AP Macro Unit 4
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
barter system
a system of exchange in which goods or services are traded directly for other goods or services without the use of money.
fiat money
currency who's value derives entirely from its official status as a means of exchange
commodity money
objects that have value in themselves and that are also used as money
3 functions of money
1. medium of exchange (easily buy goods)
2. unit of account (measures the value of goods)
3. store of value (money allows you to store purchasing power for the future)
Types of Money
1. M1 (high liquidity)- Coins/cash/checkable deposits The Money Supply
2.M2 (Medium liquidity)- M1 plus savings deposits/time deposits/ mutual funds below $100 K
M1 money supply
the most narrowly defined money supply, equal to currency in the hands of the public, time deposits & checkable deposits (demand deposits)
checkable deposits (demand deposits)
any deposit in a commercial bank or thrift institution against which a check may be written (a checking account)
M2 Money Supply
Includes all of M1 money supply plus most savings accounts, money market accounts, and certificates of deposit.
Monetary Base
the sum of currency in circulation and bank reserves
Liquidity
the ease with which an asset can be converted into cash
asset
Anything of monetary value that is owned by a firm or individual
liability
a requirement to pay money in the future
Loans
amounts of money borrowed which will accumulate interest
bonds
type of loan, when originally buying a bond the purchaser is loaning money to the issuer of the bond
coupon (of a bond)
interest rate of a bond
Stock
asset that signifies ownership in a corporation and represents claim on part of the corporations assets and earnings
financial intermediaries
financial institutions through which savers can indirectly provide funds to borrowers. Example: Banks hold your savings, then loan it out to others
bank reserves
the money deposits held in banks or at the FED
T-account
bank balence sheet
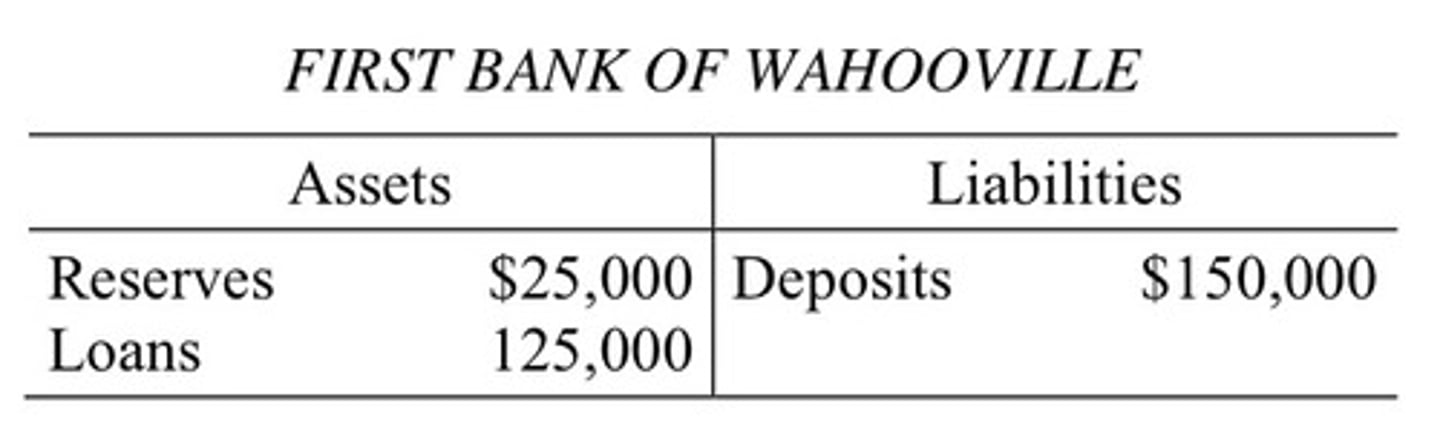
reserve ratio
the fraction of deposits that banks hold as reserves
reserve requirement
the percentage of deposits that banking institutions must legally hold in reserve
excess reserves
a bank's reserves over and above its required reserves
Total Reserves
required reserves + excess reserves
monetary policy
Government policy that attempts to manage the economy by controlling the money supply and thus interest rates.
Tools of Monetary Policy
reserve requirement, discount rate, open market operations (bonds)
federal funds rate
the interest rate at which banks make overnight loans to one another
discount rate
Interest rate the Federal Reserve charges for loans to commercial banks
open market operations
the buying and selling of government securities (bonds) to alter the supply of money. Buying bonds = bigger bucks, Selling bonds = smaller bucks
medium of exchange
Any item generally accepted to pay for a good or service; money; a convenient means of exchanging goods and services without engaging in barter.
unit of account
A standard unit in which prices can be stated and the value of goods and services can be compared
store of value
an asset that serves as a means of holding wealth
Money Supply Curve
shows the relationship between the quantity of money supplied and the interest rate. This curve is vertical and can only shift because of monetary policy
Money Demand Curve
a graphical representation of the negative relationship between the quantity of money demanded and the interest rate; the money demand curve slopes down because, other things equal, a higher interest rate increases the opportunity cost of holding money
Opportunity Cost of holding on to your money
Potential interest earned
demand for money
how much money people would like to hold in their "pockets" - access to liquid assets
expansionary monetary policy
Federal Reserve system actions to increase the money supply, lower interest rates, and expand real GDP
contractionary monetary policy
the federal reserve's decreasing the money supply to increase interest rates to reduce inflation and real GDP
loanable funds market
The market in which the demand for private investment (loans) and the supply of household savings intersect to determine the equilibrium real interest rate.
demand for loanable funds
inverse relationship between real interest rate and quantity of loans demanded. How much money firms, individuals & governments what to borrow
supply for loanable funds
Direct relationship between real interest rate and loanable funds supplied. People will invest more at higher interest rates. The amount of savings made available to be loaned out
real interest rate formula
nominal interest rate - inflation rate
crowding out
a decrease in investment that results from an increase government borrowing, causing an increase in interest rates
National Savings (Closed Economy)
Total amount of private and public savings. Closed economy means there is no trade occurring.
National Savings (Open Economy)
Total amount of private and public savings, plus net capital inflows (money coming in to country - money going out of the country). Open economy means trade is occurring.