Energy Conservation
Key Ideas
- Work is related to kinetic energy through the work–energy theorem.
- To use conservation of energy, add potential + kinetic energy at two positions in an object’s motion. This sum must be the same everywhere.
- A potential energy function can be derived for any conservative force.
Kinetic Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem
Energy: The ability to do work.

Work equals the product of the distance an object travels and the component of the force acting on that object-directed parallel to the object’s direction of motion.
One newton. meter is called a joule, abbreviated as 1 J.
Work and energy are scalar.
Work can be negative if the force is applied in the direction opposite displacement.
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion.
The kinetic energy of an object equals one-half the object’s mass times its speed squared.
Potential Energy
Potential energy: Energy of position
Gravitational PE is described by the following equation:
U = mgh
- m - the mass of an object
- g - gravitational field of 10 N/kg on Earth
- h - the height of an object above a certain point, for vertical height above the zero of potential.
Conservation of Energy: Problem-Solving Approach
Write out all the terms for the initial energy of the system
Set the sum of those terms equal to the sum of all the terms for the final energy of the system..

W in this equation stands for work done on an object.
Include this W term only when there is friction (or some other external force) involved.
Springs
The force exerted by a spring is directly proportional to the amount that the spring is compressed.

k is a constant (called the spring constant)
x is the distance that the spring has been compressed or extended from its equilibrium state.
A negative sign explains that the force of spring always acts opposite to displacement
- an extended spring pulls back toward the equilibrium position
- a compressed spring pushes toward the equilibrium position
Power
- Power = work/time
- Power is measured in joules/second, also known as watts.
Potential Energy vs. Displacement Graphs
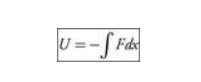
Chris on a Skateboard
Once the potential energy of an object is found as a function of position, making a U vs. x graph explains the long-term motion of the object.
The potential energy of a spring looks like a parabola.
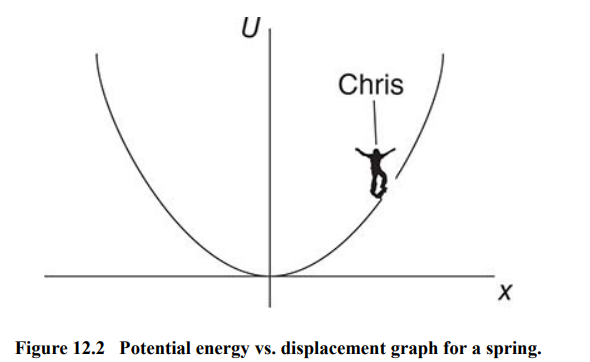
Imagine that Chris is riding a skateboard on a ramp shaped like a graph.
If he starts from some height above the bottom, Chris will oscillate back and forth, going fastest in the middle, and turning around when he runs out of energy at the right or left end
Although this is not precisely how a mass on a spring moves, the long-term properties of Chris’s motion and the motion of the mass on a spring is the same.
The mass oscillates back and forth, with its fastest speed in the middle, just like Chris does.
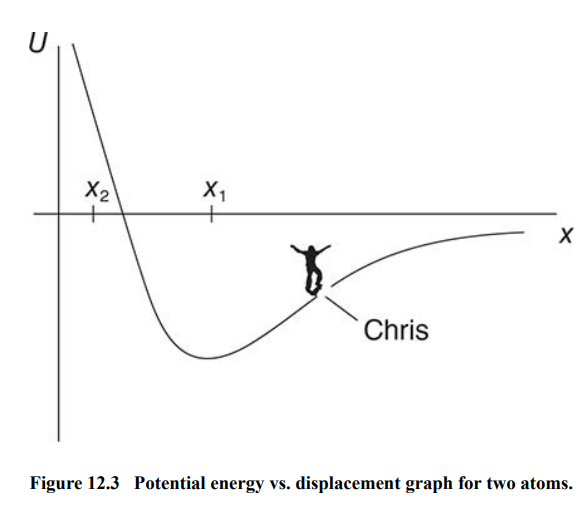
Strategy to solve:
- If Chris on his skateboard released himself from rest near position x1 , he’d just oscillate back and forth, much like in the mass on a spring problem.
- If he were to let go near the position labeled x2 , he’d have enough energy to keep going to the right as far as he wants.
- This is what happens to the atoms in molecules, too.
- If a second atom is placed pretty close to a distance x1 from the first atom, it will just oscillate back and forth about that position.
- However, if the second atom is placed very close to the first atom, it will gain enough energy to escape to a faraway place