Chapter 2: Cell Chemistry and Bioenergetics
Cell Chemistry and Bioenergetics
- Until the 19th century, people knew “Vital Force” to be responsible for all the distinctive properties.
- Organic Chemistry: It is the study of hydrocarbons and their derivatives.
Why chemistry of life is indeed special?
- Firstly, it is based on carbon compounds.
- Secondly, cells are 70% water, and life depends largely on chemical reactions.
- Thirdly, cell chemistry is enormously complex.
Chemical components of cell:
It is made up of mainly four elements including carbon(C), hydrogen(H), nitrogen(N), and oxygen(O).
A cell is formed from carbon compounds.
- Carbon has a property of catenation which helps in the self-linking of atoms of an element to form chains and rings.
- Carbon has a covalency of four.
- It confers stability to form large molecules.
A cell also contains small organic molecules:
- Sugars
- Fatty Acids
- Nucleotides
- Amino Acids
Types of bonds:
- Covalent Bond: A chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms.
- Non-Covalent Bond: The bond in which no sharing of electron pairs takes place is called a non-covalent bond.
- Hydrogen Bond: A hydrogen bond is the interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine from another molecule.
Non-Covalent attractions:
- Electrostatic attractions (ionic bonds)
- Hydrogen Bonds
- Vander Waal attractions
- Hydrophobic force
Acids: Substances that release protons when they dissolve in water thus forming H3O+ are termed acids.
- Strong Acids: Those who lose their protons quickly. Eg: Hydrochloric acid (HCL).
- Weak Acids: Those who hold on to their proton more tightly when dissolved in water. Eg: Acetic Acid (C2H5COOH)
Bases: The opposite of acid is a base. Substances that accept a proton from a water molecule are called bases.
- Strong Base: Those who readily dissociate in water to form respective ions. Eg: Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
- Weak Base: Those who have a weak tendency to reversibly accept a proton from water. Eg: Ammonia (NH3)
pH Scale: The concentration of H3O+ is expressed using a logarithmic scale called as pH scale.
- Pure water has a pH of 7.0.
- An acidic solution has a pH of <7.
- The basic solution has a pH of >7.
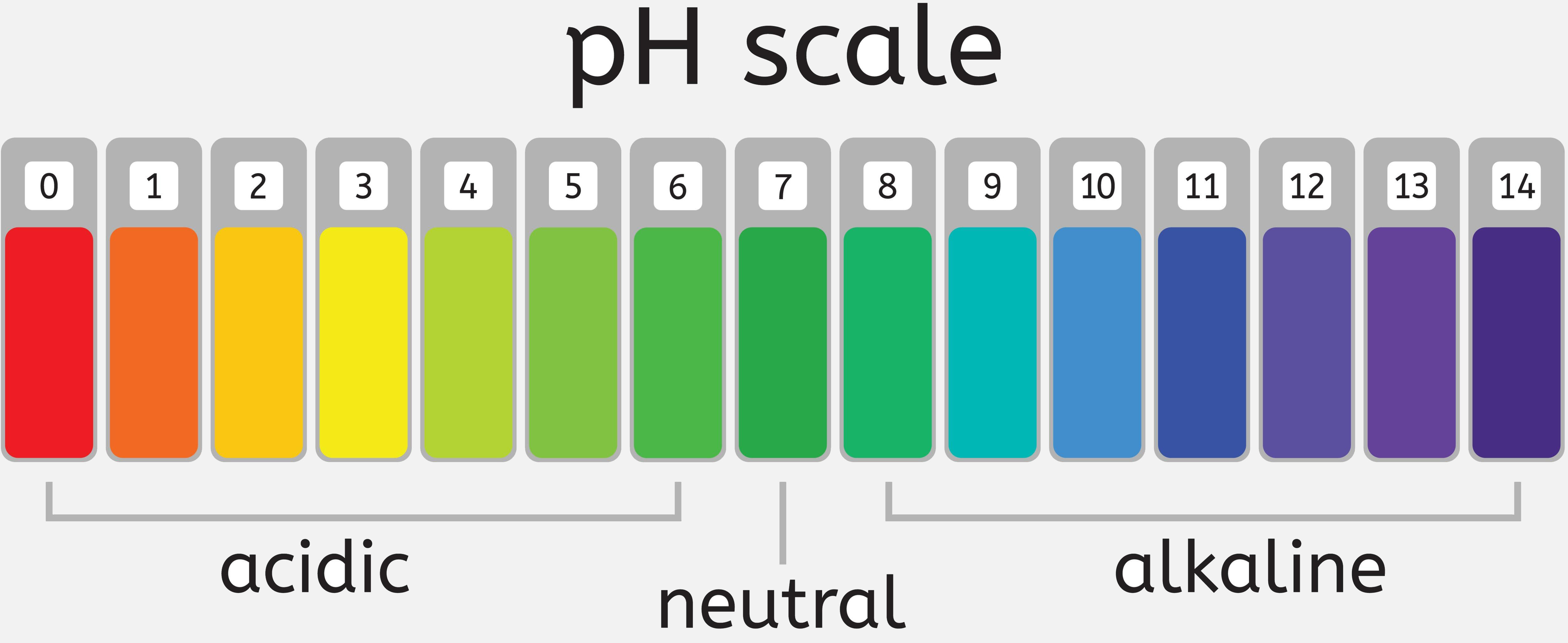
Buffers: It is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic component.
Types of molecules:
- Macromolecule: It is composed of a much larger number of atoms than ordinary molecules.
- Micromolecule: It is a small molecule that often joins together to form a larger type of molecule. It is often referred to as monomers.
Cell Metabolism
- It is the set of chemical reactions that occur to maintain life.
- Metabolism = Catabolism + Anabolism
- Catabolic Reactions: These reactions break down molecules into smaller units.
- Anabolic Reactions: These reactions use the small molecules and the energy harnessed by catabolism to drive the synthesis of molecules.
- Thermodynamics: (branch of science which deals with the energy changes taking place in all physical and chemical processes)
- Thermo (heat) + Dynamics (flow/motion)
Key terms:
- Work: The product of force and displacement is called work
- w = (- P ΔV )
- w= work done; P= pressure; ΔV = change in volume
- System: It is any region of space that is under thermodynamic investigation.
- Open system: This type of system can exchange energy as well as matter with the surrounding.
- Closed system: This type of system can exchange energy, but not matter with the surroundings.
- Surrounding: It comprises the rest of the universe apart from the system.
- Universe: It comprises the system and its surroundings together.
- Boundary: A wall or layer separating the surrounding.
- A boundary can be rigid or non-rigid.
- A boundary can be conducting or non-conducting.
- A boundary can be real or imaginary.
- Internal Energy (E): It is defined as the sum of different energies associated with its atoms and molecules.
Laws of thermodynamics:
The first law of thermodynamics:
- This law is based on the law of conservation of energy.
- Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but can be transformed from one form to another.
- The total energy of the universe is always constant.
- ΔE= q + w (a mathematical form of 1st law of thermodynamics)
- q: energy given to the system; w: work done on the system; ΔE: change in internal energy.
Enthalpy (H): Heat contained in the system measured at constant pressure. {H = E + PV}
The second law of thermodynamics: States that in the universe or any isolated system the degree of disorder always increases.
Spontaneity: It defines whether a chemical reaction will occur or not.
- Causes of spontaneity:
- Decrease in potential energy (stored energy at rest).
- Increase in randomness or disorder.
Reactions proceeds in that direction where randomness increase.
Reactions are of two types:
- Spontaneous Reaction: Reaction which can occur by itself without any external force.
- Non-Spontaneous Reaction: Reaction which cannot occur by itself.
Entropy: It is a measure of randomness or disorder in a system. The greater the disorder, the greater the entropy.
Gibb’s Energy (G): It is the part of the total energy of the system which can be converted to useful work. (∆G = ∆H -- T∆S)
- ∆G: change in Gibbs energy; ∆H: change in enthalpy; ∆S: change in entropy.
- For a reaction Y → X at 37°C, ∆G° is related to ∆G as follows:
∆G = ∆G° + RT ln [X] /[Y]
Relationship between standard Gibb’s energy change (∆G°) and Equilibrium Constant (Keq):
∆G° = - RT ln Keq
Key terms for different energy reactions:
- Oxidation: It is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state of a chemical or atoms within it.
- Reduction: It is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state of a chemical or atoms within it.
- Hydrogenation: It is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst.
- Dehydrogenation: It is the process by which hydrogen is removed from an organic compound to form a new compound.
- Activation Energy: It is the minimum amount of energy that must be provided for compounds to result in a chemical reaction.
- Enzymes: A substance produced by a living organism that acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction.
- Coenzymes: Coenzymes are small molecules. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to do so.
- Substrates: Each enzyme binds tightly to one or more molecules called substrates.
- Catalysts: A substance that can lower/increase the activation energy of a reaction.
Important Abbreviations to understand the different processes:
- ATP: Adenosine Tri Phosphate
- ADP: Adenosine Di Phosphate
- NADH: Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
- NADPH: Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate
- FADH2: Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide
- AMP: Adenosine Mono Phosphate
- PPi: Pyrophosphate
How do cells obtain energy from food?
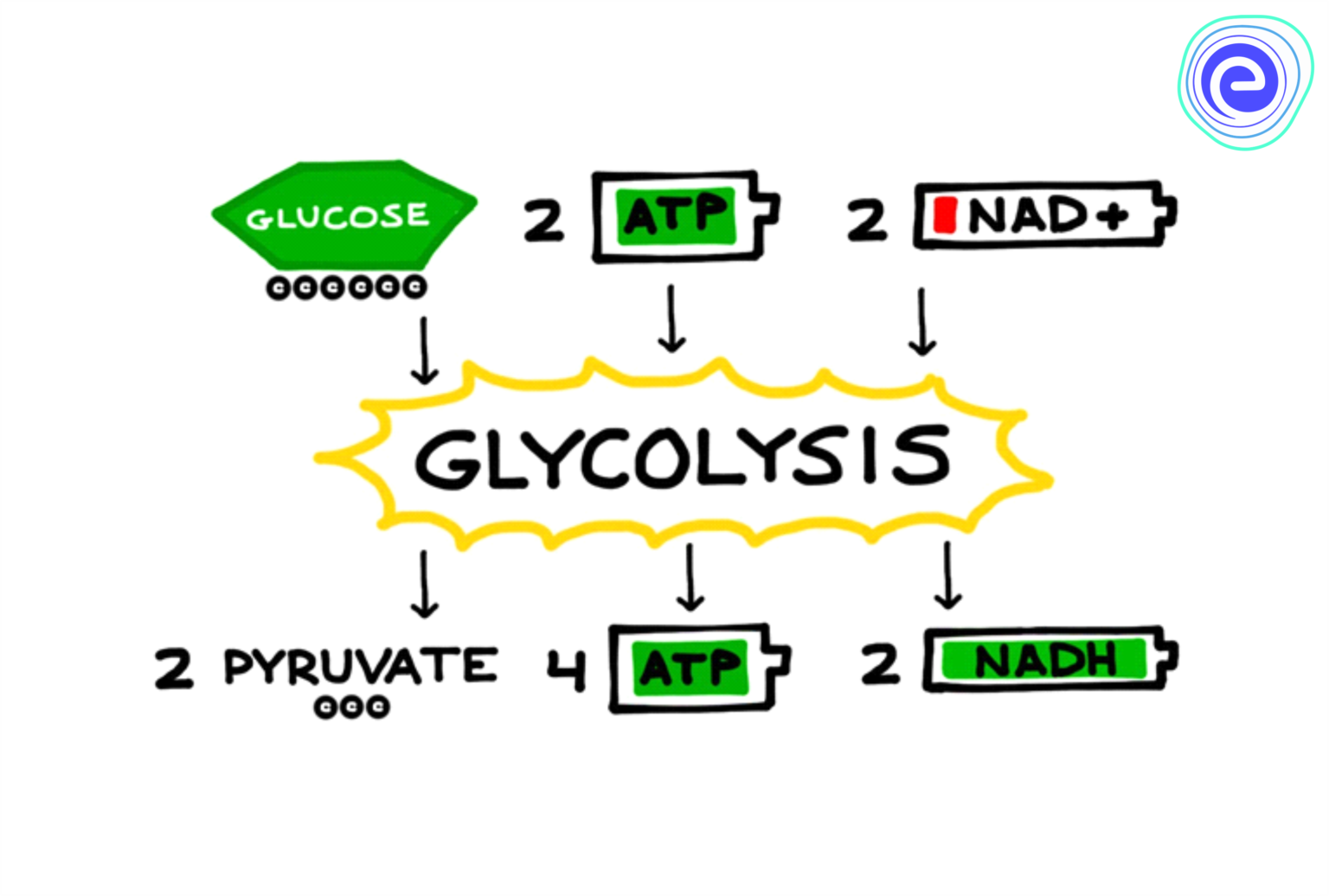
Glycolysis: The major process of oxidizing sugars is the sequence of reactions known as glycolysis.
- It is common in both aerobic (in presence of oxygen) and anaerobic (without the presence of oxygen) reactions.
- It takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- It starts with 6-carbon glucose to finally result in two molecules of 3-C pyruvate. In plants, this glucose is derived from sucrose.
- Total ATP produced: 8ATP
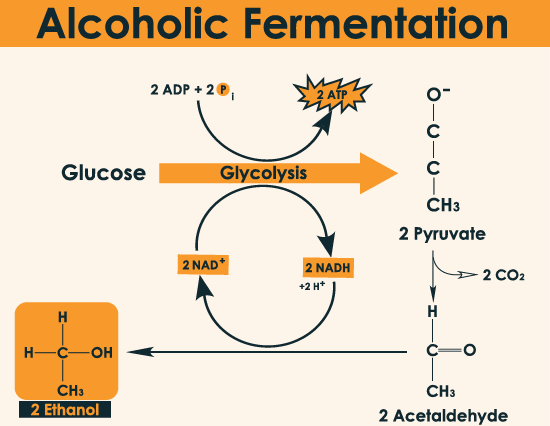
Fermentation:
- Alcoholic Fermentation:
- It occurs in yeast.
- The process is hazardous either acid or alcohol is produced. Yeats poison themselves to death when the concentration reaches about 13%.
- It yields ethyl alcohol as the final product.
- Total ATP produced: 2ATP
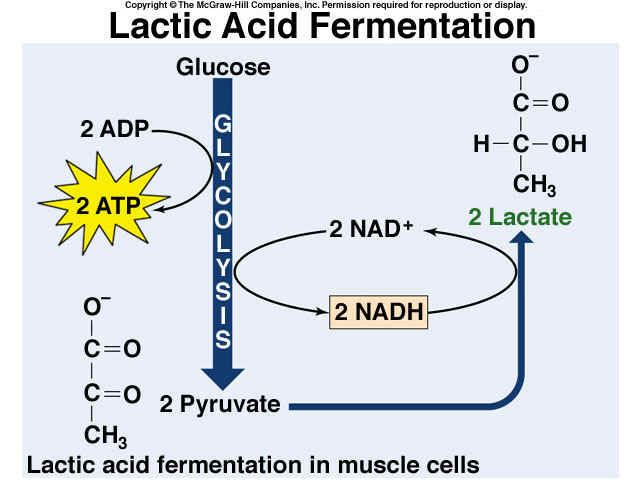
Lactic Acid Fermentation:
- It occurs in the muscles of humans during an intense workout.
- it yields lactic acid as the final product.
- Total ATP produced: 2ATP
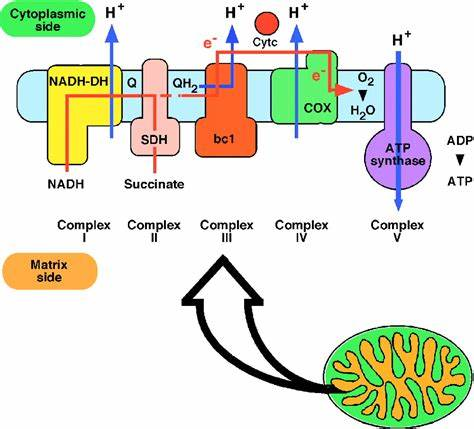
Oxidative Phosphorylation:
The process that connects glycolysis and Krebs’s Cycle.
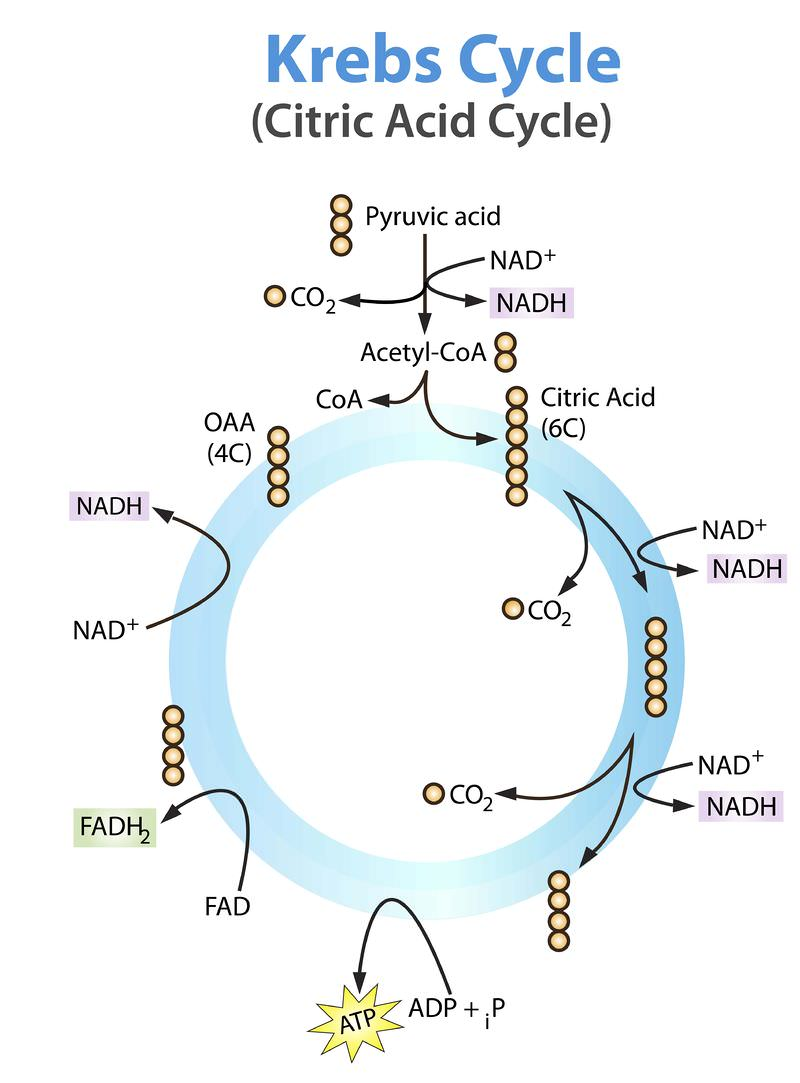
Krebs’s Cycle:
It occurs in the mitochondria matrix of the eukaryotic cell but in prokaryotes, it occurs in the cytoplasm.
Stored food in organisms:
- Fungi: Oil and glycogen
- Humans: Glycogen
- Plants: Starch