Child Developmental Psych (Final Exam)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/125
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:00 PM on 12/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
1
New cards
Nature vs Nurture
* **Nature**: influence of genetic inheritance on development
* **Nurture**: influence of learning & the environment
* **Nurture**: influence of learning & the environment
2
New cards
Developmental Psychopathology
approach that sees mental & behavioral problems as distortions of normal developmental processes rather than as illnesses
3
New cards
Incremental theories
Theories in which development is a result of continuous quantitative changes → changes in quantity
4
New cards
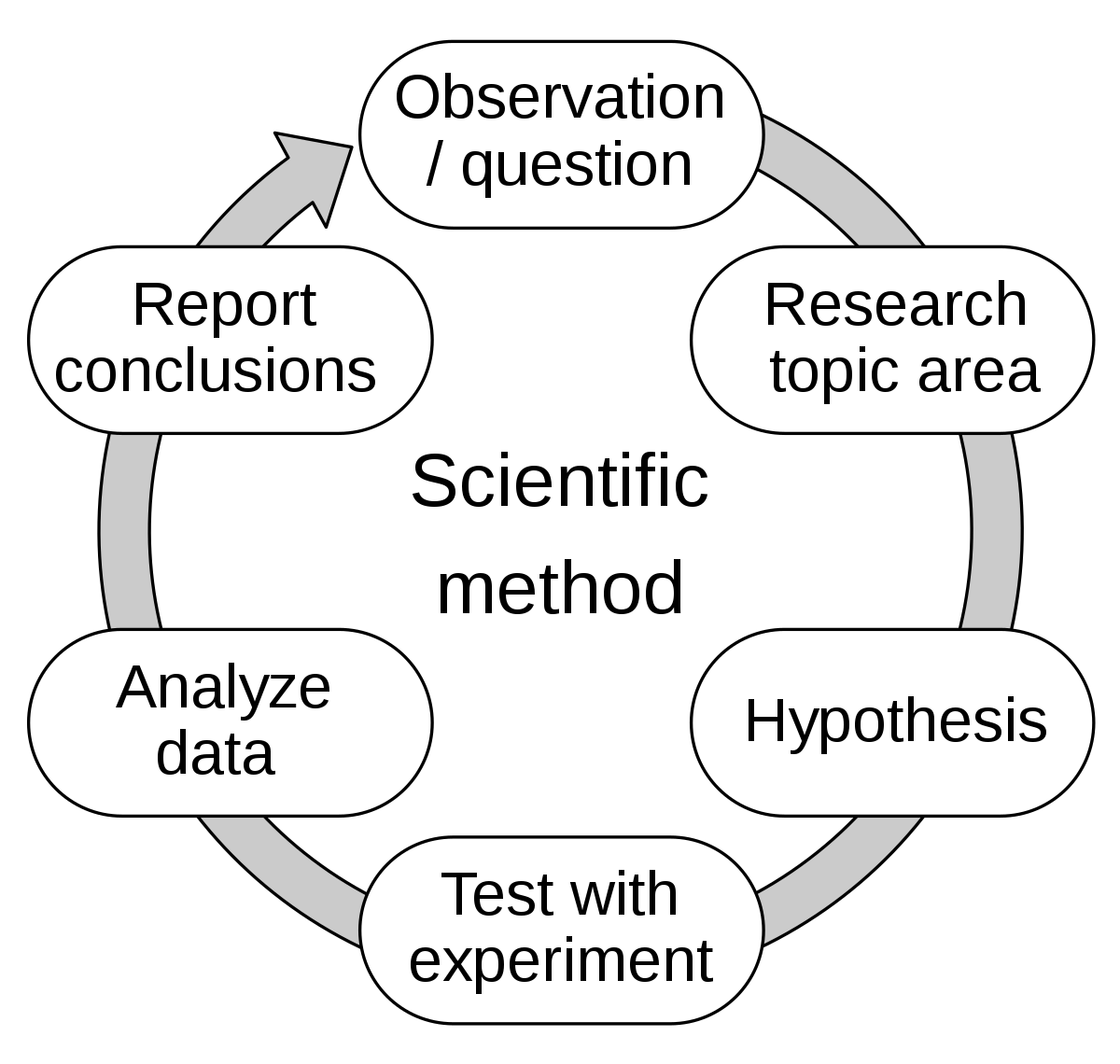
The Scientific Method & Measures
* **Operational Def**: define a concept in a way that allow us to measure it
* **Reliability**: ability of a measure to produce consistent results
* **Validity**: ability of a research tool to accurately measure
* **Reliability**: ability of a measure to produce consistent results
* **Validity**: ability of a research tool to accurately measure
5
New cards
Physiological Measures
* examine the body’s response to different stimuli
* understand processes that underlie certain behaviors
* studies infants who have limited language ability
* non-invasive
* understand processes that underlie certain behaviors
* studies infants who have limited language ability
* non-invasive
6
New cards
Natural or “Quasi” Experimental Design
research in which members of the groups are selected bc they represent different naturally occurring “treatment” conditions
\
ex. groups based on school or social categories
\
ex. groups based on school or social categories
7
New cards
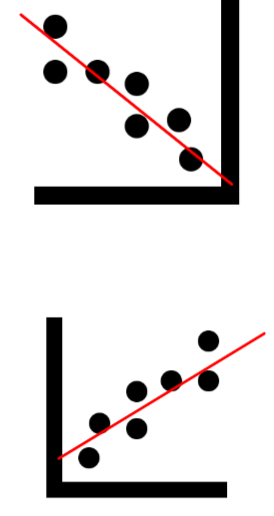
Correlation Research Design
research that measures the strength & direction of the relationship between two or more variables that are not created by the experimenter
\
correlation ≠ causation!
\
ex. sense of belonging & academic achievement
\
correlation ≠ causation!
\
ex. sense of belonging & academic achievement
8
New cards
Longitudinal Design
follows 1 group of individuals over time & looks at similar measures
9
New cards
Cross-Sectional Design
uses multiple groups of participants who represent the age span of interest to the researcher
10
New cards
Sequential Design
uses multiple groups of participants & follows them over a period of time, with beginning age of each group being the ending age of another group
11
New cards
Ethical Considerations in Research w/ Kids
* no physical or psychological harm
* consent from both kids & parents
* right to freely participate or not
* research inform parents of any threat to kid’s well-being
* use least stressful research procedure
* consent from both kids & parents
* right to freely participate or not
* research inform parents of any threat to kid’s well-being
* use least stressful research procedure
12
New cards
Mirror Test
around 2 y/o, we can’t recognize themselves in the mirror & soon afterwards our **self-concept or self-awareness** emerges
13
New cards
Harlow Monkey Experiment
* demonstrate the importance of attachments, affection, & emotional bonds
* infant monkeys preferred the comforting cloth mother & only went to the wire mother for food
* infant monkeys preferred the comforting cloth mother & only went to the wire mother for food
14
New cards
Object Permanence
infants as young as 3.5 months can understand that things continue to exist, even if you can’t see them
\
ex. knowing a toy still exist even hidden under a blanket
\
ex. knowing a toy still exist even hidden under a blanket
15
New cards
Visual Cliff Experiment
to test babies’ depth perception using an apparent, but not actual from from 1 surface to another

16
New cards
Standardized Tests
scored in a standard or consistent way to all examinees
\
tests become standardized when we establish norms (average performance of test)
\
tests become standardized when we establish norms (average performance of test)
17
New cards
Risk of Social Desirability
tendency of respondents to answer questions in a way to please the researcher or to make them look good in the researcher’s eyes
18
New cards
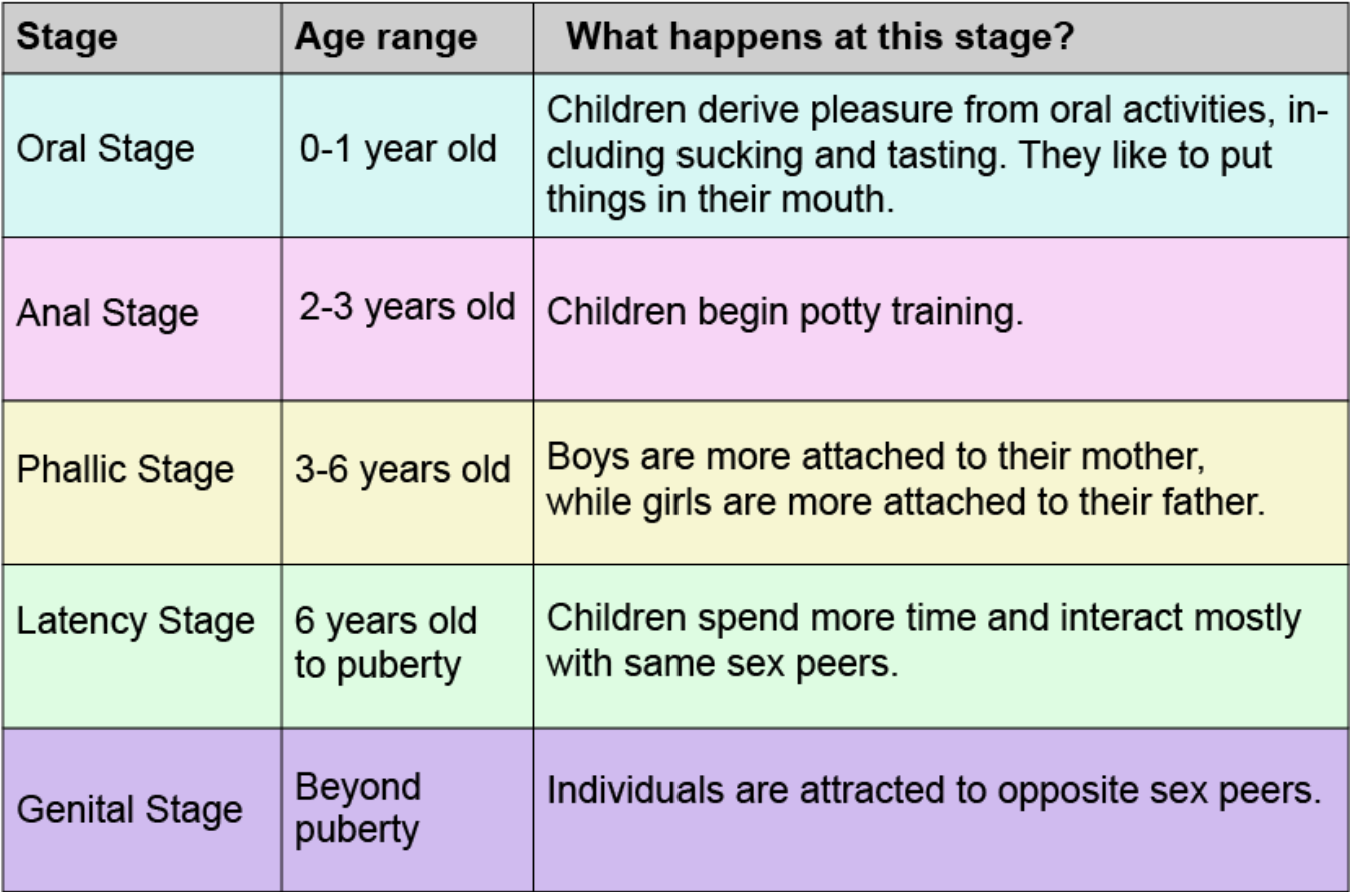
Freud’s Psychosexual Stages
kids’ unconscious thoughts & motivations help explain their behavior w/ 5 stages
19
New cards
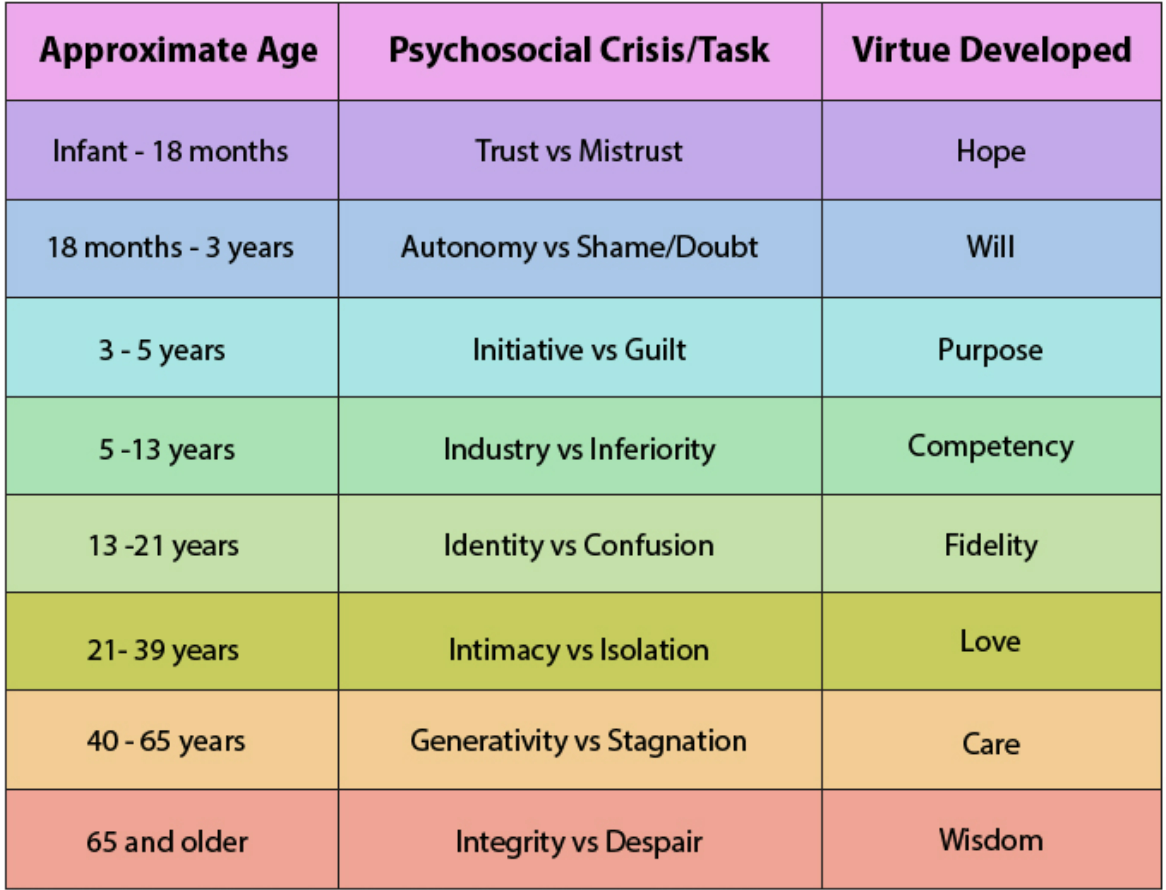
Erikson’s Psychosocial Stages
describe typical developmental issues from infancy through adolescence in 8 stages
20
New cards
Piaget’s 4 Stages of Cognitive Development
\
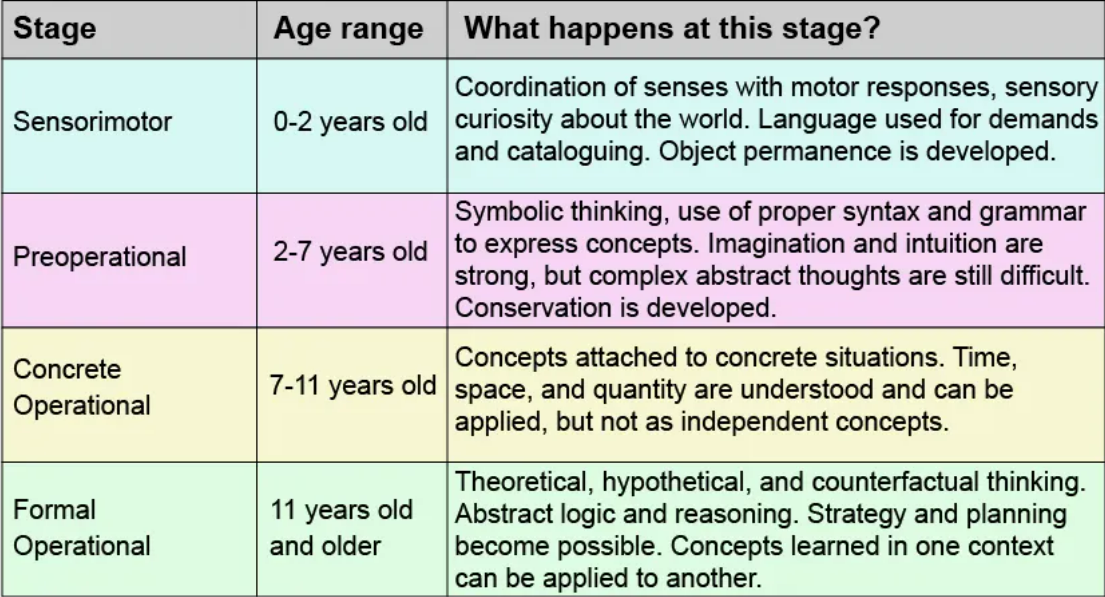
21
New cards
Piaget’s Terms
* **Schemas**: cognitive framework that places concepts, & objects into categories
* **Assimilation**: fitting new info into existing cognitive schemas
* ex. learns word dog, calls all 4-legged animals dogs
* **Accommodation**: altering one’s existing schemas in response to new info & experiences
* ex. refers a cat as a dog until corrected by a parent & can correctly distinguish between them
* **Assimilation**: fitting new info into existing cognitive schemas
* ex. learns word dog, calls all 4-legged animals dogs
* **Accommodation**: altering one’s existing schemas in response to new info & experiences
* ex. refers a cat as a dog until corrected by a parent & can correctly distinguish between them
22
New cards
Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory
* **Zone of Proximal Development:** what a child __cannot do independently__ but can do __w/ help__ from someone more skilled & knowledgeable
* ex. guiding a kid through the steps of subtraction
* **Scaffolding**: when more knowledgeable ppl __support a kid’s learning__ by providing help to move the kid __beyond__ their current level of capacity
* ex. providing a half-solved problem
\
he emphasized importance of social world & of culture in promoting cognitive growth
* ex. guiding a kid through the steps of subtraction
* **Scaffolding**: when more knowledgeable ppl __support a kid’s learning__ by providing help to move the kid __beyond__ their current level of capacity
* ex. providing a half-solved problem
\
he emphasized importance of social world & of culture in promoting cognitive growth
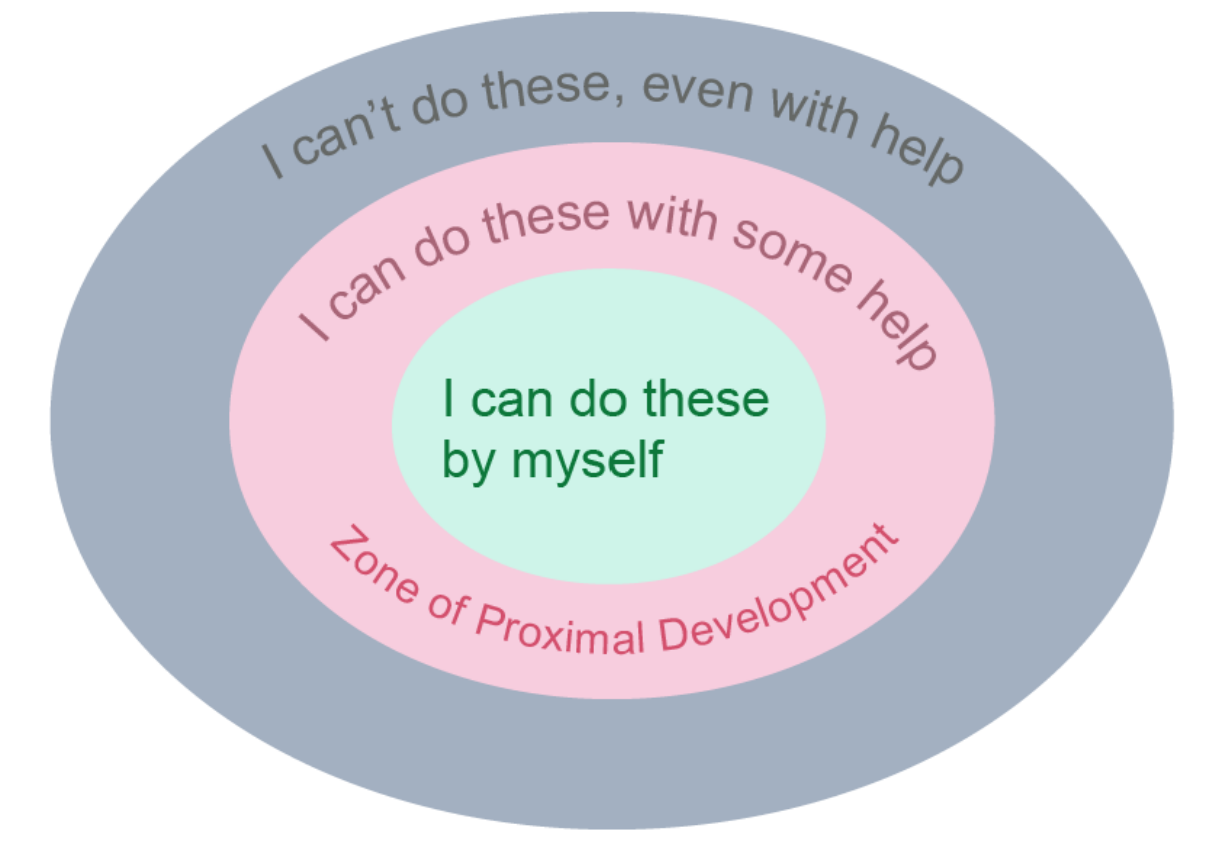
23
New cards
Bandura’s Social Learning Theory
proposed that new behaviors could be learned from observing & imitating others
\
illustrated with the famous __Bobo Doll experiment__: adults abused a doll in front of kids, which led them to mimic the aggressive behavior to the doll
\
illustrated with the famous __Bobo Doll experiment__: adults abused a doll in front of kids, which led them to mimic the aggressive behavior to the doll
24
New cards
Theory of Core Knowledge
infants are born with ‘core knowledge systems’ that support basic intuitions about the world
\
4 Areas:
1. object continuity: objects follow continuous paths through space
2. object solidity: 2 objects cannot occupy the same space
3. ppl act purposefully towards a goal
4. numbers such as seeing # of objects
\
4 Areas:
1. object continuity: objects follow continuous paths through space
2. object solidity: 2 objects cannot occupy the same space
3. ppl act purposefully towards a goal
4. numbers such as seeing # of objects
25
New cards
John B. Watson & Classical Conditioning
* **Behaviorism**: theory focused on environmental control of observable behavior
* **Classical Conditioning:** learning process where an automatic conditioned response is paired with a specific stimulus
* **Little Albert Experiment:** a previously unafraid baby was conditioned to become afraid of a rat
* **Classical Conditioning:** learning process where an automatic conditioned response is paired with a specific stimulus
* **Little Albert Experiment:** a previously unafraid baby was conditioned to become afraid of a rat
26
New cards
B.F. Skinner & Operant Conditioning
* **Operant Conditioning:** process when a response follows a behavior causes that behavior to happen
* **Reinforcement**: a response to a behavior that causes a behavior to happen __more__ (can be negative or positive)
* **Punishment**: a negative consequence or taking away a positive reinforcement to __reduce__ the likelihood of an undesirable behavior occurring
* **Reinforcement**: a response to a behavior that causes a behavior to happen __more__ (can be negative or positive)
* **Punishment**: a negative consequence or taking away a positive reinforcement to __reduce__ the likelihood of an undesirable behavior occurring
27
New cards
Ethology
study of the adaptive value of animal & human behavior in the natural environment
* imprinting: automatic process by which animals attach to their mothers
* imprinting: automatic process by which animals attach to their mothers
28
New cards
Bronfenbrenner's Ecological Systems Theory
views child development as a complex system of relationships affected by multiple levels of surrounding environments
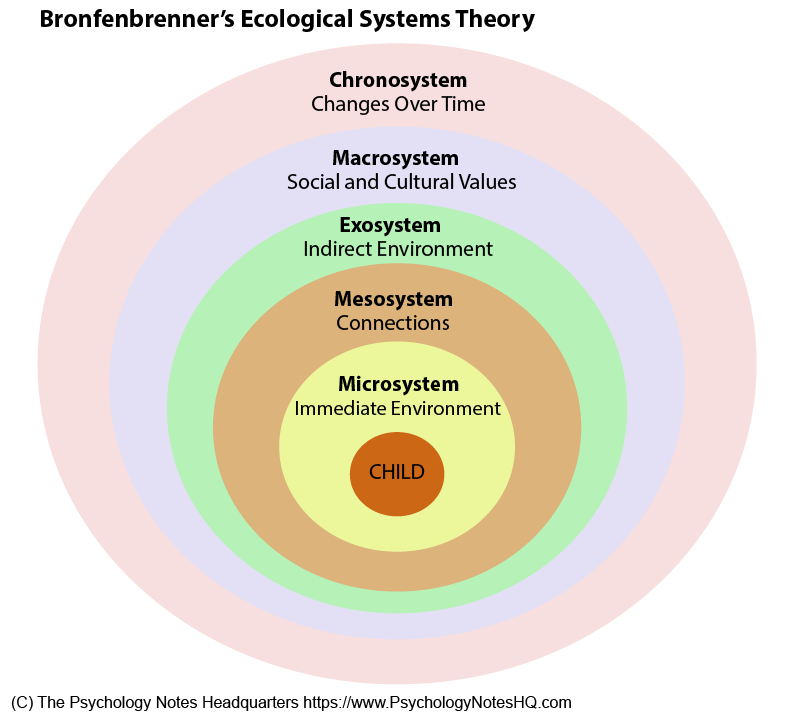
29
New cards
Identity Development
In Erikson’s psychosocial 5th stage of ==Identity vs Role Confusion==: adolescents work through complexities of finding one’s own identity
30
New cards
Attention
* Selective: paying attention to certain things
* Focused: maintaining focus overtime
* Habituation: reduction in response to a stimulus that’s repeated
* ex. no longer noticing the noisy air conditioner
* Focused: maintaining focus overtime
* Habituation: reduction in response to a stimulus that’s repeated
* ex. no longer noticing the noisy air conditioner
31
New cards
Memory
* gradually increases btw ages 1-2
* **Deferred Imitation**: infants see some action & reenact it later
* **Infantile Amnesia**: adults can’t recall events before age 3
* **Working Memory**: hold info in our mind while using that info in mental tasks
* ex. hiding an object in 1 drawer & infants able to keep location of object for brief amount of time
* **Deferred Imitation**: infants see some action & reenact it later
* **Infantile Amnesia**: adults can’t recall events before age 3
* **Working Memory**: hold info in our mind while using that info in mental tasks
* ex. hiding an object in 1 drawer & infants able to keep location of object for brief amount of time
32
New cards
Executive Function
ability of brain to coordinate attention & memory & controls behavioral response for the purpose of attaining a certain goal
33
New cards
Inhibitory Control
ability to stop a response, resist distractions & control what you pay attention to
\
ex. not eating a forbidden treat
\
ex. not eating a forbidden treat
34
New cards
Cognitive Flexibility
**Ability to switch focus as needed**
\
__Piaget’s A-not-B task__: used to assess infants’ ability to switch from location A to B when searching to a hidden object
* if infants lack it, they continue to search for object under cloth A, despite seeing it moved to cloth B
\
__Piaget’s A-not-B task__: used to assess infants’ ability to switch from location A to B when searching to a hidden object
* if infants lack it, they continue to search for object under cloth A, despite seeing it moved to cloth B
35
New cards
Social Cognition
infants begin to learn how to think about social interactions
\
ex. 8-12 months infants appear to understand others’ intentions or desires rather than just their actions
\
ex. 8-12 months infants appear to understand others’ intentions or desires rather than just their actions
36
New cards
Phonology
Study of the sounds of a language
\
* **Syntax**: grammar
* **Semantics**: meaning of words
* **Pragmatics**: the way we use language in social context
\
* **Syntax**: grammar
* **Semantics**: meaning of words
* **Pragmatics**: the way we use language in social context
37
New cards
Chomsky’s Nativism Theory
human brains are innately wired to learn language & that hearing spoken language triggers the activation of a universal grammar
\
* believes kids couldn’t learn something complex as human language as quickly unless they have a
→ __language acquisition device (LAD)__: innate capacity in brain for learning language
\
* believes kids couldn’t learn something complex as human language as quickly unless they have a
→ __language acquisition device (LAD)__: innate capacity in brain for learning language
38
New cards
Overregularization
a type of grammatical error in which kids apply a general language rule to words that don’t follow the rule or pattern
\
ex. adding -s to make the plural of an irregular noun like foot
\
ex. adding -s to make the plural of an irregular noun like foot
39
New cards
Interactionism
a theory of language development that proposes the child’s biological readiness to learn language interacts with the child’s experiences with language in the environment to bring about language development
\
ex. adults naturally simplify their speech to young kids
\
**recast**: adults repeat what kids say but recast it into more advanced grammar
\
ex. adults naturally simplify their speech to young kids
\
**recast**: adults repeat what kids say but recast it into more advanced grammar
40
New cards
Cognitive Processing Theory
learning language is a process of “data crunching,” in which the actual process of learning words & their meanings relies on the computational ability of the brain
41
New cards
Cross-Modal Transfer of Perception
perception with 1 sense, such as vision, enables recognition of that object with another sense, such as touch
42
New cards
Gross Motor Skills
skills that involve the large muscle groups of the body (legs & arms)
43
New cards
Fine Motor Skills
skills that involve small movements, mostly of the hands & fingers, but also of the lips & tongue
44
New cards
Colostrum
thick, yellow substance, filled with antibodies & nutrients, that’s produced from a women’s breasts before milk is produced
* breastmilk associated with immunities
* lower risk of cardiovascular disease
* attachment with infant
* breastmilk associated with immunities
* lower risk of cardiovascular disease
* attachment with infant
45
New cards
Cortisol
a hormone produced as part of the stress response that prepares the body to deal with threat & also shuts down nonessential functions
* elevated cortisol levels = lowered immune response & lower cognitive function
* elevated cortisol levels = lowered immune response & lower cognitive function
46
New cards
Pruning
the deterioration & disappearance of synapses that are not uses
47
New cards
Myelination
the process of laying down a fatty sheath of myelin on the neurons
48
New cards
Broca’s Area
Active in the production of speech
\
located near the motor center that produces movement of tongue & lips
\
located near the motor center that produces movement of tongue & lips
49
New cards
Wernicke’s Area
Active in processing the meaning in speech
\
located near the auditory center
\
located near the auditory center
50
New cards
Cooing
* 2-4 months
* infants produce soft vowels like ooh & aah
* learns how to have a convo before they can speak
* infants produce soft vowels like ooh & aah
* learns how to have a convo before they can speak
51
New cards
Babbling
* 4-6 months
* infants combine consonants & vowels
* makes 1-syllable sounds like ba & da
* 6-10 months, becomes repetitive bababa to more daDAW
* infants combine consonants & vowels
* makes 1-syllable sounds like ba & da
* 6-10 months, becomes repetitive bababa to more daDAW
52
New cards
Joint Attention
A process in which an individual looks at the same object that someone else is looking at, but also looks at the person to make sure that they are both involved in the same thing
53
New cards
Holophrases
infants communicate the meaning of a whole phrase in one word
\
ex. “up” might mean “pick me up”
\
ex. “up” might mean “pick me up”
54
New cards
Mutual exclusivity constraint
an assumption made by language learners that there’s 1 name for an object
55
New cards
Fast Mapping
a process by which children apply constraints & their knowledge of grammar to learn new words very quickly, often after a single exposure
56
New cards
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs)
a range of impairments in a child resulting from consumption of alcohol during pregnancy
57
New cards
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)
a condition in the child resulting from heavy or binge consumption of alcohol during pregnancy; associated with abnormal facial features, & functional problems such as with learning, memory, & attention span
58
New cards
Emotional Display Rules
culturally determined norms for when, how, & to whom emotions should or should not be shown
59
New cards
Emotion Schemas
all the associations & interpretations that an individual connects to a certain emotion
60
New cards
Social Referencing
infants (9-12 months) learn about emotions using the reaction of others to determine how to react in ambiguous situations
61
New cards
Temperament
general emotional style an individual displays in responding to experiences in the world
62
New cards
Bowlby’s Stages of Attachment
believed attachment was biological & related to infants need for protection to survive
1. ***Preattachment (birth - 6wk)***: infant sensory preferences bring infants into close connection w/ parents
2. ***Attachment in the making (6wk - 6/8m)***: infants develop stranger anxiety, differentiating those they known from those they don’t
3. ***Clear-cut Attachment (6/8m - 18m/2y)***: infant develops separation anxiety when a person they’re attached to leaves
4. ***Goal-corrected Partnership (18m+)***: toddlers create reciprocal relationships with their parents
1. ***Preattachment (birth - 6wk)***: infant sensory preferences bring infants into close connection w/ parents
2. ***Attachment in the making (6wk - 6/8m)***: infants develop stranger anxiety, differentiating those they known from those they don’t
3. ***Clear-cut Attachment (6/8m - 18m/2y)***: infant develops separation anxiety when a person they’re attached to leaves
4. ***Goal-corrected Partnership (18m+)***: toddlers create reciprocal relationships with their parents
63
New cards
Ainsworth 4 Types of Attachment
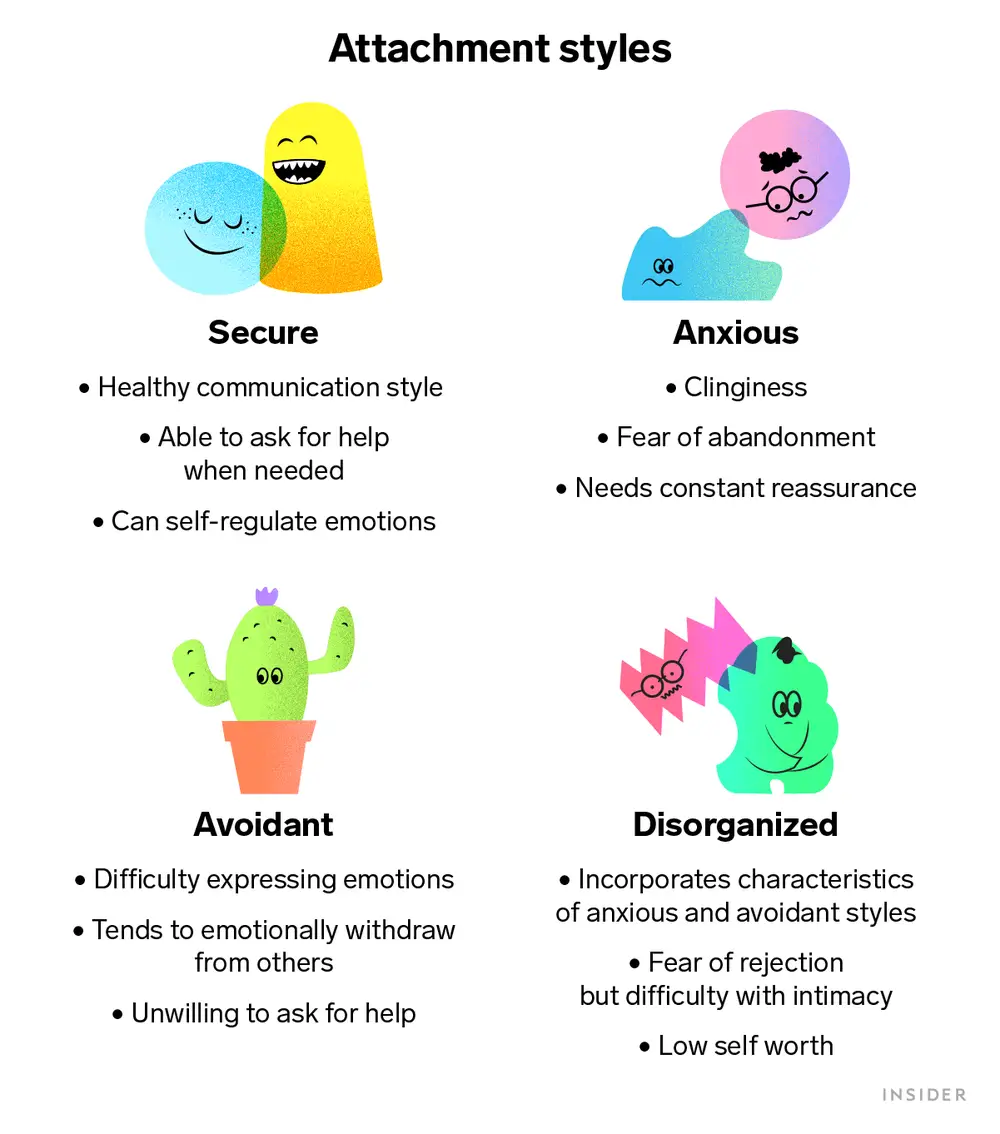
64
New cards
Stages of Prenatal Development
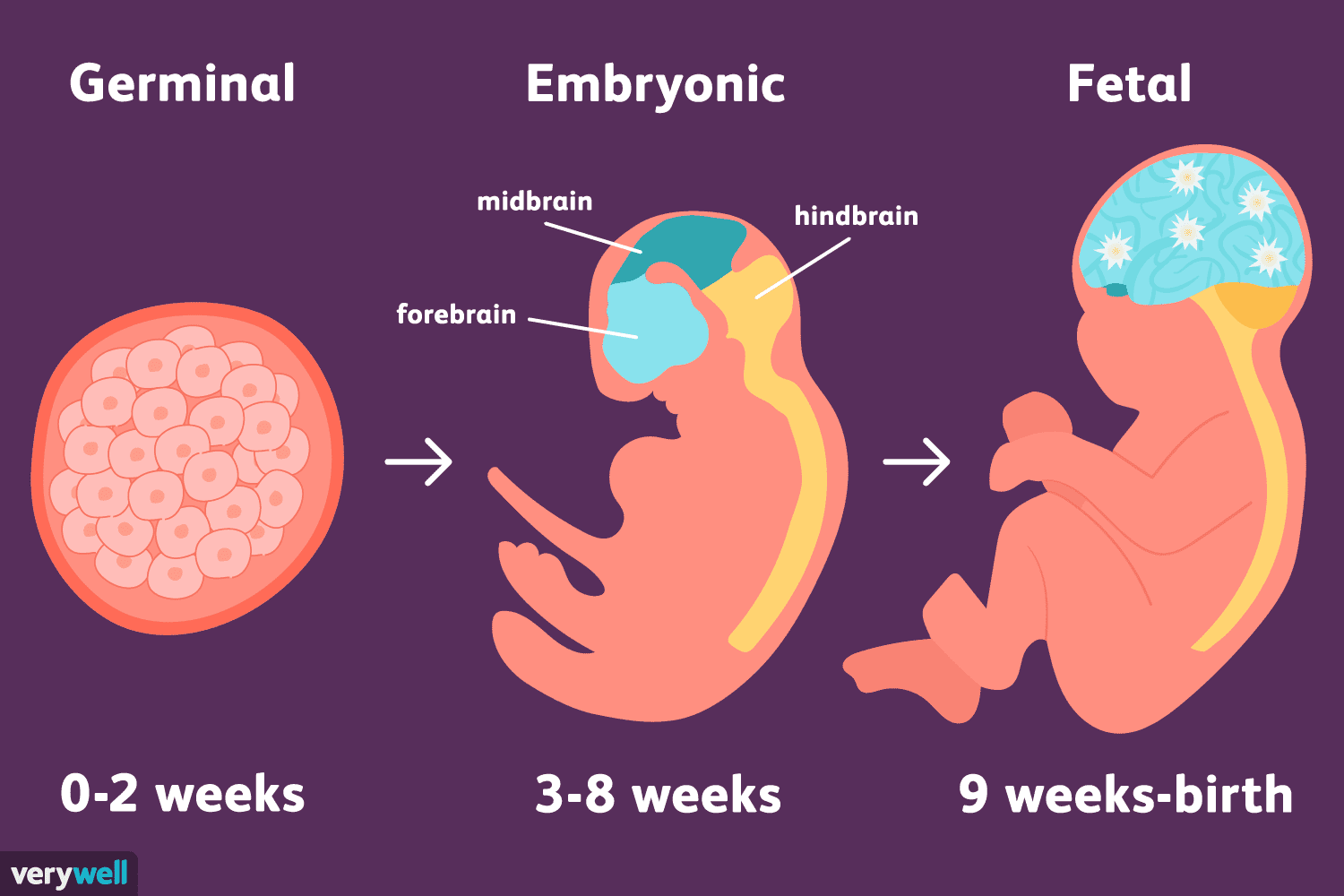
65
New cards
Teratogens
agents that can disrupt prenatal development & cause malformations or termination of the pregnancy
66
New cards
Stages of Labor
1. **Early Labor**: contractions are usually not painful, but cervix begins to thin out & dilate
2. **Active Labor**: contractions become longer, stronger, & more frequent & cervix dilates to 4 cm
3. **Transition**: contractions come in rapid succession & last up to 90 secs, which ends when cervix has dilated 10 cm
4. **Pushing/Delivery**: cervix is fully dilated & contractions push baby through birth canal, afterwards uterus contracts to expel placenta & close off blood vessels to prevent further bleeding
\
Stage 2: baby is born and the umbilical cord is clamped and cut
67
New cards
Apgar Scale
an assessment of a newborn’s overall condition at 1 min & 5 min after birth that is based on the newborn’s activity level, pulse, grimace, appearance, & respiration
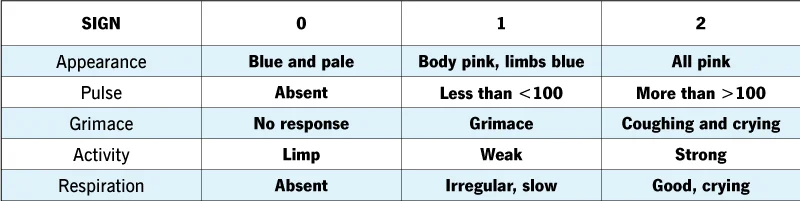
68
New cards
Depression with Peripartum Onset
some mother experience it, a major depression that occurs in the last moment of pregnancy or the first couple months after birth
69
New cards
Couvade
a sympathetic pregnancy in which a man experiences a variety of symptoms associated with pregnancy or childbirth while his partner is pregnant
* **Ritualistic**: fathers feign contractions & labor pains while mother is in labor; meant to distract evil spirits
* **Psychosomatic**: fathers experience physical symptoms associated with pregnancy
* **Ritualistic**: fathers feign contractions & labor pains while mother is in labor; meant to distract evil spirits
* **Psychosomatic**: fathers experience physical symptoms associated with pregnancy
70
New cards
How Poverty Affect Infants
poverty negatively affect the potential for cognitive development of young infants
\
ex. 6 months babies were less attentive to objects in the environment than those in higher-income fams
\
ex. 6 months babies were less attentive to objects in the environment than those in higher-income fams
71
New cards
Symbolic Thought
in this stage children can represent actions mentally rather than physically through play, language, or drawings
72
New cards
Intuitive Thought
Beginning forms of logic developing during the preoperational stage (2-7 y/o)
* **Transudative Reasoning**: making causal links where none exist
* **Conservation**: understanding that a basic quantity of something remains the same regardless of changes in appearance
* **Centration:** focus on 1 aspect of a situation
* **Decenter**: thinking more about 1 aspect of a situation at a time
* **Transudative Reasoning**: making causal links where none exist
* **Conservation**: understanding that a basic quantity of something remains the same regardless of changes in appearance
* **Centration:** focus on 1 aspect of a situation
* **Decenter**: thinking more about 1 aspect of a situation at a time
73
New cards
Egocentrism
young children have difficulty looking at the perspective of others
74
New cards
Animism
children give human characteristics to inanimate or natural things
75
New cards
Theory of Mind
ability to understand self & others as agents who act on the basis of their mental states
* diverse desires & beliefs
* knowledge access
* false belief
* hidden emotions
* sarcasm
* diverse desires & beliefs
* knowledge access
* false belief
* hidden emotions
* sarcasm
76
New cards
3 Levels of Play
1. Practice Play: performing certain behavior receptively for the mere pleasure of it (ex. jumping over a puddle)
2. Symbolic/sociodramatic Play: using symbolic representations & imagination (ex. pretending to drunk tea)
3. Games with Rules: making up rules or playing a game with rules (Ex. baseball)
77
New cards
Guided Play
combination of free play and learning where an environment that has been prepared by adults, in which they scaffold their learning
78
New cards
Telegraphic Speech
young children tend to use the simplest combinations of words necessary to get their point across
* ex. “doggy run”
later add morphemes → “the doggy ran away”
* ex. “doggy run”
later add morphemes → “the doggy ran away”
79
New cards
Reflexes
involuntary motor responses that are controlled by lower brain centers
* sucking
* crawling
* babinski (foot extension)
* palmar grasp
* sucking
* crawling
* babinski (foot extension)
* palmar grasp
80
New cards
Lateralization
localization of different functions in one hemisphere of the brain or the other
\
ex. language center appear in most ppl in left hemisphere
\
ex. language center appear in most ppl in left hemisphere
81
New cards
2 Hemispheres of Human Brain
* Ri**ght side**: receives sensory input & controls motor active on left side of body
* **Left side**: does the same for right side of body
* **Left side**: does the same for right side of body
82
New cards
Lobes of the Brain
* Brain stem: controls basic survival functions (breathing, heart rate, sleep)
* Cerebellum: receives info from sensory systems to coordinate balance & voluntary movement
* Cerebrum: higher functions of thought & action
* Occipital lobe: vision
* Temporal lobe: auditory info & enables us to understand language
* Parietal lobe: sensory input: taste, temperature, touch
* Frontal lobe: complex thoughts, planning, movement, language, & impulse control
* Cerebellum: receives info from sensory systems to coordinate balance & voluntary movement
* Cerebrum: higher functions of thought & action
* Occipital lobe: vision
* Temporal lobe: auditory info & enables us to understand language
* Parietal lobe: sensory input: taste, temperature, touch
* Frontal lobe: complex thoughts, planning, movement, language, & impulse control
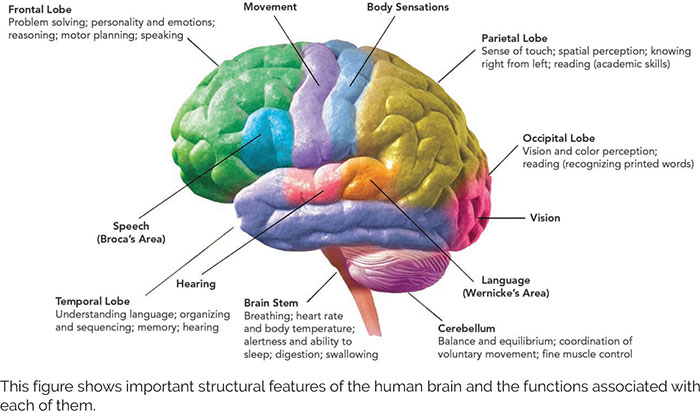
83
New cards
Limbic System
part of the brain involved in our behavioral and emotional responses
* amygdala: emotions & moods
* hippocampus: processes & stores memory
* amygdala: emotions & moods
* hippocampus: processes & stores memory
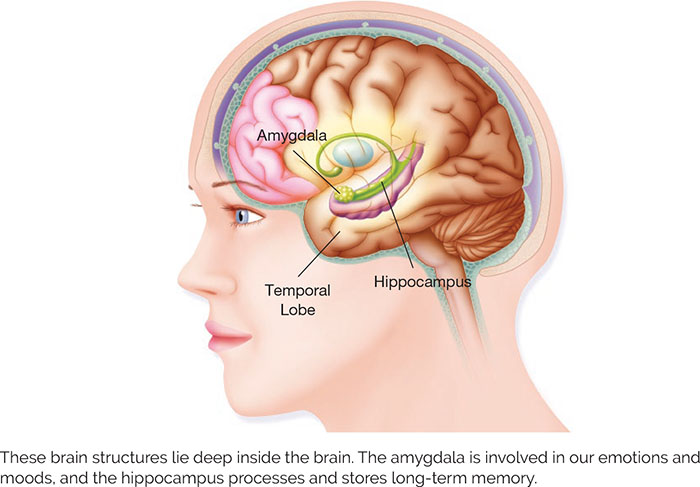
84
New cards
Synaptogenesis
development of new synapses
\
babies are born with most of the neurons that will last through their lives, but new neurons will still be created in specific areas throughout their life time
\
babies are born with most of the neurons that will last through their lives, but new neurons will still be created in specific areas throughout their life time
85
New cards
Plasticity
ability of the infant brain to change in form & function
86
New cards
Cerebral Palsy
umbrella term that describes a group of brain-based disorders that affect a person’s ability to move & maintain balance & posture
\
caused by abnormal development of brain or damage, either prenatally, during birth, or first years of life
\
caused by abnormal development of brain or damage, either prenatally, during birth, or first years of life
87
New cards
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
A disorder characterized by pervasive impairment in social communication and interaction and by restricted or repetitive behaviors, interests, or activities. Severity is classified by how much support the individual needs to function effectively.
88
New cards
Circumcision
the removal of the foreskin from the penis, common surgical procedure preformed on male infants
\
helps w/ fewer urinary tract infections
\
helps w/ fewer urinary tract infections
89
New cards
Development of the 5 Sense
* visual acuity: ability to see things in sharp detail
* infants see 20/800, clearly see at 20ft compared to adults normally see at 500ft
* hearing: by 6m can recognize their own name, but first assessed during first month of life
* smell: born with functioning sense of smell & show preferences
* taste: infants prefer sweet & react negatively to salty, sour, & bitter tastes
* touch: soothing
* infants see 20/800, clearly see at 20ft compared to adults normally see at 500ft
* hearing: by 6m can recognize their own name, but first assessed during first month of life
* smell: born with functioning sense of smell & show preferences
* taste: infants prefer sweet & react negatively to salty, sour, & bitter tastes
* touch: soothing
90
New cards
Types of Family Structure
* Nuclear Family: a married couple & their biological and/or adopted children
* Extended Family: fam structure that includes other relatives
* Extended Family: fam structure that includes other relatives
91
New cards
Divorce
* children may exhibit behavioral problems as result of parent’s distressed feelings & disruptions in routine
* infants more likely to have an insecure attachment (lack of trust)
* infants more likely to have an insecure attachment (lack of trust)
92
New cards
Adoptive Families
* Open Adoptions: children & their biological & adoptive fam have access to each other
* in US, 120,000 kids adopted each year
* in US, 120,000 kids adopted each year
93
New cards
Child Maltreatment
* ***Child Abuse:*** deliberate & intentional words & actions that harm or potentially harm a child, whether abuse is physical, sexual, or psychological
* ***Neglect:*** failure to provide for the basic physical, emotional, medical, or educational needs for a child
* ***Child Protective Services (CPS):*** investigate & intervene in instances where a child may be experiencing harm
* ***Neglect:*** failure to provide for the basic physical, emotional, medical, or educational needs for a child
* ***Child Protective Services (CPS):*** investigate & intervene in instances where a child may be experiencing harm
94
New cards
Sleep
* Infants: spend 80% of day sleeping
* Early Childhood (3-5 y): need 11-13 hrs
* Middle Childhood(7-12 y): 9-10 hrs
* Nocturnal Enuresis: involuntary emptying of bladder during sleep
* Early Childhood (3-5 y): need 11-13 hrs
* Middle Childhood(7-12 y): 9-10 hrs
* Nocturnal Enuresis: involuntary emptying of bladder during sleep
95
New cards
Body Image & Growth
***Body Image***: a person’s subjective perceptions & feelings about their physical characteristics
* kids become more body aware in early childhood & take in societal stereotypes of their culture
***Body Growth:*** rapid growth where 2-5 y/o kids grow 2.5 inches every year & gain 4-5 pounds
* kids become more body aware in early childhood & take in societal stereotypes of their culture
***Body Growth:*** rapid growth where 2-5 y/o kids grow 2.5 inches every year & gain 4-5 pounds
96
New cards
Emotional Intelligence
ability to understand & control one’s emotions, to understand the emotions of others
\
children who can regulate their emotions are more socially & academically competent & linked to lower levels of problematic behaviors
\
children who can regulate their emotions are more socially & academically competent & linked to lower levels of problematic behaviors
97
New cards
Self-Concept
young children develop an __*autobiographical memory*__ in which they have a coherent set of memories about their own lives. these memories contribute to development of __*self-concept*__ or how children think or describe themselves
98
New cards
Self-Esteem
feel very good about the characteristics they associate with themselves
99
New cards
Emotional Regulation
Ability to adapt one’s emotional responses to a particular situation
* ***Self-Control***: ability to choose goals, initiate appropriate responses, etc.
* ***Effortful Control***: consciously control their behaviors (ex. marshmallow test)
* ***Delay of Gratification:*** ability to wait until later to get something desireable
* ***Self-Control***: ability to choose goals, initiate appropriate responses, etc.
* ***Effortful Control***: consciously control their behaviors (ex. marshmallow test)
* ***Delay of Gratification:*** ability to wait until later to get something desireable
100
New cards
Social Roles
Set of cultural guidelines about how one should behavior
* start in infancy, kids learn abt behaviors that are assigned to males & females & associate with these groups
* start in infancy, kids learn abt behaviors that are assigned to males & females & associate with these groups