Chapter 11
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
what happens when the heart contracts?
oxygenated blood pumped out
what happens when the heart relaxes?
deoxygenated blood enters
pericardium
fluid filled sac that encloses the heart
atria
two upper chambers that recieve blood
ventricles
two lower chambers that pump out blood
atrioventricular valves
located between atria and ventricles
pulmonary circuit
blood travels from the right side of heart to lungs thru pul artery, gets oxygen and releases carbon dioxide, and travels back to heart through pul vein
systemic circuit
oxygenated blood in left atrium pumped to left ventricle to aorta to body.
deoxygenated blood returns to right atrium from vena cavas to right ventricles to lungs and then through left atrium.
pacemaker + location
sets rate at which heart contracts by sending electrical impulses
located on wall of right atrium
sphygmomanometer
measures blood pressure using pressure cuff
what is blood pressure mesured in
millimetres of mercury (mm Hg)
systolic pressure
highest recorded pressure in an artery when contracted
diastolic pressure
lowest recorded pressure in an artery when relaxed
what two factors does blood pressure depend on
cardiac output (blood pumped by heart per minute)
resistance of arteries (elasticity)
blood
connective tissue made of cells and tissue
open circulatory system
invertebrates; tubular heart pumps blood to sinuses, body tissues, and then back to heart.
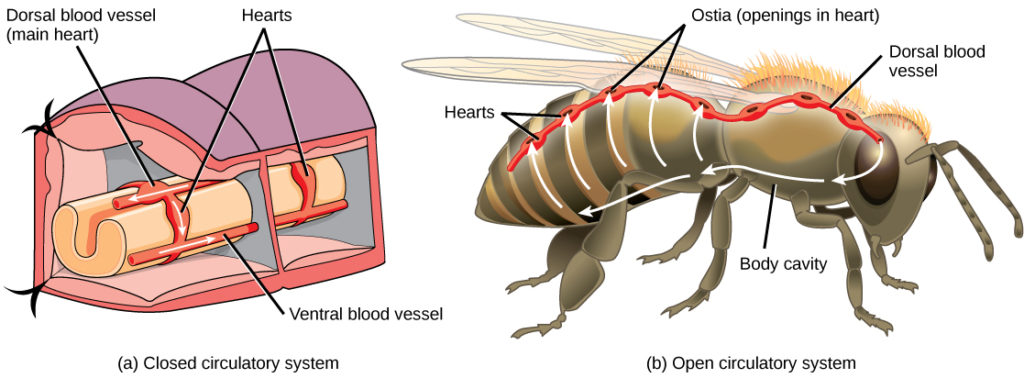
closed circulatory system
vertebrates; blood remains in blood vessels throughout body
function of blood (6)
transports oxygen, removes waste products, regulates body temp, fight infections, heals wounds
function of plasma
transports fatty acid and vitamins, fights infection
what is plasma made of?
mostly water, proteins, nutrients, waste
red blood cells + what do they contain?
cells that carry oxygen from lungs to tissues. contains hemoglobin.
hemoglobin
protein binds oxygen in lungs and releases it
where are red blood cells produced
bone marrow
shape of RBC function
increases surface area and flexibility
white blood cells functions
guard against infection, fights parasites and bacteria
pus
white blood cells and waste
where are white blood cells produced?
bone marrow
platelet
cell fragments that originate when cytoplasm of bone marrow cells divide
how do platelets stop bleeding in cuts?
they gather at the cut, release clotting factors, produce fibrin, form a scab, and prevent further loss of blood
fibrin
strand-like protein
hemophilia
condition where blood doesn’t clot causing individuals to bleed for longer.
blood vessels include
capillaries, arteries, veins
smooth muscle tissue in blood vessels function
regulates diameter
connective tissue in blood vessels function
expand and contract as blood flows
epithelial tissue in blood vessels function
lines walls
arteries
large blood vessels that carry blood from heart to tissue.
capillaries
microscopic blood vessels
have moist walls to allow for oxygen to get out, and waste in.
veins
blood vessels that return blood from capillaries to the heart
valves in veins
allow blood to flow only towards heart
diffusion
molecules move across a membrane from an area of higher concentration to lower
diffusion gradiant + where?
Gradual change in solute concentration until an equilibrium is reached.
occurs in capillaries
blood pressure
force blood exerts against artery walls.
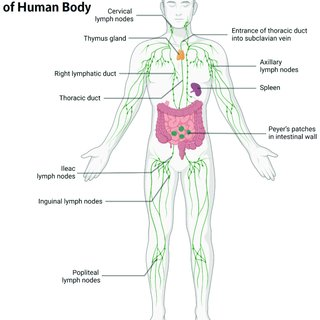
lymphatic system functions
screens fluids that leave capillaries and returns it to circulatory system
lymph
clear, watery fluid made of protein molecules, salt, glucose, etc
edema
swelling caused when lymph isn’t drained
spleen function
removes old/damaged blood cells, stores platelets, controls amount of blood, immunity
thymus
area where white blood cells mature
lymph nodes
filter out
plaque
patchwork of cholesterol, calcium, fat deposits that stick to interior walls.
atherosclerosis
narrowing of the arteries from plaque
angina pectoris
rises from mild atherosclerosis.
chest pains
treated with angioplasty
angioplasty
small metal tube expands artery
heart attack
rises from severe atherosclerosis
pain in chest, shortness of breath
arteriosclerosis
advanced stage of plaque buildup and arteries can’t stretch.
treated with heart bypass surgery
heart bypass surgery
vein/artery from another location used to make detour around blocked part.
sudden cardiac arrest
heart suddenly sops functioning
caused by coronary heart disease
cardiac defibrillator
resets heart rhythm
arrhythemia
heart beats irregularly
caused by electric activity
treated through implanting an artificial pacemaker or small defibrillator
hypertension (high blood pressure)
person’s blood pressure is 140/90 or higher
causes damaged heart and blood vessels.
heart failure
heart cannot pump blood efficiently because it cannot fill with enough blood or cannot send blood.
improve lifestyle, heart transplant.
aneurysm
bulge in the wall of an artery
caused by injuries, cgenetics, or disease
stroke
blood clot forms in an artery going to the brain
results in paralysis, loss of speech , memory, death