quizzes- contrast media
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Patient Information and Consent
The patient must be provided with sufficient
information to allow them to make an informed choice
of whether or not to accept the risks of proposed
iodinated contrast administration.
Patients should be thoroughly questioned prior to
having contrast administered and it must be
documented
Radiographic CM - two branches
1- positive, iodinated barium
2- negative, water, co2, air
negative compounds
appear less dense than the adjacent tissue
Properties of air or co2

risk of air or co2

water- neutral

risk for h2o

positive cm-
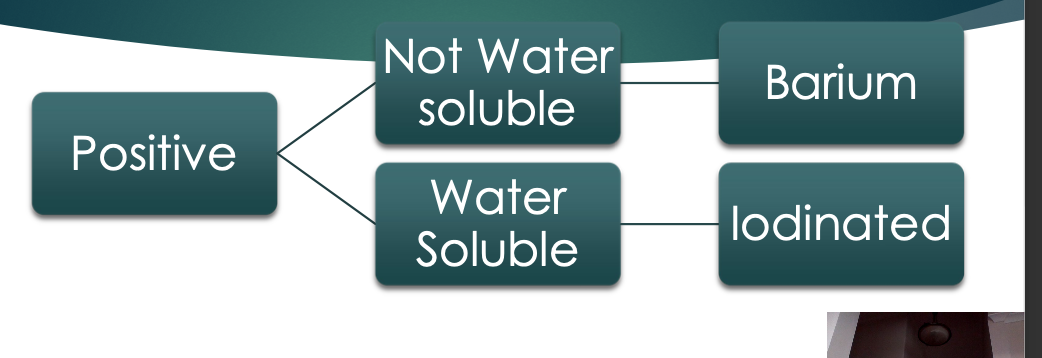
Positive Contrast Compounds appear
denser than the
surrounding tissue
Barium Sulphate ( Ba SO4)

Barium Sulphate ( Ba SO4) PROS and CONS


small bowel- barium
To demonstrate the small bowel
including the D1, D2, D3,D4 and jejunum
the barium is used thinner 1-6 times from
the thin mix. Done to investigate or
diagnose malrotation, intussusception,
Crohns, Hirschsprung's
Large bowel Barium Enema –Single or double contrast
This examination has been largely replaced by CT
colonography and colonoscopy.
It is done to investigate or diagnose tumours,
inflammatory disease, diverticular disease, polyps.
procedure
• 1-2 litres of dilute barium (1-3 times) is introduced via a rectal
catheter. Into the large bowel. This usually has a balloon ( similar to a
urinary catheter) to prevent the catheter coming out of the rectum
• The images are performed in the lateral position initially and then AP ,
decubitus AP , and obliques with the object tot “straighten out” even
section of the large bowel from the rectum to the ileo-caecal valve.
• Air is often introduced to distend the gut
• Post evacuation imaging may be included. to help demonstrate small
mural lesions.
iodine
Most of the world's industrial
iodine is obtained from brines
(water strongly saturated in salt)
associated with wells in & USA
Japan and from caliche ore
mined in Chile.
Discovered in the early 1820’s
Used in imaging since the 1920’s
It is the same mineral that is in
iodised salt
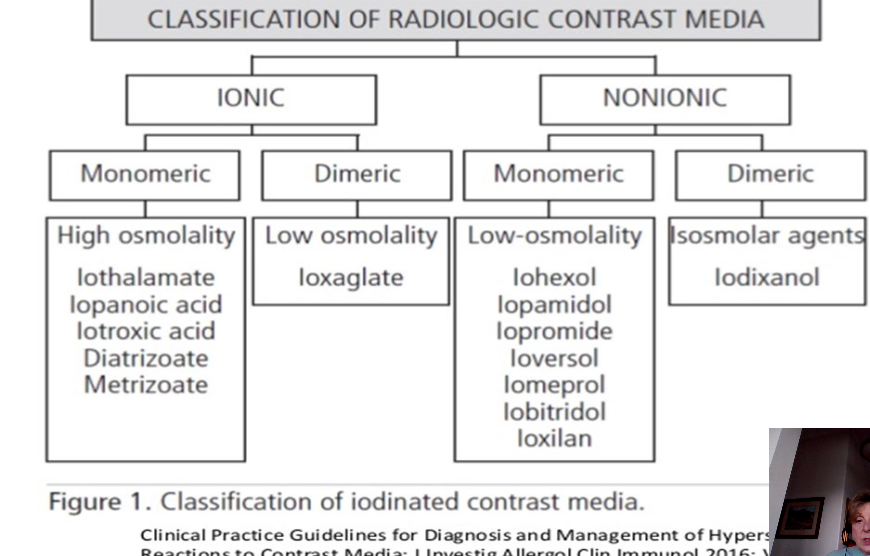
non ionic vs ionic

monomer vs dimer

osmolality
Your body has an osmolarity or 290
Your whole system is regulated to stay this way
If you have too much water you need to also
have salt to allow balance
If you are given a high osmolar compound like
CM you body needs water to balance it.
This fluid comes from your soft tissues and the
kidneys and heart are then required to move
this fluid to return you body to its normal
electrolyte balance
This is fine balance of sodium potassium, water,
vasopressin hormones

low osmolar compounds
Gastrografin
- Ioscan
- Urografin
used for sbo oral
medium osmolar compounds
omnipaque
optiray
ultravist
isovie
Can be used for most radiographic imaging including vascular
use, intrathecal, CT scanning, gut imaging
Known to produce moderate osmolar effects such as heat, pain,
taste, sensation of peeing, vagueness, headache, watery eyes,
sneezing and hives.
Higher concentrations have higher osmolarity ( higher iodine
content). But lower concentration have lower osmolarity .
Should not be given to patients who have history of
-allergic reactions to Iodine
-Renal disease without consideration
- Elevated thyroid function hormones
iso osmolar compounds
visipaque
Should not be given to patients who have history of -
allergic reactions to Iodine
-Renal disease without consideration
- Elevated thyroid function hormones
ionic status
If there are short chains of O N H then the
compound is not that stable-
It can disassociate and the free cations and
anions are attracted to other free +ions and –
ions in the body and make a new compound .
This newly compounds may be even more
toxic and produce unknown compounds and
side effects
SO ONLY USE THEM WHEN THIS HAS BEEN
CONSIDERE
A Hyper osmolar compound will
adsorb fluid from the surrounding
structures
This fluid shift in the body causes cardiac
arrythmia, changes in blood pressure, which
leads to fainting.
The higher the concentration of iodine in the
compound, the higher the osmolarity ,
A high osmolar product contributes to the
taste, heat sensation , vomiting and the
peeing sensation, vagueness, lacrymisation.,
muscle twitching
Osmolarity ( Osmolality)100
SO ONLY USE A HIGH OSMOLAR
PRODUCT IF THERE IS NO
ALTERNATIVE
When to use High osmolar CM
Diluted as a bowel labeller( 3-5%)
As a diagnostic and /or
therapeutic agent for Small bowel
obstructions ( e.g. faecal loading,
shocked gut, adhesive bowel
obstruction
100mls of 76% maximum dosage
100mls of Gastrografin $25, 100mls
of Omnipaque,
(Ultravist, Optiray or similar $12)
Which concentration – 180, 240, 300, 350
375
You need to be able to see the CM on the image
A higher number of gram per mls makes it denser
But it is also higher in osmolarity
it is more vicious
A 240 is preferred for children and neonates while 350 is
normal for adults
ICM can be diluted
Storage
ICM should be stored in its original packing on
a shelf away from radiation.
It MUST be used before its expiry date
It should be checked for crystals or clarity
before injecting
IA CM warmer is NOT a store cupboard and the
stock should be rotated and not kept warm for
more than 28 days
The temperature should be monitored. CM
should not be kept above its recommended
temperature.
Risks for any iodine and gadolinium
Previous allergic reaction
2. Allergic history- asthma, hay fever, etc
3. Poor renal function ( dialysis, renal trauma, stones, infections)
4. Vasculopathy
5. Diabetes type 1 & 2
6. Drug interaction
7. Pregnancy
8. Medical History
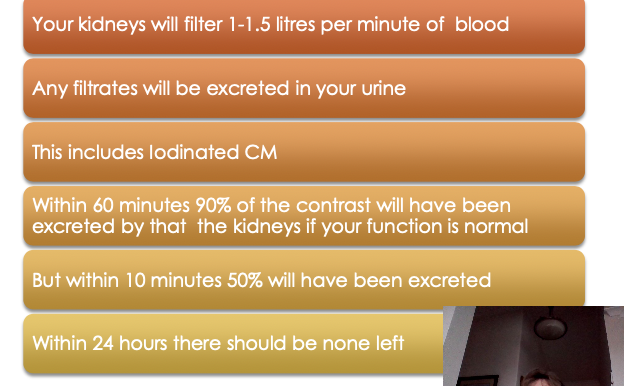
Renal Function
Iodinated CM is excreted
though the urine
It is filtered by the nephrons
The glomerulus and via the
Bowmans capsule and
collecting system to the
urinary bladd
Renal
Function
and
checking
It is measured as eGFR- estimated glomerular
function from a POC blood check
Renal function over 60 is normal
>45 is considered low
And <15 is renal failure
It is affected by trauma, vasculopathy (
history of stroke, HT, vascular disease, renal
cysts, single kidney, infections)
Old age may not be a good determinate of
renal function
Renal
impairment tests
(estimated Glomerular
Function
rate
the eGFR takes into account your age, your
sex and your ethnic background. It is what we
call a normalized test. It measures how well
your kidneys are working.
Serum creatinine level
not normally raised until GFR ↓ by 50%
Renal
Excretion
Contraindications /risk factor- Thyroid
• Patients who have an over active
thyroid gland should not be given
ICM. It can produce an array of side
effects that can be life threatening. (
MNG, Graves disease)
• An Under active thyroid is not a
concern
• ICM may make thyroid function testing
less accurate for up to 6 months.
The allergic response
Allergic reactions, are linked to an antibody produced by the
body called immunoglobulin E (IgE).
Each IgE antibody can be very specific..
When a susceptible person is exposed to an allergen, the body
starts producing a large quantity of similar IgE antibodies. The
next exposure to the same allergen may result in an allergic
reaction.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction will vary depending on the type
and amount of allergen encountered and the manner in which
the body's immune system reacts to that allergen.
Recognising an allergic reaction
Lie the person flat> administer
adrenaline, oxygen> call help line
Sneezing, Tingling of lips, Swelling of face,
lips, eyes , Hives, Abdominal pian vomiting,
Pale, floppy , difficulty in breathing or
talking, tightness of throat , collapse
Treatment of Allergic reactions
Oxygen- this will improve blood
oxygenation
Adrenaline ( epinephrine- to support
the heart and respiratory system-
given IM, IV)
Antihistamine-( Phenergan IV- takes 10-15 minutes to work
Steroid – also slow acting – 15-30 minutes to reduce
swelling
Bronchodilators- may help wheeze later
Contraindications /risk factor-
Other medications
Metformin- a support drug to stabilise diabetic patients
and their blood sugars. If patients have poor renal
function and are on Metformin , then ICM should not
be given ( this applies to Gadolinium also)
• Beta Blockers- as these slow the heart rate, they may
affect the use of adrenaline during a cardiac crisis
• Some chemo therapy drugs- these drugs may interact
with CM
Concerns that may be raised-
these are not contraindications
1. Breast feeding
• There is no evidence that any iodine crosses into the breast milk,
but if concerns are raised then 24 hours is considered a sufficient
time to excrete the majority of the CM
2. Multiple injection of ICM
• There is some evidence that multiple injections of ICM may
produce a reduction in RF. But this may be reduced with
sufficient hydration and renal function surveillance.
3. Pregnancy
• ICM is considered safe for the a pregnant patient.
CVC line patency –
PICCS, PORTS
They can get blocked with a
substance called fibrin which is like a
clot.
• These prevent the line being patent
or sometimes false blockage
• Or the line can get damaged and
break.
• A small amount of IV contrast is
injected into the line an images
taken in fluoroscopy at 15 frames
/sec to see blood flow