APES Mod 27 - Irrigation and Pest Control Methods
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What types of water are used for irrgation?
Ground water and surface water (rivers and streams)
What is the largest use of freshwater worldwide?
agriculture
What percent of freshwater consumption is used for irrigation in the U.S?
70%
Where is groundwater stored?
aquifers
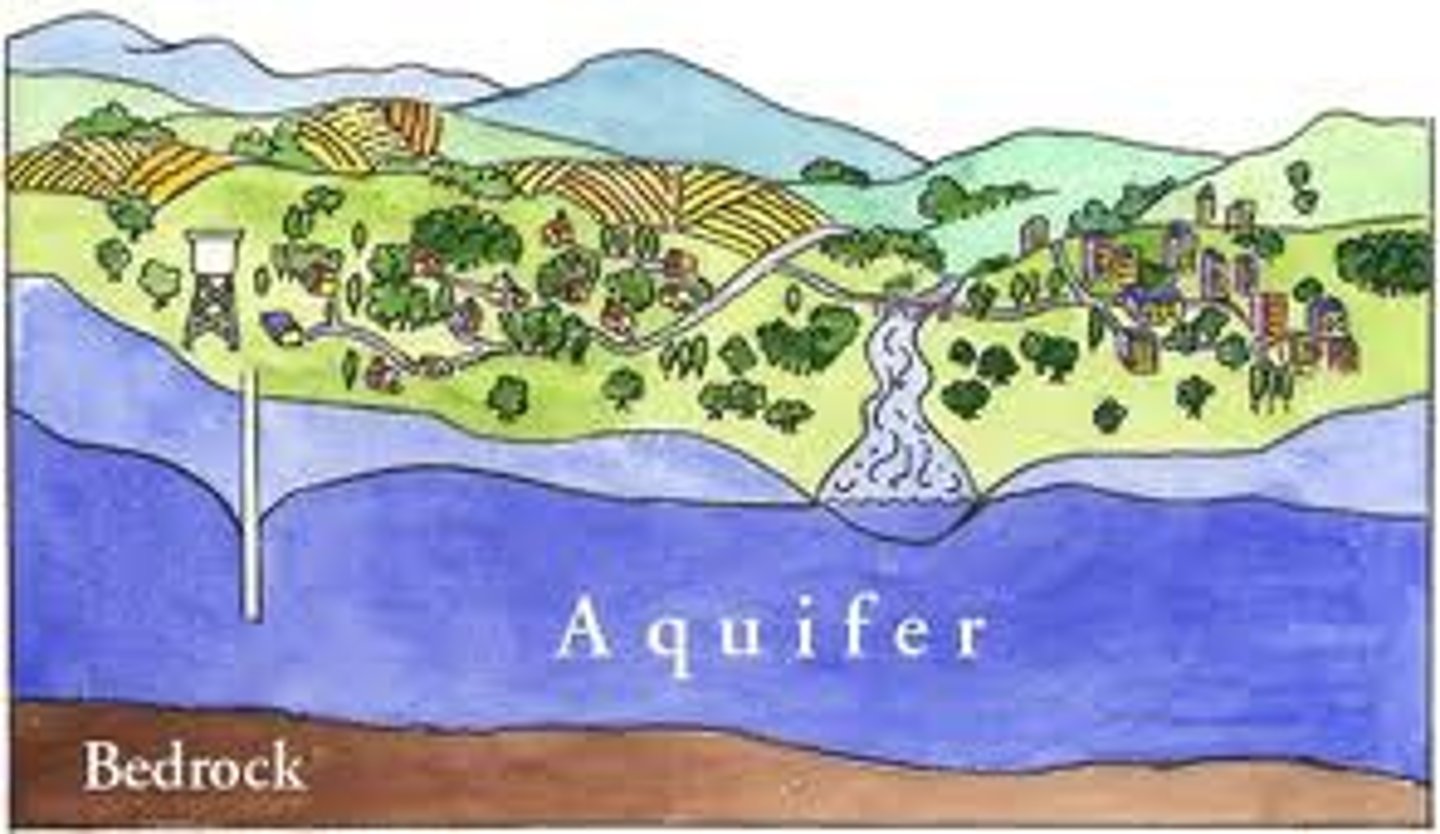
aquifer
pore spaces found within permeable layers of rock underneath the soil that store groundwater
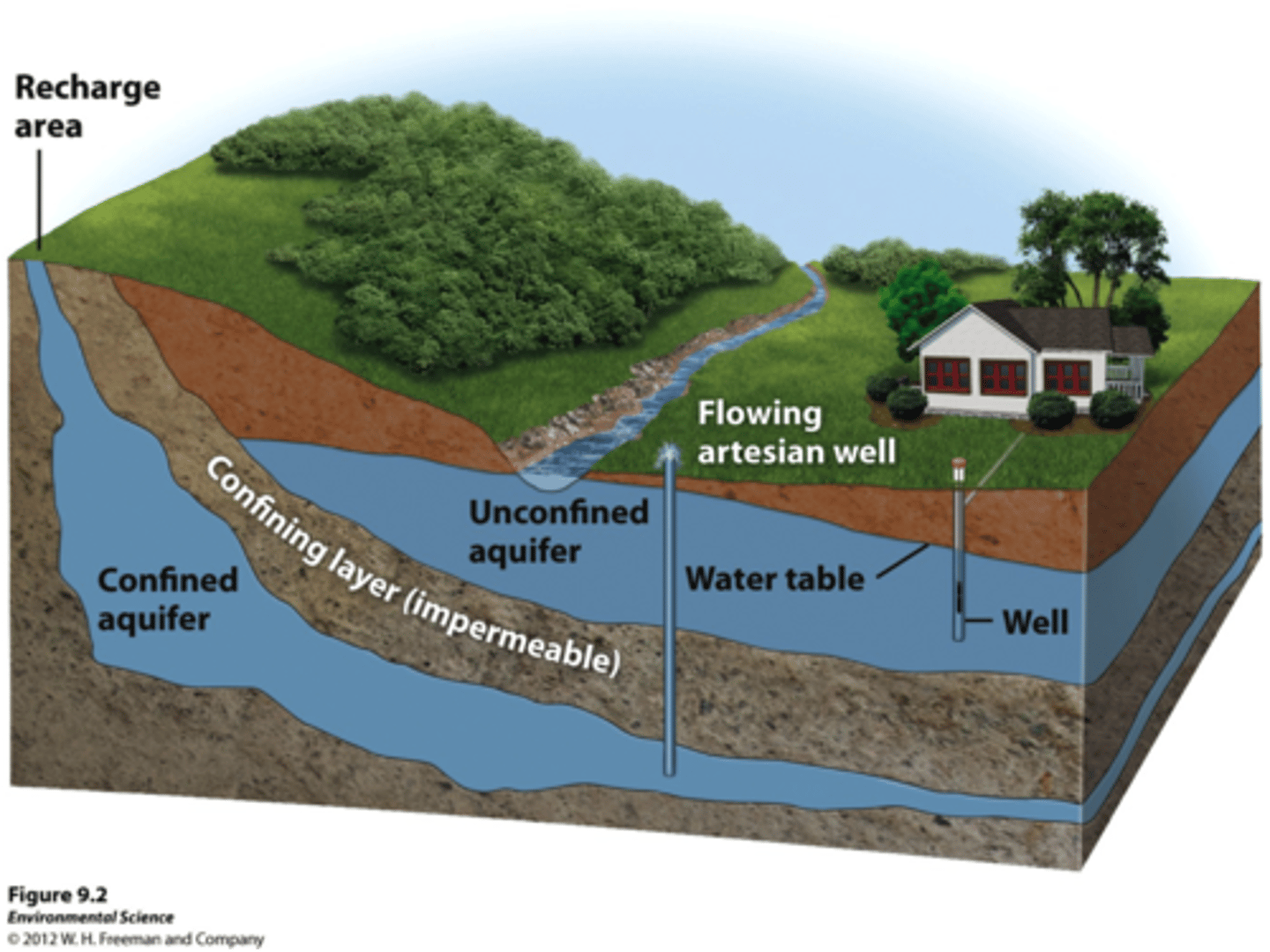
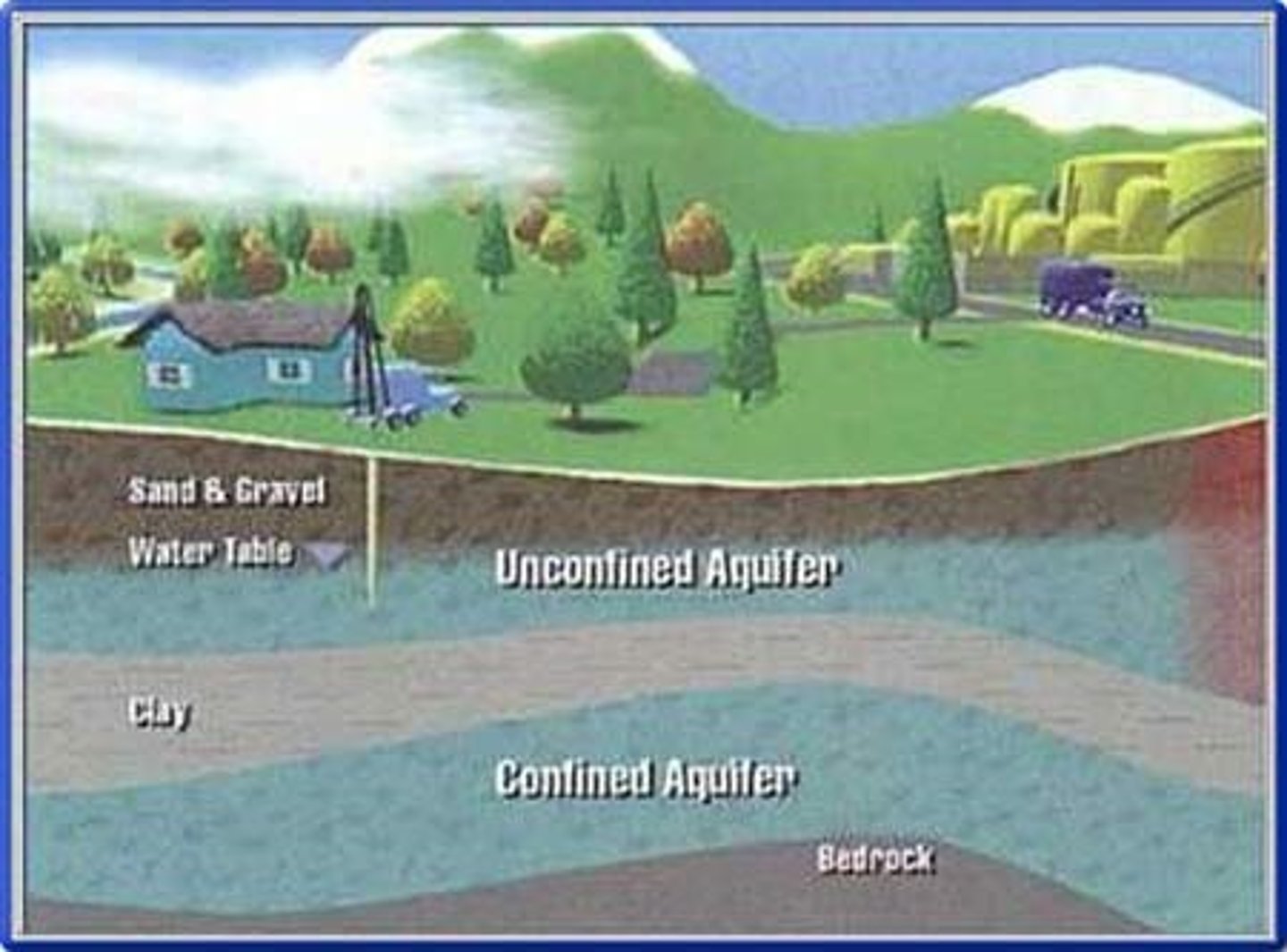
what type of aquifer does water easily flow in and out of?
unconfined aquifers
unconfined aquifer
porous rock covered by soil out of which water can easily flow
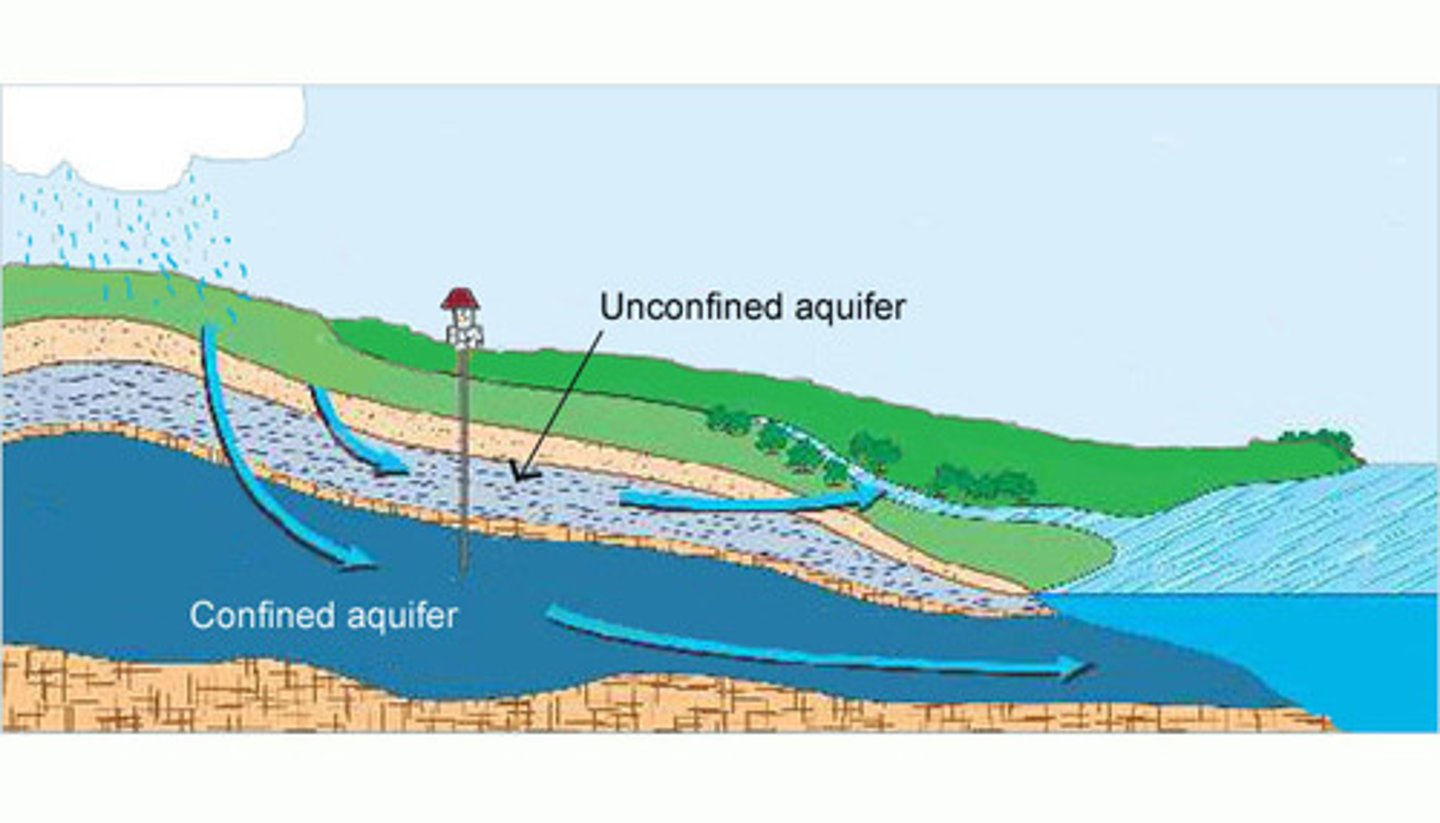
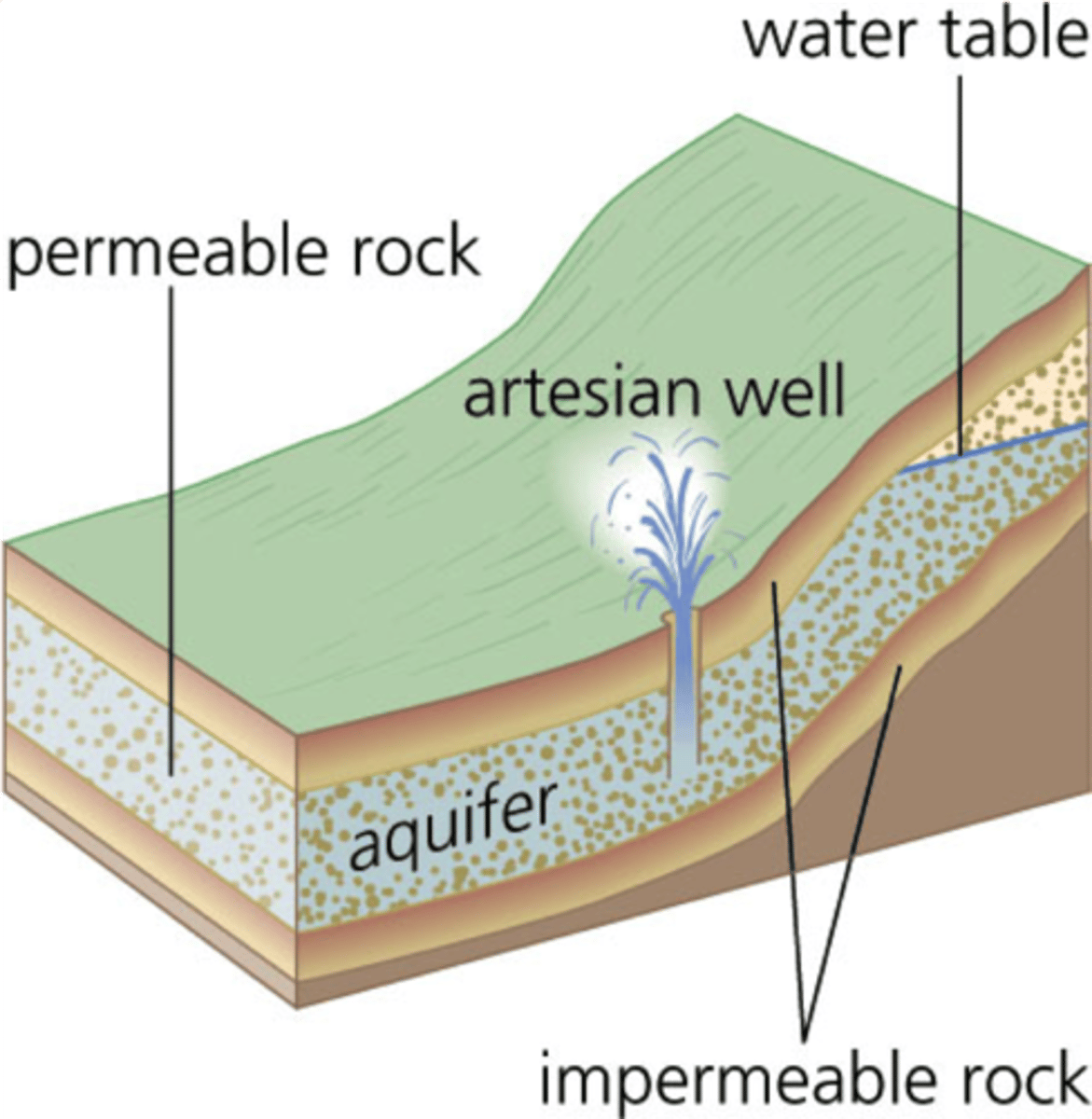
confined aquifer
an aquifer surrounded by a layer of impermeable rock or clay that impedes water flow
How can a confined aquifer be recharged?
if the impermeable layer of rock has a surface opening that can serve as a recharge area
water table
the uppermost level at which groundwater in a given areafully saturates the rock or soil
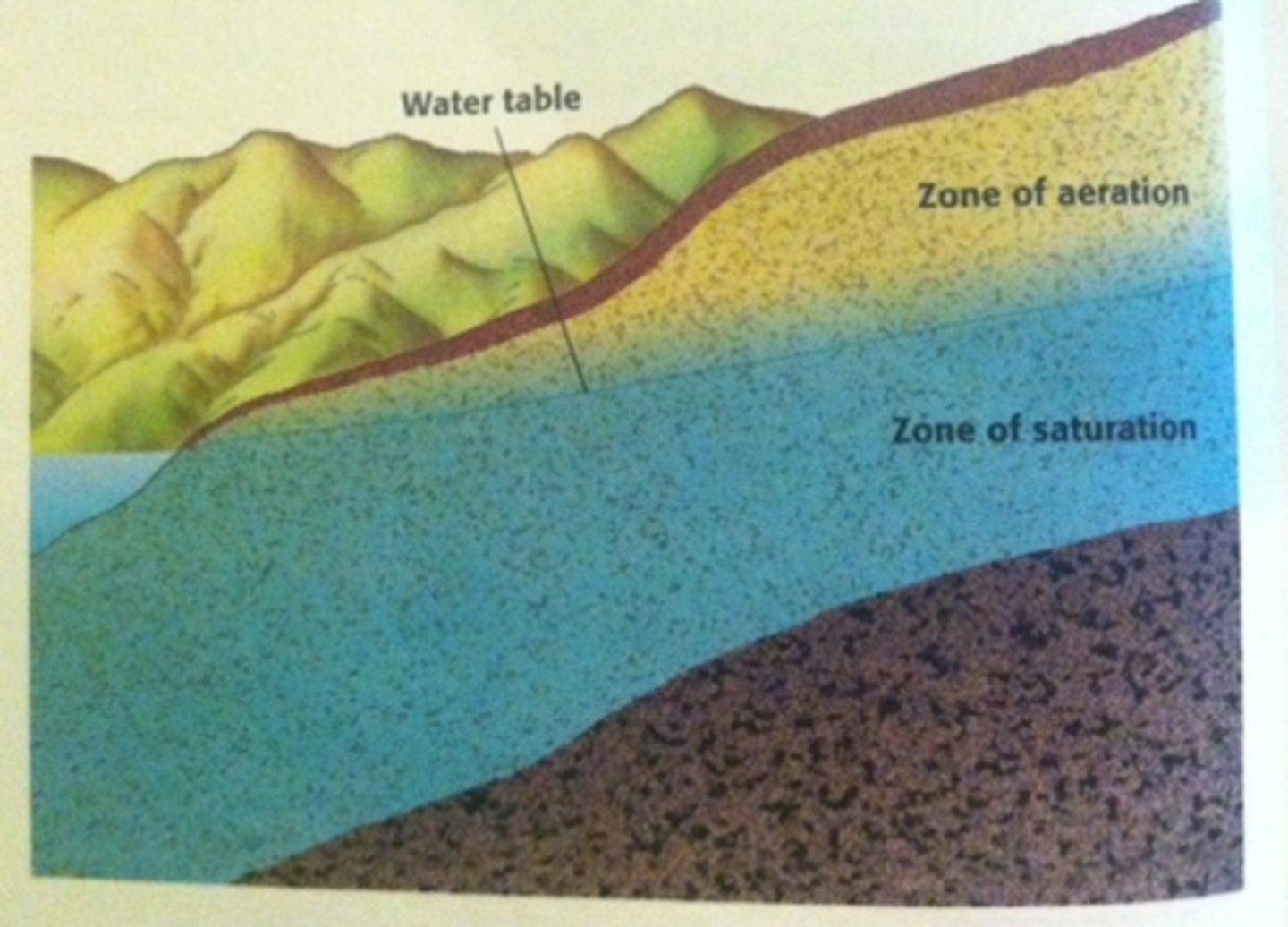
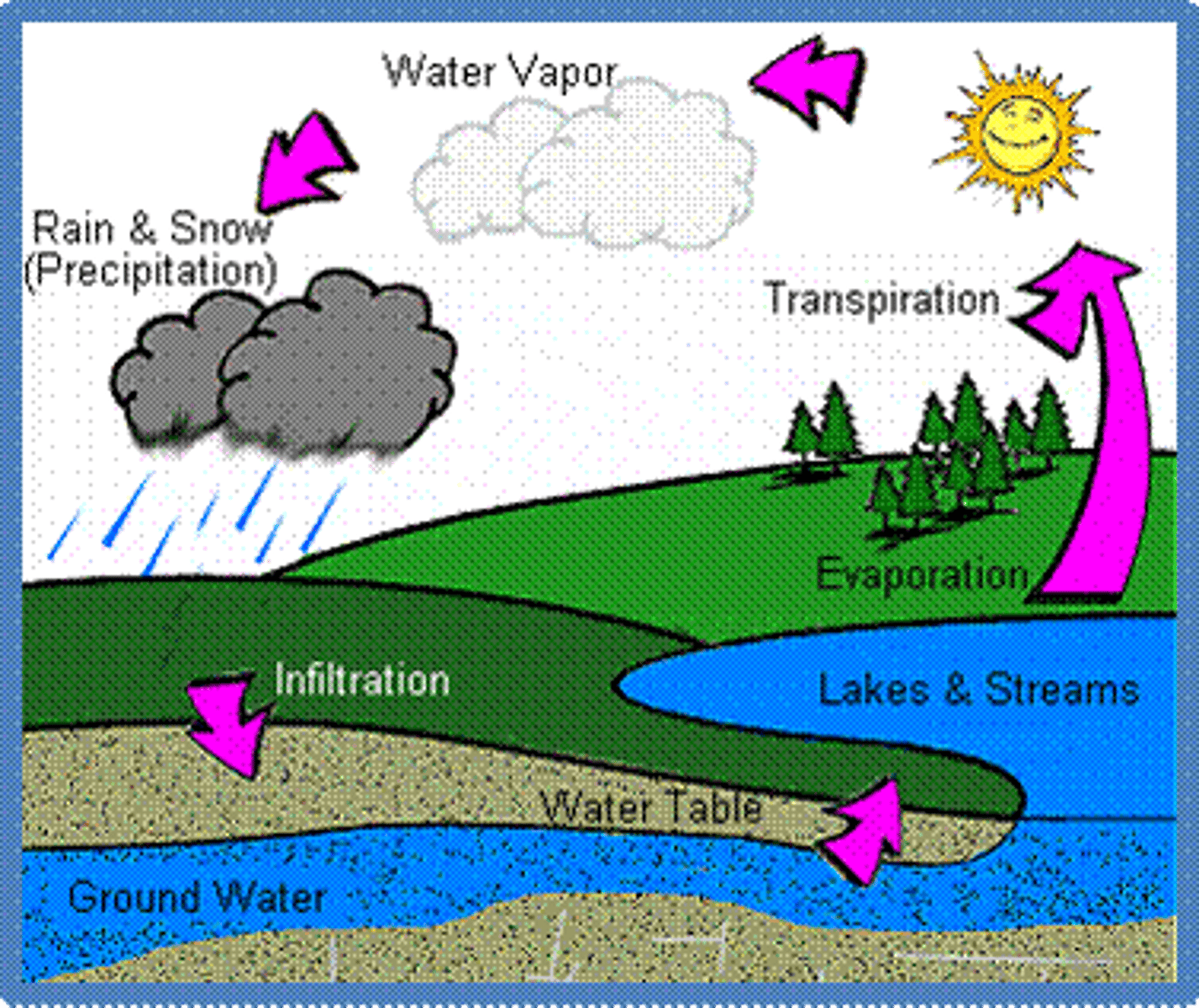
groundwater recharge
the process by which water from precipitation percolates through the soil and works its way into an aquifer.
how are aquifers important for plants?
plant roots access groundwater through aquifers and water tables
spring
water that naturally percolates up to the surface

what do wells use as a source of water?
aquifers!
how do modern wells bring water to the surface?
by using pumps
artesian well
a well created by drilling a hole into a confined aquifer; water naturally rises because of pressure within the aquifer
why are unconfined aquifers much more likely to be contaminated w/ chemicals released by human activities?
the grounfwater in an unconfined aquifer may originate from water that fell to the ground last year or even last week; it is a rapid and direct connection w/ the surface
How long does it take for confined aquifers to recharge?
10,000-20,000 yrs
Why is large-scale use of water from a confined aquifer unsustainable?
the withdrawl of water is faster than recharge
water footprint
the total daily per capita use of freshwaterfor a country or the world
What are the four major crop irrigation techniques?
- furrow irrigation
- flood irrigation
- spray irrigation
- drip irrigation
what does it mean if irrigation is efficient?
that a large percent of the water is accessible by plants
- ex) if a technique is 60% effective, that means that 60% of water is accesible by the plants and the other 40% either runs off the field or evaporates
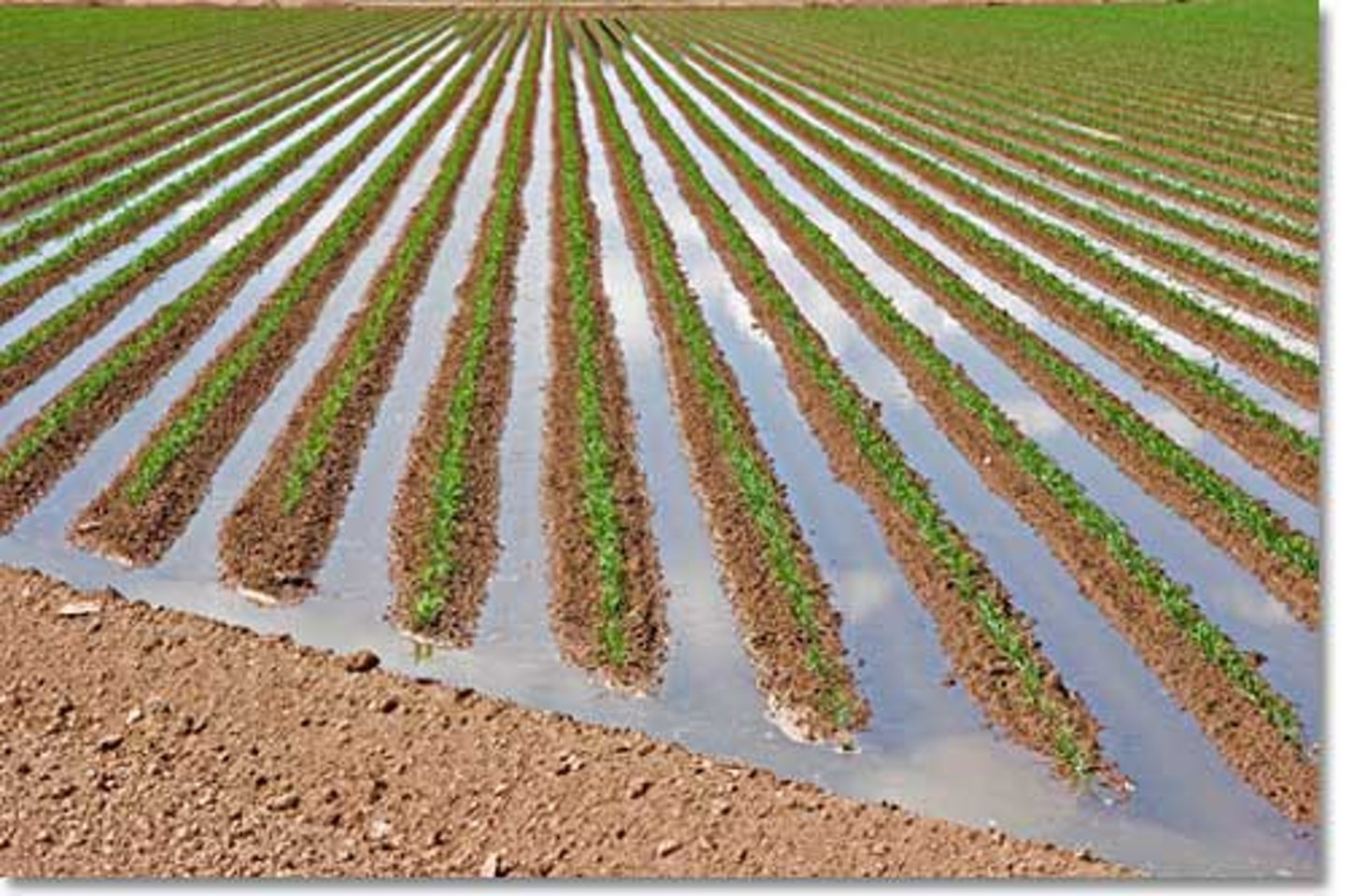
furrow irrigation
- the farmer digs trenches along the crop and fills them with water
- easy and inexpensive
- the oldest technique
- 67% efficient

flood irrigation
- the entire field is flooded w/ water
- 66-80% efficiency
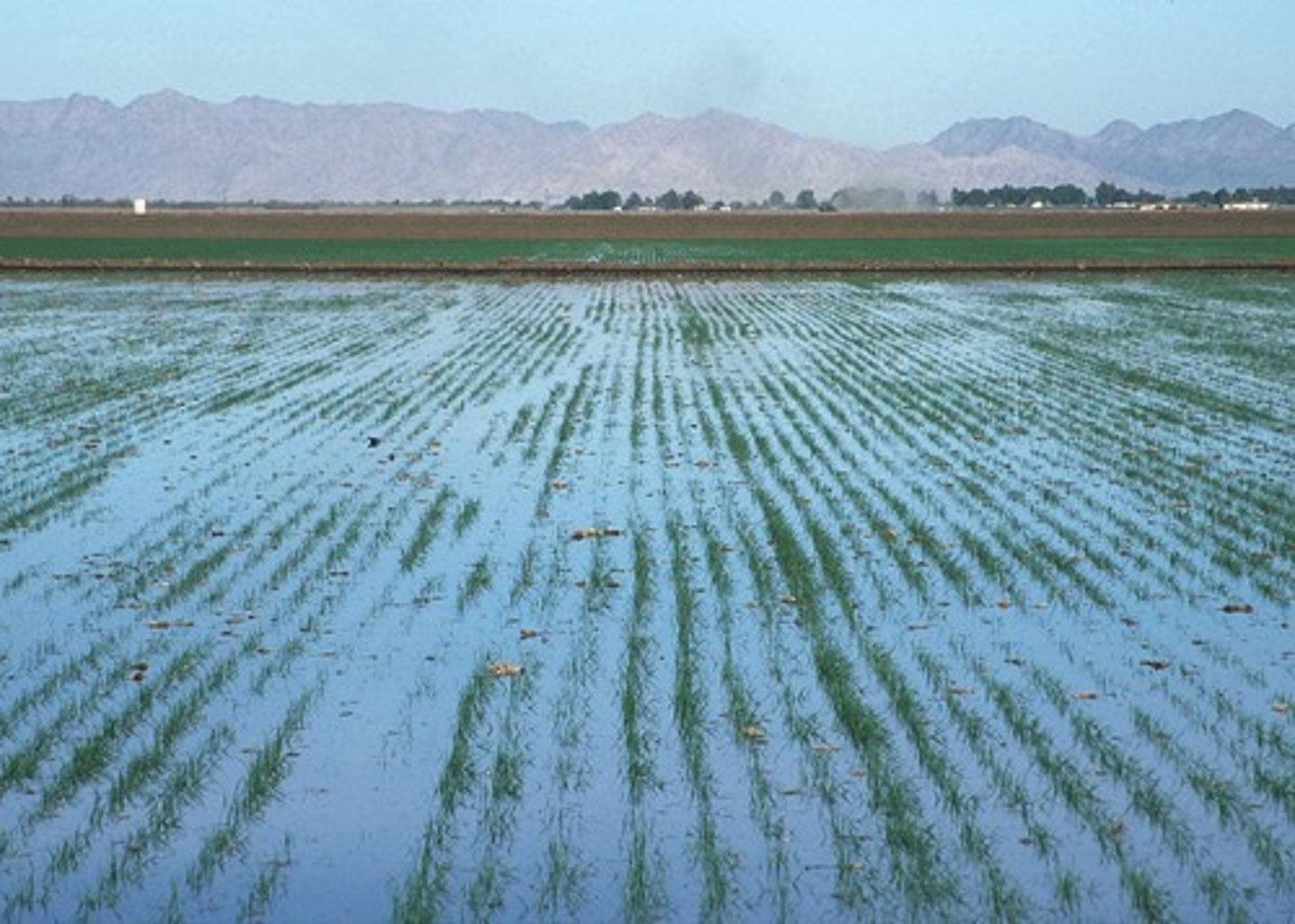

flood irrigarion negative
- can lead to increased risk of waterlogging
^^ by depriving roots of O2, waterlogging can reduce O2 concentrations in soil pore space and impair root growth
spray irrigation
- water is pumped into an apparatus that contains a series of spray nozzles
- 75-95% efficient
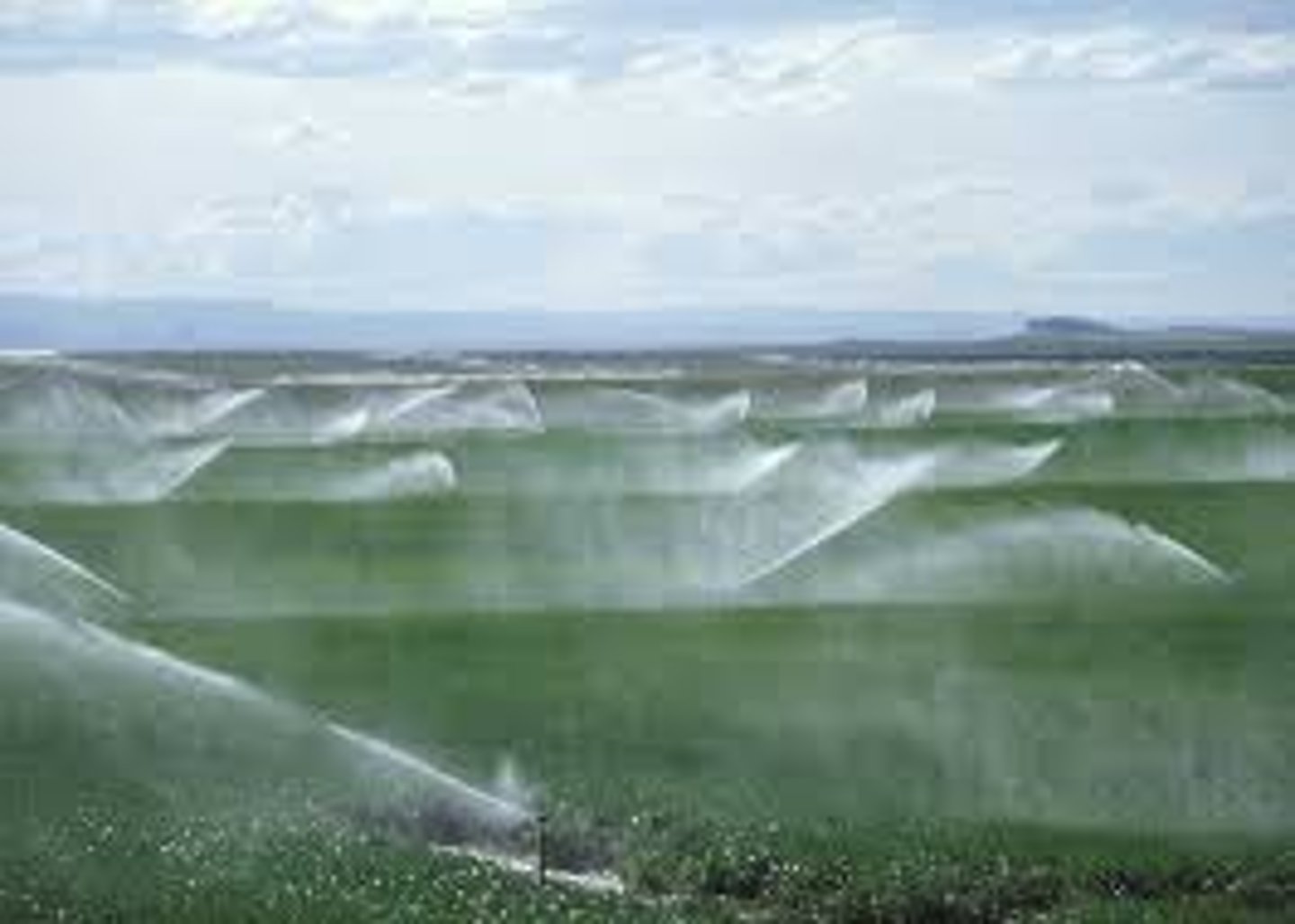

spray irrigation disadvantages
- it is more expensive than furrow or flood irrigation
- uses a fair amount of energy
drip irrigation
- a slowly dripping hose on the ground beneath the soil delivers water directly to the plant roots
- 95% efficient
- reduces weed growth bc the surface remains dry, discouraging weed germination
- expensive
What are the three major adverse consequences of irrigation?
- waterlogging
- salinization
- aquifer depletion
waterlogging
causes low O2 confitions that reduce the ability of plant roots to take up O2
- this can reduce crop yield or kill the crop
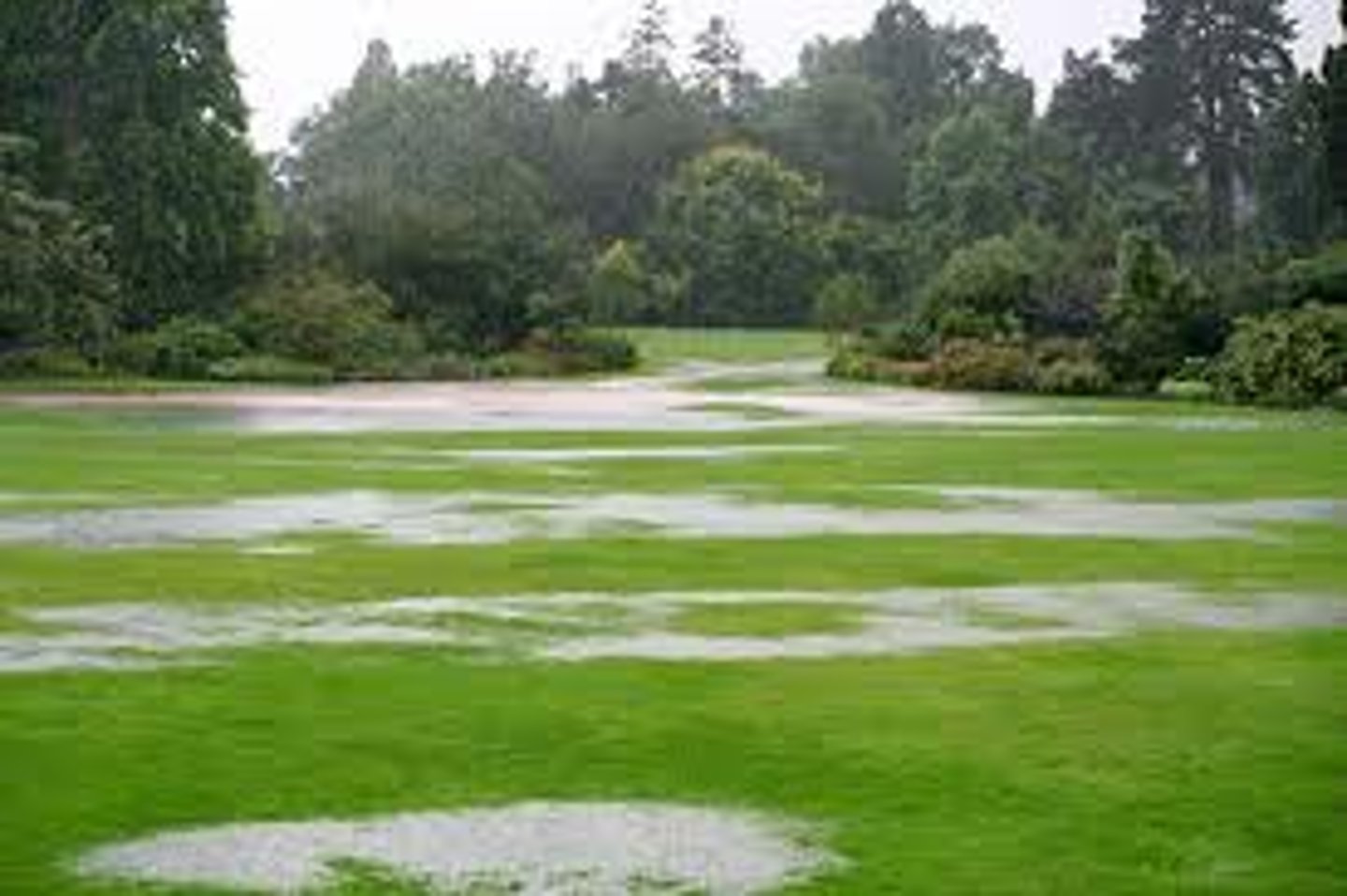

salinization
occurs when water evaporates and leaves behind salts, which can become toxic to plants at high concentrations
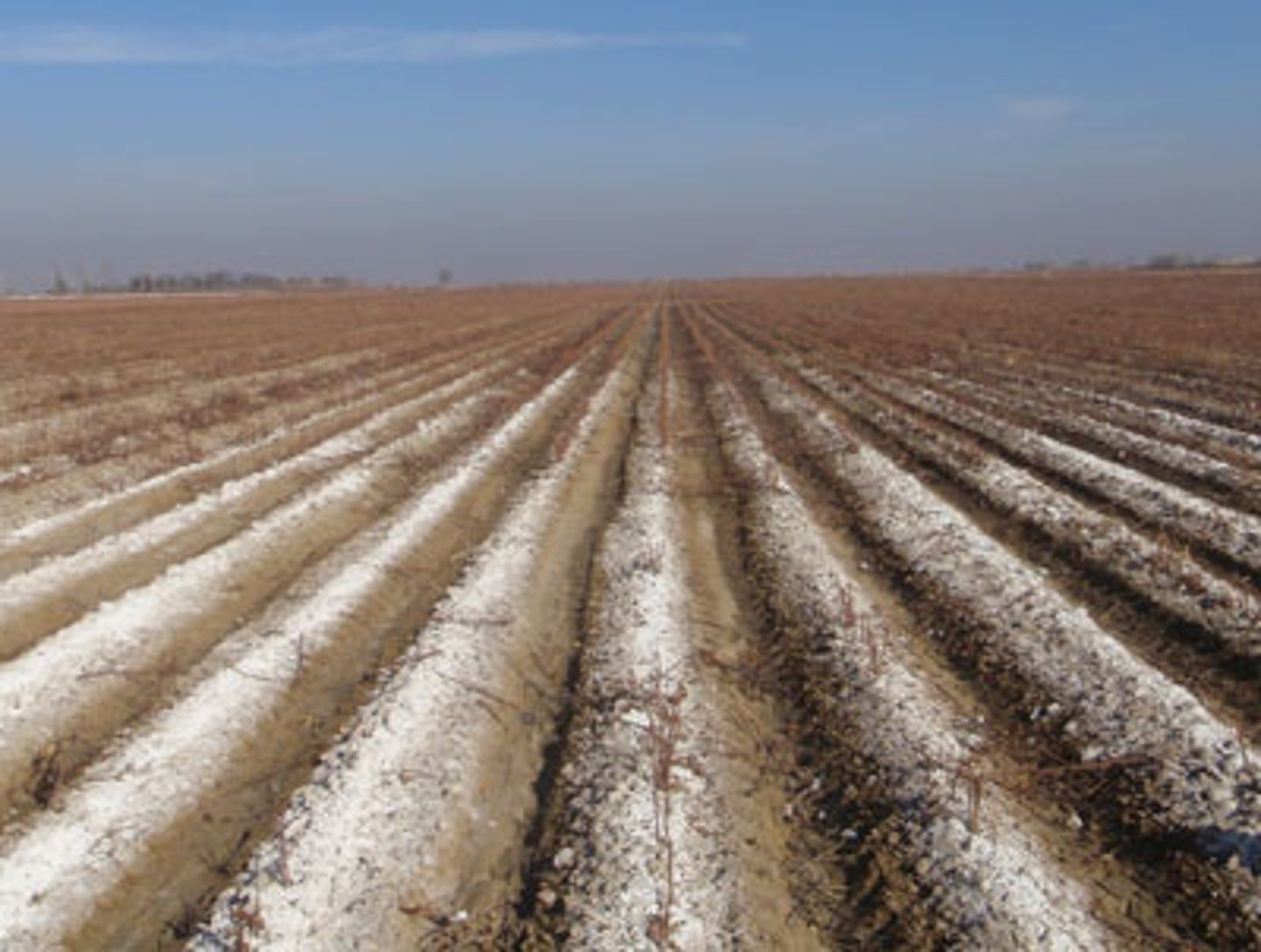

aquifer depletion
occurs when the rate of withdrawl is faster than the rate of recharge
- can cause spring-fed streams to dry up as the water table drops farther from ground surface
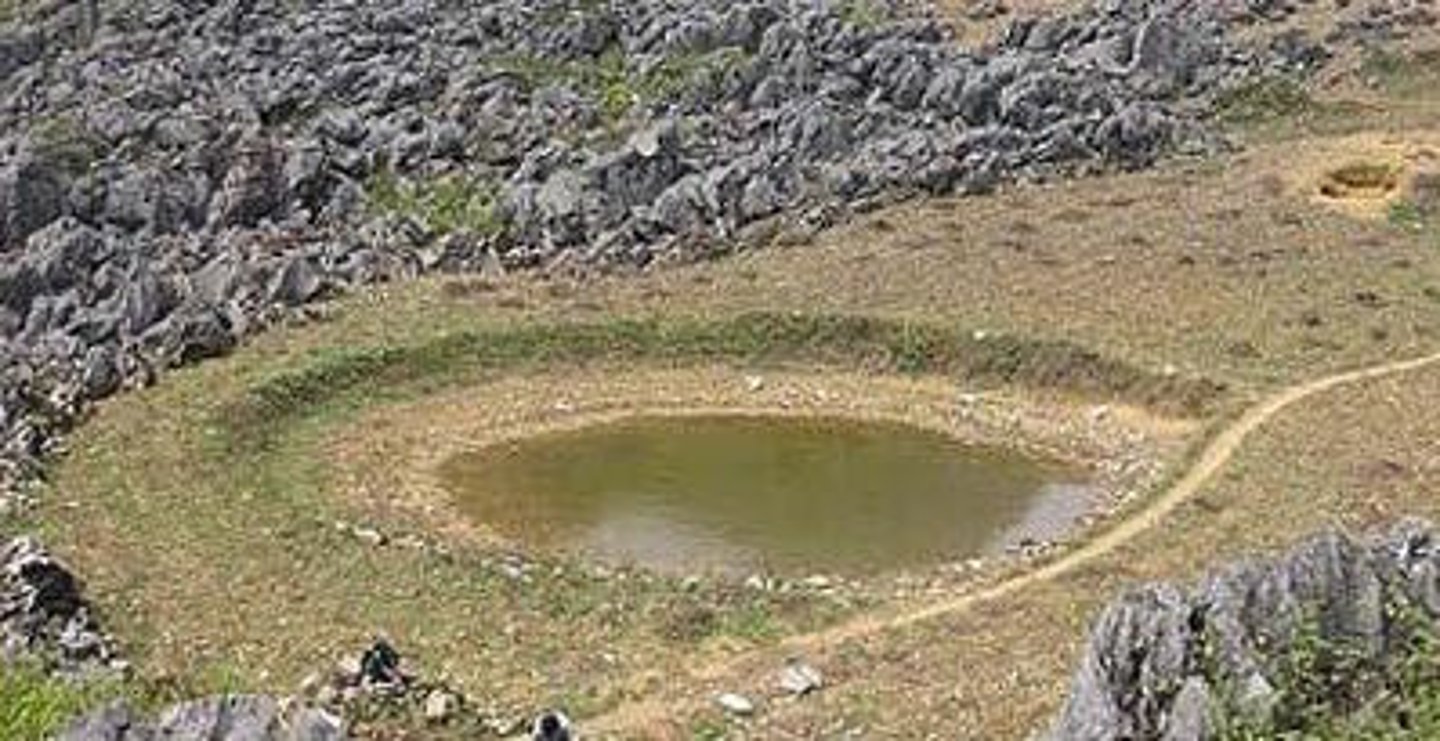

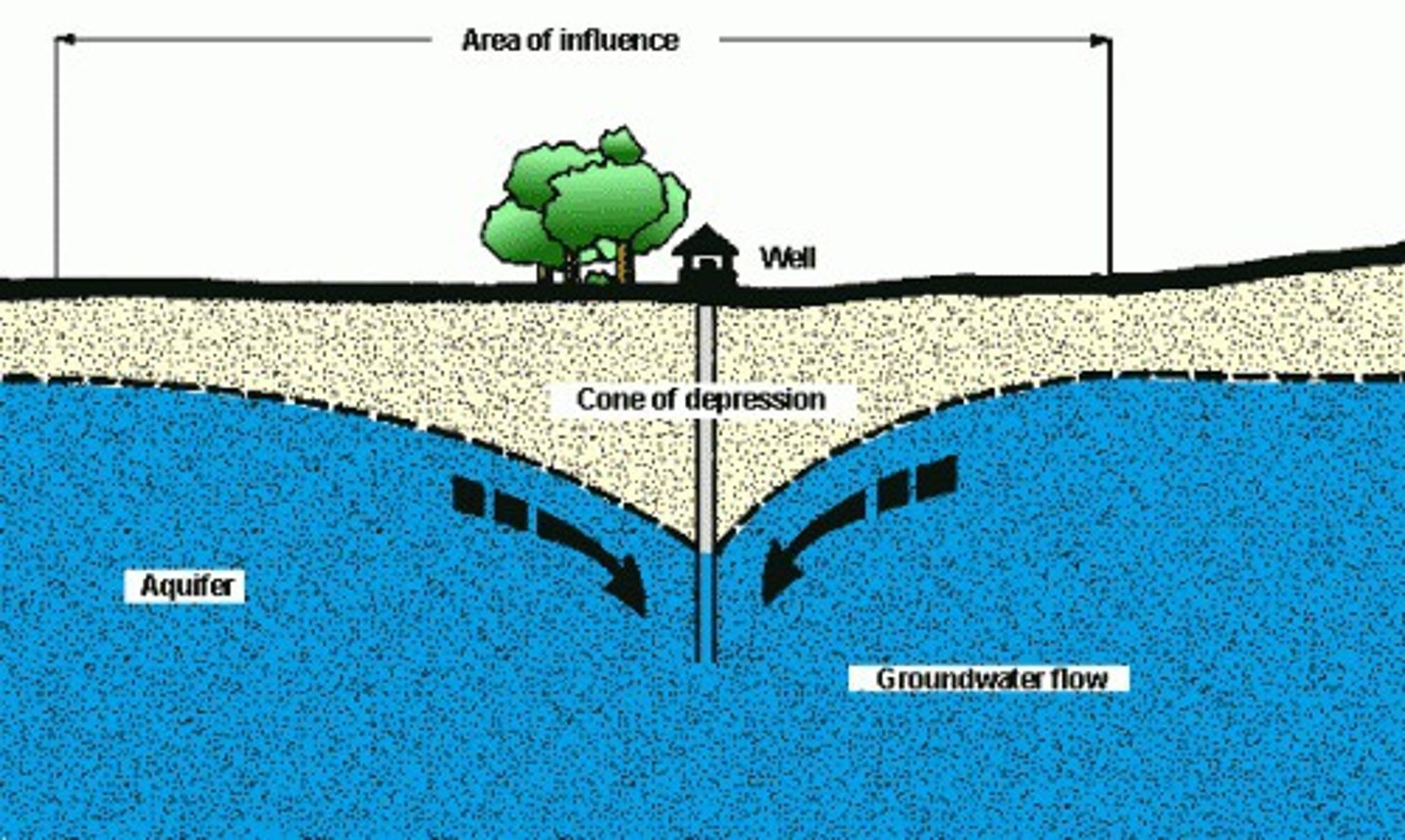
cone of depression
an area lacking groundwater due to rapid withdrawal by a nearby well
fungicide
substance that kills fungi or inhibits their growth
rodenticide
Pesticide that kills, repels, controls rodents

Persistent pesticide
A pesticide that remains in the environment for a long time.
persistent pesticide disadvantages
- can injure or kill more than their intended targets
- the chemical used to make these have been found to accumulate in the fatty tissues of some animals
nonpersistent pesticides
Pesticides that break down rapidly, usually in weeks or months
is the overall environmental impact of nonpersistent pesticides always lower than that of persistent pesticides?
no
- nonpersisten pesticides must be applied more oftern due to their lack of longevity, so their impact is not always lower
integrated pest management (IPM)
An agricultural practice that uses a variety of techniques designed to minimize pesticide inputs
IPM technique examples
- crop rotation
- intercropping
- using pest-resistant crop varities
- create habitats for predators of pests
pesticide resistance
a trait possessed by certain individuals that are exposed to a pesticide and survive (and thus pass on the trait)
how is the cycle of pesticide development and pest resistance a type of artificial selection?
the pesticide is artifically selecting against indivduals of the crop population that are susceptible to the pesticide
pesticide treadmill
A cycle of pesticide development, followed by pest resistance, followed by new pesticide development
environmental impacts of pesticides
- they may kill beneficial organisms
- chemical pesticides can runoff into water and pollute it
- they can harm the farmworkers