Suspensions (20)
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Reminder: What is a dispersed system?
A mixture of two substances, where the dispersed phase is distributed throughout the dispersion medium
What are the components of the dispersed system in suspensions?
Dispersed phase: solid
Dispersion medium: liquid
Suspensions are ________ liquid forms
Biphasic
What is a coarse dispersion?
A heterogenous dispersed system where the dispersed molecules are over 1000 nm in size. Common type is suspensions
What are the five routes of administration of suspensions?
Oral, ocular, topical, rectal, and parenteral
Define a suspension
A heterogenous system consisting of two phases in which the insoluble drug is dispersed throughout the dispersion medium
What normally composes the dispersed phase and dispersion mediums in a suspension?
Dispersed phase: Insoluble drug
Dispersion medium: Could be water, alcohol, glycerol (aqueous) or sesame oil, almond oil, peanut oil (nonaqueous)
What is one property of a suspension that is different from that of a solution or colloid?
If left to rest, the particles of a suspension will settle out
2 multiple choice options
What are some advantages of using suspensions?
Can be helpful in patients with trouble swallowing, easy way to dispense unstable drugs, can be used in systemic and local treatment, and exhibit a higher bioavailability that other dosage forms
Describe the order of bioavailability in dosage froms
solution > suspension > capsule > compressed tablet > coated tablet
What are some disadvantages of using suspensions?
Uniform and accurate dose is hard to obtain, difficult to formulate, and sedimentation/compaction can cause issues.
What is the theory of suspension?
interaction of the particles determines the stability of the suspension. Suspensions are physically unstable due to caking/unfavorable reactions between particles.
What are three components of the interactions between the dispersed phase and the dispersed medium?
Sedimentation, wetting of the solid phase, and electrokinetic potential (flocculating)
Describe sedimentation
Occurs when particles settle out of suspension and are deposited due to gravity.
What does stokes law describe?
Describes the velocity of sedimentation for a particle falling through a liquid
What is stokes law?
v= d^2(Ps-Po)g/18ηo
What is d?
diameter of the particle in cm
What is Ps?
density of the dispersed phase in g/ml
What is Po?
density of the dispersed medium in g/ml
What is g?
acceleration due to gravity
What is ηo?
Viscosity of the dispersion medium
What is v?
Velocity of sedimentation in cm/sec
Describe what happens to the velocity of sedimentation as particle size increases
Sedimentation rate also increases. They can settle faster
Large particles over 5 µm has what texture in a suspension?
Gritty and is irritating
Small particles easily form what in a suspension?
Hard cake
Describe how the difference in density between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium affects sedimentation
Ps
Describe what happens to the velocity of sedimentation as viscosity increases
Sedimentation rate decreases, particles cant move very well
What is the effect of the increase in viscosity of a suspension on the suspended particles?
Decrease in settling of the suspended particles
2 multiple choice options
What is comminution?
The grinding of a solid to reduce particle size to a finer state
What is comminution used to enhance?
Dissolution rates and absorption
What is levigation?
Reducing particle size through addition of liquid in which solid isn't soluble. Common in small preparations of ointments and suspensions
What is jet milling?
A type of reduction of particles to a finer state
Describe the nature of vehicles containing thixotropic compounds/polymers
Plastic or pseudo-plastic like in nature
Describe how thixotropic compounds prevent sedimentation
The three dimensional structure will trap particles so that they do not settle
What happens to the thixotropic network when shaken?
The network is destroyed and administration is facilitated
What are suspending agents?
Viscosity modifier or thickening agent
What are some common suspending agents?
Natural, semisynthetic, and synthetic hydrocolloids and clay
How do hydrocolloids act as suspending agents?
Hydrophilic colloids coat the surface of hydrophobic drug particles in more than one layer (multimolecular)
Reminder: Solid particles have to be ________ to be dispersed in a liquid
wetted
Reminder: Degree of _______ will determine whether a solid can be dispersed in a liquid
wetting
What are two types of solids that can compose the dispersed phase?
Diffusible and Indiffusible solids
Describe diffusible solids and how they are wetted
Light and easily wetted by water, stay dispersed long enough for doses to be accurately measured, and redisperse easily if settled
Describe indiffusible solids and how they are wetted
Not easily wetted, some particles form large clumps in the liquid while others remain on the surface
Reminder: How can you determine the wetting of a solid?
Through the contact angle
How can you increase the wetting of a solid?
By adding a wetting agent
How do wetting agents increase the wetting of a solid?
They reduce surface tension and contact angle which promotes the movement of solvent across solute particles in the medium.
Why can solids sometimes be difficult to disperse in liquid vehicles?
Due to the layer of adsorbed air on the surface on the solid. Solids float on the surface until all air is displaced
What are two types of wetting agents?
Surfactants and glycerin (and similar hygroscopic substances)
Describe surfactants role in wetting
Reduce the interfacial tension between the solid and liquid vehicle. This lowers the contact angle, air is displaced from the surface and wetting is promoted
Give an example of a surfactant that aids in wetting
Polysorbate 80
Describe glycerins role in wetting
Flows into the voids between particles to displace air and reduce liquid-air interfacial tension so that water can penetrate and wet the solid.
Reminder: What is zeta potential?
A measure of magnitude of the electrical charge at the electrical double layer, expresses the magnitude of repulsive forces between particles
In order to develop a suitable suspension, you need to control the?
Rate of settling, ease of re-dispersion, and prevention of caking of the particles into a dense mass
Why might dispersed solids in a liquid medium have a charge in relation to the medium?
Due to selective adsorption of a particular ionic species present in the vehicle or the ionization of a functional group in a particle.
Ions that give a particle its charge are called?
Potential-determining ions that serve to repel particles of like charges
What is immediately adjacent to the surface of the solid particle with a specific charge?
Tightly bound solvent molecules and counter ions
What are flocculated suspensions?
Flocs (loose aggregates) are formed, increasing sedimentation rate due to increase in size of particles.
What are deflocculated suspensions?
Individual particles that do not form loose aggregates with other particles. The sedimentation rate is slower
How does a slower sedimentation rate cause cracking?
It is difficult to redisperse the particles with agitation. Deflocculated suspensions don't move as well flocculated suspensions
Describe flocculation
The formation of light, fluffy groups of particles held together by weak van der Waals forces
What do flocculating agents enhance?
Re-dispersibility
What are the three types of flocculating agents?
electrolytes, surfactants, polymers
How are surfactants classified?
By the charge of their polar head group (cationic, anionic, nonionic)
How can surfactants be used to form flocculating suspensions?
They can arrange around the solid particles and their tails provide bridges between the particles
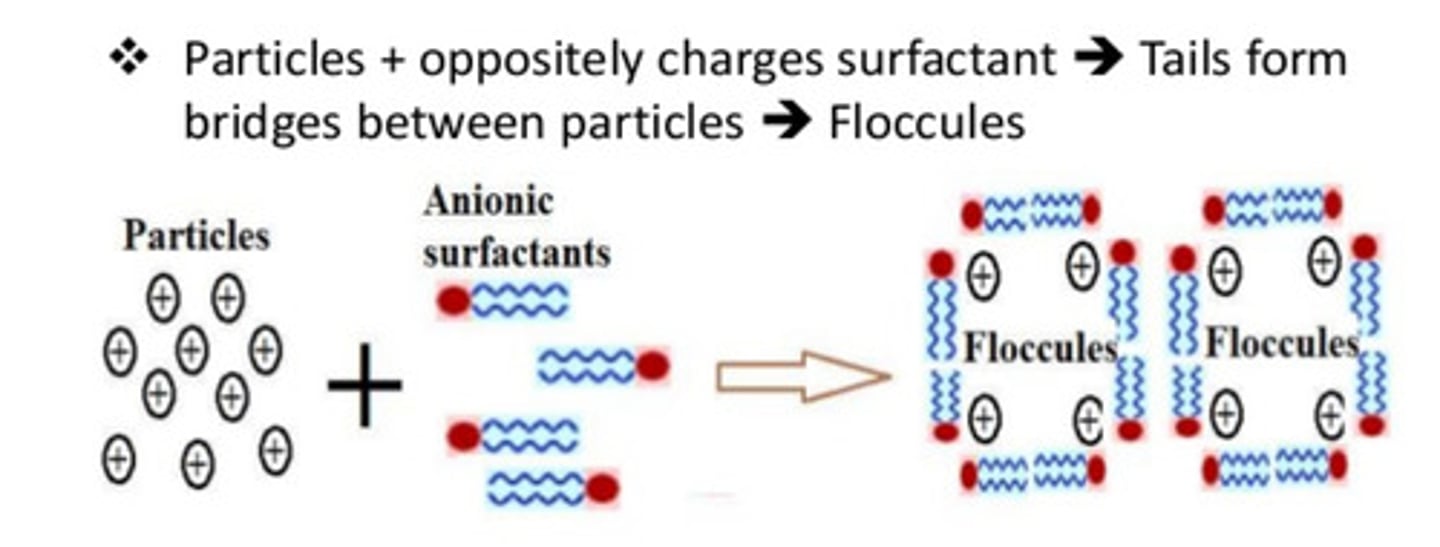
What are polymers?
long chains of monomers with high molecular weights (starch, carbomers, tragacanth, etc)
How can polymers be used to form flocculating suspensions?
Part of the polymer chain is adsorbed on the particle surface with the remaining parts projecting in the dispersion medium. Bridging occurs between particles with polymers
How are suspensions evaluated?
By determining their physical stability
What are two useful parameters for evaluating suspensions?
Sedimentation volume and degree of flocculation
What is sedimentation volume (F)?
Ratio of volume of sediments to that of the whole suspension
F=1
No sedimentation, no clear supernatant
F=0.5
50% of the total volume is occupied by sediment
F>1
Sediment volume is greater than the original volume due to formation of floccules which are fluffy and loose