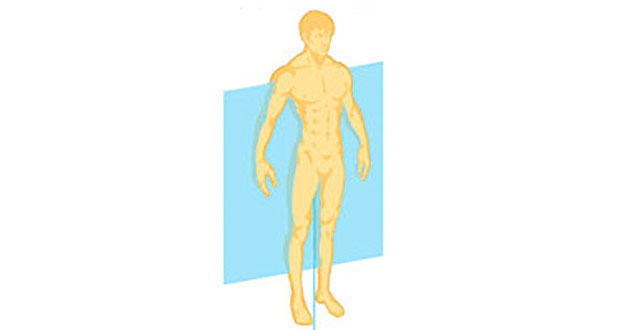
frontal plane
runs vertically from right to left; divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
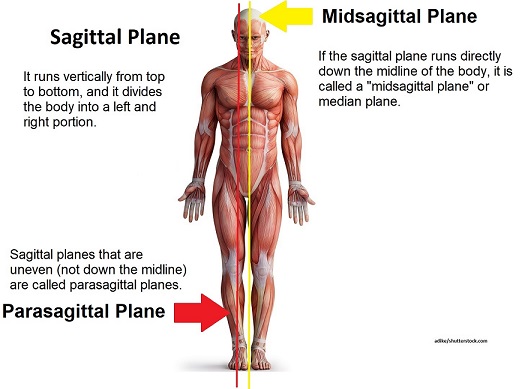
sagittal plane
separates the body into left and right portions
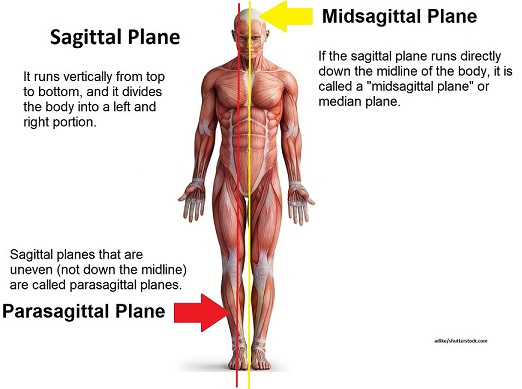
midsagittal plane
divides the body into left and right parts equally at the midline
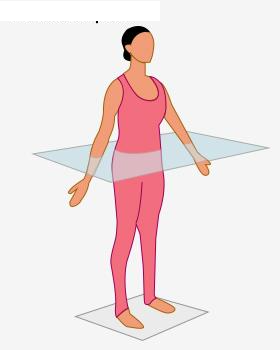
transverse plane
separates or divides the body into superior and inferior portions
right
towards the right side of the body
left
towards the left side of the body
inferior (caudal/tail: animal)
below
superior (cephalic/head: animal
above
anterior (ventral: belly)
towards the front
posterior (dorsal: back)
towards the back
proximal (proximus: nearest)
closer to the point of attachment
distal
farther from a point of attachment
lateral
away from the body’s midline
medial
towards the body’s midline
superficial
towards/ on the surface
deep
away from the surface
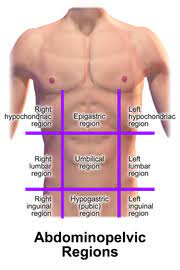
UMBILICAL REGION
the area around the umbilicus; sections of the small & large intestines, inferior vena cava and abdominal aorta
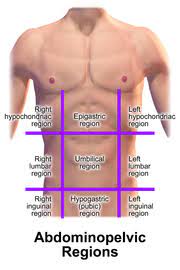
EPIGASTRIC REGION
it is superior to the umbilical region; most of the pancreas, portions of the stomach, liver, inferior vena cava, abdominal aorta and duodenum
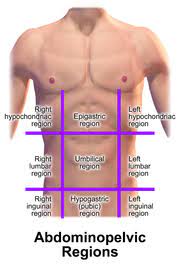
HYPOGASTRIC REGION
it is inferior to the umbilical region; it is the pubic area
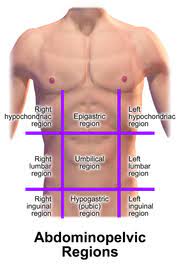
RIGHT AND LEFT ILIAC REGIONS
either side of the hypogastric region; inguinal regions
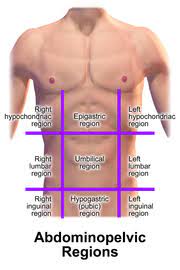
RIGHT AND LEFT LUMBAR REGIONS
either side of the umbilical region; the loin regions
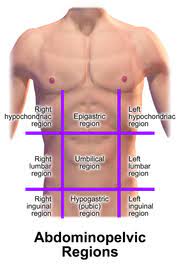
RIGHT AND LEFT HYPOCHONDRIAC REGIONS
either side of the epigastric region
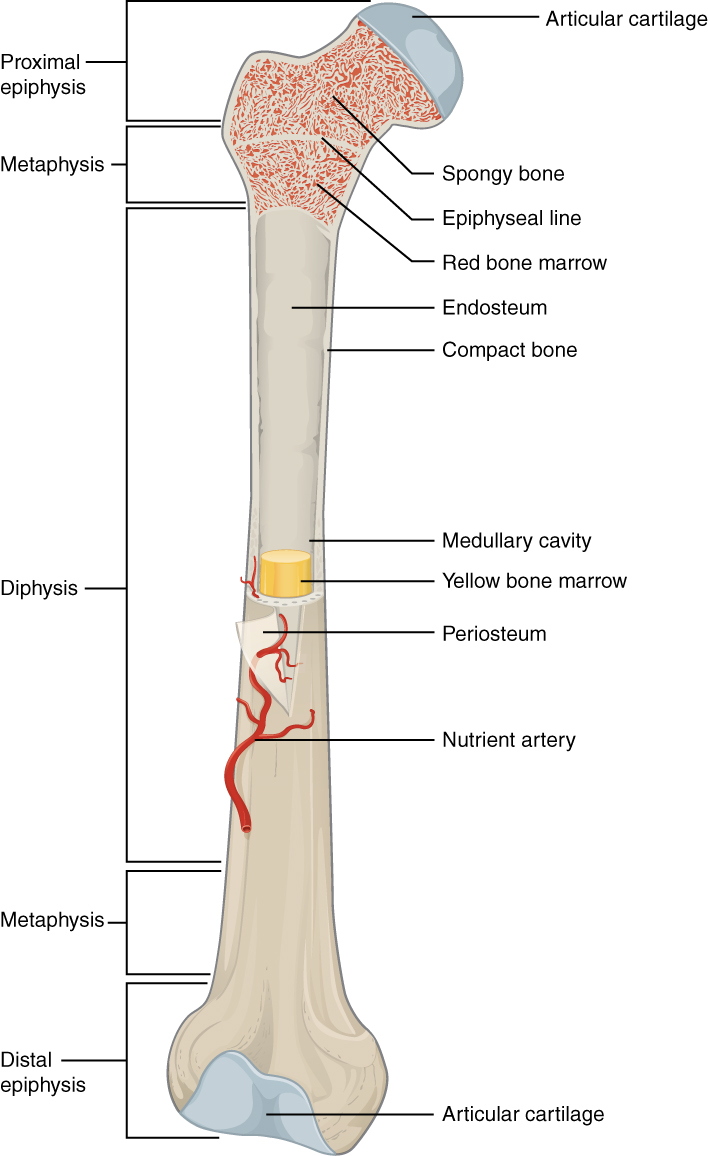
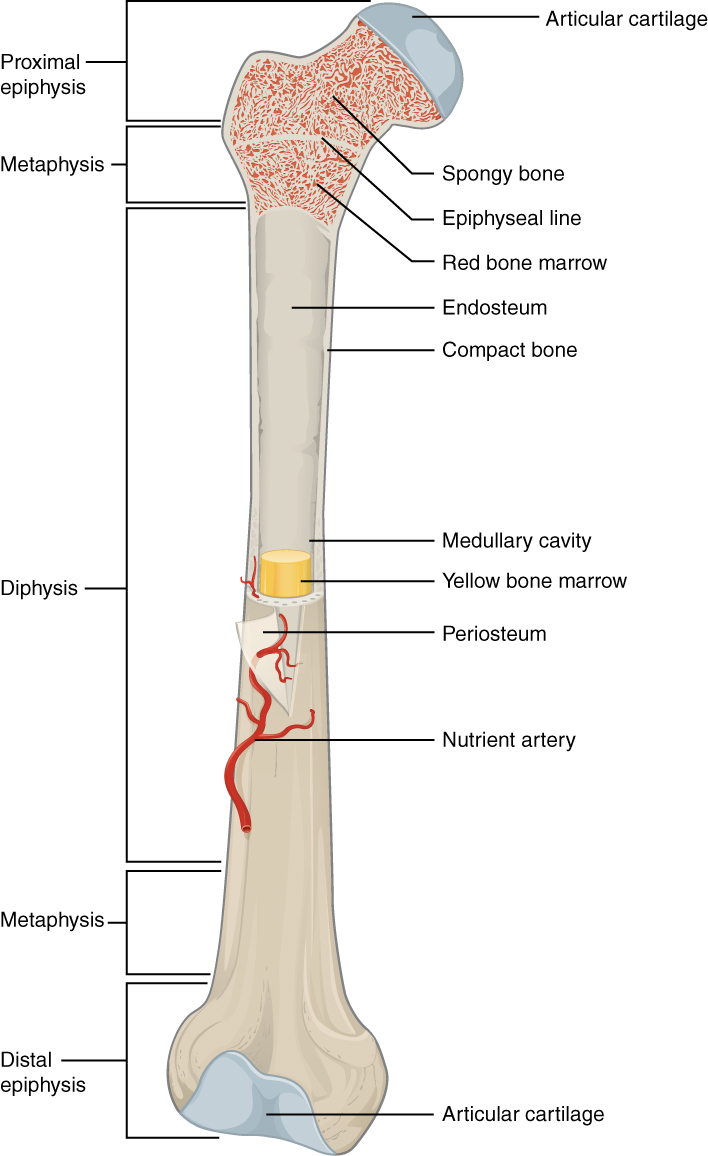
epiphyseal line
an epiphyseal plate that stops growing in length and becomes ossified
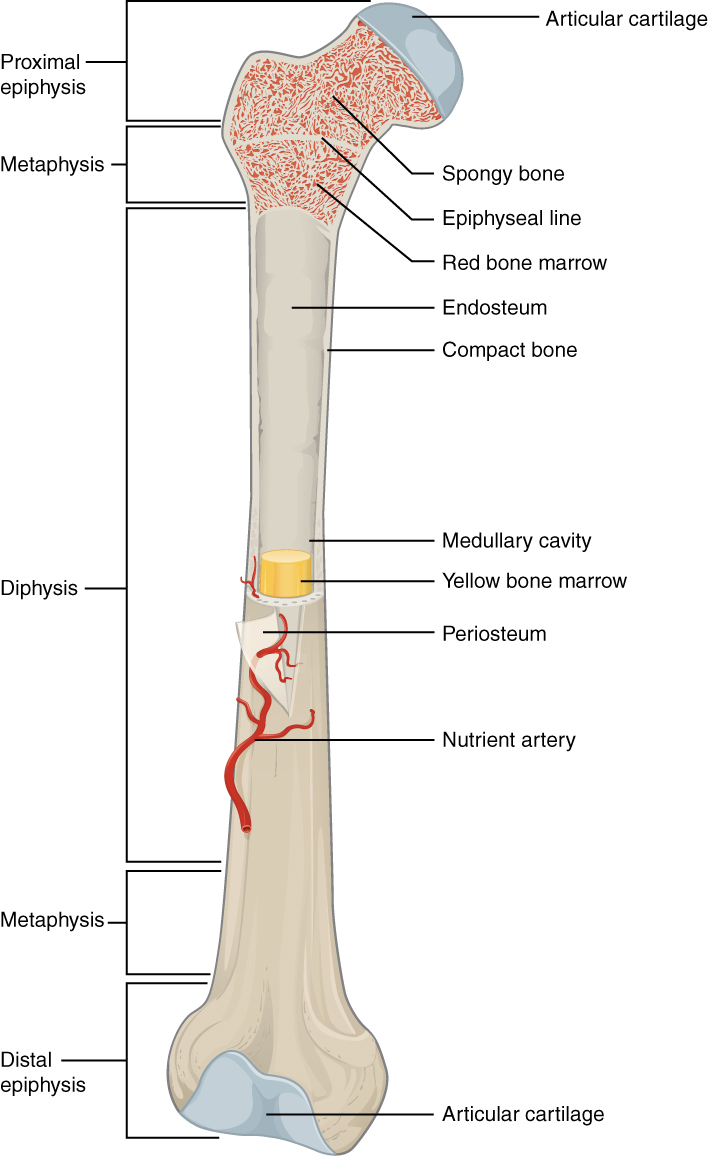
red marrow cavity
small, irregular cavities that contain red bone marrow
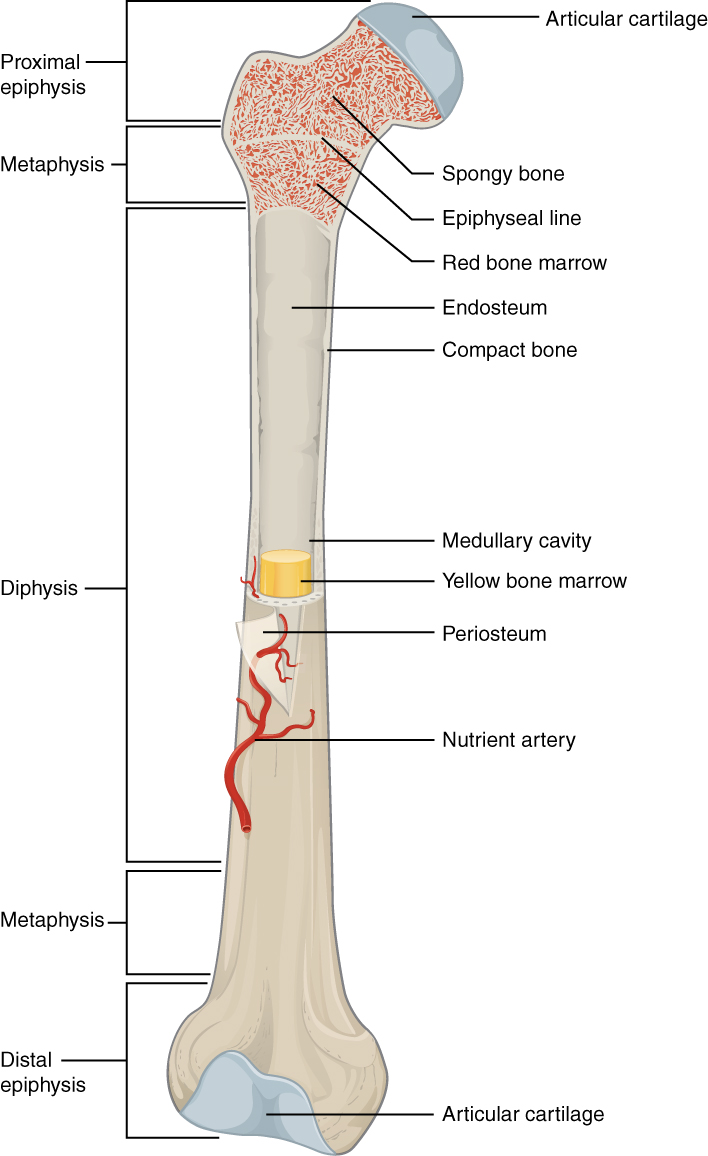
nutrient artery
found in the periosteum; an artery that supplies the medullary cavity of the long bone
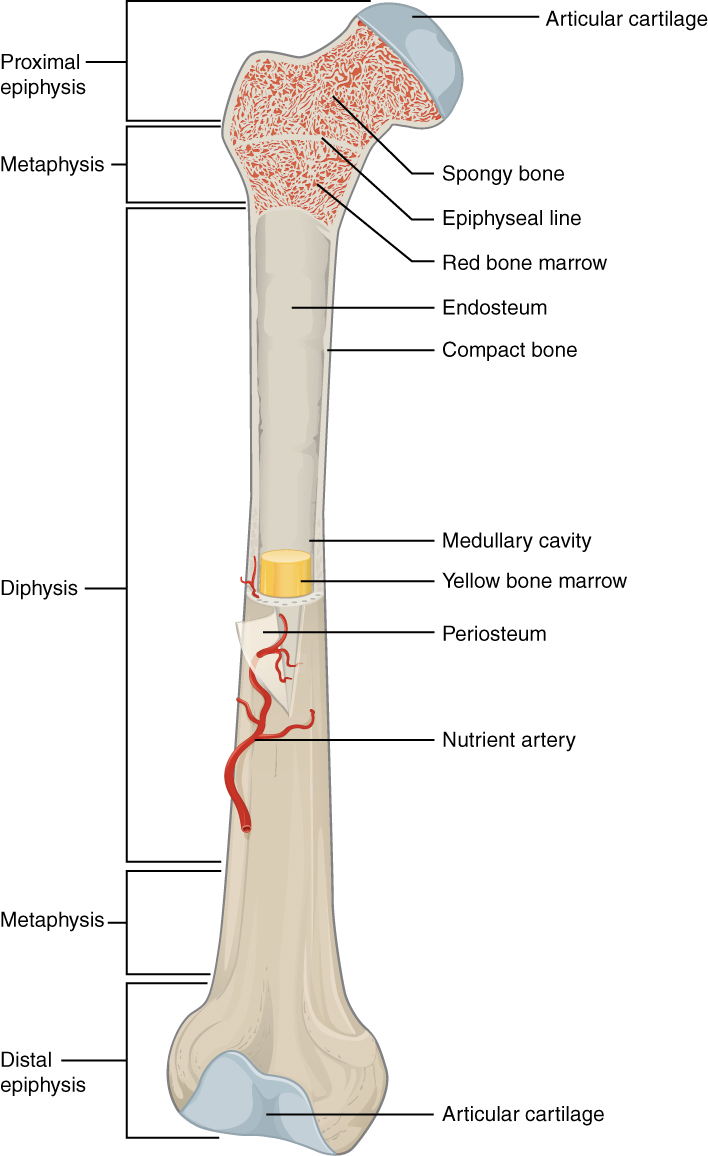
medullary cavity
hollow center of a long bone; large cavity within the diaphysis
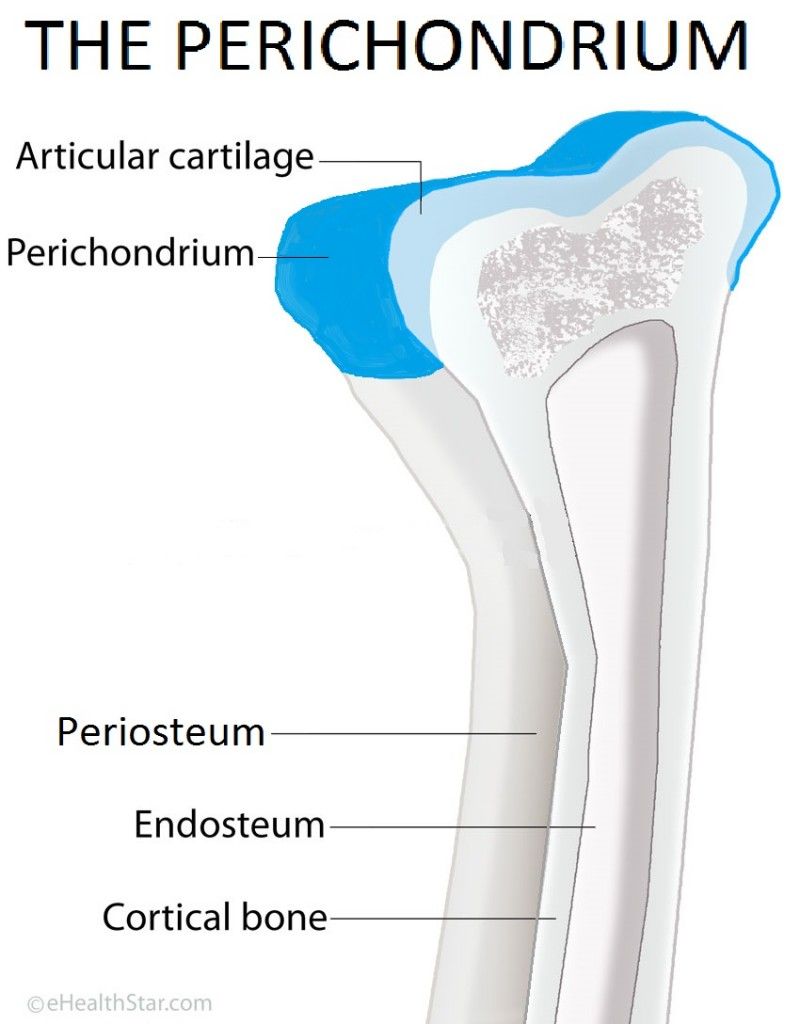
Articular cartilage
a type of hyaline cartilage that covers the ends of bones where they come together to form joints, has no perichondrium, blood vessels, or nerves
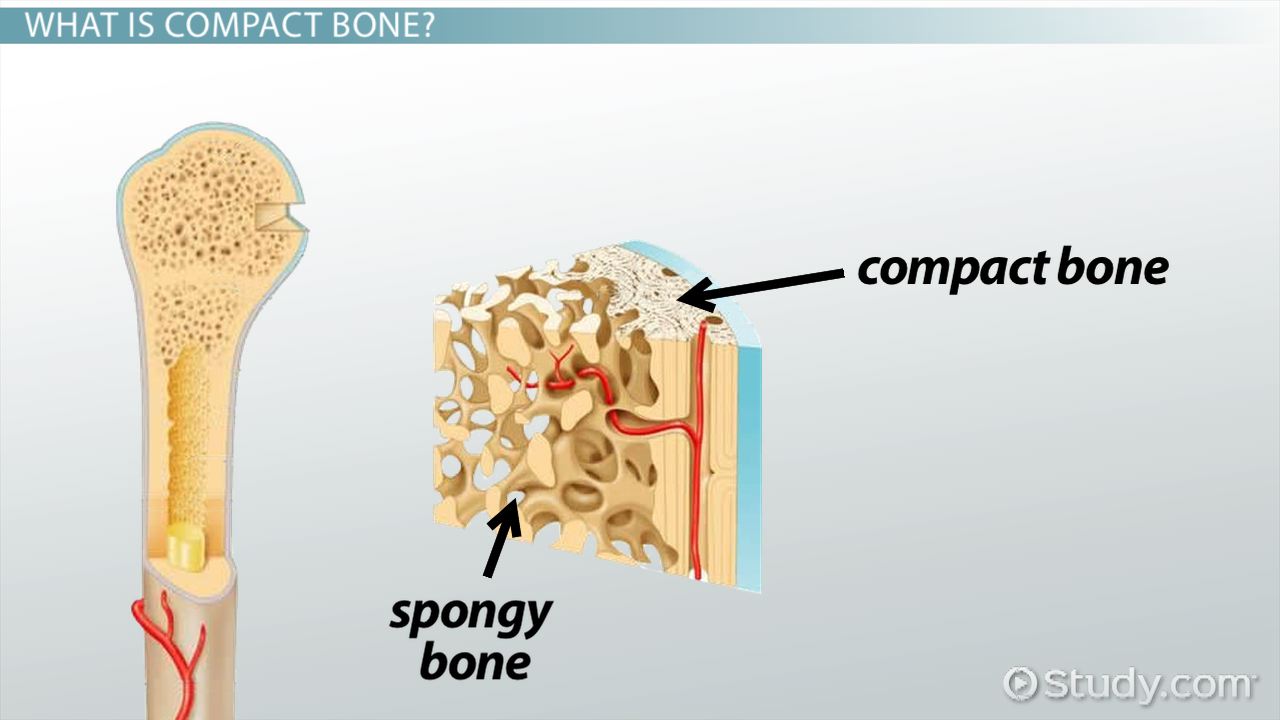
compact bone
solid, outer layer surrounding each bone; has more matrix and is denser with fewer pores, lamellae is primarily oriented around blood vessels
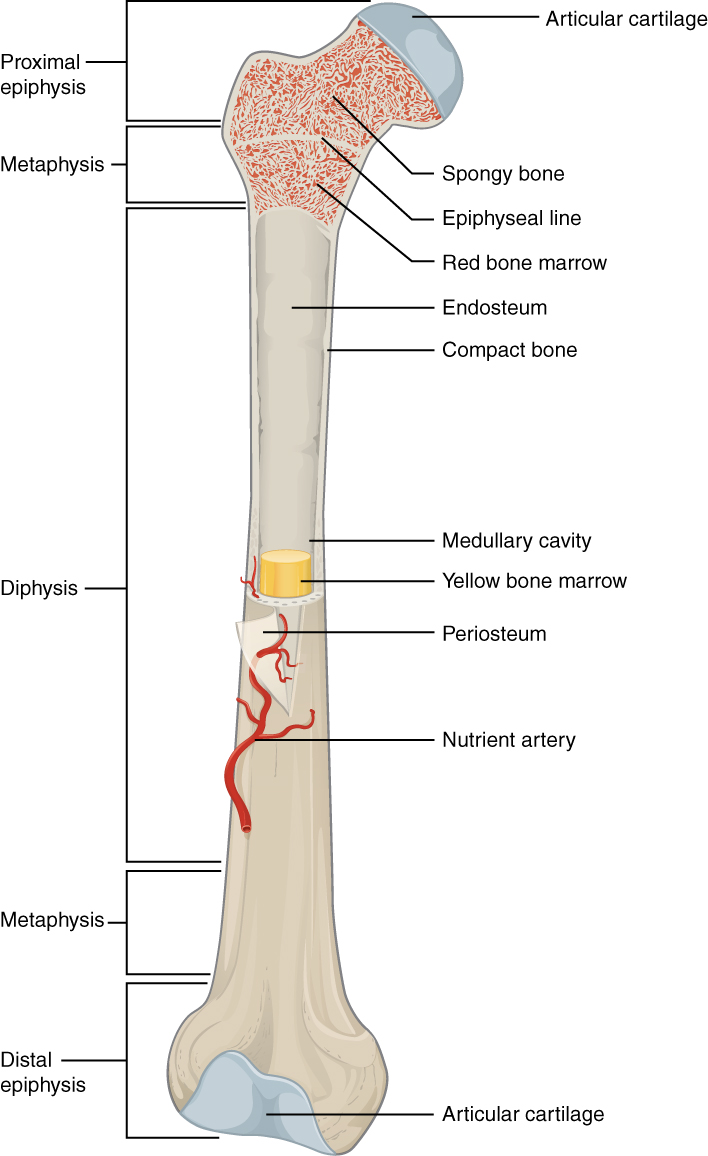
yellow marrow
type of bone present in the medullary cavity in adults
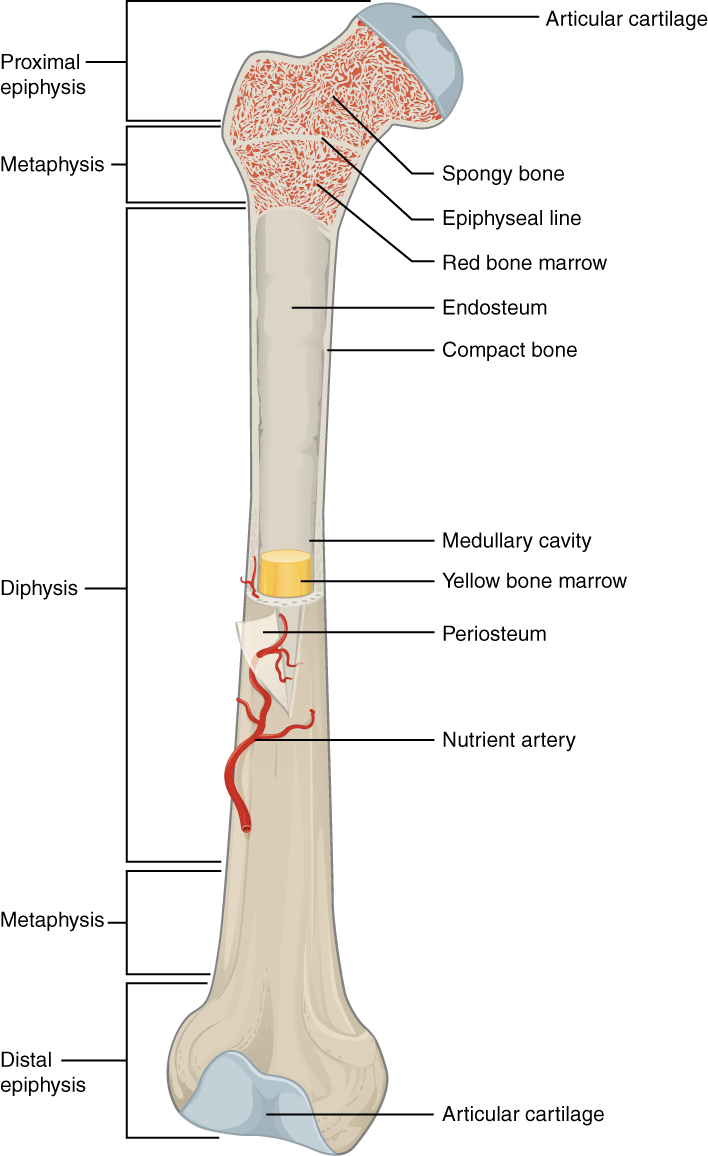
periosteum
outer, double-layered connective tissue membrane with ligaments and tendons attached to bone; blood vessels and nerve pathways
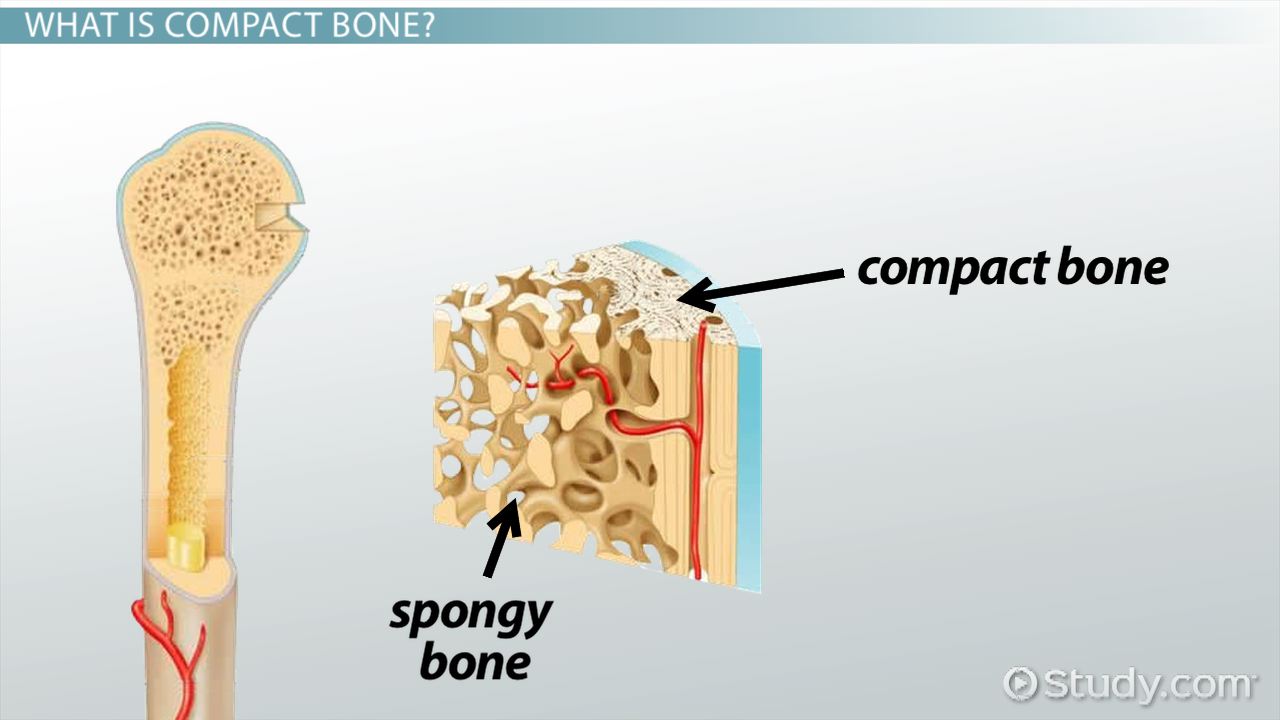
spongy bone
consists of interconnecting rods or plates of bone called trabeculae, surrounded by compact bone, less bone matrix and space than compact bone
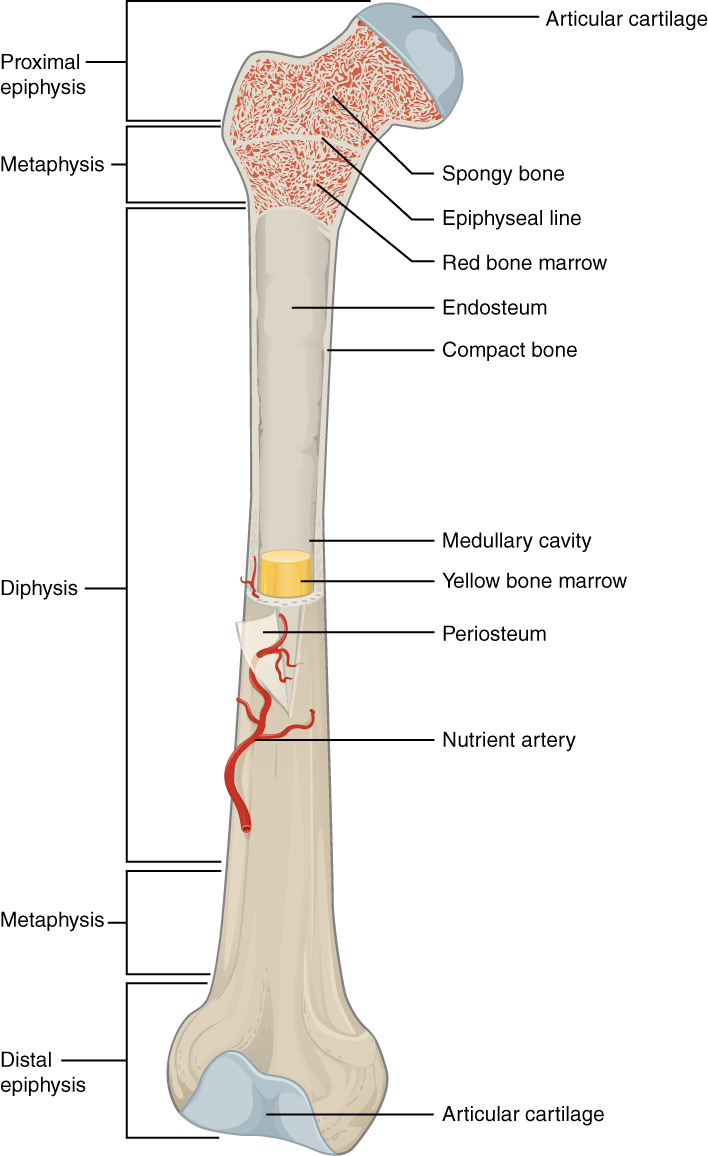
diaphysis
center portion of a long bone, composed primarily of compact bone
endosteum
thin connective tissue membrane lining the inner (medullary) cavities of bone
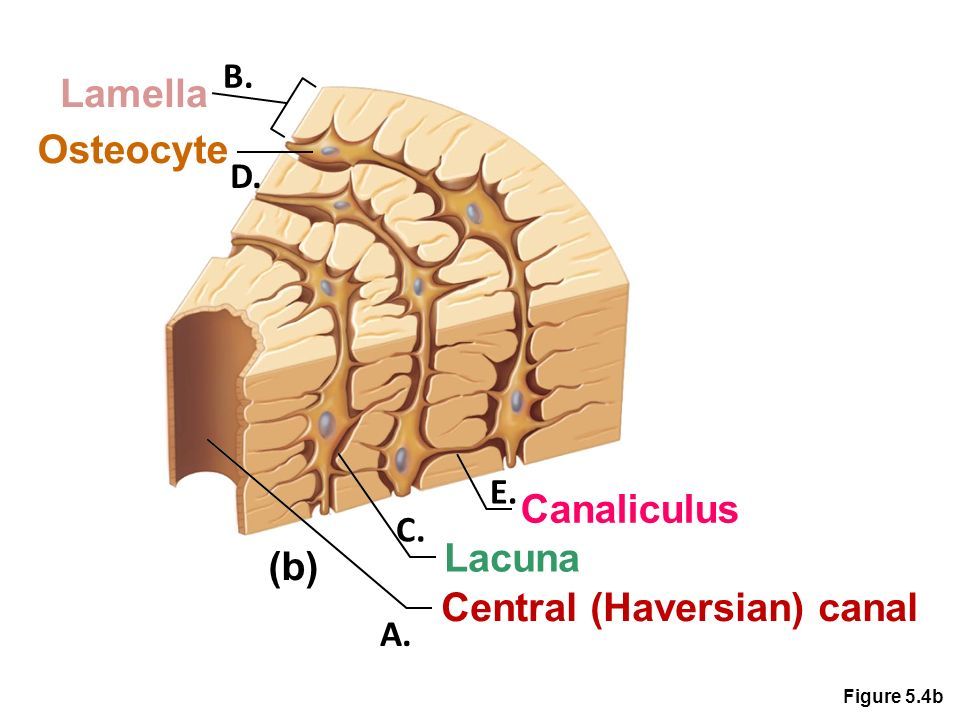
canaliculi
minute canals connecting osteocytes of an osteon
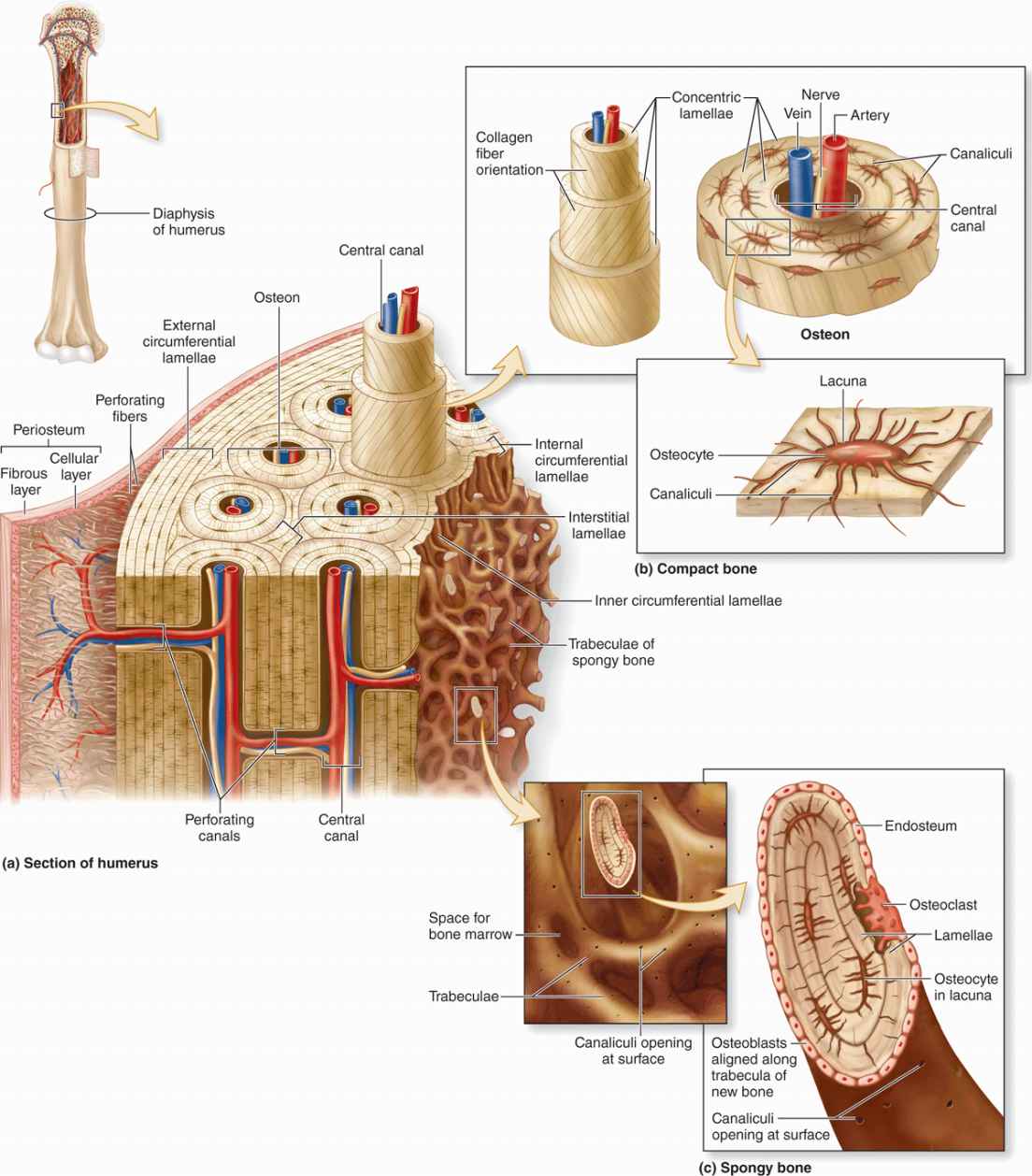
central canal
longitudinal canal carrying blood vessels and nerves
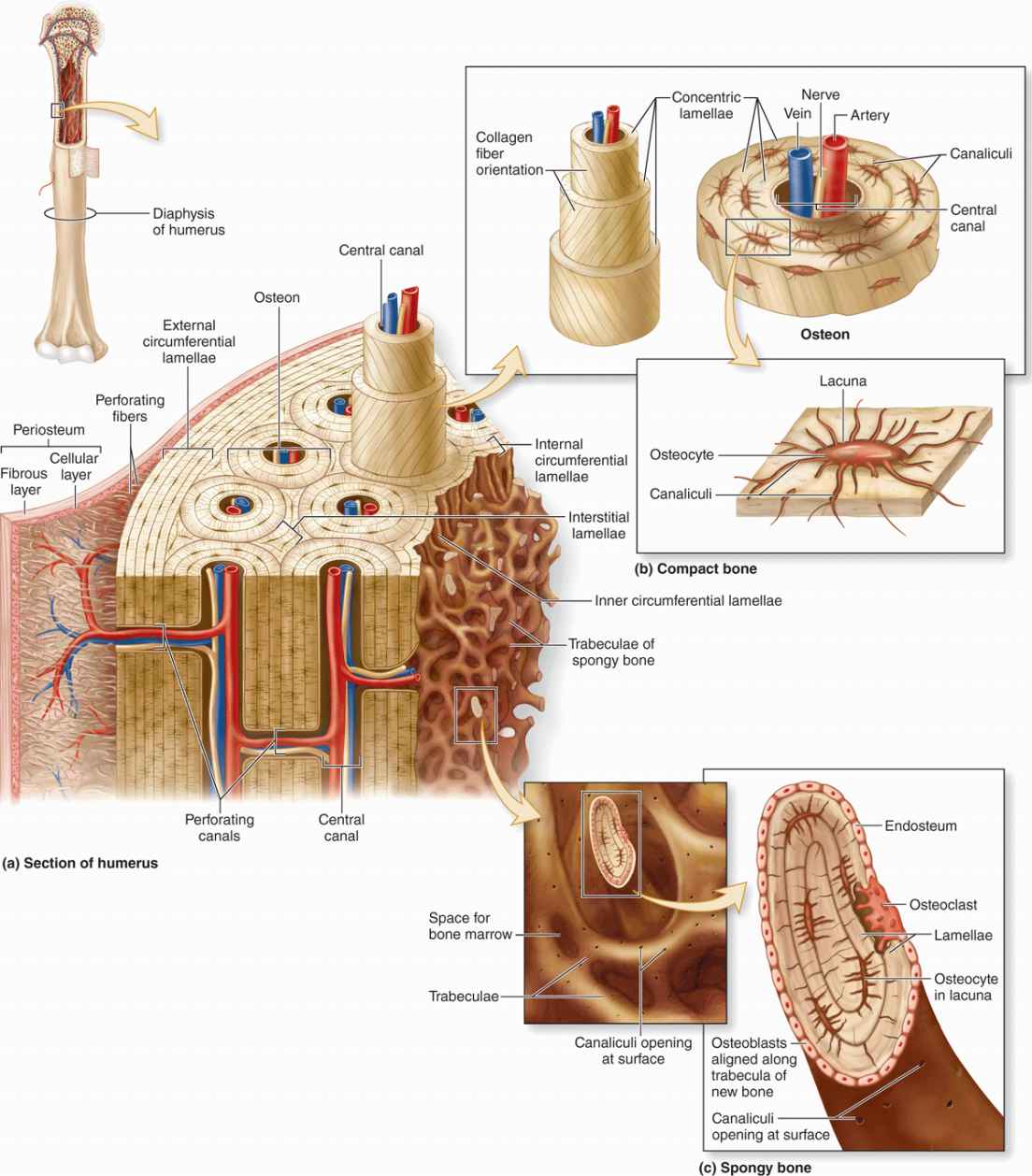
concentric lamellae
layers of bony matrix lining the central canal
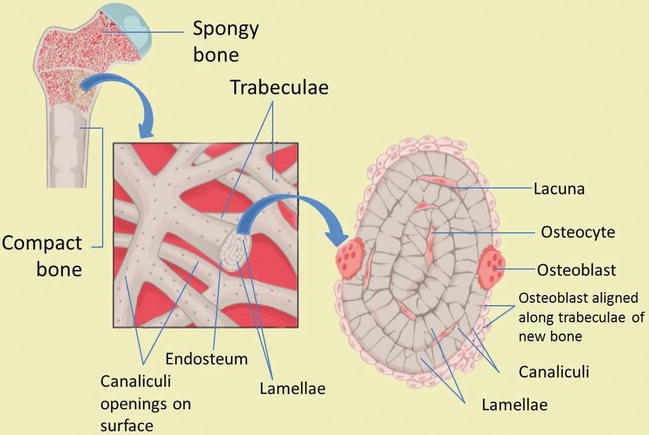
lacunae
site of osteocytes
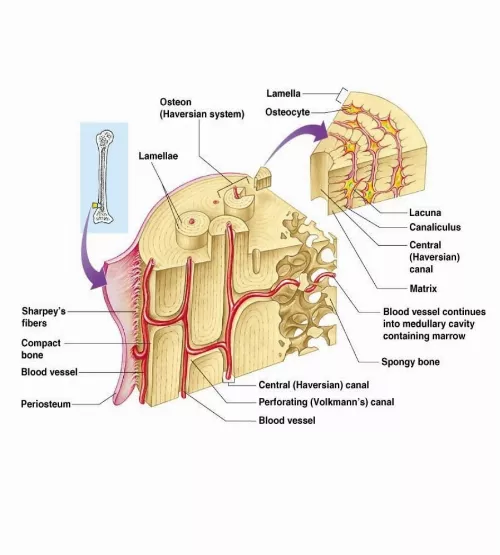
matrix
inorganic salts deposited in organic ground substance
epidermis
a stratified squamous epithelium with no blood vessels; prevents water loss and resist abrasion
dermis
composed of dense collagenous tissue; responsible for skin’s structural strength
subcutaneous tissue/ hypodermis
attaches skin to bone; serves as shock absorber and insulates deeper tissues from extreme temperature changes
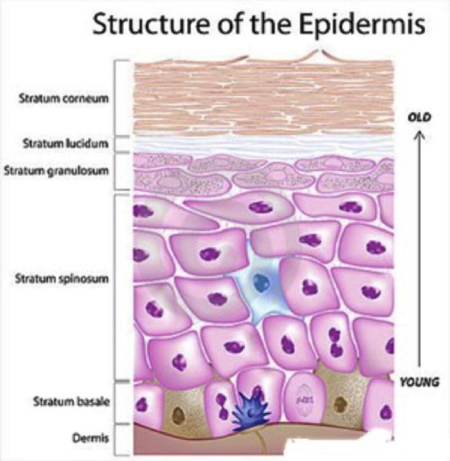
stratum basale
have cells that undergo mitosis every 19 days; takes 40-56 days before cells reach the surface
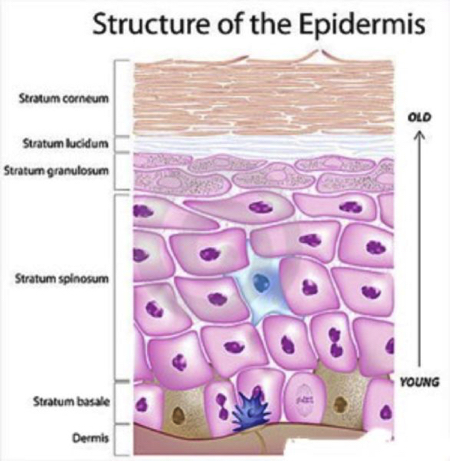
stratum spinosum
8-10 spiny-appearing cells with elongated edges; keratin fibers and lamellar bodies accumulate
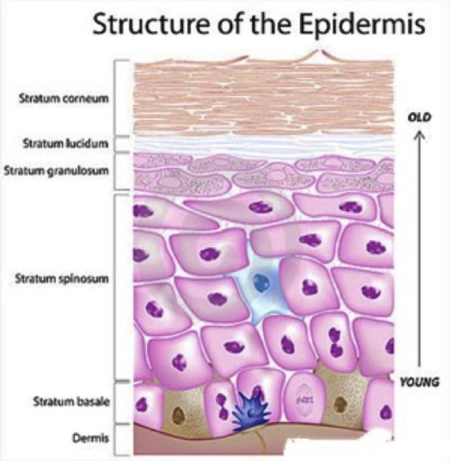
stratum granulosom
2-5 layers of flattened diamond-shaped cells; keratohyalin accumulates in cells
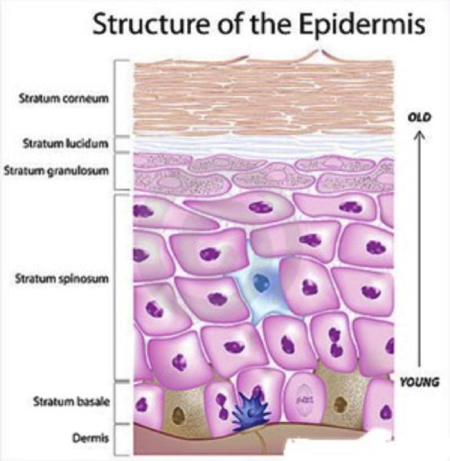
stratum lucidum
thin zone of dead keratinocytes; most exposed to friction
stratum corneum
at least 25 layers of dead cells joined together by desmosomes; layer that sloughs off dead squamous cells
dermal papillae
allows blood to supply nutrients, remove waste products, help regulate temp.
papillary layer
top layer of dermis
reticular layer
bottom layer of dermis; orientation of fibers produce cleavage lines, tension lines, Langer’s lines
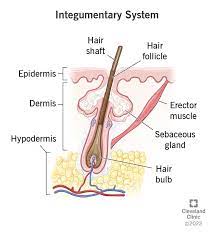
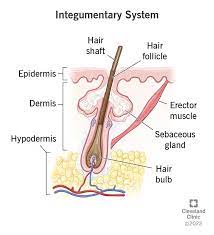
hair
dense and covers most of the body surface; s found everywhere on the skin except the palms, the soles, the lips, the nipples, parts of the external genitalia, and the distal segments of the fingers and toe