CH3 - Analyzing EKG Rhythm Strips
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
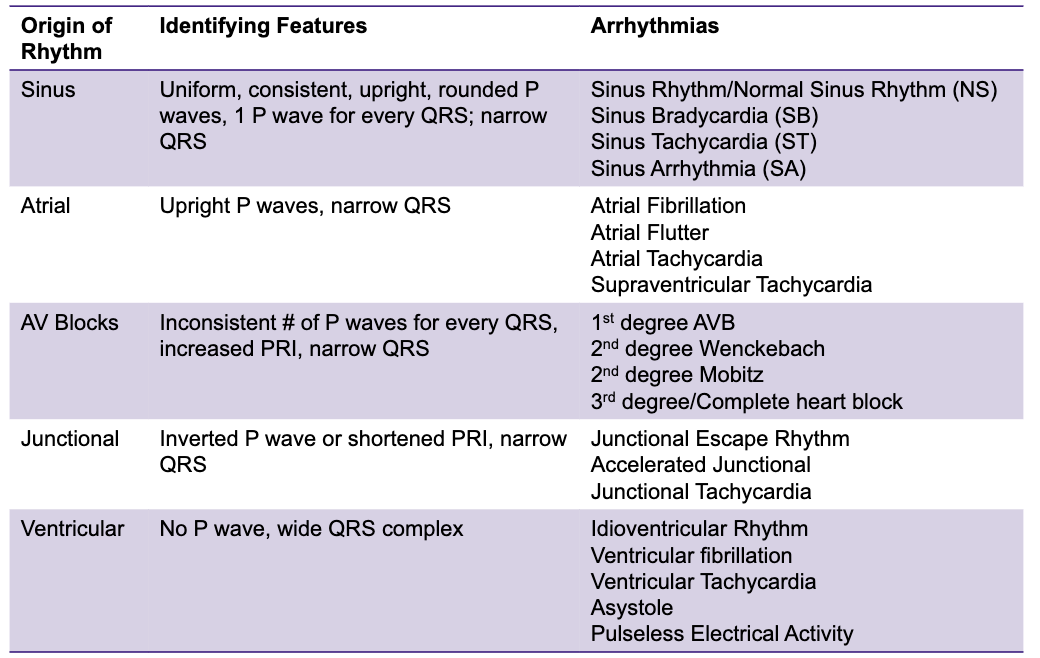
EKG 5-Step Analysis Method
Regularity
Are the R-R interval evenly spaced? Is it regulat?
Rate
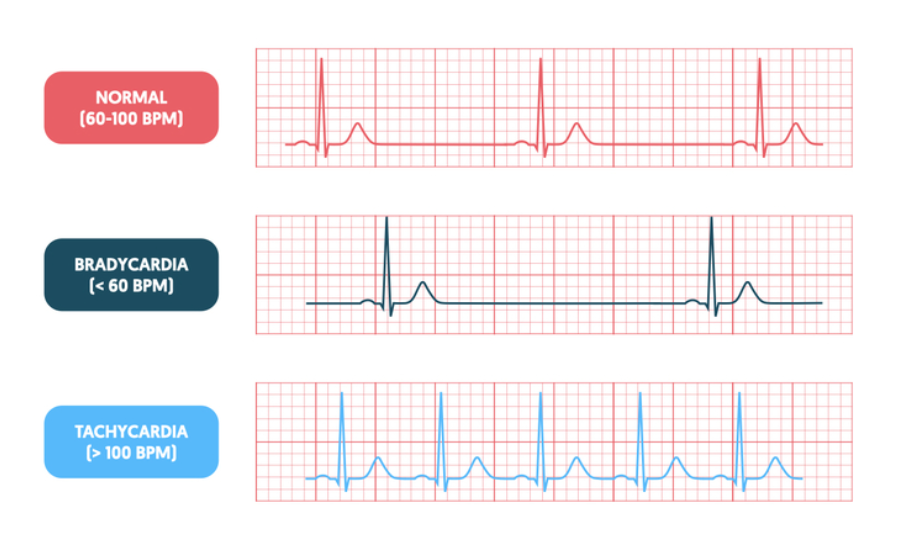
What is the HR?
Bradycardia: <60bpm
Tachycardia: >100bpm
Normal: 60-100
P Waves
Are P waves present?
Upright?
One for every QRS?
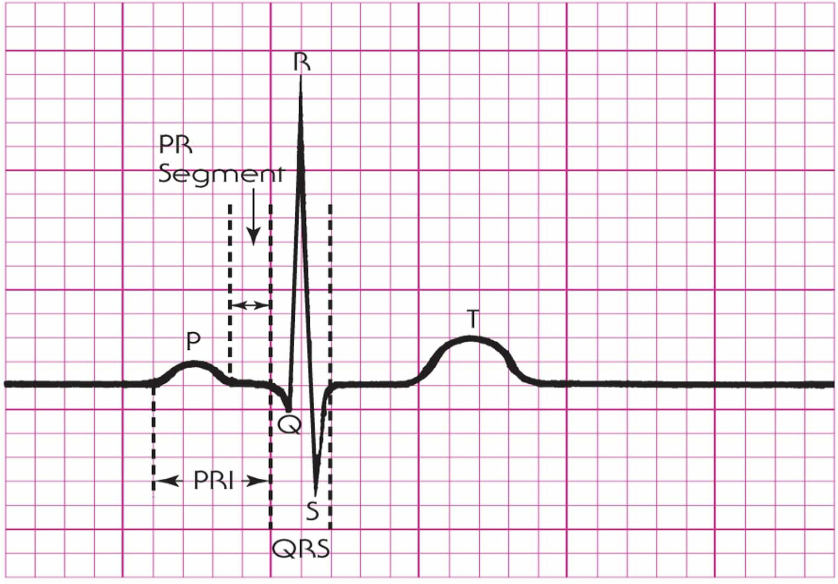
PR Internval
What is the PR interval
Normal: 0.12-0.20s
QRS Complex
Is it narrow or wide
Normal: <0.11s
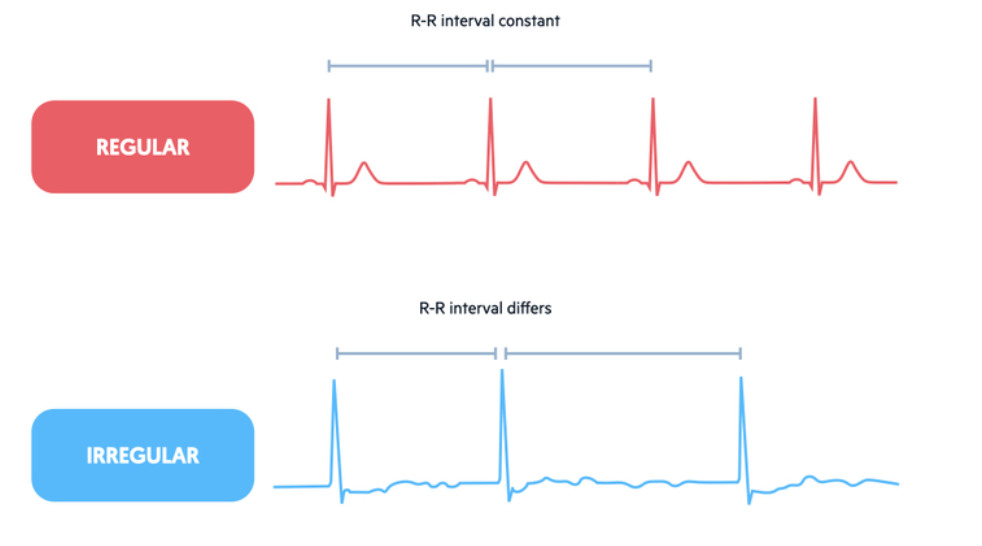
What to ask yourself for Regularity?
Is it regular?
Is it irregular?
Are there any patterns to the irregularity?
Are there any ectopic beats? If so are they early or late?
How to check for Regularity?
Check spacing between R-R intervals across the strip → if consistent, the rhythm is regular
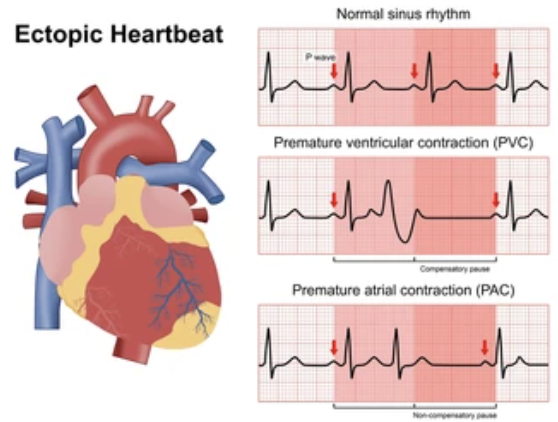
Explain Ectopic beat
When a single beat arises from an ectopic focus (a site outside of the SA node) within the conduction system
Common use to suggest that the site became irritable and overrode the sinus node
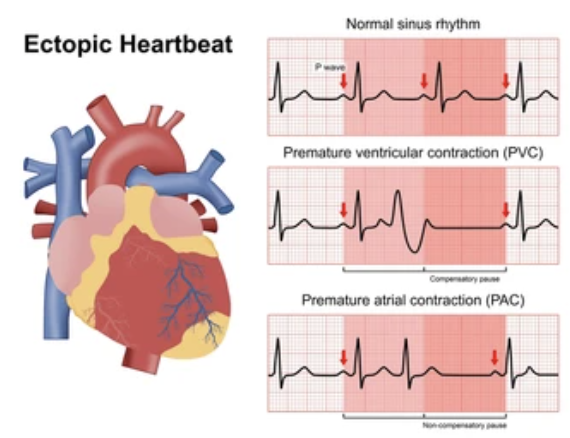
How to tell if ectopic beat is caused by irritability or escape?
An early or premature beat would be an indication of irritability
An escape beat would be preceded by a prolonged R-R cycle
What to ask yourself for Rate?
What is the exact rate
Is the atrial rate the same as ventricular rate?
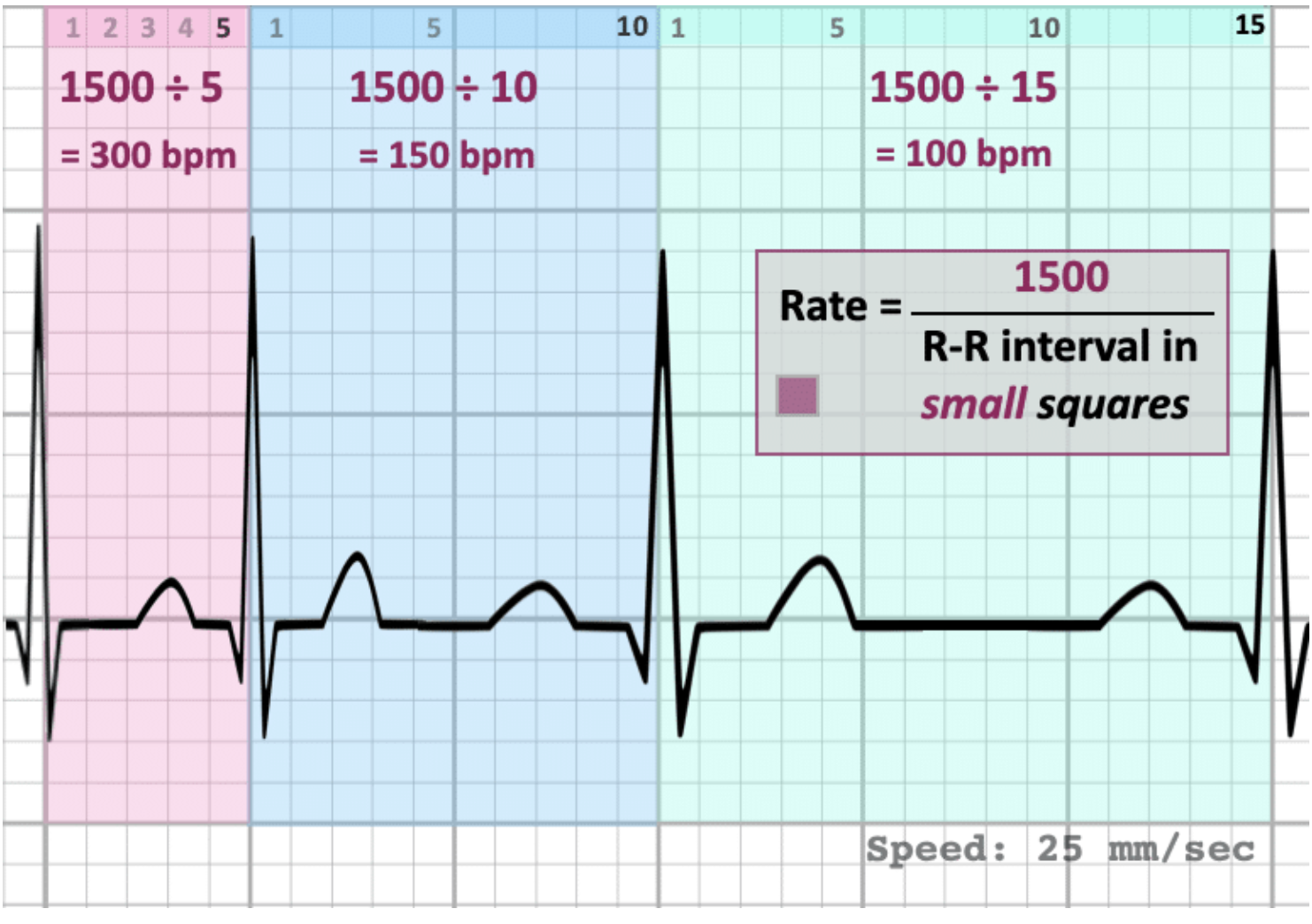
How to ACCURATELY measure Heart Rate?
6 second method: Count the number of R waves in a 6 second strip x 10
Used for regular or irregular rhythms
Small box method: HR = 1500/ # Small boxes
What to ask yourself for P waves?
Are P waves present?
Are the P waves regular?
Is there one P wave for every QRS?
Is the P wave in front of the QRS or behind it?
Is the P wve normal and upright in Lead II?
Are there more P waves than QRS?
Do all the P waves look alike?
Are the irregular P eaves associated with ectopic beats?
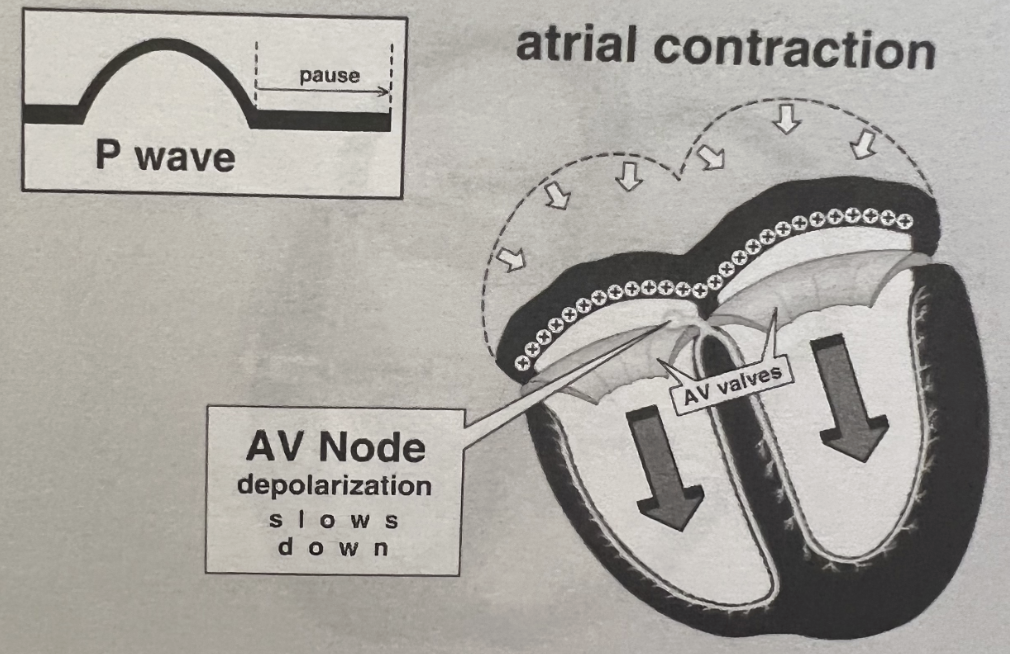
P waves represent what on an EKG tracing?
Atrial depolarization
What to ask yourself for PRI?
Are all the PRIs constant?
Is the PRI measurement within normal range?
IS the PRI varies is there a pattern to changing measurements?
PRI represent what on an EKG tracing?
Measures time from the start of atrial depolarization to the start of ventricular depolarization
What is the normal range for PRI?
0.12 - 0.20 seconds
3-5 small boxes
A Prolonged PRI indicates what?
1st Degree AV block → A delay in electrical conduction from the atria to the ventricles usually at the AV node
Normal = 0.12 - 0.20 seconds
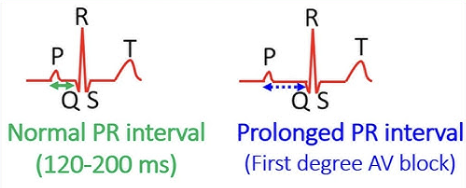
A Shorten PRI indicates what?
Impulses may be bypassing the AV node
Normal = 0.12 - 0.20 seconds
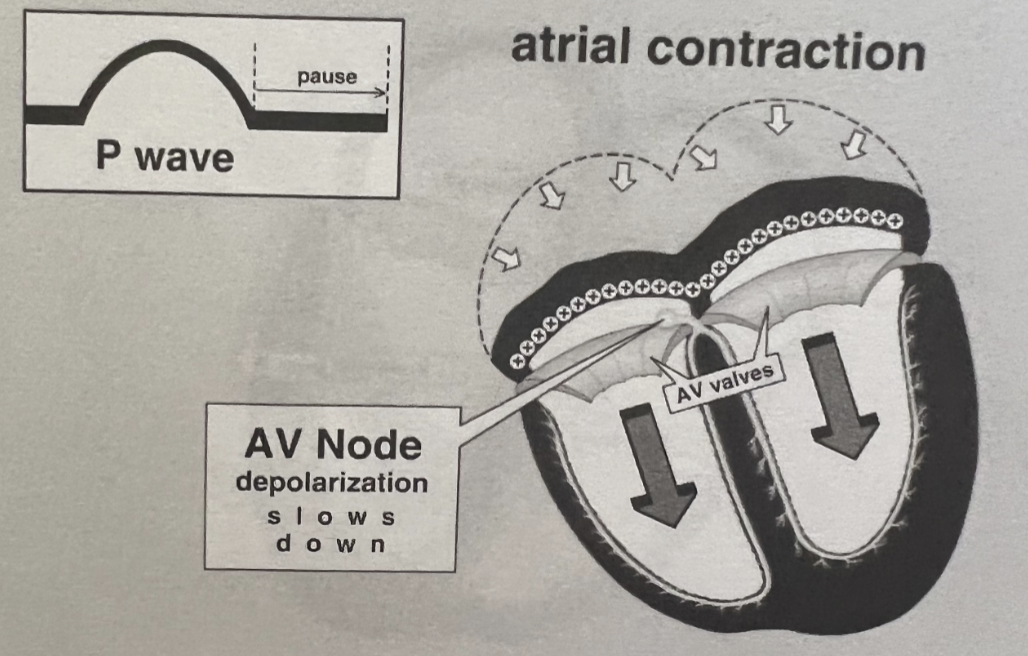
What is the Role of the AV Node?
Acts as a gatekeeper between atria and ventricles → responsible for “holding” impulses until the ventricles are able to receive them
Slow conduction allow time for:
Atrial contraction (atrial kick)
Ventricular filling
Can act as a backup pacemaker if SA node fails
What to ask yourself for QRS Complex?
Are all the QRS complexes of equal duration?
What is the measument of the QRS complex?
Is the QRS measurement within normal limits?
Do all the QRS complexes look alike?
Are the unusual QRS complexes associated with ectopic beats?
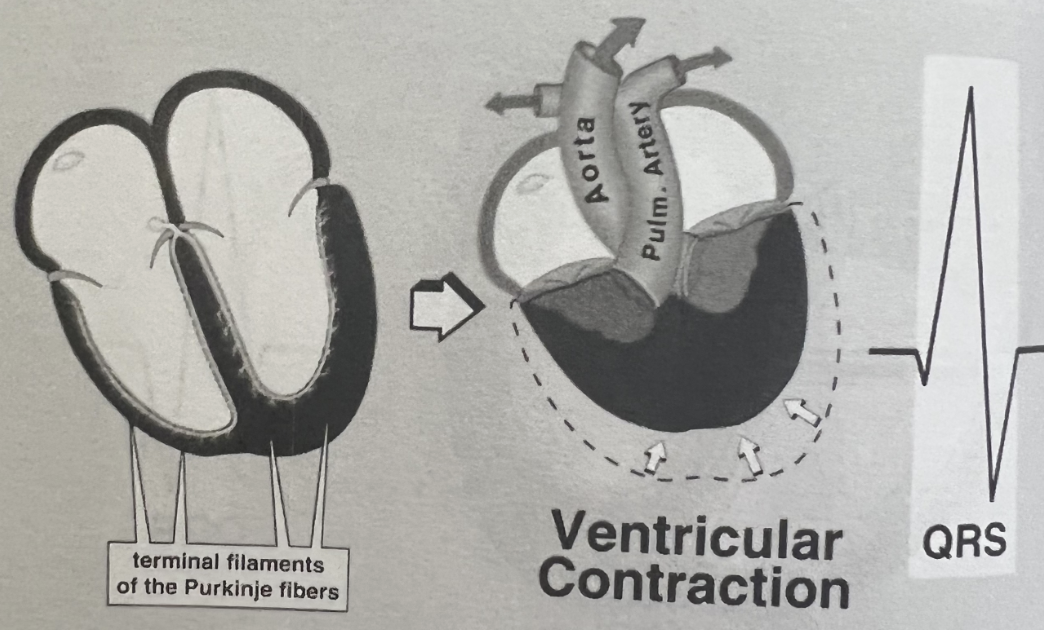
QRS waves represent what on an EKG tracing?
Ventricular depolarization
Normal: <0.11 second
What does a narrow/wide QRS complex mean?
Narrow
A supra-ventricular focus
Wide
A ventricular pacemaker or a supra-ventricular pacemaker that was delayed
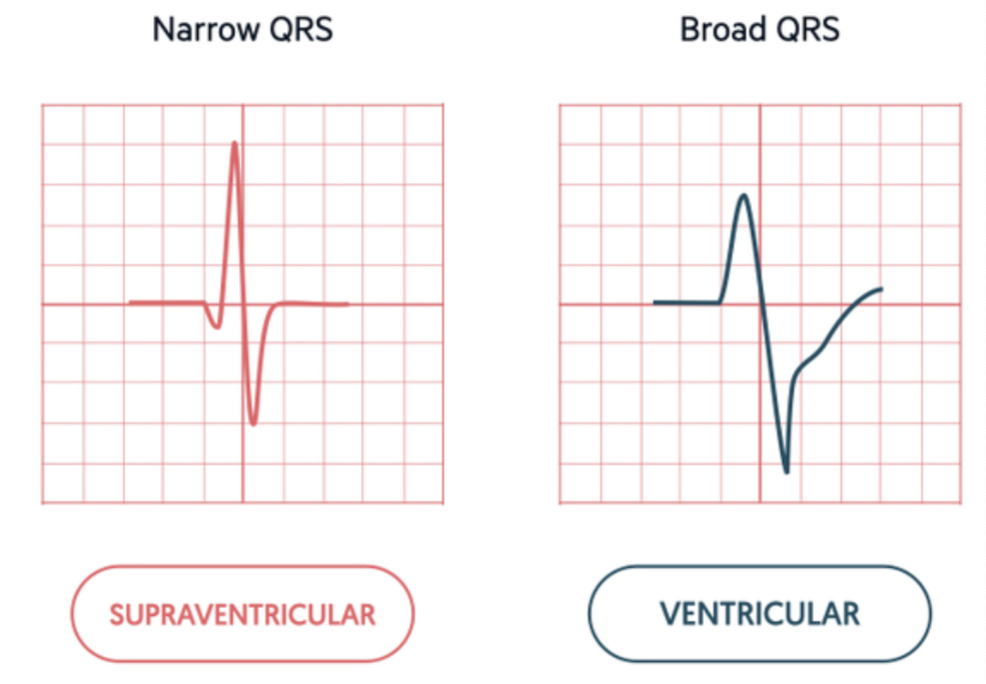
Distinguish between Supra-ventricular & Ventricular
Supra-ventricular → Originates above the the ventricles (SA node, atria, or AV node)
Narrow QRS
Visible waves
Ventricular → Originates in the ventricles
Wide QRS
Often no P wave or P not related to QRS
EX: supra-ventricular pacemaker that way delayed with the ventricular conduction system