electricity
y7 recap
a switch needs to be closed to activate a circuit
electrons (-)
protons (+)
neutrons (both)
voltage is the amount of energy
electricity is measured in volts
electrons, protons and neutrons make up an atom, and they start to flow
electricity is measured with an ammeter → flows of electrons
conductors allow electrons to flow, but insulators dont
current is measured in amps
basic electricity units
current (I) → rate of flow of charge (electrons)
unit → amps (A)
voltage (V) → the “push” that moves the electrons around the circuit, and is also known as the potential difference
unit → volts (V)
resistance
wires which have a higher resistance make electrons harder to pass through the atoms in the wire
resistance = voltage / current
R = V / I
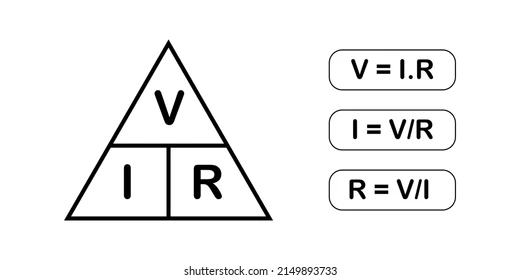
unit of resistance = ohm = Ω
fuses
safety feature in a circuit
a thin short piece of wire with high resistance
when heated up, melts and breaks the circuit if there is too much current
resistance calculation examples
VOLTAGE | CURRENT | RESISTANCE |
|---|---|---|
10 | 5 | 2 |
100 | 20 | 5 |
VOLTAGE | RESISTANCE | CURRENT |
|---|---|---|
20 | 2 | 10 |
5 | 0.5 | 10 |
CURRENT | RESISTANCE | VOLTAGE |
|---|---|---|
2 | 5 | 10 |
10 | 3 | 30 |
circuit types
series circuit → where one component follows directly after another with no junctions and only has one loop
parallel circuit → different components are connected on different branches of the wire and has more than one loop
the resistance in series circuits is larger than in a parallel circuit, meaning that the bulbs are dimmer
flow of electrons
the current in a circuit depends on the voltage and the resistance
the current will be bigger if the resistance is smaller
inside a metal wire electrons collide with atoms and transfer energy to them
conductors are materials that contain lots of charges that are free to move
insulators contain fewer charges that can move
resistance in conductors is more than in insulators
magnetic and non-magnetic material
a non magnetic material is not attracted by a magnet
a magnetic material is attracted by a magnet
a magnet is either repelled or attracted by another magnet
iron (Fe), nickel (Ni), cobalt (Co) and steel are all magnetic
a domain is a collection of magnetic materials of individual electrons
in a magnetic material, the domains point in different directions until they are near a magnet. then they move and point in the direction of the magnet
in a magnet, all the domains always point in the same direction
non-magnetic materials dont have domains
making a magnet
to make a nail into a magnet, you can stroke it gently with a magnet.
when the nail is magnetised it is called an induced magnet (temporary magnet)
we can test the strength of the magnet by observing how many paperclips it can lift
with more strokes, the strength of the magnet will increase and it will be able to pick up more paperclips
electromagnets
an electromagnet is a type of magnet in within the magnetic field is produced by an electric current
the magnetic field around a wire which carries a current is in the form of circles
the direction of the field depends on the direction of the current
solenoids
to make a magnetic field stronger, rather than using just a single wire, a device called a Solenoid is used
a solenoid is a coil of wire with a current flowing through it
to make a magnetic field even stronger, a core made of magnetic material is placed inside the coil
by wrapping the wire in a coil, the magnetic fields add up to form a magnetic field like that of a bar magnet
it’s possible to increase the strength of a solenoid by increasing the current through the solenoid, introducing an iron core, or increasing the number of twists/coils of the wire on the solenoid
uses of electromagnets
applications of electromagnets
lifting scrap cars
the relay switch
the motor
the relay switch is a special type of switch turned on and off by an electromagnet, and is used in items such as doorbells and starter motors in cars
when a current flows through a coil, an electromagnetic field is set up
the field attract an iron armature, whose other end pushes the contacts together, completing the circuit
when the current is switched off, the contacts open again, switching the circuit off