Microbio Midterm #1
1/230
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
231 Terms
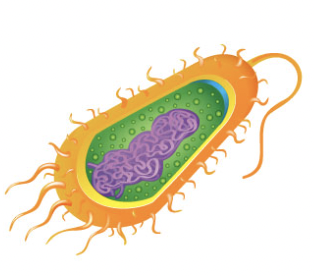
Characteristics of prokaryotes
Simple
Smaller
Unicellular
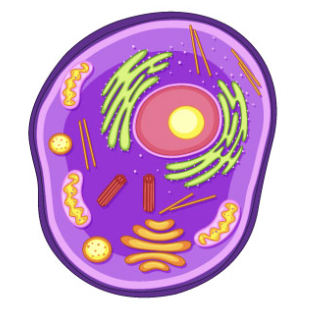
Characteristics of eukaryotes
Larger
Complex
Often multicellular
For what fraction of Earth's history were prokaryotes the only life form?
The first 2 billion years
What are the six major groups of microbes?
Bacteria
Algae
Protozoa
Fungi
Helminths
Viruses
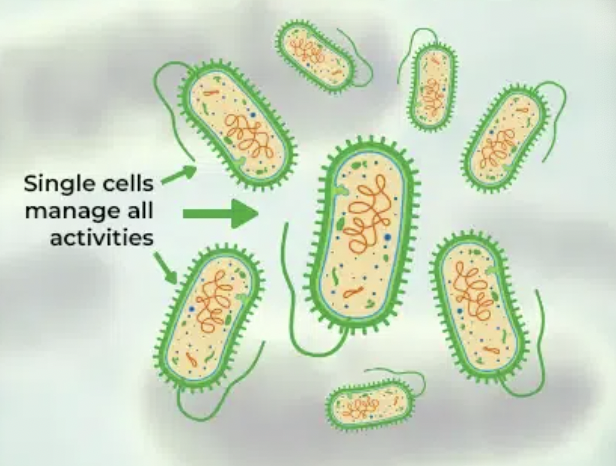
What is unicellular?
Composed of one type of cell
What is multicelluar?
Composed of multiple types of cells.
Bacteria
Unicellular
Account for all prokarytoes
Crucial part of the ecosystem
What are three crucial tasks prokaryotes serve in the ecosystem?
Nitrogen fixation
Photosynthesis
Decomposition

Algae
Photosynthetic eukaryote
Type of protist
Most are unicellular, some are multicellular
Protozoa
Unicellular eukaryotes (all are unicellular)
Not photosynthetic
Type of protist

Fungi
Eukaryotes that feed on decaying matter
Unicellular or multicellular
Differentiated by certain cellular structures
Helminths
Multicellular eukaryotes
Parasitic worms
Viruses
Non-cellular (neither eukaryotic or prokaryotic)
Infectious particles with no metabolism of their own
Reproduce by stealing host function
Centi-
10^{-2}
Milli-
10^{-3}
Micro-
10^{-6}
Nano-
10^{-9}
Pico-
10^{-12}
Pathogen
Microorganisms that cause disease

Primary pathogens
Microbes that cause disease in otherwise healthy individuals

Opportunistic pathogen
Microbes that cause disease in individuals with weakened/ damage immune systems; only when opportunity is given

Where are infectious diseases most impactful?
In developing countries/areas with limited healthcare
Why are infectious diseases more impactful in developing countries?
Lack of access to clean water, vaccines, and medicine.
Who first described cells?
Robert Hooke, contributed to the development of the cell theory (1660s)
Cell theory
All living things are composed of cells

Who first observed unicellular organisms?
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
What is the scientific method?
Observe the world
Propose a hypothesis to explain what you observe
Think of testable predictions based on your hypothesis
Perform experiments testing your prediction
Results are consistent → hypothesis is supported
Results aren’t consistent → hypothesis might be false or needs revision.
A hypothesis supported by enough test → theory, with time → law or principle
Spontaneous generation
The outdated idea that life arises spontaneously from nonliving matter
What are Louis Pasteur’s key contributions?
Disproved spontaneous generation
Developed pasteurization
Improved vaccines
Biogenesis
Living things give rise to other living things
Pasteurization
Brief heating of foods to kill most bacteria that cause it to spoil
What did Florence Nightingale contribute?
Founded modern nursing; promoted hygiene to reduce infection.
What did Joseph Lister contribute?
Introduced aseptic techniques in medicine that prevented surgical infections

Aseptic techniques
Redesigning and sterilizing surgical instruments between uses to prevent microbial contamination in medical and laboratory setting. Results in additional reduction in preventable deaths
Germ theory of disease
Disease is caused by tiny, invisible organisms (“germs”). Proposed by Koch and Pasteur, led to the development of vaccines and antibiotics
What did Robert Koch do?
Developed Koch’s postulates linking microbes to disease.
What are Koch’s Postulates?
The organism must be present in all cases of the disease
Must be able to isolate the organism and grow it in a pure culture
Pure culture of the organism must cause disease in a new host
Must be able to isolate the organism again from the new host
Who developed the first vaccine and how?
Edward Jenner used cowpox to protect against smallpox.
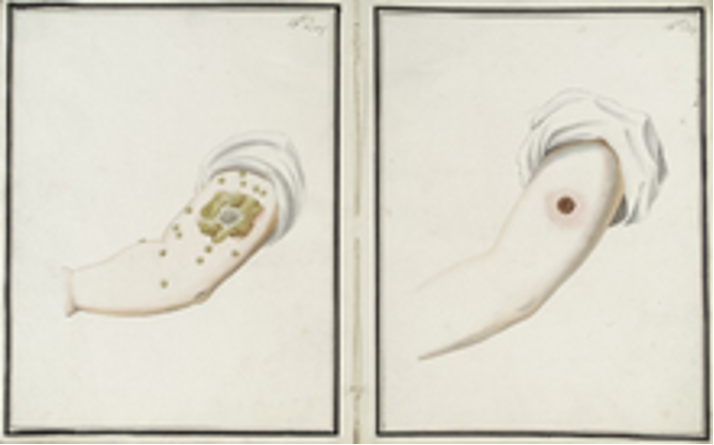

Jenner’s vaccines method
Discover disease
Search for a closely related disease that is less harmful
Use as a vaccine

Pasteur’s vaccine method
Discover disease
Kill or cripple the disease organism
Use as a vaccine
What’s the difference between Jenner’s and Pasteur’s
Jenner's method uses a weakened or inactivated pathogen to stimulate immunity
Who discovered penicillin?
Alexander Fleming, leaving to the developmented of antibiotics
Antibiotics
Kill or inhibits bacterial growth without harming host cells. Improper use of antibiotics can render them useless
Must give a large enough dose
Must give the dose for a long time
What’s a domain?
The highest taxonomic rank
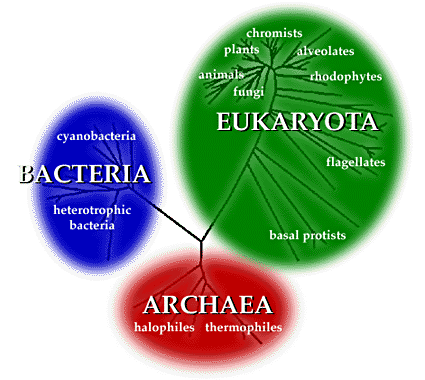
What are the 3 domain systems?
Domain Bacteria
Domain Archaea
Domain Eukarya
What’s a kingdom?
A broad classification within a domain
What are the kingdoms in Eukarya
Kingdom Animalia
Kingdom Fungi
Kingdom Plantae
Kingdom Protista
What’s a genus?
A group of closely related species
What’s considered a species in eukaryotes?
An organism that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
What’s considered a species in prokaryotes?
Organisms that are similar
Strain
A subpopulation in a species that has some slight differences between themselves and other members of the species
ex. E.coli 0157:H7 (pathogen), E..coli K12 (laboratory strain)
The six “I’s”
Inoculation
Incubation
Isolation
Inspection
Information gathering
Identification
What are the different types of microscopes
Bright-field
Dark-field
Fluorescence
Electron microscopy
Bright-field
Forms an image when light is transmitted through the specicment
Can be used for both live, unstained materials, and preserved stained materials

Dark-field
Uses peripheral light that is reflected off the sides of a specifiment itself
Used for live cells
Fluorescence
Ultraviolet light is used ot illuminate the speciemen
For tagged antibodies
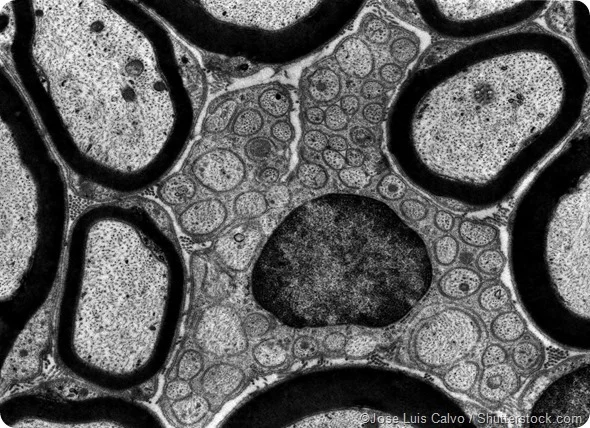
Electron microscopy
Forms an image with a beam of electrons that can be made to travel in wavelike patterns.
Black and white images
Used for internal structures of cell and viruses

What is a dichotomous identification key?
A tool used to identify organisms based on a series of yes or no choices
What are the methods of identification?
Specimen collection and culturing
Identification methods
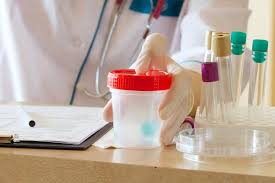
Specimen collection
Sample sites for either direct examination, culturing
What are some of the main concerns in sample collection?
Sampling handling
Transport
Storage
What are the identification methods?
Phenotypic
Genotypic
Serological
Phenotypic
Identifies microbes based on observable characteristics:
Microscopic and macroscopic morphology
Physiological/biochemical
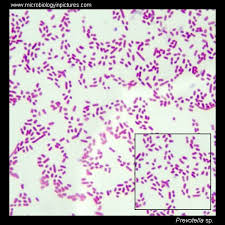
Microscopic morphology
Looking at cell shape and arrangement through different types of staining
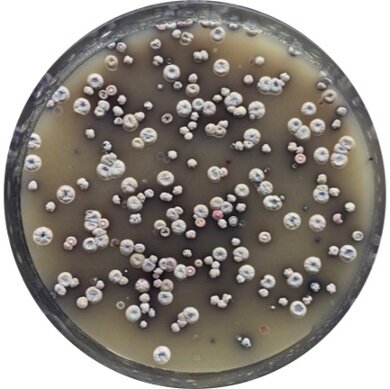
Macroscopic morphology
Observing visible characteristics such as appearance of a culture or colony; visible to the naked eye
Advantages of micro and macroscopic morphology
Easy, fast
Inexpensive
Disadvantages of micro and macroscopic morphology
Less specific
Imprecise
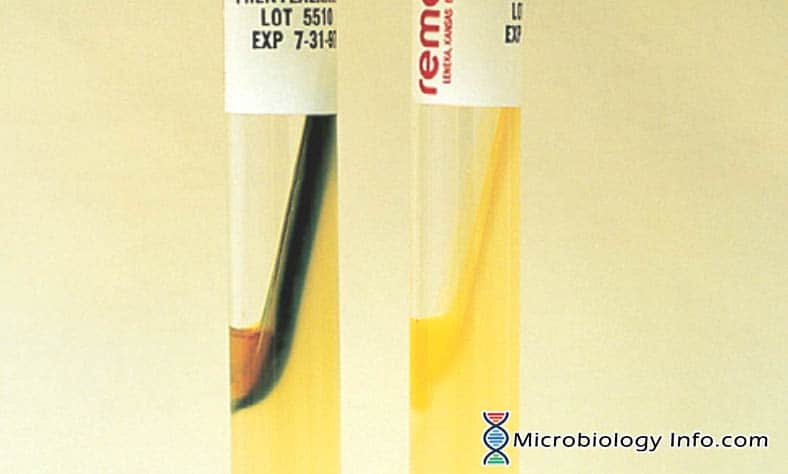
Physiological/biochemcial
Testing bacteria for ability to carry out various reactions
e.g. ferement carbohydrates, growing on high salts, break down gelatin
Advantages of physiological/biochemcial
Capable of identifying nearly any microbe, with enough test
Disadvantages of physiological/biochemcial
Relatively slow
Need pure culture first
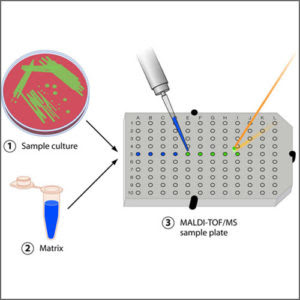
MALDI-TOF
Cell samples are hit with a laser, ionizing the samples, then analyzing
Advantages of MALDI-TOF
Fast and accurate
Disadvantages of MALDI-TOF
Expensive equipment
Genotypic methods
Techniques used to analyze genetic material, such as DNA and RNA, for microbial identification and characterization:
PCR
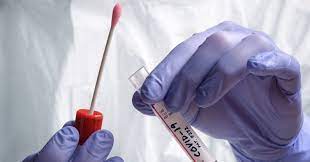
PCR
A rapid technique that can test for the presence of specific DNA sequences from tiny amount of DNA within hours
Advantages of PCR
Fast and precise
Disadvantages of PCR
Requires specific primers (you have to know what you’re looking for)
Serological methods
Techniques that use antibodies to detect microbial antigens:
Antibody testing
Serotyping
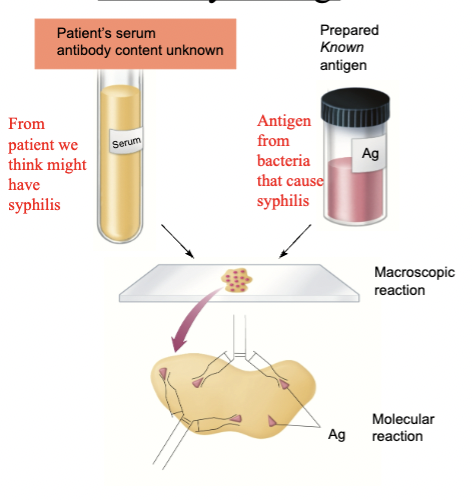
Antibody testing
Determines if a patient is producing antibodies against a pathogen using a known antigen
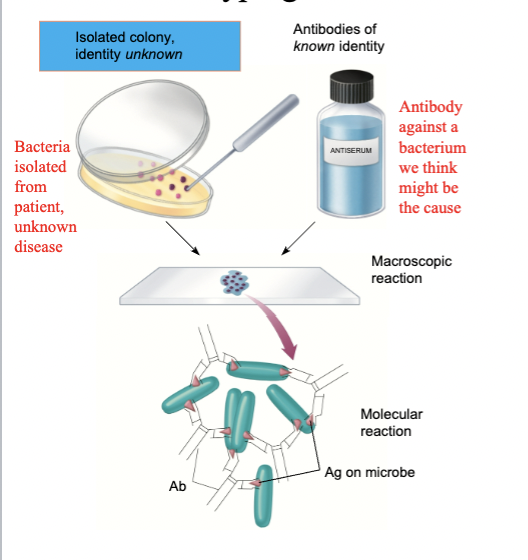
Serotyping
Testing an isolated microbe with specific antibodies to see if they have the right antigen
Advantages of serological test
Fast and sensitive
Disadvantages of serological test
Require a specific antibody for each microbe being test for
What is a serovar?
A distinct strain of a bacterial species, identified by surface antigens
What’s an atom?
Smallest divisible component of matter. Made up of protons, electrons, neutrons
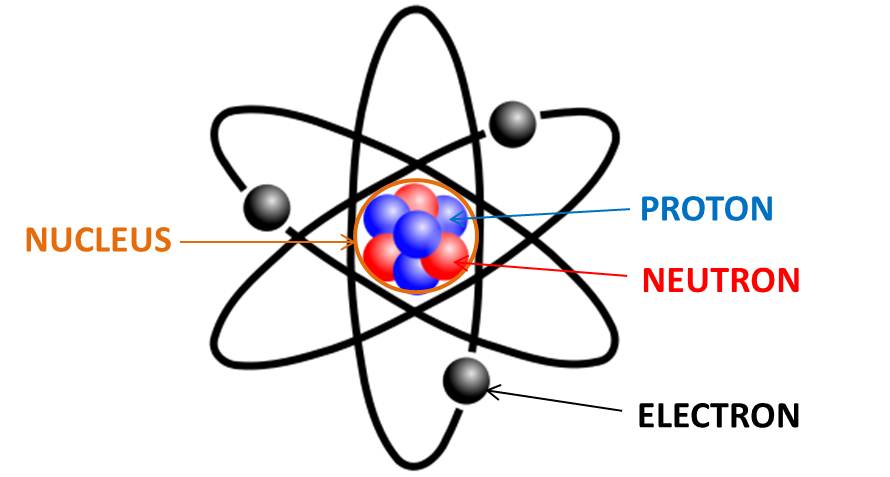
Proton
A positively charged particle
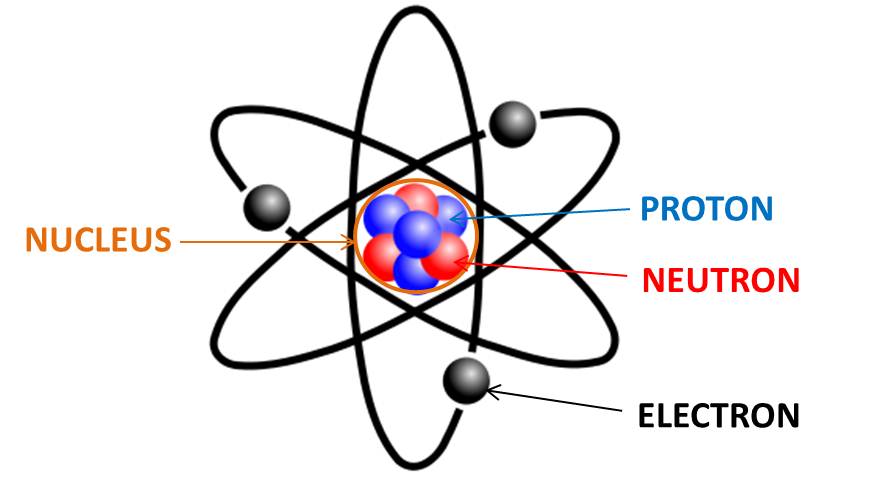
Electron
A negatively charged particle
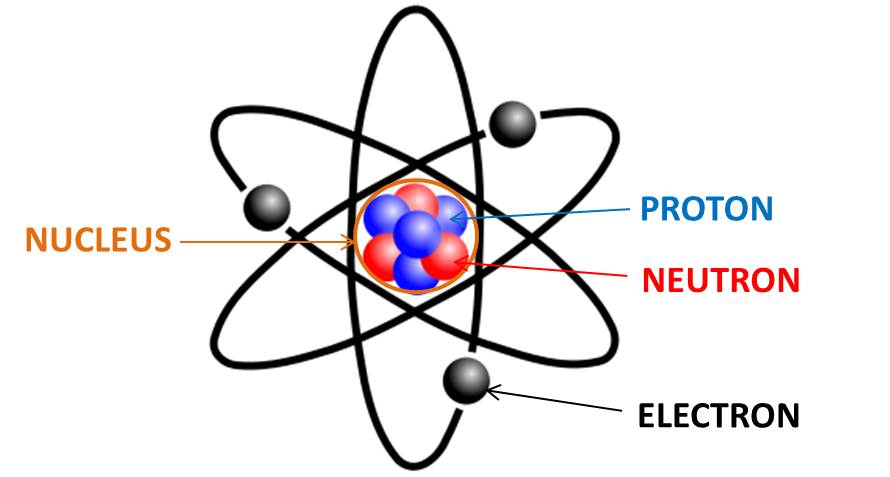
Neutron
An uncharged particle
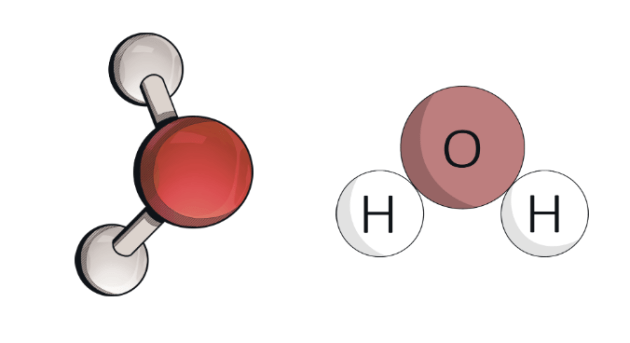
What’s a molecule?
Made of two or more atoms that share electrons
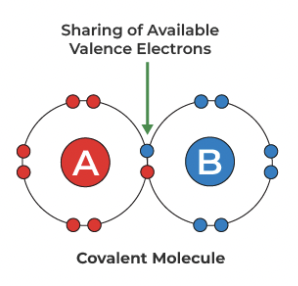
Covalent bond
Molecules with shared electrons
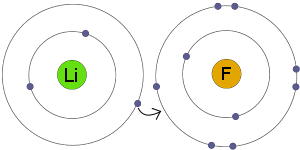
Ionic bond
Electron transfer among oppositely charged ions to fill valance shell
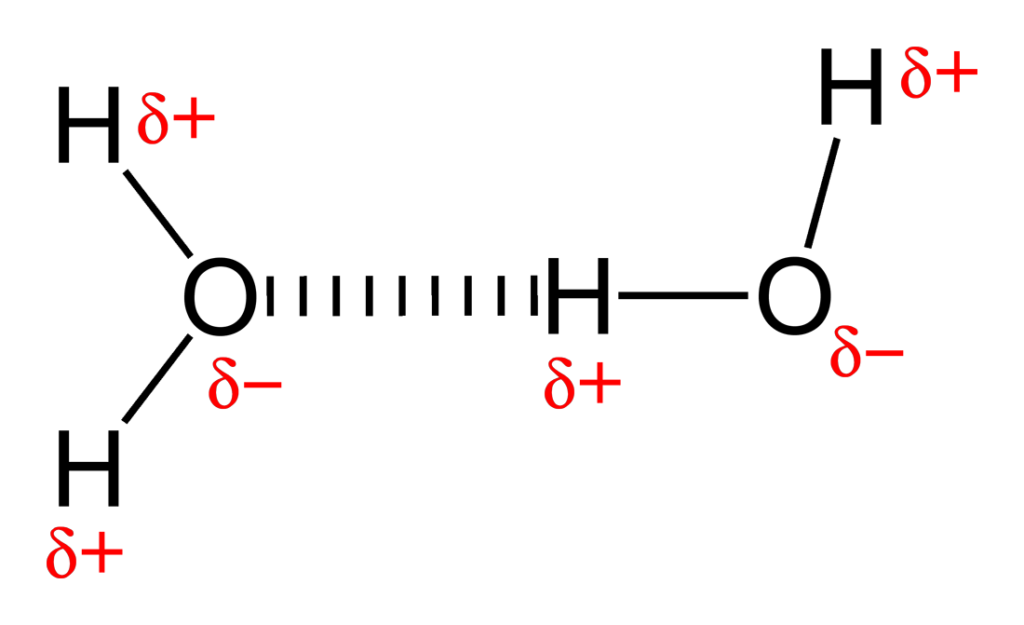
Hydrogen bond
Weak attraction between a hydrogen atom from one molecule and a oxygen or nitrogen atom of another molecule
What are the 6 elements that make up most of the molecules in all living things?
Hydrogen
Carbon
Nitrogen
Oxygen
Sulfur
Phosphorus
What does pH measure?
How acidic or basic a substance is

Acidic
When a solution has a high concentration of hydrogen ions
pH <7

Neutral
pH = 7

Basic
When a solution has a low concentration of hydrogen ions and a high concentration of hydroxide ions (also known as alkaline)
pH = >7
What are the four major macromolecules?
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Amino acids
Nucleotides
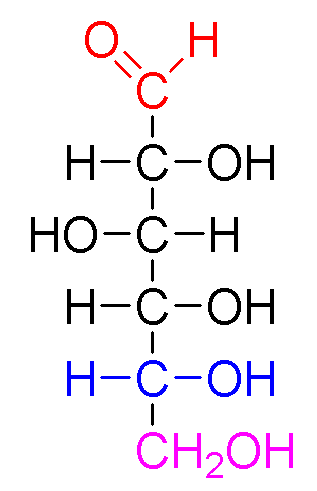
Carbohydrates
Made of C, O, and H atoms
Hydrophilic
Crucial part in energy metabolism and cellular structure
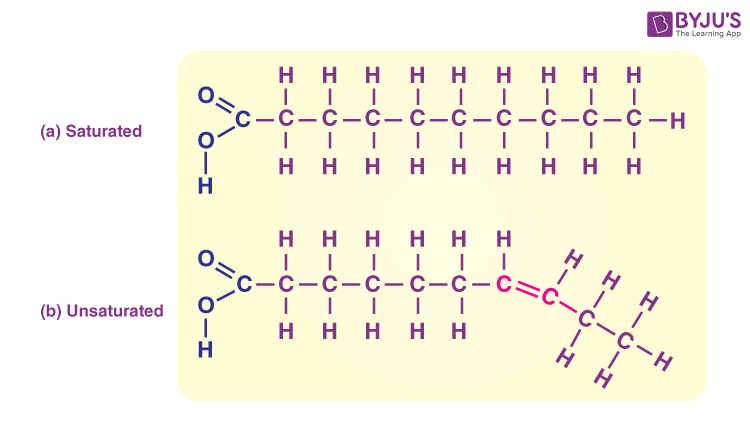
Lipids
Made of a long C-H chain with O atoms
Hydrophobic
Crucial part in energy storage and cellular structures
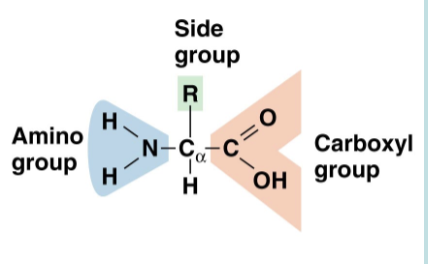
Amino acids
Made of C,O, H, N (sometimes contains S)
Make proteins that do almost all the work in a cell